iOS 7增加了UIKit Dynamics库,其集成于UIKit框架中,将2D物理引擎引入了UIKit,提供了以最简单方式实现真实物理动画功能。UIKit动力学的引入,并不是为了替代CoreAnimation或UIView动画,绝大多数情况下,CA或UIView动画仍然是最优方案,只有在需要引入逼真交互设计的时候,才需要使用UIKit动力学。如果你在开发电子游戏,那么应该使用SpritKit。
动力项(UIDynamicItem)是任何遵守UIDynamicItem协议的对象,相当于现实世界中的一个基本物体。自iOS 7开始,UIView和UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes默认实现了上述协议,你也可以自行实现该协议以便在自定义的类中使用动力效果动画(UIDynamicAnimator),但很少需要这样做。
动力行为(UIDynamicBehavior)为动力项(UIDynamicItem)提供不同的2D物理动画,即指定UIDynamicItem应该如何运动、适用哪些物理规则。在这里UIDynamicBehavior类似一个抽象类,没有实现具体行为,因此一般使用这个类的子类来对一组UIDynamicItem应遵守的行为规则进行描述。UIDynamicBehavior可以独立作用,多个动力行为同时作用时遵守力的合成。
UIKit Dynamics库的核心在于UIDynamicAnimator,其封装了底层iOS物理引擎,是动力行为(UIDynamicBehavior)的容器,动力行为添加到容器内才会发挥作用,为动力项(UIDynamicItem)提供物理相关的功能和动画。
当所有item处于暂停时,
animator自动暂停,并且当动力行为参数改变、添加或移除动力行为或动力项时自动恢复。
使用动力学(dynamics)的步骤是:配置一个或多个UIDynamicBehavior,其中为每个UIDynamicBehavior指定一个或多个UIDynamicItem,最后添加这些UIDynamicBehavior到UIDynamicAnimator。
UIDynamciBehavior有以下六个子类:
- UIGravityBehavior:重力行为,重力的大小和方向可以配置,并会同等作用于所有关联对象。
- UICollisionBehavior:碰撞行为,提供两个或多个视图对象碰撞的能力,或视图对象和边界碰撞的能力。
- UIPushBehavior:对一个或多个动力项施加连续(continuous)或瞬时(instantaneous)力的行为,导致这些动力项改变位置。
- UIAttachmentBehavior:描述一个view和一个锚点相连接的情况,也可以描述view和view之间的连接情况。
- UISnapBehavior:将view通过动画吸附到某个点上。吸附的过程类似弹簧作用,使动力项朝向目标点甩出,到达目标点后其初始运动随着时间的推移而减弱,最终物体停止在目标点。
- UIFieldBehavior:将基于场的物理学应用于动力项对象。场的行为定义了可以应用诸如磁力(magnetism)、拖拽(dragging)、电场(electric)、漩涡(vortex)、辐射(radial)、线性重力(linear gravity)、噪声(noise)、涡流(turbulence)、弹簧场(SpringField)等力的区域。
还有另外一个重要的类是UIDynamicItemBehavior,用于修改指定动力项的以下属性:
- allowsRotation:BOOL型值,用于指定
UIDynamicItem是否旋转。默认值是YES。 - angularResistance:旋转阻力,物体旋转过程的阻力大小。值的范围是
0到CGFLOAT_MAX,值越大,阻力越大。 - density:动力项的密度(density)和动力项大小(size),决定了其参与
UIKit动力行为(包括摩擦、碰撞、推动等)的表现。例如,假设有两个相同密度但不同大小的动态项目,item1是100*100points,item2是100*200points,即item2的有效质量是item1的二倍,在弹性碰撞时,item1和item2会展现出与自然界相同的动量守恒。一个100p * 100p的动力项,density为1.0,施加1.0的力,会产生100points每平方秒的加速度。 - elasticity:弹力。范围是
0到1.0,0表示没有弹性,1.0表示完全弹性碰撞。默认值为0。 - friction:摩擦力。默认值
0表示没有摩擦力,1.0表示很强摩擦。为了取得更大摩擦力,可以使用更大值。 - resistance:线性阻力。物体移动过程中受到的阻力。默认值
0表示没有线性阻力,上限CGFLOAT_MAX为完全阻力。如果此属性值为1.0,则动态项一旦没有作用力会立即停止。 - anchored:BOOL型值,指定动力项是否固定在当前位置。被固定的动力项参与碰撞时不会被移动,而是像边界一样参与碰撞。默认值是
NO。
目前为止,对UIKit Dynamics的整体介绍已经结束,下一步将通过demo学习具体使用。
1. 创建demo
和往常一样,将在创建的demo上添加代码来学习UIKit Dynamics。
打开Xcode,点击File > New > File…,选择iOS > Application > Single View Application模板,点击Next;在Product Name中填写UIKitDynamics,Language为Objective-C,点击Next;选择文件位置,点击Create创建工程。
该demo将分为五个部分,为此把UITabBarController设置为根控制器。每一部分作为单独视图控制器添加到UITabBarController。
选中ViewController.h和ViewController.m并删除。使用快捷键command+N添加文件,选择iOS > Source > Cocoa Touch Class模板,点击Next;Class名称为FirstViewController,Subclass of为UIViewController,点击Next;选择文件位置,点击Create创建文件。
重复上面添加文件步骤,依次添加下面名称文件:
- SecondViewController
- ThirdViewController
- FourthViewController
- FifthViewController
最后添加一个Class为TabBarController,Subclass of为UITabBarController的文件。完成后Project Navigator 如下图:
进入AppDelegate.m,导入TabBarController.h,在application: didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:方法中设定根控制器为TabBarController。
- (BOOL)application:(UIApplication *)application didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:(NSDictionary *)launchOptions {
// 设定根控制器
self.window = [[UIWindow alloc] initWithFrame:[UIScreen mainScreen].bounds];
self.window.backgroundColor = [UIColor whiteColor];
self.window.rootViewController = [[TabBarController alloc] init];
[self.window makeKeyAndVisible];
return YES;
}
进入TabBarController.m,导入之前添加的五个视图控制器,并将其添加到TabBarController,同时设定各视图控制器标题。
#import "TabBarController.h"
// 导入视图控制器
#import "FirstViewController.h"
#import "SecondViewController.h"
#import "ThirdViewController.h"
#import "FourthViewController.h"
#import "FifthViewController.h"
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
// 初始化视图控制器 设定标题 tabBarItem图片
UIImage *image = [UIImage imageNamed:@"circle"];
FirstViewController *firstVC = [[FirstViewController alloc] init];
firstVC.title = @"First";
firstVC.tabBarItem.image = image;
SecondViewController *secVC = [[SecondViewController alloc] init];
secVC.title = @"Second";
secVC.tabBarItem.image = image;
ThirdViewController *thirdVC = [[ThirdViewController alloc] init];
thirdVC.title = @"Third";
thirdVC.tabBarItem.image = image;
FourthViewController *fourthVC = [[FourthViewController alloc] init];
fourthVC.title = @"Fourth";
fourthVC.tabBarItem.image = image;
FifthViewController *fifthVC = [[FifthViewController alloc] init];
fifthVC.title = @"Fifth";
fifthVC.tabBarItem.image = image;
// 设置标签栏控制器的根视图
[self setViewControllers:@[firstVC, secVC, thirdVC, fourthVC, fifthVC] animated:YES];
}
上面的代码非常简单,记得添加图片到Assets.xcassets,可以通过文章底部链接下载源码获取。
2. 重力行为、碰撞行为之初体验
2.1 重力行为 UIGravityBehavior
为了体现重力行为作用,我们在FirstViewController添加一个圆,填充颜色以使其看起来像一个球。最后为其添加UIGravityBehavior。
进入FirstViewController.m文件,在私有接口部分声明以下属性:
@interface FirstViewController ()
@property (strong, nonatomic) UIDynamicAnimator *animator;
@property (strong, nonatomic) UIView *orangeBall;
@end
第一个声明的为UIDynamicAnimator对象。之前已经说过,UIDynamicAnimator自身不能工作,添加其他行为后才可以,稍后添加重力行为。声明的UIView对象用于演示重力行为。
打开FirstViewController.m,进入viewDidLoad方法中,配置刚声明的两个属性。
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
// 1.初始化、配置orangeBall
self.orangeBall = [[UIView alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectMake(self.view.bounds.size.width/2-25, 100, 50, 50)];
self.orangeBall.backgroundColor = [UIColor orangeColor];
self.orangeBall.layer.cornerRadius = 25;
[self.view addSubview:self.orangeBall];
// 2.初始化animator
self.animator = [[UIDynamicAnimator alloc] initWithReferenceView:self.view];
}
上述代码分步说明:
- 初始化、配置
orangeBall。圆形由self.orangeBall.layer.cornerRadius = 25;代码生成。 - 初始化
animator。初始化时需要Reference View,相当于力学参考系,只有当想要添加力学的UIView是Reference View的子视图时,UIDynamicAnimator才发生作用。
在FirstViewController.m底部添加以下方法,并在其中初始化UIGravityBehavior。
- (void)testGravity {
// 1.初始化重力行为
UIGravityBehavior *gravity = [[UIGravityBehavior alloc] initWithItems:@[self.orangeBall]];
// 2.添加重力行为到UIDynamicAnimator
[self.animator addBehavior:gravity];
}
上述代码分步说明:
- 初始化
UIGravityBehavior,它的参数为NSArray类型,可以把所有需要添加重力作用的视图添加到该数组。在这个示例中,只需要添加orangeBall。 - 如果想要让行为有效,必需添加行为到
UIDynamicAnimator容器。使用animator对象的addBehavior:方法添加重力行为。
进入到viewDidLoad方法,调用上述方法。
- (void)viewDidLoad {
...
// 调用testGravity方法
[self testGravity];
}
在模拟器运行app,如下所示:
现在重力效果带动orangeBall向下跌落。事实上,orangeBall在跌出可见区域后,仍然在继续下滑,下面进行验证。
UIDynamicBehavior类有void(^action)(void)块属性,其子类也会继承该属性。animator会在每步(step)动画调用该块,也就是action中添加的代码会在动力动画运行过程中不断执行。在testGravity方法初始化graviy后添加以下代码:
- (void)testGravity {
...
gravity.action = ^{
NSLog(@"%f",self.orangeBall.center.y);
};
...
}
在上面的代码中,把块赋值给重力行为gravity的action属性,在块中用NSLog输出orangeBall中心的y坐标,用以表示其位置。运行app,可以在控制台看到不断输出的数字,并且相邻值的差不断增大,在orangeBall离开可见区域后,控制台继续输出。事实上,此时orangeBall正在做自由落体运动。
如果对块不熟悉,可以查看我的另一篇文章:Block的用法
2.2 碰撞行为 UICollisionBehavior
通过上面代码,我们为orangeBall添加了UIGravityBehavior,但让视图在重力行为作用下无限下滑没有意义。如果orangeView在撞到tar bar顶部后开始弹跳,最终停止会更有用途,就像生活中的球跌落到地上。
UICollisionBehavior可以实现碰撞功能。使用UICollisionBehavior的步骤是初始化碰撞行为并制定碰撞边界,添加碰撞行为到animator。更新后代码如下:
- (void)testGravity {
...
// 3.初始化碰撞行为、制定边界
UICollisionBehavior *collision = [[UICollisionBehavior alloc] initWithItems:@[self.orangeBall]];
[collision addBoundaryWithIdentifier:@"tabbar" fromPoint:self.tabBarController.tabBar.frame.origin toPoint:CGPointMake(self.tabBarController.tabBar.frame.origin.x + self.tabBarController.tabBar.frame.size.width, self.tabBarController.tabBar.frame.origin.y)];
[self.animator addBehavior:collision];
}
在初始化时指定orangeBall为UICollisionBehavior的作用对象,使用addBoundaryWithIdentifier: fromPoint: toPoint:方法添加tab bar上部为边界。最后添加collision到animator。
除上面的添加边界方法外,还有以下三种添加边界的方法:
-
translatesReferenceBoundsIntoBoundary:BOOL类型值,指定是否把reference view作为碰撞边界。默认为NO。 -
addBoundaryWithIdentifier: forPath::添加指定Bezier Path作为碰撞边界。 -
setTranslatesReferenceBoundsIntoBoundaryWithInsets::设定某一区域作为碰撞边界。
运行demo,如下所示:
现在orangeBall遇到边界会弹跳,不会直接穿过。我们在开始部分介绍到UIDynamicItemBehavior用于修改动力项属性,现在初始化一个UIDynamicItemBehavior,修改其elasticity属性。更新后testGravity方法如下:
- (void)testGravity {
...
// 4.初始化UIDynamicItemBehavior 修改elasticity
UIDynamicItemBehavior *ballBehavior = [[UIDynamicItemBehavior alloc] initWithItems:@[self.orangeBall]];
ballBehavior.elasticity = 0.7;
[self.animator addBehavior:ballBehavior];
}
elasticity默认值为0,范围是0到1.0,0表示没有弹性,1.0表示完全弹性碰撞。这里把值设为0.7。
运行app,显示如下:
现在已经了解了UIDynamicItemBehavior的使用方法,你可以尝试一下其他属性。
UICollisionBehavior类遵守UICollisionBehaviorDelegate协议,该协议内有以下方法:
-
collisionBehavior: beganContactForItem: withBoundaryIdentifier: atPoint:动力项与边界碰撞开始时被调用。 -
collisionBehavior: beganContactForItem: withItem: atPoint:动力项与动力项之间碰撞开始时被调用。 -
collisionBehavior: endedContactForItem: withBoundaryIdentifier:动力项与边界碰撞结束时调用。 -
collisionBehavior: endedContactForItem: withItem:动力项与动力项之间碰撞结束时调用。
实际使用中,可以根据上面代理方法执行其他操作。
3. 重力行为、碰撞行为和推动行为具体应用
通过第一部分的学习,我们已经基本了解了UIKit Dynamics的使用,但这个弹跳球在实际中没有太大用途。基于此,在第二部分将创建一个更有实用价值的示例。
在显示、隐藏菜单组件时,使用UIKit Dynamics可以获得更好的动画效果。这一部分示例想要达到的效果为:使用UISwipeGestureRecognizer手势自左向右滑,从左侧弹出一个占据半个屏幕的菜单。使用同样手势自右向左滑动,隐藏弹出菜单。在弹出菜单后面,另一个半透明的视图将会显示在主视图之上,防止误点击到主视图;当弹出菜单隐藏时,半透明视图隐藏。如下所示:
上面弹出菜单中的选项将不可使用,只需要实现显示、隐藏功能。
为实现弹出、隐藏菜单功能我们添加一个UIView,而没有添加另一个视图控制器。对于整个app的菜单,你应该创建一个视图控制器,以便于你可以从任何视图控制器访问菜单。这里将不会这样做,因为这已成为自定义视图控制器转换,不再符合这里要说明的问题。
弹出菜单中的选项将使用UITableView显示。最终,菜单视图、表视图和背景视图共同用于显示弹出项,UIDynamicAnimator处理所有动画。
进入SecondViewController.m,声明以下属性。
#import "SecondViewController.h"
@interface SecondViewController ()
@property (strong, nonatomic) UIView *menuView;
@property (strong, nonatomic) UIView *backgroundView;
@property (strong, nonatomic) UITableView *menuTable;
@property (strong, nonatomic) UIDynamicAnimator *animator;
@end
在实现部分前,添加以下预定义,用于指定menuView的宽度为视图控制器视图宽度的二分之一。
@end
#define menuWidth self.view.frame.size.width/2
@implementation SecondViewController
在实现部分使用懒加载初始化刚声明的属性。
// 1.设置背景视图
- (UIView *)backgroundView {
if (!_backgroundView) {
_backgroundView = [[UIView alloc] initWithFrame:self.view.frame];
_backgroundView.backgroundColor = [UIColor lightGrayColor];
_backgroundView.alpha = 0.0;
}
return _backgroundView;
}
// 2.设置菜单视图
- (UIView *)menuView {
if (!_menuView) {
_menuView = [[UIView alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectMake(-menuWidth, 20, menuWidth, self.view.frame.size.height - self.tabBarController.tabBar.frame.size.height)];
_menuView.backgroundColor = [UIColor colorWithRed:0.2 green:0.2 blue:0.2 alpha:1.0];
}
return _menuView;
}
// 3.设置表视图
- (UITableView *)menuTable {
if (!_menuTable) {
_menuTable = [[UITableView alloc] initWithFrame:self.menuView.bounds style:UITableViewStylePlain];
_menuTable.backgroundColor = [UIColor clearColor];
_menuTable.alpha = 1.0;
_menuTable.scrollEnabled = NO;
_menuTable.separatorStyle = UITableViewCellSeparatorStyleNone;
_menuTable.delegate = self;
_menuTable.dataSource = self;
}
return _menuTable;
}
// 4.初始化UIDynamicAnimator
- (UIDynamicAnimator *)animator {
if (!_animator) {
_animator = [[UIDynamicAnimator alloc] initWithReferenceView:self.view];
}
return _animator;
}
上述代码的分步说明如下:
- 背景视图大小与当前视图大小一致,设置为透明色。
- 菜单视图宽度为窗口宽度一半,初始化时使其位于左侧不可见区域。
- 设置表视图大小和菜单视图大小一致,初始化完成后将其添加到菜单视图。
- 初始化
UIDynamicAnimator。
上面的代码都很简单,就不再详细说明。Xcode此时会发出警告,这是因为我们已经将我们的类设置为表视图的委托和数据源,但却没有遵守各自的协议。在interface后添加协议后代码如下:
@interface SecondViewController ()
遵守上述协议后,Xcode会提示没有实现必需实现的协议方法。现在实现所有我们需要的方法,其中表视图共五行,每行一个选项,点击每行时其状态从选中变为取消选中。
#pragma mark - UITableViewDataSource
- (NSInteger)numberOfSectionsInTableView:(UITableView *)tableView {
return 1;
}
- (NSInteger)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView numberOfRowsInSection:(NSInteger)section {
return 5;
}
- (UITableViewCell *)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView cellForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath {
UITableViewCell *cell = [tableView dequeueReusableCellWithIdentifier:reuseIdentifier forIndexPath:indexPath];
cell.textLabel.text = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"Option %li",indexPath.row + 1];
cell.textLabel.textColor = [UIColor lightGrayColor];
cell.textLabel.font = [UIFont preferredFontForTextStyle:UIFontTextStyleBody];
cell.textLabel.textAlignment = NSTextAlignmentCenter;
cell.backgroundColor = [UIColor clearColor];
return cell;
}
#pragma mark - UITableViewDelegate
- (CGFloat)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView heightForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath {
return 50;
}
- (void)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView didSelectRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath {
[[tableView cellForRowAtIndexPath:indexPath] setSelected:NO];
}
开始下一步之前,在实现部分前定义cell的标识符如下:
@end
#define menuWidth self.view.frame.size.width
static NSString * const reuseIdentifier = @"CellIdentifier";
@implementation SecondViewController
进入viewDidLoad方法,将背景视图和菜单视图添加到视图控制器视图,将表视图添加到菜单视图,最后注册cell。更新后如下:
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
// 添加背景视图 菜单视图 表视图
[self.view addSubview:self.backgroundView];
[self.view addSubview:self.menuView];
[self.menuView addSubview:self.menuTable];
// 注册cell
[self.menuTable registerClass:[UITableViewCell class] forCellReuseIdentifier:reuseIdentifier];
}
backgroundView和menuView添加到视图控制器视图上,menuTable添加到menuView上。
现在开始实现弹出、隐藏动画部分。如果我们仔细考虑一下,你会发现菜单视图弹出和隐藏的动画是相同的,只是方向相反。这意味着可以在一个方法内定义动力行为,其方向根据menuView所处状态而定。
在实现之前,先看一下要显示菜单的动力行为。首先,需要一个碰撞行为,以便让视图在指定边界发生碰撞,而不是从屏幕一边滑动到另一边。其次,添加方向向右的重力行为,以便让menuView看起来像被边界拖拽着滑动。再添加一个UIDynamicItemBehavior属性中的elasticity,这样看起来就很好了。但还可以添加一个UIPushBehavior让menuView移动的快一些。在隐藏menuView时使用相同动力行为,只是方向相反。
我们将在实现部分添加以下方法,用于实现动画的主要部分。
- (void)toggleMenu:(BOOL)shouldOpenMenu {
// 移除所有动力行为
[self.animator removeAllBehaviors];
// 根据参数shouldOpenMenu 获取重力方向 推力方向 边界位置
CGFloat gravityDirectionX = shouldOpenMenu ? 1.0 : -1.0;
CGFloat pushMagnitude = shouldOpenMenu ? 20.0 : -20.0;
CGFloat boundaryPointX = shouldOpenMenu ? menuWidth : -menuWidth;
// 添加重力行为
UIGravityBehavior *gravityBehavior = [[UIGravityBehavior alloc] initWithItems:@[self.menuView]];
gravityBehavior.gravityDirection = CGVectorMake(gravityDirectionX, 0);
[self.animator addBehavior:gravityBehavior];
// 添加碰撞行为
UICollisionBehavior *collisionBehavior = [[UICollisionBehavior alloc] initWithItems:@[self.menuView]];
[collisionBehavior addBoundaryWithIdentifier:@"menuBoundary" fromPoint:CGPointMake(boundaryPointX, 20) toPoint:CGPointMake(boundaryPointX, self.tabBarController.tabBar.frame.origin.y)];
[self.animator addBehavior:collisionBehavior];
// 添加推力行为
UIPushBehavior *pushBehavior = [[UIPushBehavior alloc] initWithItems:@[self.menuView] mode:UIPushBehaviorModeInstantaneous];
pushBehavior.magnitude = pushMagnitude;
[self.animator addBehavior:pushBehavior];
// 设置menuView的elasticity属性
UIDynamicItemBehavior *menuViewBehavior = [[UIDynamicItemBehavior alloc] initWithItems:@[self.menuView]];
menuViewBehavior.elasticity = 0.4;
[self.animator addBehavior:menuViewBehavior];
// 设置backgroundView alpha值
self.backgroundView.alpha = shouldOpenMenu ? 0.5 : 0;
}
上述代码每一步都很简单,这里有以下几点需要注意:
- 在代码开始部分,移除
animator内所有动力行为。因为当使用相反手势,隐藏menuView时,需要添加的行为与已存在的行为冲突,同时存在动画不能正常运行。 - 初始化推力行为中参数
mode:有两个可用参数,UIPushBehaviorModeInstantaneous表示施加瞬时力,即一个冲量;UIPushBehaviorModeContinuous表示施加连续的力。 -
backgroundView的alpha由现在所处状态决定。
如果你想要施加的重力需要结合物体自身质量,请使用后面讲到的
UIFieldBehavior,场行为支持线性和径向引力场,其引力大小和动力项自身质量有关,且力大小与距场行为中心远近相关,导致施加到不同物体上的力大小不同。
在主屏幕上使用手势右滑,menuView出现;在menuView上左滑,menuView隐藏。最方便的方法就是当手势触发时调用同一个方法,在调用方法内根据手势方向调用toggleMenu:方法,并设置对应参数。
进入viewDidLoad,添加手势。
- (void)viewDidLoad {
...
// 添加右滑手势
UISwipeGestureRecognizer *showMenuGesture = [[UISwipeGestureRecognizer alloc] initWithTarget:self action:@selector(handleGesture:)];
showMenuGesture.direction = UISwipeGestureRecognizerDirectionRight;
[self.view addGestureRecognizer:showMenuGesture];
// 添加左滑手势
UISwipeGestureRecognizer *hideMenuGesture = [[UISwipeGestureRecognizer alloc] initWithTarget:self action:@selector(handleGesture:)];
hideMenuGesture.direction = UISwipeGestureRecognizerDirectionLeft;
[self.menuView addGestureRecognizer:hideMenuGesture];
}
上面添加手势的代码有两点不同。其一,手势方向相反;其二,手势添加到的视图不同,右滑手势添加到view,左滑手势添加到menuView。你也可以在视图控制器视图上再添加一个左滑手势,方便用户在主视图上左滑隐藏menuView,如果遇到问题,可以通过文章底部网址下载demo源码查看。
在实现部分实现手势中handleGesture:方法,根据手势方向为toggleMenu:设置不同参数。
- (void)handleGesture:(UISwipeGestureRecognizer *)gesture {
if (gesture.direction == UISwipeGestureRecognizerDirectionRight) {
[self toggleMenu:YES];
} else {
[self toggleMenu:NO];
}
}
现在运行app,尝试使用手势弹出、隐藏menuView,也可以自行修改其他属性。
这篇文章将多次用到手势识别器(UIGestureRecognizer),如果你还不熟悉,可以查看我的另一篇文章:手势控制:点击、滑动、平移、捏合、旋转、长按、轻扫
4. 附着行为UIAttachmentBehavior
在这一部分,将添加UIPushBehavior、UIAttachmentBehavior和UIDynamicItemBehavior几种动力行为到image,随后拖动image产生如下效果:
4.1 构建界面
下载图片并添加到Assets.xcassets。进入到ThirdViewController.m,添加以下声明。
@interface ThirdViewController ()
@property (strong, nonatomic) UIImageView *imageView;
@property (strong, nonatomic) UIView *redView;
@property (strong, nonatomic) UIView *blueView;
@property (assign, nonatomic) CGRect orangeBounds;
@property (assign, nonatomic) CGPoint orangeCenter;
@property (strong, nonatomic) UIDynamicAnimator *animator;
@property (strong, nonatomic) UIAttachmentBehavior *attachmentBehavior;
@property (strong, nonatomic) UIPushBehavior *pushBehavior;
@property (strong, nonatomic) UIDynamicItemBehavior *itemBehavior;
@end
redView和blueView用于表示UIDynamics物理引擎动画的点,blueView表示触摸开始的点,redView表示表示手指触摸点,也是imageView的锚点。
使用懒加载初始化、配置前三个视图属性。
- (UIImageView *)imageView {
if (!_imageView) {
CGPoint center = self.view.center;
_imageView = [[UIImageView alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectMake(0, 0, 240, 240)];
_imageView.center = CGPointMake(center.x, center.y*2/3);
_imageView.image = [UIImage imageNamed:@"AppleLogo.jpg"];
_imageView.userInteractionEnabled = YES;
}
return _imageView;
}
- (UIView *)redView {
if (!_redView) {
_redView = [[UIView alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectMake(0, 0, 10, 10)];
_redView.center = CGPointMake(self.view.center.x, self.view.center.y*2/3);
_redView.backgroundColor = [UIColor redColor];
}
return _redView;
}
- (UIView *)blueView {
if (!_blueView) {
_blueView = [[UIView alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectMake(80, 400, 10, 10)];
_blueView.backgroundColor = [UIColor blueColor];
}
return _blueView;
}
将上面初始化的属性添加到view。
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
[self.view addSubview:self.imageView];
[self.view addSubview:self.redView];
[self.view addSubview:self.blueView];
}
在viewDidLoad中为imageView添加平移手势识别器UIPanGestureRecognizer,用于拖动图片视图。
- (void)viewDidLoad {
...
// 为imageView添加平移手势识别器
UIPanGestureRecognizer *pan = [[UIPanGestureRecognizer alloc] initWithTarget:self action:@selector(handleAttachmentGesture:)];
[self.imageView addGestureRecognizer:pan];
}
在imageView识别到平移手势时,会调用以下方法。在该方法内用view和imageView不同坐标系统输出当前手势位置。
- (void)handleAttachmentGesture:(UIPanGestureRecognizer *)panGesture {
CGPoint location = [panGesture locationInView:self.view];
CGPoint boxLocation = [panGesture locationInView:self.imageView];
switch (panGesture.state) {
// 手势开始
case UIGestureRecognizerStateBegan:
NSLog(@"Touch started position: %@",NSStringFromCGPoint(location));
NSLog(@"Location in image started is %@",NSStringFromCGPoint(boxLocation));
break;
// 手势结束
case UIGestureRecognizerStateEnded:
NSLog(@"Touch ended position: %@",NSStringFromCGPoint(location));
NSLog(@"Location in image ended is %@",NSStringFromCGPoint(boxLocation));
break;
default:
break;
}
}
现在运行app,拖动视图上的Apple logo,可以看到控制台输出如下:
Touch started position: {237.66665649414062, 294.66665649414062}
Location in image started is {150.66665649414062, 169.33332316080728}
Touch ended position: {144, 288.66665649414062}
Location in image ended is {57, 163.33332316080728}
4.2 添加UIDynamicAnimator和UIAttachmentBehavior
现在要做的就是通过使用UIAttachmentBehavior让imageView随手指移动。在此之前,先将imageView的frame保存到属性中。更新后viewDidLoad方法如下:
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
self.orangeBounds = self.imageView.bounds;
self.orangeCenter = self.imageView.center;
...
}
当手势识别器识别到手势开始时,初始化UIAttachmentBehavior,更新redView和blueView位置。最后添加UIAttachmentBehavior到UIDynamicAnimator。更新后的handleAttachmentGesture:方法如下:
- (void)handleAttachmentGesture:(UIPanGestureRecognizer *)panGesture {
...
switch (panGesture.state) {
// 手势开始
case UIGestureRecognizerStateBegan:
// NSLog(@"Touch started position: %@",NSStringFromCGPoint(location));
// NSLog(@"Location in image started is %@",NSStringFromCGPoint(boxLocation));
// 1.移除所有动力行为
[self.animator removeAllBehaviors];
// 2.通过改变锚点移动imageView
UIOffset centerOffset = UIOffsetMake(boxLocation.x - CGRectGetMidX(self.imageView.bounds), boxLocation.y - CGRectGetMidY(self.imageView.bounds));
self.attachmentBehavior = [[UIAttachmentBehavior alloc] initWithItem:self.imageView offsetFromCenter:centerOffset attachedToAnchor:location];
// 3.redView中心设置为attachmentBehavior的anchorPoint blueView的中心设置为手势手势开始的位置
self.redView.center = self.attachmentBehavior.anchorPoint;
self.blueView.center = location;
// 4.添加附着行为到animator
self.animator = [[UIDynamicAnimator alloc] initWithReferenceView:self.view];
[self.animator addBehavior:self.attachmentBehavior];
break;
// 手势结束
...
}
上述代码分布说明如下:
- 首先移除已存在的动力行为,不然动力行为间会产生冲突。
- 先计算出手势与
imageView中心偏移,初始化attachmentBehavior。 -
redView中心设置为attachmentBehavior的anchorPoint,blueView的中心设置为手势手势开始的位置location。 - 初始化
animator时指定其坐标系统为self.view,添加附着行为到animator。
现在让anchorPoint跟随手指移动,在上面代码后添加如下代码:
- (void)handleAttachmentGesture:(UIPanGestureRecognizer *)panGesture {
...
// 手势改变
case UIGestureRecognizerStateChanged:
self.attachmentBehavior.anchorPoint = [panGesture locationInView:self.view];
self.redView.center = self.attachmentBehavior.anchorPoint;
break;
// 手势结束
...
}
上面的代码可以让anchorPoint和redView中心与当前手指位置一致,当手指移动时,手势识别器调用该方法更新anchorPoint,animator会自动动态更新视图位置。如果手动更新了动力项位置,则需要使用animator调用updateItemUsingCurrentState:方法更新动力项位置。
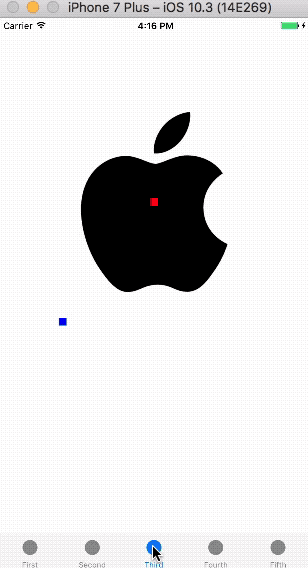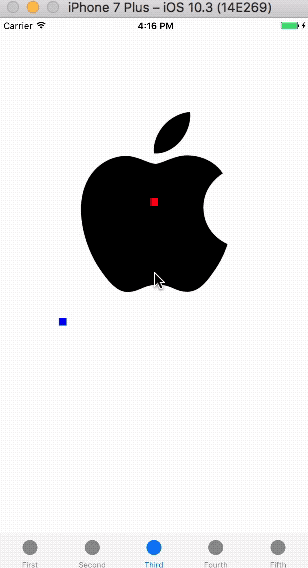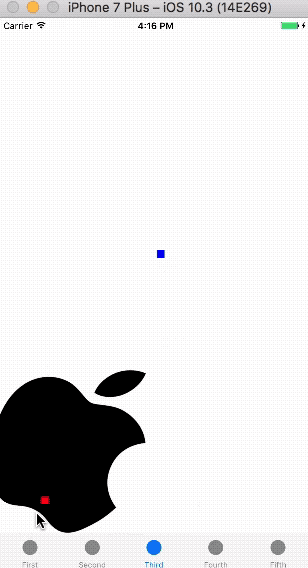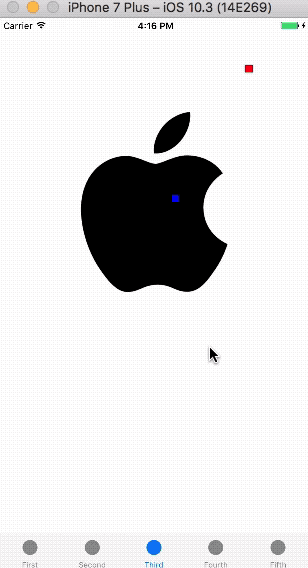
运行demo,拖拽图片,显示如下:
在拖拽结束后,让imageView恢复到原来位置更美观一些。在实现部分添加如下方法:
- (void)resetDemo {
[self.animator removeAllBehaviors];
[UIView animateWithDuration:0.5 animations:^{
self.imageView.bounds = self.originalBounds;
self.imageView.center = self.originalCenter;
self.imageView.transform = CGAffineTransformIdentity;
}];
}
在handleAttachmentGesture:方法UIGestureRecognizerStateEnded部分调用该方法。
- (void)handleAttachmentGesture:(UIPanGestureRecognizer *)panGesture {
...
// 手势结束
case UIGestureRecognizerStateEnded:
// NSLog(@"Touch ended position: %@",NSStringFromCGPoint(location));
// NSLog(@"Location in image ended is %@",NSStringFromCGPoint(boxLocation));
[self resetDemo];
break;
default:
break;
}
}
运行demo,这次拖拽完毕imageView会自动回到初始位置。
4.3 添加UIPushBehavior
在这一部分,需要在停止拖动时分离imageView,并施加冲量,以便在释放时可以继续其轨迹。
在实现部分前添加以下两个常量。
@end
static CGFloat const ThrowingThreshold = 1000;
static CGFloat const ThrowingVelocityPadding = 15;
@implementation ThirdViewController
ThrowingThreshold表示imageView要想继续移动而不立即返回到原始位置所需要的最低速度。ThrowingVelocityPadding是一个魔术数字,用于影响推力大小。
继续在handleAttachmentGesture:方法,更新UIGestureRecognizerStateEnded内代码后如下:
- (void)handleAttachmentGesture:(UIPanGestureRecognizer *)panGesture {
...
// 手势结束
case UIGestureRecognizerStateEnded:
// NSLog(@"Touch ended position: %@",NSStringFromCGPoint(location));
// NSLog(@"Location in image ended is %@",NSStringFromCGPoint(boxLocation));
// 1.移除attachmentBehavior
[self.animator removeBehavior:self.attachmentBehavior];
// 2.当前运行速度 推动行为力向量大小
CGPoint velocity = [panGesture velocityInView:self.view];
CGFloat magnitude = sqrtf(velocity.x * velocity.x + velocity.y * velocity.y);
if (magnitude > ThrowingThreshold) {
// 3.添加pushBehavior
UIPushBehavior *pushBehavior = [[UIPushBehavior alloc] initWithItems:@[self.imageView] mode:UIPushBehaviorModeInstantaneous];
pushBehavior.pushDirection = CGVectorMake(velocity.x / 10, velocity.y / 10);
pushBehavior.magnitude = magnitude / ThrowingVelocityPadding;
self.pushBehavior = pushBehavior;
[self.animator addBehavior:self.pushBehavior];
// 4.修改itemBehavior属性 以便让imageView产生飞起来的感觉
NSInteger angle = arc4random_uniform(20) - 10;
self.itemBehavior = [[UIDynamicItemBehavior alloc] initWithItems:@[self.imageView]];
self.itemBehavior.friction = 0.2;
self.itemBehavior.allowsRotation = YES;
[self.itemBehavior addAngularVelocity:angle forItem:self.imageView];
[self.animator addBehavior:self.itemBehavior];
// 5.一定时间后 imageView回到初始位置
[self performSelector:@selector(resetDemo) withObject:nil afterDelay:0.3];
}
else
{
[self resetDemo];
}
break;
default:
break;
}
}
上述代码的分布说明如下:
- 移除
attachmentBehavior,否则手势停止时imageView会立即停止。这里的移除不需要判断被移除项是否存在,如果被移除项为nil,或不是该animator的动力项,animator会自动忽略该移除方法。 - 通过手势获得当前速度,计算出力大小。
- 若
imageView与手势分离时的速度大于ThrowingThreshold,添加UIPushBehavior。这里的推力为瞬时力,所以mode:参数为UIPushBehaviorModeInstantaneous。力的方向根据向量的x和y决定。最后添加pushBehavior到animator。 - 这一部分设置
UIDynamicItemBehavior属性,让imageView产生飞起来的感觉。你可以自行修改其他属性,体会各种属性产生的不同效果。 - 通过
performSelector: withObject: afterDelay:方法,在一定时间后,让imageView回归到初始位置。
运行demo,可以看到效果如下:
5. 吸附行为UISnapBehavior
使用UISnapBehavior可以把视图吸附到一个新位置,视图移动的过程就像受弹簧拉力而动。在这一部分,我们将通过点击屏幕将视图吸附到点击处。
进入到FourthViewController.m,声明以下属性。
@interface FourthViewController ()
@property (strong, nonatomic) UIView *purpleView;
@property (strong, nonatomic) UIDynamicAnimator *animator;
@property (strong, nonatomic) UISnapBehavior *snapBehavior;
@end
初始化purpleView和animator,并设置purpleView背景颜色为purpleColor。
- (UIView *)purpleView {
if (!_purpleView) {
_purpleView = [[UIView alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectMake(0, 0, 50, 50)];
_purpleView.center = self.view.center;
_purpleView.backgroundColor = [UIColor purpleColor];
}
return _purpleView;
}
- (UIDynamicAnimator *)animator {
if (!_animator) {
_animator = [[UIDynamicAnimator alloc] initWithReferenceView:self.view];
}
return _animator;
}
在viewDidLoad方法中添加点击手势识别器,手指点击的位置用于吸附purpleView。在添加点击手势前,添加purpleView到view。
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
[self.view addSubview:self.purpleView];
// 添加点击手势
UITapGestureRecognizer *tapGesture = [[UITapGestureRecognizer alloc] initWithTarget:self action:@selector(handleTapGesture:)];
[self.view addGestureRecognizer:tapGesture];
}
当用户点击屏幕时,点击手势识别器会调用handleTapGesture:方法,下面实现该方法。
- (void)handleTapGesture:(UITapGestureRecognizer *)tapGesture {
// 1.获得点击屏幕位置
CGPoint touchPoint = [tapGesture locationInView:self.view];
// 2.snapBehavior存在时 移除
if (self.snapBehavior) {
[self.animator removeBehavior:self.snapBehavior];
}
// 3.初始化snapBehavior 设定damping值
self.snapBehavior = [[UISnapBehavior alloc] initWithItem:self.purpleView snapToPoint:touchPoint];
self.snapBehavior.damping = 0.3;
[self.animator addBehavior:self.snapBehavior];
}
上述代码的分布说明如下:
- 获得点击屏幕位置。
- 因为只能存在一个激活的
snapBehavior,当snapBehavior存在时,将其从animator移除。这里也可不做判断直接移除。 - 初始化
snapBehavior,初始化时指定动力项为purpleView,snapToPoint:参数指定吸附点为屏幕点击位置。减震系数damping值范围是0.0至1.0,值越小震动幅度越大,默认值是0.5。最后添加snapBehavior到animator。
运行demo,点击屏幕任意位置查看效果。
6. 场行为UIFieldBehavior
UIFieldBehavior将基于场的物理学应用于动力项对象,场行为定义了可以应用诸如重力(gravity)、磁力(magnetism)、阻力(drag)、速度(velocity)、湍流(turbulence)等力的区域。使用UIFieldBehavior时,要先创建所需场行为,之后配置场强度(strength)属性和其他所需属性。
创建UIFieldBehavior后,使用addItem:方法将该场行为与动力项关联起来。对于很多场行为,你还必须为动力项配置UIDynamicItemBehavior属性以便让场可以对其施加作用,如density属性。最后将配置好的UIFieldBehavior添加到UIDynamicAnimator以便在用户界面执行动画。
场行为的position属性用于定义场行为在用户界面中的位置,场行为的region属性定义了场行为作用的区域。region区域以position为中心,region可以是圆形或长方形,也可以用不同方式组建区域复杂的region。
所有场行为都有strength属性,用于定义场强度。大部分场行为也会用到falloff属性,使场强随距离变化。根据场的类型和需要配置其他属性,如minimumRadius、direction、smoothness和animationSpeed等属性。
在这里将创建radialGravityField和vortexField两个场行为,并与UIView对象blueView关联起来。因这里场行为的类型,需要使用UIDynamicItemBehavior对象配置blueView的density属性。
进入FifthViewController.m,声明以下属性。
@interface FifthViewController ()
@property (strong, nonatomic) UIView *blueView;
@property (strong, nonatomic) UIDynamicAnimator *animator;
@property (strong, nonatomic) UIFieldBehavior *radialGravityField;
@property (strong, nonatomic) UIFieldBehavior *vortexField;
@end
使用懒加载配置blueView和animator,初始化后在viewDidLoad方法中将blueView添加到view。
- (UIView *)blueView {
if (!_blueView) {
_blueView = [[UIView alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectMake(0, 0, 50, 50)];
_blueView.center = CGPointMake(self.view.center.x*2/3, self.view.center.y*2/3);
_blueView.layer.cornerRadius = _blueView.frame.size.width/2;
_blueView.layer.backgroundColor = [UIColor blueColor].CGColor;
}
return _blueView;
}
- (UIDynamicAnimator *)animator {
if (!_animator) {
_animator = [[UIDynamicAnimator alloc] initWithReferenceView:self.view];
}
return _animator;
}
使用懒加载初始化radialGravityField。
- (UIFieldBehavior *)radialGravityField {
if (!_radialGravityField) {
// 1.使用类方法初始化radialGravityField
_radialGravityField = [UIFieldBehavior radialGravityFieldWithPosition:self.view.center];
// 2.指定radialGravityField区域
_radialGravityField.region = [[UIRegion alloc] initWithRadius:300];
// 3.设置场强
_radialGravityField.strength = 1.5;
// 4.场强随距离变化
_radialGravityField.falloff = 4.0;
// 5.场强变化的最小半径
_radialGravityField.minimumRadius = 50.0;
}
return _radialGravityField;
}
上述代码分步说明如下:
- 使用类方法
radialGravityFieldWithPosition:初始化radialGravityBehavior,模拟地心引力,指定场行为的位置在视图的中心。 -
region指定场行为作用区域为半径300point的圆。radialGravityBehavior对区域外动力项不能施加作用。 - 设定场强为
1.5,strength的默认值为1.0。相同strength值在不同类型场行为中有不同作用力大小,确定该值最佳方法是尝试不同值,直到获得所需的效果。 -
fallOff定义了场强strength随距离场行为中心距离增加而减小的速度。距离每超过minimumRadius时,falloff会施加一次作用。该属性默认值是0,产生场强不会随距离变化的均匀区域。在这里,设置fallOff值为4.0。 - 开始计算场强度新值的最小距离。距离小于
minimumRadius时,按照等于minimumRadius计算。除此之外,只有到达最小距离时falloff才会有效。minimumRadius默认值很小,但不为零。在这里,设置minimumRadius值为50.0。
初始化vortexField。
- (UIFieldBehavior *)vortexField {
if (!_vortexField) {
// 1.初始化vortexField
_vortexField = [UIFieldBehavior vortexField];
// 2.设置position为视图中心
_vortexField.position = self.view.center;
_vortexField.region = [[UIRegion alloc] initWithRadius:200];
_vortexField.strength = 0.005;
}
return _vortexField;
}
上述代码的分布说明如下:
- 使用类方法
vortexField初始化vortexField,模拟涡流力。 - 设定
vortexField的position为视图控制器中心。
在viewDidAppear:方法添加动力项到动力行为,将动力行为添加到animator。
- (void)viewDidAppear:(BOOL)animated {
[super viewDidAppear:animated];
// 1.开启调试模式
[self.animator setValue:[NSNumber numberWithBool:YES] forKey:@"debugEnabled"];
// 2.配置动力项密度
UIDynamicItemBehavior *blueViewBehavior = [[UIDynamicItemBehavior alloc] initWithItems:@[self.blueView]];
blueViewBehavior.density = 0.5;
[self.animator addBehavior:blueViewBehavior];
// 3.添加动力项到动力行为
[self.vortexField addItem:self.blueView];
[self.radialGravityField addItem:self.blueView];
// 4.添加动力行为到animator
[self.animator addBehavior:self.vortexField];
[self.animator addBehavior:self.radialGravityField];
}
在1中开启调试模式,可以让我们看到场行为的强度和方向(下图中红线)。强度越大,红色虚线越显著。下图1strength为1.5,图2strength为50,其他属性相同。
运行demo,显示如下:
你可以添加其他场行为到blueView,查看各种场行为的效果。
总结
UIKit Dynamics是一个非常有用的库,利用系统提供的各种动力行为并设置适当的属性,可以为UI添加很多逼真动画。使用物理引擎是要耗费一定CPU资源的,特别是在碰撞检测时。使用中可以组合使用多种动力行为,但不要让彼此冲突。UIKit Dynamics可以与他动画结合使用,以创建更复杂的UI动画。
Demo名称:UIKitDynamics
源码地址:https://github.com/pro648/BasicDemos-iOS
参考资料:
- iOS 7 UIKit Dynamic 学习总结
- WWDC 2013 Session笔记 - UIKit Dynamics入门
- Adding Animated Effects to iOS App Using UIKit Dynamics
- How To Toss Views Using UIKit Dynamics
- Add Snap Behaviour Tutorial in iOS8 with Swift
- Dynamic animations: UIFieldBehavior
欢迎更多指正:https://github.com/pro648/tips/wiki