引言
随着互联网的快速发展,当前以步入移动互联、物联网时代。用户访问系统入口也变得多种方式,由原来单一的PC客户端,变化到PC客户端、各种浏览器、手机移动端及智能终端等。同时系统之间大部分都不是单独运行,经常会涉及与其他系统对接、共享数据的需求。所以系统需要升级框架满足日新月异需求变化,支持业务发展,并将框架升级为微服务架构。“API网关”核心组件是架构用于满足此些需求
很多互联网平台已基于网关的设计思路,构建自身平台的API网关,国内主要有京东、携程、唯品会等,国外主要有Netflix、Amazon等。
业界相关网关框架
业界为了满足这些需求,已有相关的网关框架。
1、基于nginx平台实现的网关有:kong、umbrella等
2、自研发的网关有:zuul1、zuul2等
但是以上网关框架只能是满足部分需求,不能满足企业的所有要求,就我而言,我认为最大的问题是没有协议转换及OPS管理控制平台
网关概览
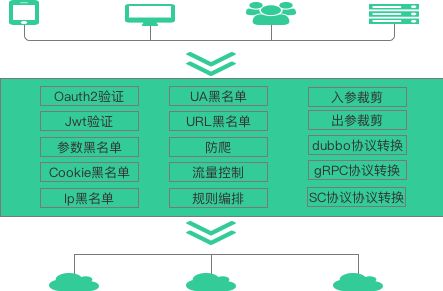
- 面向 Web 或者移动 App
这类场景,前端应用通过 API 调用后端服务,需要网关具有认证、鉴权、缓存、服务编排、监控告警等功能。 - 面向合作伙伴开放 API
这类场景,主要为了满足业务形态对外开放,与企业外部合作伙伴建立生态圈,此时的 API 网关注重安全认证、权限分级、流量管控、缓存等功能。 - 企业内部系统互联互通
这类场景,主要为了企业内部存在不同部门,而部门之间技术栈的不同,使用的通信协议或框架不同,需要一个通用的网关来支持内部系统互联及互通,此时API网关会更注重协议转换的功能,比如说gRPC和Dubbo的协议转换
另外:对于微服务架构下,如果基于HTTP REST传输协议,API网关还承担了一个内外API甄别的功能,只有在API网关上注册了的API还能是真正的堆外API
网关组成部分
整个网关系统由三个子系统组成:
- GateWay Proxy:
负责接收客户端请求、执行过滤器、 路由请求到后端服务,并处理后端服务的请求结果返回给客户端 - GateWay OPS:
提供统一的管理界面,开发人员可在此进行 API、定义过滤器及定义过滤器规则 - GateWay Monitor:
主要由Prometheus来拉取GateWay Proxy的系统情况,由运维人员监控整个GateWay Proxy的健康状况及API统计情况
网关技术架构
说明:
1) 整个网关基于Netty NIO来实现同步非阻塞是HTTP服务,网关是外部API请求的HTTP服务端,同时是内部服务的客户端,所以有Netty Server Handler和Netty Client Handler的出现;
2)对于Netty Server Handler来说,当一个HTTP请求进来时,他会把当前连接转化为ClientToProxyConnection,它是线程安全的,伴随当前此HTTP请求的生命周期结束,它也负责ClientToProxyConnection的生命周期的维护;
3)对于Netty Client Handler来说,当ClientToProxyConnection需要传递请求到内部服务时,会新建(或者获取原来已建)的ProxyToServerConnection来进行内部的请求,它也是线程安全的;
4)对于Filter来说,他运行在ClientToProxyConnection上,插入请求进来及收到后端请求之间;
网关技术细节
- 网络IO模型:
网络模型可以分为阻塞IO、非阻塞IO、IO复用、信号驱动IO和异步IO
网络IO操作(read/write系统调用)其实分成了两个步骤:
第一:发起IO请求 ;第二:实际的IO读写(内核态与用户态的数据拷贝)
阻塞与非阻塞IO的区别在于第一步,发起IO请求的进程是否会被阻塞,如果阻塞直到IO操作完成才返回那么就是传统的阻塞IO,如果不阻塞,那么就是非阻塞IO;
同步IO和异步IO的区别在于第二步,实际的IO读写(内核态与用户态的数据拷贝)是否需要进程参与,如果需要进程参与则是同步IO,如果不需要进程参与就是异步IO;
如果实际的IO读写需要请求进程参与,那么就是同步IO。因此阻塞IO、非阻塞IO、IO复用、信号驱动IO都是同步IO
从以上来看HTTP请求是适合同步非阻塞的方式,一个HTTP请求必然有REQUEST和RESPONSE,而在zuul2上实现的真正网络IO也是同步非阻塞,只不过在HttpAsyncEndpoint这个Filter执行HTTP请求时采用了异步方式,如下:
@Override
public Observable applyAsync(HttpRequestMessage input)
{
if (error != null) {
return Observable.create(subscriber -> {
Throwable t = new RuntimeException("Some error response problem.");
subscriber.onError(t);
});
}
else if (response != null) {
return Observable.just(response);
}
else {
return Observable.just(new HttpResponseMessageImpl(input.getContext(), input, 200));
}
}
从以上分析,网关选择同步非阻塞方式是一个合适的选择
- 协议转换
1) HTTP ----> gRPC
gRPC基于protobuf来做传输,所以整个在gRPC的客户端来说,必须有protobuf的数据来描述当前此次gRPC请求,而proto文件是一个合适的数据描述方式,grpc-web 也是如此来做http请求的转换
具体步骤是:
1) 将proto文件转化为protobuf的FileDescriptorSet对象,该对象描述了所有的proto内容,而转化也很简单,利用protobuf提供的命令即可转化,在这里我使用的是:
com.github.os72
protoc-jar
provided
其中转化的过程如下:
public FileDescriptorSet invoke() throws ProtocInvocationException {
Path wellKnownTypesInclude;
try {
wellKnownTypesInclude = setupWellKnownTypes();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new ProtocInvocationException("Unable to extract well known types", e);
}
Path descriptorPath;
try {
descriptorPath = Files.createTempFile("descriptor", ".pb.bin");
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new ProtocInvocationException("Unable to create temporary file", e);
}
ImmutableList protocArgs = ImmutableList.builder()
.addAll(scanProtoFiles(discoveryRoot)).addAll(includePathArgs(wellKnownTypesInclude))
.add("--descriptor_set_out=" + descriptorPath.toAbsolutePath().toString())
.add("--include_imports").build();
invokeBinary(protocArgs);
try {
return FileDescriptorSet.parseFrom(Files.readAllBytes(descriptorPath));
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new ProtocInvocationException("Unable to parse the generated descriptors", e);
}
}
2:根据FileDescriptorSet获取gRPC的入参和出参描述符,然后再创建gRPC所需要的MethodDescriptor方法描述对象
- 获取protobuf的MethodDescriptor来获取入参和出参的Descriptor
private static Pair findDirectyprotobuf(final ApiRpcDO rpcDo) {
byte[] protoContent = rpcDo.getProtoContext();
FileDescriptorSet descriptorSet = null;
if (protoContent != null && protoContent.length > 0) {
try {
descriptorSet = FileDescriptorSet.parseFrom(protoContent);
ServiceResolver serviceResolver = ServiceResolver.fromFileDescriptorSet(descriptorSet);
ProtoMethodName protoMethodName = ProtoMethodName
.parseFullGrpcMethodName(rpcDo.getServiceName() + "/" + rpcDo.getMethodName());
//MethodDescriptor是protobuf的方法描述对象
MethodDescriptor protoMethodDesc =
serviceResolver.resolveServiceMethod(protoMethodName.getServiceName(),
protoMethodName.getMethodName(), protoMethodName.getPackageName());
return new ImmutablePair(protoMethodDesc.getInputType(),
protoMethodDesc.getOutputType());
} catch (InvalidProtocolBufferException e) {
LOG.error(e.getMessage(), e);
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
return null;
}
- 构建gRPC所需要的方法描述对象
private MethodDescriptor createGrpcMethodDescriptor(
String serviceName, String methodName, Descriptor inPutType, Descriptor outPutType) {
String fullMethodName = MethodDescriptor.generateFullMethodName(serviceName, methodName);
//MethodDescriptor是grpc的方法描述对象
return io.grpc.MethodDescriptor.newBuilder()
.setType(MethodType.UNARY)//
.setFullMethodName(fullMethodName)//
.setRequestMarshaller(new DynamicMessageMarshaller(inPutType))//
.setResponseMarshaller(new DynamicMessageMarshaller(outPutType))//
.setSafe(false)//
.setIdempotent(false)//
.build();
}
2) HTTP ----> dubbo
在dubbo的框架设计中,其中已经包含了泛化调用的设计,所以在这块,基本上就延用了dubbo的泛化调用来实现http转dubbo的协议,而关于dubbo的参数部分,可以指定参数映射规范,利用参数裁剪的技术对http请求参数进行抽取,如果dubbo的接口是java类型,则直接抽取,如果是pojo,按照dubbo的用户文档,把他组成一个Map的数据结构即可,而操作这一步需要映射规则
- 参数裁剪
利用了JsonPath jsonPath及Freemarker模板可以实现参数裁剪的效果,其设计思路可以参照,amazon的做法,实现效果如下:
<#assign json = input.path("$")>
[
{
"name": "${json.name}",
"mobile": "${json.mobile}",
"idNo": "${json.idNo}"
}
]
- API规则编排
利用了Drools的drl语言,再利用参数裁剪,实现API的组装及编排
package io.github.tesla.gateway.netty.filter.drools
import io.github.tesla.gateway.netty.filter.help.BodyMapping
import io.github.tesla.gateway.netty.filter.help.HeaderMapping
import io.github.tesla.gateway.netty.filter.help.DroolsContext
declare User
name : String
mobile : String
idNo : String
end
rule "condition: call userService to judge user is normal"
no-loop true
when
$body:BodyMapping()
$header:HeaderMapping()
$context:DroolsContext()
then
User user = new User();
user.setName($body.json("$.name"));
user.setMobile($body.json("$.mobile"));
user.setIdNo($body.json("$.idNo"));
String userInfo = $context.toJSONString(user);
String returnUserInfo = $context.callService("tesla","/user",userInfo, "POST");
User returnUser = $context.parseObject(returnUserInfo,User.class);
insert(returnUser);
end
rule "condition: judge to jingdong or internal service"
no-loop true
when
$user:User(name=="test",mobile=="123")
$context:DroolsContext()
then
$context.setResponse("www.baidu.com");
end
结束语
整个网关目前基本完成并且也开源到GitHub上,欢迎拍砖及使用
tesla