1、单链表
(1) “H x”,表示向链表头插入一个数x。
(2) “D k”,表示删除第k个输入的数后面的数(当k为0时,表示删除头结点)。
(3) “I k x”,表示在第k个输入的数后面插入一个数x(此操作中k均大于0)。
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
// head 表示头结点的下标
// e[i] 表示节点i的值
// ne[i] 表示节点i的next指针是多少
// idx 存储当前已经用到了哪个点
static int N = 100010;
static int head = - 1;
static int[] e = new int[N];
static int[] ne = new int[N];
static int idx = 0;
// 将x插到头结点
public static void add_to_head(int x)
{
e[idx] = x;
ne[idx] = head;
head = idx ++;
}
// 将下标是k的点后面的点删掉
public static void remove(int k)
{
ne[k] = ne[ne[k]];
}
// 将x插到下标是k的点后面
public static void add(int k,int x)
{
e[idx] = x;
ne[idx] = ne[k];
ne[k] = idx ++ ;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
int m = scan.nextInt();
while(m -- > 0)
{
String op = scan.next();
if(op.equals("H"))
{
int x = scan.nextInt();
add_to_head(x);
}
else if(op.equals("D"))
{
int k = scan.nextInt();
if(k == 0) head = ne[head];
else remove(k - 1);
}
else
{
int k = scan.nextInt();
int x = scan.nextInt();
add(k - 1, x);
}
}
for(int i = head; i != -1; i = ne[i])
System.out.print(e[i]+ " ");
}
}
2、双链表
实现一个双链表,双链表初始为空,支持5种操作:
(1) 在最左侧插入一个数;
(2) 在最右侧插入一个数;
(3) 将第k个插入的数删除;
(4) 在第k个插入的数左侧插入一个数;
(5) 在第k个插入的数右侧插入一个数
现在要对该链表进行M次操作,进行完所有操作后,从左到右输出整个链表。
注意:由于是从第2的位置开始存结点,所以里面中第k个插入的数,意思是指第(k + 1)的位置的数
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
static int N = 100010;
static int[] e = new int[N];
static int[] l = new int[N];
static int[] r = new int[N];
static int idx;
//在节点a的右边插入一个x
public static void insert(int a,int x)
{
e[idx] = x;
l[idx] = a;
r[idx] = r[a];
l[r[a]] = idx;
r[a] = idx;
idx ++;
}
//删除结点a
public static void remove(int a)
{
r[l[a]] = r[a];
l[r[a]] = l[a];
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
int m = scan.nextInt();
//0是左端点,1是右端点
r[0] = 1;
l[1] = 0;
idx = 2;
while(m -- > 0)
{
String op = scan.next();
//“L x”,表示在链表的最左端插入数x。
if(op.equals("L"))
{
int x = scan.nextInt();
insert(0,x);
}
//“R x”,表示在链表的最右端插入数x。
else if(op.equals("R"))
{
int x = scan.nextInt();
insert(l[1],x);
}
// “D k”,表示将第k个插入的数删除,由于是从2开始存结点,所以意思是删除第(k + 1)位置的结点
else if(op.equals("D"))
{
int k = scan.nextInt();
remove(k + 1);
}
//“IL k x”,表示在第k个插入的数左侧插入一个数。
else if(op.equals("IL"))
{
int k = scan.nextInt();
int x = scan.nextInt();
insert(l[k + 1],x);
}
else
{
int k = scan.nextInt();
int x = scan.nextInt();
insert(k + 1,x);
}
}
for(int i = r[0];i != -1;i = r[i])
System.out.println(e[i]);
}
}
优化输入
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class Main{
static int N = 100010;
static int[] e = new int[N];
static int[] l = new int[N];
static int[] r = new int[N];
static int idx;
//在节点a的右边插入一个x
public static void insert(int a,int x)
{
e[idx] = x;
l[idx] = a;
r[idx] = r[a];
l[r[a]] = idx;
r[a] = idx;
idx ++;
}
//删除结点a
public static void remove(int a)
{
r[l[a]] = r[a];
l[r[a]] = l[a];
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int m = Integer.parseInt(reader.readLine());
//0是左端点,1是右端点
r[0] = 1;
l[1] = 0;
idx = 2;
while(m -- > 0)
{
String[] str = reader.readLine().split(" ");
//“L x”,表示在链表的最左端插入数x。
if(str[0].equals("L"))
{
int x = Integer.parseInt(str[1]);
insert(0,x);
}
//“R x”,表示在链表的最右端插入数x。
else if(str[0].equals("R"))
{
int x = Integer.parseInt(str[1]);
insert(l[1],x);
}
// “D k”,表示将第k个插入的数删除,由于是从2开始存结点,所以意思是删除第(k + 1)位置的结点
else if(str[0].equals("D"))
{
int k = Integer.parseInt(str[1]);
remove(k + 1);
}
//“IL k x”,表示在第k个插入的数左侧插入一个数。
else if(str[0].equals("IL"))
{
int k = Integer.parseInt(str[1]);
int x = Integer.parseInt(str[2]);
insert(l[k + 1],x);
}
else
{
int k = Integer.parseInt(str[1]);
int x = Integer.parseInt(str[2]);
insert(k + 1,x);
}
}
for(int i = r[0];i != 1;i = r[i])
System.out.print(e[i]+" ");
}
}
3、栈
实现一个栈,栈初始为空,支持四种操作:
(1) “push x” – 向栈顶插入一个数x;
(2) “pop” – 从栈顶弹出一个数;
(3) “empty” – 判断栈是否为空;
(4) “query” – 查询栈顶元素。
现在要对栈进行M个操作,其中的每个操作3和操作4都要输出相应的结果。
注意:tt = 0,从第1个位置开始存
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
static int N = 100010;
//从1开始存放数值
static int[] stk = new int[N];
static int tt = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
int m = scan.nextInt();
while(m -- > 0)
{
String op = scan.next();
if(op.equals("push"))
{
int x = scan.nextInt();
stk[++ tt] = x;
}
else if(op.equals("pop")) tt--;
else if(op.equals("empty"))
{
if(tt == 0) System.out.println("Yes");
else System.out.println("NO");
}
else System.out.println(stk[tt]);
}
}
}
4、队列
实现一个队列,队列初始为空,支持四种操作:
(1) “push x” – 向队尾插入一个数x;
(2) “pop” – 从队头弹出一个数;
(3) “empty” – 判断队列是否为空;
(4) “query” – 查询队头元素。
现在要对队列进行M个操作,其中的每个操作3和操作4都要输出相应的结果。
注意:tt = -1,从第0个位置开始存,hh 表示队头,tt表示队尾
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
static int N = 100010;
static int[] q = new int[N];
//hh 表示队头,tt表示队尾
static int hh = 0;
static int tt = -1;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
int m = scan.nextInt();
while(m-- > 0)
{
String op = scan.next();
if(op.equals("push"))
{
int x = scan.nextInt();
q[++ tt] = x;
}
else if(op.equals("pop")) hh ++;
else if(op.equals("empty"))
{
if(hh <= tt) System.out.println("NO");
else System.out.println("YES");
}
else
{
System.out.println(q[hh]);
}
}
}
}
5、单调栈
常见模型:找出每个数左边离它最近的比它大/小的数
暴力情况:
单调栈模拟:
模版
常见模型:找出每个数左边离它最近的比它大/小的数
int tt = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
{
while (tt && check(stk[tt], i)) tt -- ;
stk[ ++ tt] = a[i];
}
题目
例如:给定一个长度为N的整数数列,输出每个数左边第一个比它小的数,如果不存在则输出-1。
实现代码
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
static int N = 100010;
//从1开始存放数值
static int[] stk = new int[N];
static int tt = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scan.nextInt();
int[] a = new int[n];
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++)
a[i] = scan.nextInt();
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++)
{
int x = a[i];
while(stk[tt] >= x) tt --;
if(tt == 0) System.out.print(-1 + " ");
else System.out.print(stk[tt] + " ");
stk[++ tt] = x;
}
}
}
6、单调队列
常见模型:找出滑动窗口中的最大值/最小值
给定一个大小为n≤10^6的数组。
有一个大小为k的滑动窗口,它从数组的最左边移动到最右边。
您只能在窗口中看到k个数字。
每次滑动窗口向右移动一个位置。
以下是一个例子:
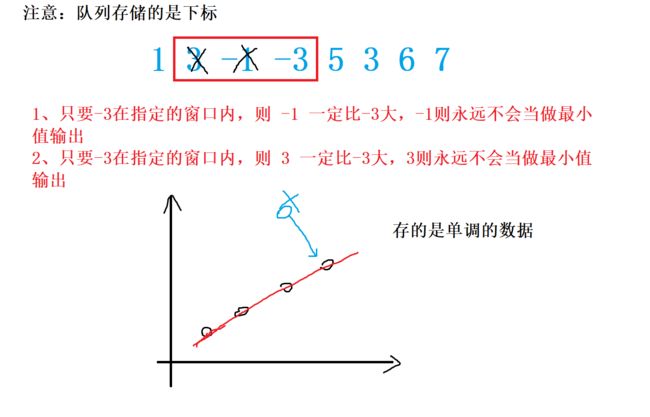
该数组为[1 3 -1 -3 5 3 6 7],k为3。
您的任务是确定滑动窗口位于每个位置时,窗口中的最大值和最小值。
以求最小值为例,求最大值完全与最小值对称
模版
常见模型:找出滑动窗口中的最大值/最小值
int hh = 0, tt = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ )
{
while (hh <= tt && check_out(q[hh])) hh ++ ; // 判断队头是否滑出窗口
while (hh <= tt && check(q[tt], i)) tt -- ;
q[ ++ tt] = i;
}
求窗口最小值模版:
int hh = 0, tt = -1;
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++)
{
//判断队头是否已经滑出窗口
if(hh <= tt && i - k + 1 > q[hh]) hh ++;
//维护单调队列的单调性
while(hh <= tt && a[q[tt]] >= a[i]) tt --;
q[++ tt] = i;
//打印
if(i >= k - 1) log.write(a[q[hh]] + " ");
}
求窗口最大值模版:
int hh = 0, tt = -1;
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++)
{
//判断队头是否已经滑出窗口
if(hh <= tt && i - k + 1 > q[hh]) hh ++;
//维护单调队列的单调性
while(hh <= tt && a[q[tt]] <= a[i]) tt --;
q[++ tt] = i;
//打印
if(i >= k - 1) log.write(a[q[hh]] + " ");
}
总代码:
import java.io.*;
public class Main{
static int N = 1000010;
static int[] q = new int[N];
static int[] a = new int[N];
//hh记录出队列处
static int hh = 0;
//tt记录进队列处
static int tt = -1;
public static void main(String[] args) throws NumberFormatException, IOException {
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
BufferedWriter log = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
String[] s = reader.readLine().split(" ");
int n = Integer.parseInt(s[0]);
int k = Integer.parseInt(s[1]);
String[] str = reader.readLine().split(" ");
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++)
{
a[i] = Integer.parseInt(str[i]);
}
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++)
{
//判断队头是否已经滑出窗口
if(hh <= tt && i - k + 1 > q[hh]) hh ++;
//维护单调队列的单调性
while(hh <= tt && a[q[tt]] >= a[i]) tt --;
q[++ tt] = i;
if(i >= k - 1) log.write(a[q[hh]] + " ");
}
log.write("\n");
hh = 0; tt = -1;
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++)
{
//判断队头是否已经滑出窗口
if(hh <= tt && i - k + 1 > q[hh]) hh ++;
//维护单调队列的单调性
while(hh <= tt && a[q[tt]] <= a[i]) tt --;
q[++ tt] = i;
if(i >= k - 1) log.write(a[q[hh]] + " ");
}
// 关闭输入输出流
log.flush();
reader.close();
log.close();
}
}
7、KMP
两个字符窜的匹配问题
KMP是什么,做什么用的
KMP全称为Knuth Morris Pratt算法,三个单词分别是三个作者的名字。KMP是一种高效的字符串匹配算法,用来在主字符串中查找模式字符串的位置(比如在“hello,world”主串中查找“world”模式串的位置)。
题目:
给定一个模式串S,以及一个模板串P,所有字符串中只包含大小写英文字母以及阿拉伯数字。
模板串P在模式串S中多次作为子串出现。
求出模板串P在模式串S中所有出现的位置的起始下标。
暴力枚举
s[]是模式串,p[]是模板串, n是s的长度,m是p的长度
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
{
bool flag = true;
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j ++ )
{
if (s[i + j - 1] != p[j])
{
flag=false;
break;
}
}
}
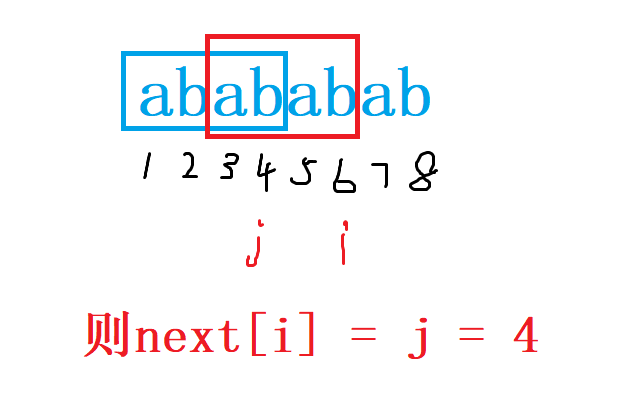
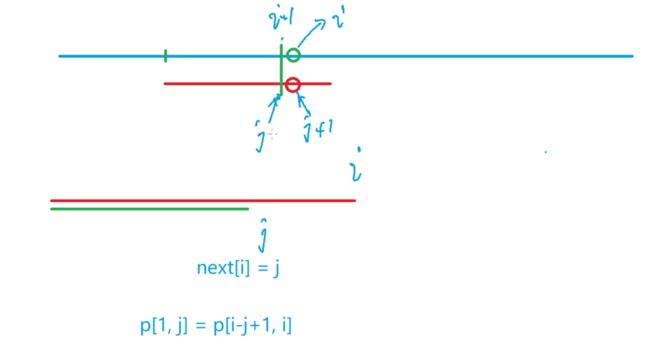
next[i]记录的是p数组的最大后缀等于最大前缀时的最大前缀末尾的位置,即必须要小于i,所以next[1]必须等于0,i就只能从2开始循环了。
如图所示:
分析:比较的位置是s[]数组的第i个位置和p[]数组的第j+1个位置的元素
KMP的时间复杂度是O(n)
模版:
KMP —— 模板题 AcWing 831. KMP字符串
求Next数组:
// s[]是模式串,p[]是模板串, n是s的长度,m是p的长度
for (int i = 2, j = 0; i <= m; i ++ )
{
while (j && p[i] != p[j + 1]) j = ne[j];
if (p[i] == p[j + 1]) j ++ ;
ne[i] = j;
}
// 匹配
for (int i = 1, j = 0; i <= n; i ++ )
{
while (j && s[i] != p[j + 1]) j = ne[j];
if (s[i] == p[j + 1]) j ++ ;
if (j == m)
{
j = ne[j];
// 匹配成功后的逻辑
}
}
// 此处s[]是模式串,p[]是模板串, m是s的长度,n是p的长度
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
static int N = 10010, M = 100010;
static int[] ne = new int[N];
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scan.nextInt();
String p = " " + scan.next();
int m = scan.nextInt();
String s = " " + scan.next();
//求p模版的next数组
for(int i = 2,j = 0;i <= n;i++)
{
while(j != 0 && p.charAt(j + 1) != p.charAt(i))
j = ne[j];
if(p.charAt(j + 1) == p.charAt(i)) j ++;
ne[i] = j;
}
for(int i = 1,j = 0;i <= m;i++)
{
while(j != 0 && p.charAt(j + 1) != s.charAt(i))
j = ne[j];
if(p.charAt(j + 1) == s.charAt(i)) j ++;
if(j == n)
{
System.out.print(i - n + " ");
j = ne[j];
}
}
}
}
8、Trie字典树
维护一个字符串集合,支持两种操作:
“I x”向集合中插入一个字符串x;
“Q x”询问一个字符串在集合中出现了多少次。
共有N个操作,输入的字符串总长度不超过 105,字符串仅包含小写英文字母。
输入格式
第一行包含整数N,表示操作数。
接下来N行,每行包含一个操作指令,指令为”I x”或”Q x”中的一种。
输出格式
对于每个询问指令”Q x”,都要输出一个整数作为结果,表示x在集合中出现的次数。
每个结果占一行。
分析:
son[N] 对应的是所有节点
son[N][26] 表示每个节点的所有儿子
cnt[N] 表示以当前这个点结尾的结点有多少个
idx 表示当前用到哪个下标(类似单链表的idx),下标是0的点,既是根节点,又是空节点
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
static int N = 100010;
//存每个点的所有儿子
static int[][] son = new int[N][26];
//以当前这个点结尾的结点有多少个
static int[] cnt = new int[N];
//当前用到哪个下标,下标是0的点,既是根节点,又是空节点
static int idx = 0;
// 插入一个字符串
public static void insert(String x)
{
int p = 0;//从根结点开始
for(int i = 0;i < x.length();i++)
{
int u = x.charAt(i) - 'a';//当前子节点的编号
//如果p这个节点不存在这个儿子,则把它创建出来(有路就直接走,没有路搭个桥都要走过去)
if(son[p][u] == 0) son[p][u] = ++ idx;
p = son[p][u];
}
cnt[p] ++;
}
// 查询字符串出现的次数
public static int query(String x)
{
int p = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < x.length();i++)
{
int u = x.charAt(i) - 'a';
if(son[p][u] == 0) return 0;
p = son[p][u];
}
return cnt[p];
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scan.nextInt();
while(n -- > 0)
{
String op = scan.next();
if(op.equals("I"))
{
String x = scan.next();
insert(x);
}
else
{
String x = scan.next();
System.out.println(query(x));
}
}
}
}
9、并查集
1、将两个集合合并
2、询问两个元素是否在一个集合当中
时间复杂度近乎
基本原理:每个集合用一棵树来表示,树根的编号就是整个集合的编号,每个节点存储它的父节点,表示的父节点
问题1:如何判断树根 if(p[x] == x)
问题2:如何求x的集合编号 while(p[x] != x) x = p[x]
问题3:如何合并两个集合 px是x的集合编号,py是y的集合编号,p[px ] = py
模版
(1)朴素并查集:
int p[N]; //存储每个点的祖宗节点
// 返回x的祖宗节点
int find(int x)
{
if (p[x] != x) p[x] = find(p[x]);
return p[x];
}
// 初始化,假定节点编号是1~n
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) p[i] = i;
// 合并a和b所在的两个集合:
p[find(a)] = find(b);
(2)维护size的并查集:
int p[N], size[N];
//p[]存储每个点的祖宗节点, size[]只有祖宗节点的有意义,表示祖宗节点所在集合中的点的数量
// 返回x的祖宗节点
int find(int x)
{
if (p[x] != x) p[x] = find(p[x]);
return p[x];
}
// 初始化,假定节点编号是1~n
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
{
p[i] = i;
size[i] = 1;
}
// 合并a和b所在的两个集合:
p[find(a)] = find(b);
size[b] += size[a];
(3)维护到祖宗节点距离的并查集:
int p[N], d[N];
//p[]存储每个点的祖宗节点, d[x]存储x到p[x]的距离
// 返回x的祖宗节点
int find(int x)
{
if (p[x] != x)
{
int u = find(p[x]);
d[x] += d[p[x]];
p[x] = u;
}
return p[x];
}
// 初始化,假定节点编号是1~n
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
{
p[i] = i;
d[I] = 0;
}
// 合并a和b所在的两个集合:
p[find(a)] = find(b);
d[find(a)] = distance; // 根据具体问题,初始化find(a)的偏移量
(1)朴素并查集
一共有n个数,编号是1~n,最开始每个数各自在一个集合中。
现在要进行m个操作,操作共有两种:
1、“M a b”,将编号为a和b的两个数所在的集合合并,如果两个数已经在同一个集合中,则忽略这个操作;
2、“Q a b”,询问编号为a和b的两个数是否在同一个集合中;
输入格式
第一行输入整数n和m。
接下来m行,每行包含一个操作指令,指令为“M a b”或“Q a b”中的一种。
输出格式
对于每个询问指令”Q a b”,都要输出一个结果,如果a和b在同一集合内,则输出“Yes”,否则输出“No”。
每个结果占一行。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
static int N = 100010;
static int[] p = new int[N];
public static int find(int x)//返回x的祖宗节点 + 路径压缩
{
if(p[x] != x) p[x] = find(p[x]);
return p[x];
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scan.nextInt();
int m = scan.nextInt();
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++) p[i] = i;
while(m -- > 0)
{
String op = scan.next();
if(op.equals("M"))
{
int a = scan.nextInt();
int b = scan.nextInt();
p[find(a)] = find(b);
}
else
{
int a = scan.nextInt();
int b = scan.nextInt();
if(find(a) == find(b)) System.out.println("Yes");
else System.out.println("No");
}
}
}
}
(2)维护size的并查集
给定一个包含n个点(编号为1~n)的无向图,初始时图中没有边。
现在要进行m个操作,操作共有三种:
1、“C a b”,在点a和点b之间连一条边,a和b可能相等;
2、“Q1 a b”,询问点a和点b是否在同一个连通块中,a和b可能相等;
3、“Q2 a”,询问点a所在连通块中点的数量;
输入格式
第一行输入整数n和m。
接下来m行,每行包含一个操作指令,指令为“C a b”,“Q1 a b”或“Q2 a”中的一种。
输出格式
对于每个询问指令”Q1 a b”,如果a和b在同一个连通块中,则输出“Yes”,否则输出“No”。
对于每个询问指令“Q2 a”,输出一个整数表示点a所在连通块中点的数量
每个结果占一行。
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
static int N = 100010;
static int[] p = new int[N];
static int[] size = new int[N];
public static int find(int x)
{
if(p[x] != x) p[x] = find(p[x]);
return p[x];
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scan.nextInt();
int m = scan.nextInt();
//初始化
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++)
{
p[i] = i;
size[i] = 1;
}
while(m -- > 0)
{
String op = scan.next();
if(op.equals("C"))
{
int a = scan.nextInt();
int b = scan.nextInt();
a = find(a);
b = find(b);
//若在相同的集合则不需要合并,否则合并
if(a != b)
{
p[a] = b;
size[b] += size[a];
}
}
else if(op.equals("Q1"))
{
int a = scan.nextInt();
int b = scan.nextInt();
if(find(a) == find(b))
{
System.out.println("Yes");
}
else
{
System.out.println("No");
}
}
else
{
int a = scan.nextInt();
System.out.println(size[find(a)]);
}
}
}
}
10、堆
如何手写一个堆?
1、插入一个数 heap[++ size ] = x , up(size)
2、求集合当中的最小值 heap[1]
3、删除最小值 heap[1] = heap[size]; size--; down(1)
4、删除任意一个元素 heap[k] = heap[size];size --; up(k),down(k)
5、修改任意一个元素 heap[k] = x; up(k),down(k)
注意:4和5中,后两个操作只会执行一个,直接把两个写上,结果不变,不需判断
(1)O(n)的复杂度进行堆化
for(int i = n/2;i >= 1;i--) down(i);
(2)更改堆元素后重建堆时间:
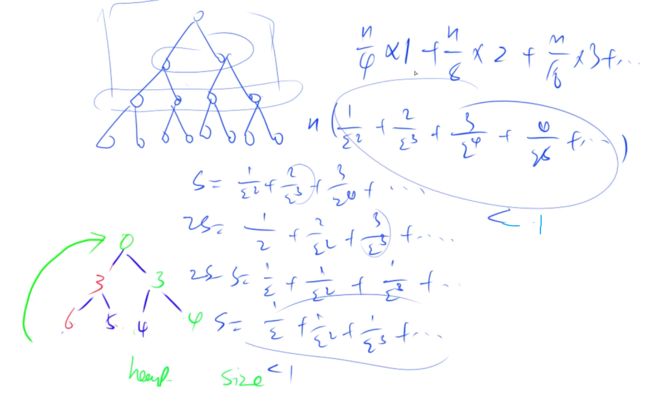
推算过程:循环(n - 1)次,每次都是从根节点往下循环查找,所以每一次时间是,总时间:,因此,堆排序的时间复杂度为
(1)堆排序
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
static int N = 100010;
static int[] h = new int[N];
static int size ;
public static void swap(int u,int t)
{
int x = h[u];
h[u] = h[t];
h[t] = x;
}
//哪个位置下沉操作
public static void down(int u)
{
int t = u;
if(u * 2 <= size && h[u * 2] < h[t]) t = u * 2;
if(u * 2 + 1 <= size && h[u * 2 + 1] < h[t]) t = u * 2 + 1;
if(u != t)
{
swap(u,t);//交换u和t位置的值
down(t);
}
}
//哪个位置上升
public static void up(int u)
{
while(u/2 > 0 && h[u] < h[u/2])
{
swap(u,u/2);
u /= 2;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scan.nextInt();
int m = scan.nextInt();
size = n;
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++) h[i] = scan.nextInt();
//O(n)的复杂度进行堆化
for(int i = n/2;i >= 1;i--) down(i);
while(m -- > 0)
{
System.out.print(h[1]+" ");
h[1] = h[size --];
down(1);
}
}
}
(2)模拟堆
维护一个集合,初始时集合为空,支持如下几种操作:
“I x”,插入一个数x;
“PM”,输出当前集合中的最小值;
“DM”,删除当前集合中的最小值(数据保证此时的最小值唯一);
“D k”,删除第k个插入的数;
“C k x”,修改第k个插入的数,将其变为x;
现在要进行N次操作,对于所有第2个操作,输出当前集合的最小值。
输入格式
第一行包含整数N。
接下来N行,每行包含一个操作指令,操作指令为”I x”,”PM”,”DM”,”D k”或”C k x”中的一种。
输出格式
对于每个输出指令“PM”,输出一个结果,表示当前集合中的最小值。
每个结果占一行。
// h[N]存储堆中的值, h[1]是堆顶,x的左儿子是2x, 右儿子是2x + 1
// ph[k]存储第k个插入的点在堆中的位置
// hp[k]存储堆中下标是k的点是第几个插入的
注意:在”D”操作的时候,一定要先把插进去的元素对应的位置进行记录,否则heap_swap()时会造成提前置换,亲身踩坑
k = ph[k];//记录第k个插入元素的下标
heap_swap(k,size);
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
static int N = 100010;
// h[N]存储堆中的值, h[1]是堆顶,x的左儿子是2x, 右儿子是2x + 1
// ph[k]存储第k个插入的点在堆中的位置
// hp[k]存储堆中下标是k的点是第几个插入的
static int[] h = new int[N];
static int[] ph = new int[N];
static int[] hp = new int[N];
static int size = 0;//表示堆的大小
public static void heap_swap(int u,int t)
{
//交换两个位置的值
int x = h[u];
h[u] = h[t];
h[t] = x;
//交换ph的指向位置
ph[hp[u]] = t;
ph[hp[t]] = u;
//交换hp的指向位置
int m = hp[u];
hp[u] = hp[t];
hp[t] = m;
}
//哪个位置下沉操作
public static void down(int u)
{
int t = u;
if(u * 2 <= size && h[u * 2] < h[t]) t = u * 2;
if(u * 2 + 1 <= size && h[u * 2 + 1] < h[t]) t = u * 2 + 1;
if(u != t)
{
heap_swap(u,t);//交换u和t位置的值
down(t);
}
}
//哪个位置上升
public static void up(int u)
{
while(u/2 > 0 && h[u] < h[u/2])
{
heap_swap(u,u/2);
u /= 2;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scan.nextInt();
int m = 0;//表示第几个数
while(n -- > 0)
{
String op = scan.next();
//“I x”,插入一个数x;
if(op.equals("I"))
{
int x = scan.nextInt();
size ++;
m ++;
h[size] = x;
ph[m] = size; hp[size] = m;
up(size);
}
//“PM”,输出当前集合中的最小值;
else if(op.equals("PM"))
{
System.out.println(h[1]);
}
//“DM”,删除当前集合中的最小值(数据保证此时的最小值唯一);
else if(op.equals("DM"))
{
heap_swap(1,size);
size --;
down(1);
}
//“D k”,删除第k个插入的数;
else if(op.equals("D"))
{
int k = scan.nextInt();
k = ph[k];//记录第k个插入元素的下标
heap_swap(k,size);
size --;
up(k);
down(k);
}
//“C k x”,修改第k个插入的数,将其变为x;
else
{
int k = scan.nextInt();
int x = scan.nextInt();
k = ph[k];
h[k] = x;
up(k);
down(k);
}
}
}
}
11、哈希表
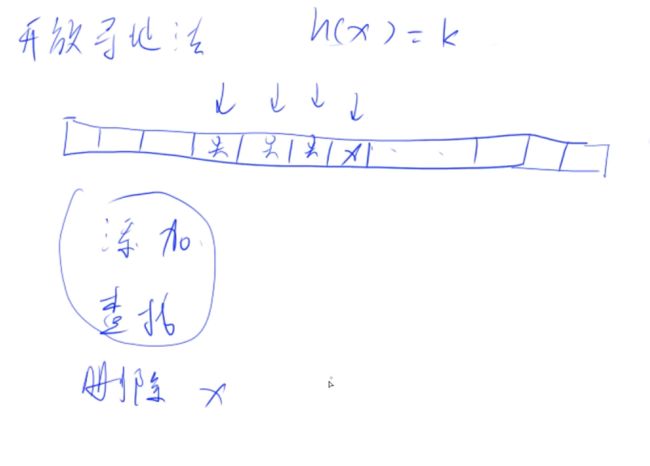
(1)开放寻址法(蹲坑位法)
1、取模找到该位置,若有人在坑里,则继续找,知道有空坑就跳去下一个坑
2、保证取模后的位置在指定的范围中,需要考虑到负数取模的情况
-17 % 10 的计算结果如下:r = (-17) - (-17 / 10) x 10 = (-17) - (-1 x 10) = -7
17 % -10 的计算结果如下:r = 17 - (17 / -10) x (-10) = (17) - (-1 x -10) = 7
-17 % -10 的计算结果如下:r = (-17) - (-17 / -10) x (-10) = (-17) - (1 x -10) = -7
因此,int k = (x % N + N) % N;
3、取N时,需要取比人数多的2~3倍的质数
4、0x3f3f3f3f比10^9次方大,不会被使用到,可以标识为没用过
开放寻址法代码
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
static int N = 200003;
static int[] h = new int[N];
static int idx = 0;
// 如果x在哈希表中,返回x的下标;如果x不在哈希表中,返回x应该插入的位置
public static int find(int x)
{
int k = (x % N + N) % N;
while(h[k] != x && h[k] != 0x3f3f3f3f)
{
k ++;
if(k == N) k = 0;
}
return k;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scan.nextInt();
Arrays.fill(h, 0x3f3f3f3f);//初始化h[]数组的值为0x3f3f3f3f
while(n -- > 0)
{
String op = scan.next();
int x = scan.nextInt();
if(op.equals("I"))
{
h[find(x)] = x;
}
else
{
if(h[find(x)] == x) System.out.println("Yes");
else System.out.println("No");
}
}
}
}
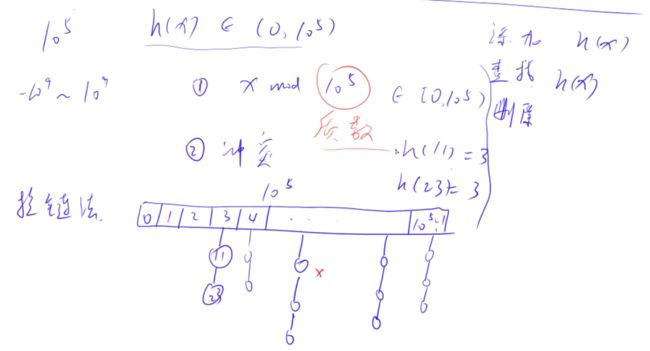
(2)拉链法:
红色圈圈要取的是比10^5方大的质数
拉链法代码
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
static int N = 100003;
static int[] h = new int[N];
static int[] e = new int[N];//值
static int[] ne = new int[N];//指针
static int idx = 0;
// 向哈希表中插入一个数
public static void insert(int x)
{
int k = (x % N + N) % N;
e[idx] = x;
ne[idx] = h[k];
h[k] = idx ++;
}
// 在哈希表中查询某个数是否存在
public static boolean find(int x)
{
int k = (x % N + N) % N;
for(int i = h[k];i != -1; i = ne[i])
{
if(e[i] == x)
return true;
}
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scan.nextInt();
Arrays.fill(h, -1);//初始化h[]数组的值为-1
while(n -- > 0)
{
String op = scan.next();
int x = scan.nextInt();
if(op.equals("I"))
{
insert(x);
}
else
{
if(find(x)) System.out.println("Yes");
else System.out.println("No");
}
}
}
}
(3)字符窜哈希
思路:用一个k进制的角度,把一个字符串看成一个数字
核心思想:将字符串看成P进制数,P的经验值是131或13331,取这两个值的冲突概率低
小技巧:取模的数用2^64,这样直接用unsigned long long存储,溢出的结果就是取模的结果
给定一个长度为n的字符串,再给定m个询问,每个询问包含四个整数l1,r1,l2,r2,请你判断[l1,r1]和[l2,r2]这两个区间所包含的字符串子串是否完全相同。
字符串中只包含大小写英文字母和数字。
输入格式
第一行包含整数n和m,表示字符串长度和询问次数。
第二行包含一个长度为n的字符串,字符串中只包含大小写英文字母和数字。
接下来m行,每行包含四个整数l1,r1,l2,r2,表示一次询问所涉及的两个区间。
注意,字符串的位置从1开始编号。
输出格式
对于每个询问输出一个结果,如果两个字符串子串完全相同则输出“Yes”,否则输出“No”。
每个结果占一行。
数据范围
1≤n,m≤10^5
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
static int N = 100010;
static int P = 131;
static long[] h = new long[N];
static long[] p = new long[N];//p进制中每个位置对应的值
static int idx = 0;
public static long get(int L,int R)
{
return h[R] - h[L - 1] * p[R - L + 1];
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String[] str1 = reader.readLine().split(" ");
int n = Integer.parseInt(str1[0]);
int m = Integer.parseInt(str1[1]);
String s = reader.readLine();
p[0] = 1;
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++)
{
h[i] = h[i - 1] * P + s.charAt(i - 1);
p[i] = p[i - 1] * P;
}
while(m -- > 0)
{
String[] str2 = reader.readLine().split(" ");
int L1 = Integer.parseInt(str2[0]);
int R1 = Integer.parseInt(str2[1]);
int L2 = Integer.parseInt(str2[2]);
int R2 = Integer.parseInt(str2[3]);
if(get(L1,R1) == get(L2,R2)) System.out.println("Yes");
else System.out.println("No");
}
}
}