React和React-native在编程的思想上是完全一样的,所以要写出好的RN代码,学学React的思想很有必要。本文是学习facebook官方文章《Thinking in React》的记录,包括关键点的翻译和自己的理解。
英文原文地址
这片文章大部分是翻译和简化,小部分是自己理解。
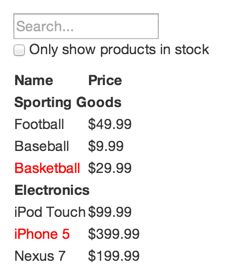
先看看需求
假设我们需要实现这样一个可过滤的商品列表
而且我们有这样的JSON API
[
{category: "Sporting Goods", price: "$49.99", stocked: true, name: "Football"},
{category: "Sporting Goods", price: "$9.99", stocked: true, name: "Baseball"},
{category: "Sporting Goods", price: "$29.99", stocked: false, name: "Basketball"},
{category: "Electronics", price: "$99.99", stocked: true, name: "iPod Touch"},
{category: "Electronics", price: "$399.99", stocked: false, name: "iPhone 5"},
{category: "Electronics", price: "$199.99", stocked: true, name: "Nexus 7"}
];
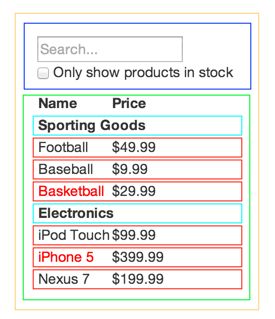
将设计稿分解成Component层次
使用矩形线框来确定Component和子Component。这里要遵循单一职责原则,一个Component只做一件事情。
- FilterableProductTable-橙色:根节点
- SearchBar-蓝色:处理用户输入
- ProductTable-绿色:根据用户输入展现商品列表
- ProductCategoryRow-蓝绿色:显示分类名称
- ProductRow-红色:显示单个商品信息
如下为树状结构
FilterableProductTable
|- SearchBar
|- ProductTable
|- ProductCategoryRow
|- ProductRow
完成静态页面
var ProductCategoryRow = React.createClass({
render: function() {
return ({this.props.category}
{name}
{this.props.product.price}
);
}
});
var ProductTable = React.createClass({
render: function() {
var rows = [];
var lastCategory = null;
this.props.products.forEach(function(product) {
if (product.category !== lastCategory) {
rows.push(
Name
Price
{rows}
);
}
});
var SearchBar = React.createClass({
render: function() {
return (
);
}
});
var FilterableProductTable = React.createClass({
render: function() {
return (
需要注意完成静态页面的时候不要使用state,因为state都是用于保存用户交互结果的。而且每个组件都只有render()方法,根组件FilterableProductTable将通过props获得数据模型,这种单向数据流使得React能很好的模块化,响应也很快。
state和props是React中的两种数据模型,理解两者的区别很重要。简单的理解props是外部传递进来的数据,state是用户和组件交互时产生的数据。更加详细的说明可以参考Facebook的另一篇官方文章
小而全的state
这个例子中的数据包括
- 商品列表
- 用户输入的搜索关键字
- 复选框的状态
- 过滤后的商品列表
判断数据是否为state的标准
- 外部传入的不是state
- 不会变化的不是state
- 可以通过其他state和props计算得到的不是state
根据以上原则,是state的为
- 用户输入的搜索关键字
- 复选框的状态
state的作用域
var ProductCategoryRow = React.createClass({
render: function() {
return ({this.props.category}
{name}
{this.props.product.price}
);
}
});
var ProductTable = React.createClass({
render: function() {
var rows = [];
var lastCategory = null;
this.props.products.forEach(function(product) {
if (product.name.indexOf(this.props.filterText) === -1 || (!product.stocked && this.props.inStockOnly)) {
return;
}
if (product.category !== lastCategory) {
rows.push(
Name
Price
{rows}
);
}
});
var SearchBar = React.createClass({
render: function() {
return (
);
}
});
var FilterableProductTable = React.createClass({
getInitialState: function() {
return {
filterText: '',
inStockOnly: false
};
},
render: function() {
return (
确定state的作用域就是要确定哪个Component应该持有这个state,这里有几个步骤。
- 找到所有render()中会用到这个state的Component
- 找到一个Component包括包含了所有1中的Component
- 2中的Component或者它的上级Component持有这个state
- 如果你找不到一个有意义的Component持有这个state,就在这些节点之上创造一个新的Component来持有这个state
在我们的例子中
- ProductTable需要根据状态来确定显示的列表项目,SearchBar也需要状态来显示搜索文本和复选框状态
- 所以包含两者的公共Component是FilterableProductTable
- FilterableProductTable持有state也是有明确意义的
所以我们在FilterableProductTable中持有state,然后将state作为props传递给ProductTable和SearchBar
反向数据流
ar ProductCategoryRow = React.createClass({
render: function() {
return ({this.props.category}
{name}
{this.props.product.price}
);
}
});
var ProductTable = React.createClass({
render: function() {
var rows = [];
var lastCategory = null;
this.props.products.forEach(function(product) {
if (product.name.indexOf(this.props.filterText) === -1 || (!product.stocked && this.props.inStockOnly)) {
return;
}
if (product.category !== lastCategory) {
rows.push(
Name
Price
{rows}
);
}
});
var SearchBar = React.createClass({
handleChange: function() {
this.props.onUserInput(
this.refs.filterTextInput.value,
this.refs.inStockOnlyInput.checked
);
},
render: function() {
return (
);
}
});
var FilterableProductTable = React.createClass({
getInitialState: function() {
return {
filterText: '',
inStockOnly: false
};
},
handleUserInput: function(filterText, inStockOnly) {
this.setState({
filterText: filterText,
inStockOnly: inStockOnly
});
},
render: function() {
return (
这一部分在原文中稍微有些复杂。简而言之:state在FilterableProductTable中,但是真正的交互发生在SearchBar的字元素中,所以需要从子向父传递信息。这里主要是通过回调机制实现的。
- 由FilterableProductTable通过props.onUserInput传一个回调函数handleUserInput给SearchBar。
- 在文本或者复选状态发生变化时,通过onChange指定调用SearchBar的handleChange
- handleChange通过refs获取文本和复选框状态,并执行回调函数。refs的机制文中并没有详述。
- handleUserInput中改变state,并更新页面