老男孩Linux运维58期课堂笔记
作者:于冬
归档:课堂笔记
日期:3.28
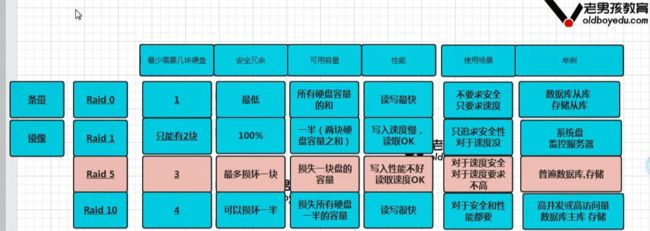
1、什么是Raid
Raid是廉价冗余磁盘阵列(Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disk)的简称, 有时也简称磁盘阵列(Disk Array)
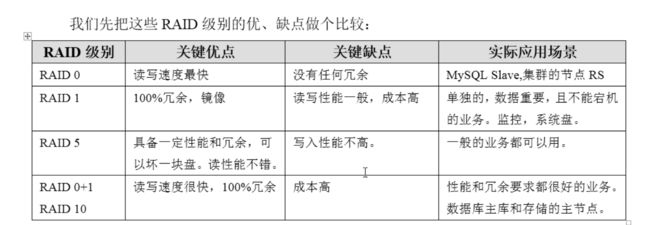
RAID 的优缺点
2、Raid 级别介绍
RAID分为两类:
软RAID,系统层面实现的,性能差。
硬RAID,硬件层面实现的,性能好。
主板板载RAID:功能弱,0,1
独立RAID卡:功能强,0,1,5,10 *****工作选择。
LVM全称(Logic Volume Management (Manager))逻辑卷管理,它的最大用途是可以【灵活的管理磁盘的容量】,让磁盘分区可以随意放大或缩小,便于更好的应用磁盘的剩余空间,如果过于强调性能与备份,那么还是应该使用RAID功能,而不是LVM。
LVM是软件层面实现的,性能太低。性能降低5-10%。
买服务器插满磁盘,分区规划好,永远都不需要LVM。
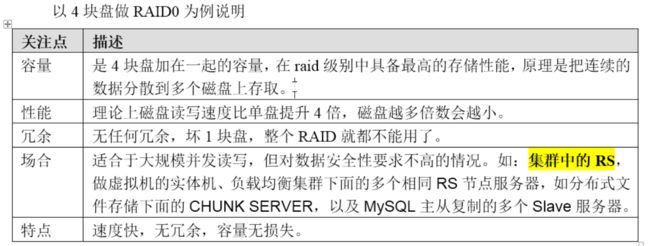
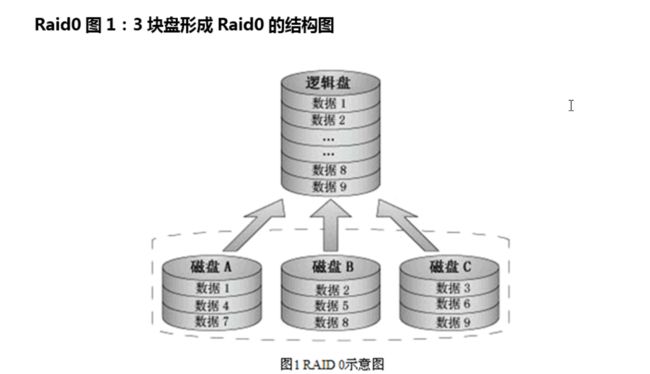
3、Raid0
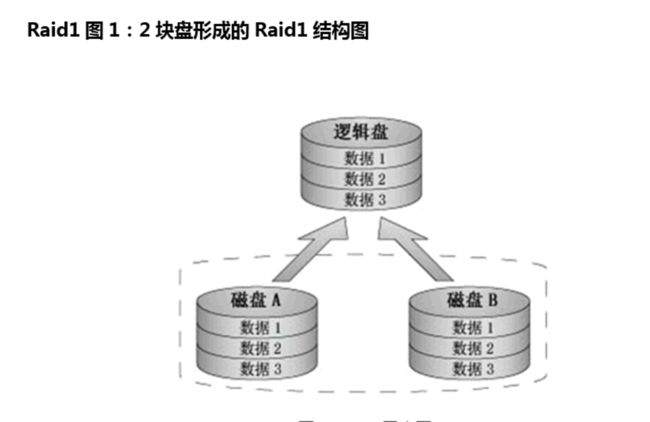
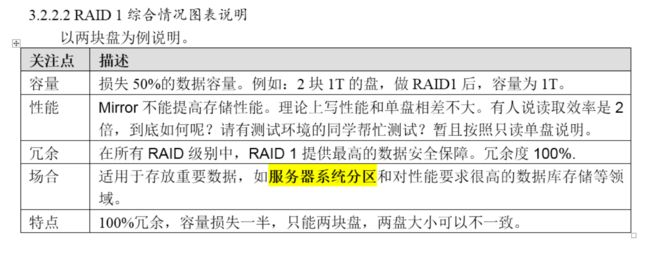
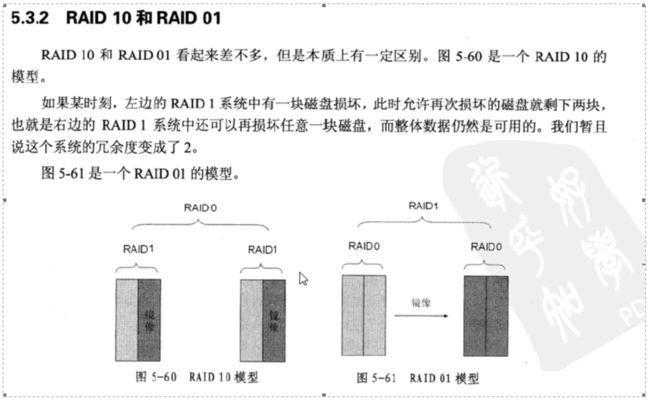
4、RAID1
它的宗旨是最大限度的保证用户数据的可用性和可修复性。
RAID1的操作方式是把用户写入一个磁盘的数据百分之百地自动复制到另外
一个磁盘上,从而实现存储双份的数据。
raid 1的优缺点
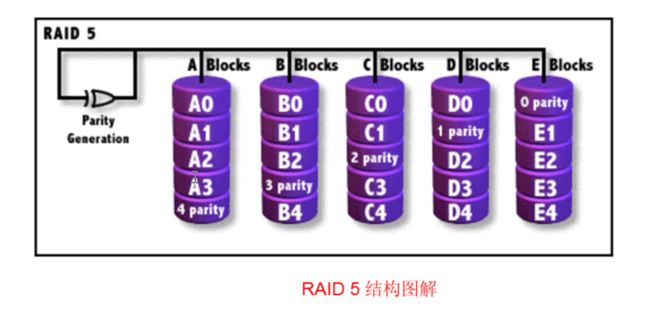
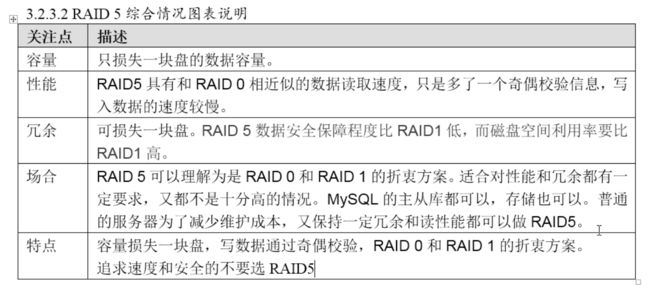
5、RAID5
RAID5 可理解为是RAID0和RAID1的拆衷方案
6、RAID10
7、分区知识:
(1)什么是分区?
磁盘分区就相当于给磁盘打隔断。
(2)磁盘和分区在Linux里的命名。
IDE /dev/hda hdb
SCSI sda sdb
分区数字表示:sda1 sda2 sda3
(3)磁盘分区类型和特点:
1、主分区(primary)P
1)系统中必须要存在的分区,系统盘选择主分区安装。
2)数字编号只能是1-4.sda1、sda2、sda3、sda4。
3)主分区最多四个,最少一个。
2、扩展分区(extend)E
1)相当于一个独立的小磁盘。独立的分区表,不能独立存在。
2)有独立的分区表。
3)不能独立存在,即不能直接存放数据。
4)必须在扩展分区上建立逻辑分区才能存放数据。
5)占用主分区的编号(主分区+扩展分区)之和最多4个。
6)扩展分区可以没有,最多只能有一个。
3、逻辑分区(logic)L
2)数字编号只能是从5开始。
3)存放于扩展分区之上。
4)存放任意普通数据。
磁盘分区注意事项要点
一块硬盘的分区方式只能为如下组合之一:
(1)任意多个主分区,但要求1≤主分区数量≤4。
例如:一个硬盘可以分为4个主分区3个主分区2个主分区或1个主分区。
(2)扩展分区可以和主分区组合,但要求2≤(主分区+扩展分区)数量≤4)。
例如:3个主分区+1个扩展分区或2个主分区+1个扩展分区或1个主分区+1个扩展分区。
当总分区的数量大于4个的时候,必须提前分一个扩展分区,扩展分区最多只能有一个。
(3)如果要分成四个磁盘分区的话,那么最多就是可以:
P + P + P + P
P + P + P + E
问题:如果给一个磁盘分6个分区有哪些方案,同时写出分区/dev/sda(数字)。
3P+1E(3L) 1 2 3 5 6 7
2P+1E(4L) 12 5678
1P+1E(5L) 1 56789
分区分完了,空间还有剩余浪费掉空间。
P + P + P + P
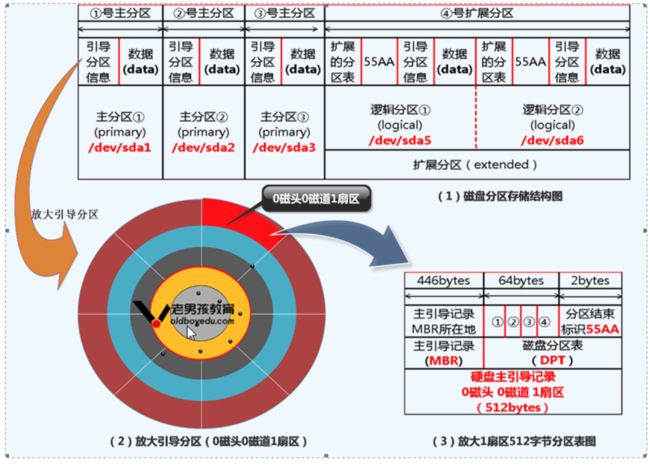
(4)磁盘分区工作原理:
磁盘是按柱面分区的。
磁盘分区登记的地点,磁盘分区表。
磁盘分区表存放分区结果信息的。
磁盘分区表位置,0磁道0磁头1扇区(512字节)
占用1扇区的前446字节(系统引导信息的)后面的64字节(分区表),
剩下2个字节分区结束标志。
磁盘分区表的容量是有限的,64字节,一个分区固定占16字节。
64/16=4分区(主分区+扩展分区)
8、磁盘分区实战
磁盘分区关键就是修改64字节的的分区表而已。
磁盘分区常用命令fdisk,修改MBR分区表,MBR格式。
缺陷,被修改的磁盘大小不能大于2T。
磁盘分区其他命令parted,gpt分区格式,既能修改小于2T也能修改大于2T的磁盘。
小于2T就用fdisk
大于2T就用parted
9、创建主分区操作
Command (m for help): n 创建分区
Partition type:
p primary (0 primary, 0 extended, 4 free)
e extended
Select (default p): p 指定创建的是主分区
Partition number (1-4, default 1): 1 指定分区号码
First sector (2048-20479, default 2048):
Using default value 2048
Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (2048-20479, default 20479): +5M 指定分区大小
Partition 1 of type Linux and of size 5 MiB is set
创建扩展分区
Command (m for help): n
Partition type:
p primary (1 primary, 0 extended, 3 free)
e extended
Select (default p): e 指定创建扩展分区
Partition number (2-4, default 2):
First sector (12288-20479, default 12288):
Using default value 12288
Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (12288-20479, default 20479): 不输大小表示剩余全部空间
Using default value 20479
Partition 2 of type Extended and of size 4 MiB is set
创建逻辑分区:
Command (m for help): n
Partition type:
p primary (1 primary, 1 extended, 2 free)
l logical (numbered from 5)
Select (default p): l 需要首先创建好扩展分区
Adding logical partition 5
First sector (14336-20479, default 14336):
Using default value 14336
Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (14336-20479, default 20479):
Using default value 20479
Partition 5 of type Linux and of size 3 MiB is set
输出分区信息
Command (m for help): p
Disk /dev/sdb: 10 MB, 10485760 bytes, 20480 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk label type: dos
Disk identifier: 0x43a2def7
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 2048 12287 5120 83 Linux
/dev/sdb2 12288 20479 4096 5 Extended
/dev/sdb5 14336 20479 3072 83 Linux
调整分区类型
Command (m for help): t
Partition number (1,2, default 2): 1
Hex code (type L to list all codes): 8e
Changed type of partition 'Linux' to 'Linux LVM'
删除分区操作
Command (m for help): d
Partition number (1,2,5, default 5): 5
Partition 5 is deleted
10、分区操作命令帮助
fdisk /dev/sdb --- 对磁盘进行分区命令
Command action
d delete a partition--- 删除一个分区
l list known partition types--- 列出分区类型(8e Linux LVM)
m print this menu --- 输出帮助信息
n add a new partition --- 创建新的分区
p print the partition table --- 输出分区信息
q quit without saving changes --- 不做任何改变进行退出
t change a partition's system id --- 改变分区类型
w write table to disk and exit --- 保存分区配置
11、磁盘分区的工作原理
磁盘是按柱面分区的