The thief has found himself a new place for his thievery again. There is only one entrance to this area, called the "root." Besides the root, each house has one and only one parent house. After a tour, the smart thief realized that "all houses in this place forms a binary tree". It will automatically contact the police if two directly-linked houses were broken into on the same night.
Determine the maximum amount of money the thief can rob tonight without alerting the police.
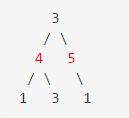
Example 1:
Maximum amount of money the thief can rob = 3 + 3 + 1 = 7.
Example 2:
Maximum amount of money the thief can rob = 4 + 5 = 9.
Credits:Special thanks to @dietpepsi for adding this problem and creating all test cases.
Subscribe to see which companies asked this question.
在上次打劫完一条街道之后和一圈房屋之后,窃贼又发现了一个新的可以打劫的地方,但这次所有的房子组成的区域比较奇怪,聪明的窃贼考察地形之后,发现这次的地形是一颗二叉树。与前两次偷窃相似的是每个房子都存放着特定金额的钱。你面临的唯一约束条件是:相邻的房子装着相互联系的防盗系统,且当相邻的两个房子同一天被打劫时,该系统会自动报警。
算一算,如果今晚去打劫,你最多可以得到多少钱,当然在不触动报警装置的情况下。
样例
窃贼最多能偷窃的金钱数是 3 + 3 + 1 = 7.
窃贼最多能偷窃的金钱数是 4 + 5 = 9.
分析
Step I -- Think naively
初看这个问题,显然这个问题与递归和最优子结构有关:如果我们想要从根节点rob到最大值,我们当然希望我们对它的左子节点和右子节点做相同的操作。
所以i,如果我们定义一个rob函数,rob(root)将会返回我们能从根节点开始rob的最大值,那么现在的问题的关键就在于如何从rob(root)得到rob(root.left)和rob(root.right)。
显然对于树的问题我们可以使用递归的方法,显然当这棵树为空的时候,结果是0,直接返回就可以了。
对于root节点来说,只有两种情况,一种就是rob打劫root节点,一种就是不打劫root节点。首先我们分析第一种情况,打劫root节点
- 如果我们已经打劫了root节点,那么根据题目的要求,我们就不能打劫root的左子节点,和右子节点,所以,接下来的情况就有四种(root.left.left, root.left.right, root.right.left, root.right.right),就是root的孙子辈的节点。把孙子辈节点的值加起来就行了。
- 如果我们不打劫root节点,那么根据题目要求,我们可以打劫左子树和右子树。
我们把这两种情况分别求出来,最后取最大值就是root节点的值。
public int rob(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null)
return 0;
int val = root.val;
if(root.left != null) {
val += rob(root.left.left) + rob(root.left.right);
}
if(root.right != null) {
val += rob(root.right.left) + rob(root.right.right);
}
return Math.max(val, rob(root.left) + rob(root.right));
}
Step II -- Think one step further
在第一种方法中,我们只考虑了最优子结构,而没有考虑子问题的重复计算,我们分析一下,我们为了获得rob(root),我们需要计算rob(root.left), rob(root.right), rob(root.left.left), rob(root.left.right), rob(root.right.left), rob(root.right.right);但是我们计算rob(root.left)的时候我们又会去计算一遍rob(root.left.left), rob(root.left.right),这样就重复计算了,实际上是没有必要的部分,所以我们考虑将已经计算过的结果存起来,如果下次需要直接存取就行了,而不需要重复计算一遍,所以这就变成了动态规划的问题:“最优子结构”+“重复子问题”,我们在本题中用一个hashmap来存储子问题的解。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public int rob(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null)
return 0;
HashMap map = new HashMap<>();
return helper(root, map);
}
private int helper(TreeNode root, HashMap map) {
if(root == null)
return 0;
if(map.containsKey(root))
return map.get(root);
int val = root.val;
if(root.left != null)
val += helper(root.left.left, map) + helper(root.left.right, map);
if(root.right != null)
val += helper(root.right.left, map) + helper(root.right.right, map);
val = Math.max(val, helper(root.left, map) + helper(root.right, map));
map.put(root, val);
return val;
}
}
Step III -- Think one step back
我们继续思考,为什么我们会出现重复子问题的计算,这是因为我们没有记录每个子问题的状态的类别,我们知道每个节点就两种情况,打劫不打劫,但是前面两种都没有记录这种状态信息,所以在计算时就会重复计算。我们考虑,我们考虑保存每个解的状态,是打劫还是没打劫。
If we were able to maintain the information about the two scenarios for each tree root, let's see how it plays out. Redefine rob(root) as a new function which will return an array of two elements, the first element of which denotes the maximum amount of money that can be robbed if root is not robbed, while the second element signifies the maximum amount of money robbed if it is robbed.
因为只有两种状态所以我们用一个数组来保存,当0时,就为不打劫当前节点,当为1时,就为打劫当前节点。
所以当为0时,我们只需要返回左子树和右子树的最大和即可,当为1时,我们只需要将root节点的值加上不打架左子树和右子树的结果返回,也就是左子树状态码0和右子树状态码为0的状态。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public int rob(TreeNode root) {
int[] res = robSub(root);
return Math.max(res[0], res[1]);
}
private int[] robSub(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return new int[2];
int[] left = robSub(root.left);
int[] right = robSub(root.right);
int[] res = new int[2];
res[0] = Math.max(left[0], left[1]) + Math.max(right[0], right[1]);
res[1] = root.val + left[0] + right[0];
return res;
}
}