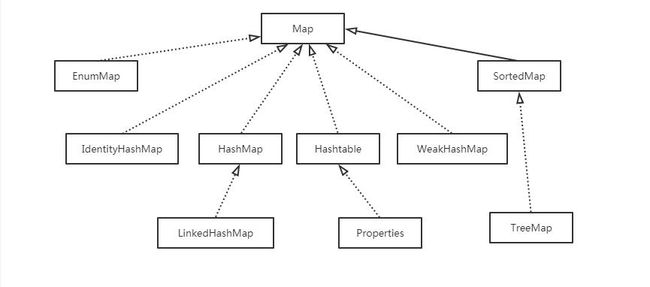
TreeMap和HashMap的区别和共同点
| TreeMap | HashMap | |
|---|---|---|
| 实现 | SortMap接口,基于红黑树 | 基于哈希散列表实现 |
| 存储 | 默认按键的升序排序 | 随机存储 |
| 遍历 | Iterator遍历是排序的 | Iterator遍历是随机的 |
| 键值对 | 键、值都不能为null | 只允许键、值均为null |
| 安全 | 非并发安全Map | 非并发安全Map |
| 效率 | 低 | 高 |
TreeMap 简介
- TreeMap 是一个有序的key-value集合,它是通过红黑树实现的。
- TreeMap 继承于AbstractMap,所以它是一个Map,即一个key-value集合。
- TreeMap 实现了NavigableMap接口,意味着它支持一系列的导航方法。比如返回有序的key集合。
- TreeMap 实现了Cloneable接口,意味着它能被克隆。
- TreeMap 实现了java.io.Serializable接口,意味着它支持序列化。
TreeMap基于红黑树(Red-Black tree)实现。该映射根据其键的自然顺序进行排序,或者根据创建映射时提供的 Comparator 进行排序,具体取决于使用的构造方法。
TreeMap的基本操作 containsKey、get、put 和 remove 的时间复杂度是 log(n) 。
另外,TreeMap是非同步的。 它的iterator 方法返回的迭代器是fail-fastl的。
TreeMap的构造函数
// 默认构造函数。使用该构造函数,TreeMap中的元素按照自然排序进行排列。
TreeMap()
// 创建的TreeMap包含Map
public TreeMap(Map m)
// 指定Tree的比较器
public TreeMap(Comparator comparator)
// 创建的TreeSet包含m
public TreeMap(SortedMap m)
TreeMap数据结构
java.lang.Object
↳ java.util.AbstractMap
↳ java.util.TreeMap
public class TreeMap
extends AbstractMap
implements NavigableMap, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
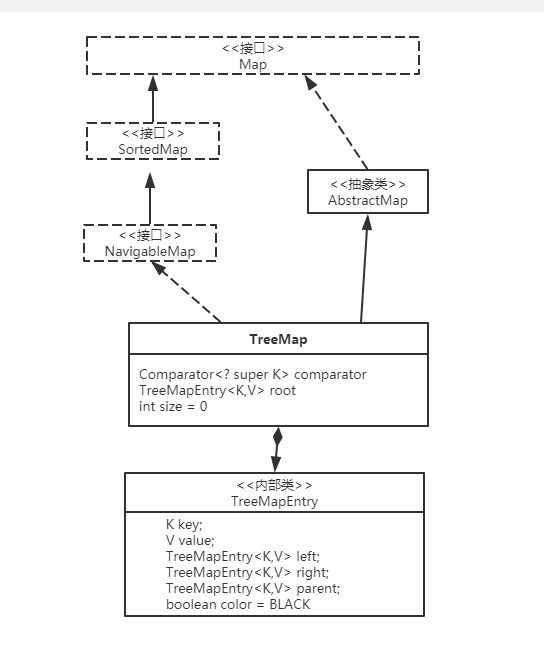
TreeMap与Map关系如下图:
从图中可以看出:
-
- TreeMap实现继承于AbstractMap,并且实现了NavigableMap接口。
-
- TreeMap的本质是R-B Tree(红黑树),它包含几个重要的成员变量: root, size, comparator。root 是红黑数的根节点。它是TreeMapEntry类型,TreeMapEntry是红黑数的节点,它包含了红黑数的6个基本组成成分:key(键)、value(值)、left(左孩子)、right(右孩子)、parent(父节点)、color(颜色)。TreeMapEntry节点根据key进行排序,Entry节点包含的内容为value。
红黑数排序时,根据TreeMapEntry中的key进行排序;TreeMapEntry中的key比较大小是根据比较器comparator来进行判断的。size是红黑数中节点的个数。
关于红黑数的具体算法,请参考"红黑树(一) 原理和算法详细介绍"。
TreeMap源码解析(基于JDK1.8)
插入操作
public V put(K key, V value) {
TreeMapEntry t = root;// 获取根节点
if (t == null) {
// 如果根节点为空,则将该元素设置为根节点
if (comparator != null) {//如果比较器不为空,比较key值
if (key == null) {
comparator.compare(key, key);//
}
} else {
if (key == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("key == null");
} else if (!(key instanceof Comparable)) {
//如果key值没有实现Comparable接口,这里会报异常
throw new ClassCastException(
"Cannot cast" + key.getClass().getName() + " to Comparable.");
}
}
// END Android-changed: Work around buggy comparators. http://b/34084348
root = new TreeMapEntry<>(key, value, null);
size = 1;
modCount++;
return null;
}
int cmp;
TreeMapEntry parent;
// split comparator and comparable paths
Comparator cpr = comparator;
//如果比较器对象不为空,表示key已经实现了Comparable接口
if (cpr != null) {
do {// 循环比较并确定元素应插入的位置(也就是找到该元素的父节点)
parent = t; // t就是root
// 调用比较器对象的compare()方法,该方法返回一个整数
cmp = cpr.compare(key, t.key);
if (cmp < 0) // 待插入元素的key"小于"当前位置元素的key,则查询左子树
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0) // 待插入元素的key"大于"当前位置元素的key,则查询右子树
t = t.right;
else // "相等"则替换其value。
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
else { // 如果比较器对象为空,使用默认的比较机制
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Comparable k = (Comparable) key;
do { / 同样是循环比较并确定元素应插入的位置(也就是找到该元素的父节点)
parent = t;
cmp = k.compareTo(t.key); // 同样调用比较方法并返回一个整数
if (cmp < 0) // 待插入元素的key"小于"当前位置元素的key,则查询左子树
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0) // 待插入元素的key"大于"当前位置元素的key,则查询右子树
t = t.right;
else // "相等"则替换其value。
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
// 根据key找到父节点后新建一个节点
TreeMapEntry e = new TreeMapEntry<>(key, value, parent);
if (cmp < 0) // 根据比较的结果来确定放在左子树还是右子树
parent.left = e;
else
parent.right = e;
fixAfterInsertion(e);
size++; // 集合大小+1
modCount++; // 集合结构被修改次数+1
return null;
}
获取元素操作
//获取指定key的value
public V get(Object key) {
TreeMapEntry p = getEntry(key);
return (p==null ? null : p.value);
}
//根据指定的key获取节点
final TreeMapEntry getEntry(Object key) {
// Offload comparator-based version for sake of performance
if (comparator != null)
return getEntryUsingComparator(key);
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Comparable k = (Comparable) key;
TreeMapEntry p = root;
//循环找k
while (p != null) {
//从p节点开始比较,
int cmp = k.compareTo(p.key);
if (cmp < 0) //如果当前节点的key,比p节点的key小,移动到左孩子
p = p.left;
else if (cmp > 0) //如果当前节点的key,比p节点的key大,移动到右孩子
p = p.right;
else //如果相等,返回p。
return p;
}
return null;
}
//有比较器时,获取节点
final TreeMapEntry getEntryUsingComparator(Object key) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
K k = (K) key;
Comparator cpr = comparator; //获取比较器
if (cpr != null) {
TreeMapEntry p = root;
while (p != null) {
int cmp = cpr.compare(k, p.key); //从p节点开始比较,
if (cmp < 0)
p = p.left; //如果当前节点的key,比p节点的key小,移动到左孩子
else if (cmp > 0) //如果当前节点的key,比p节点的key大,移动到右孩子
p = p.right;
else p = p.right;
return p;
}
}
return null;
}
删除元素的操作
public V remove(Object key) {
//根据key值查找节点
TreeMapEntry p = getEntry(key);
if (p == null)
return null;
//获取该节点的值,作为返回值
V oldValue = p.value;
//删除节点
deleteEntry(p);
return oldValue;
}
private void deleteEntry(TreeMapEntry p) {
modCount++;
size--;
//如果p有两个孩子
if (p.left != null && p.right != null) {
TreeMapEntry s = successor(p); //获取p的继承节点
p.key = s.key; //将s的key设置为p的key
p.value = s.value; //将s的value设置为p的value
p = s;
} // p has 2 children
// Start fixup at replacement node, if it exists.
//开始修复被移除节点的树结构
//如果p有左孩子,获取左孩子,没有就获取右孩子
TreeMapEntry replacement = (p.left != null ? p.left : p.right);
if (replacement != null) {
// Link replacement to parent
replacement.parent = p.parent;
if (p.parent == null) //如果p没有父亲,p就是root节点
root = replacement; //将replacement设置为root节点
else if (p == p.parent.left) //如果p是父节点的左孩子
p.parent.left = replacement; //将replacement设置为p的父亲的左孩子
else
p.parent.right = replacement; //否则,将replacement设置为p的父亲的右孩子
// Null out links so they are OK to use by fixAfterDeletion.
//解除p节点的父亲和p节点的左右孩子的引用
p.left = p.right = p.parent = null;
// Fix replacement
if (p.color == BLACK) //颜色修复
fixAfterDeletion(replacement);
//p的父亲为null,说明p只有自己一个节点
} else if (p.parent == null) { // return if we are the only node.
root = null;
} else { // No children. Use self as phantom replacement and unlink.
if (p.color == BLACK) //如果p是黑色
fixAfterDeletion(p); //调整
if (p.parent != null) {
if (p == p.parent.left) //p是父亲的左孩子
p.parent.left = null; //删除引用
else if (p == p.parent.right) //p是父亲的右孩子
p.parent.right = null; //删除引用
p.parent = null; /删除p对父亲的引用
}
}
}
使用案例
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeMap treeMap = new TreeMap();
treeMap.put("m", "梅西");
treeMap.put("c", "C罗");
treeMap.put("n", "内马尔");
treeMap.put("b", "布冯");
Iterator> it = treeMap.entrySet().iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
Entry entry = it.next();
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + " : " + entry.getValue());
}
}
//输出结果
b : 布冯
c : C罗
m : 梅西
n : 内马尔
上面在贴出的插入元素源码中说过,使用TreeMap,k值要实现Comparable 接口,这里的Key值是String类型,下面代码可以看到,String类,已经实现了Comparable接口
public final class String
implements java.io.Serializable, Comparable, CharSequence
如果key值是一个对象,使用方式如下
//注意这里实现了Comparable接口
public class People implements Comparable {
private String name;
private int age;
public People(String name,int age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
//当compareTo方法返回0的时候集合中只有一个元素
//当compareTo方法返回正数的时候集合会怎么存就怎么取
//当compareTo方法返回负数的时候集合会倒序存储
@Override
public int compareTo(People o) {
int num = this.name.compareTo(o.name); //姓名是主要条件
return num == 0 ? this.age - o.age : num; //年龄是次要条件
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeMap treeMap = new TreeMap();
treeMap.put(new People("MeiXi",18), "梅西");
treeMap.put(new People("BuFeng",18), "布冯18");
treeMap.put(new People("CLuo",15), "C罗");
treeMap.put(new People("NeiMaEr",15), "内马尔");
treeMap.put(new People("BuFeng",15), "布冯");
Iterator> it = treeMap.entrySet().iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
Entry entry = it.next();
People people = entry.getKey();
System.out.println(people.getName()+" : "+people.getAge() + " : " + entry.getValue());
}
}
//输出结果
BuFeng : 15 : 布冯
BuFeng : 18 : 布冯18
CLuo : 15 : C罗
MeiXi : 18 : 梅西
NeiMaEr : 15 : 内马尔
使用自定义比较器
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeMap tMap = new TreeMap(new Comparator(){
public int compare(String o1,String o2){
//用正负表示大小值,这里用的是o2.compareTo(o1),表示倒序
//如果是o1.compareTo(o2),会正序排序
return o2.compareTo(o1);
}
});
tMap.put("MeiXi", "梅西");
tMap.put("CLuo", "C罗");
tMap.put("NeiMaEr", "内马尔");
tMap.put("BuFeng", "布冯");
Iterator> iter = tMap.entrySet().iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()) {
Entry entry = iter.next();
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + " : " + entry.getValue());
}
}
//输出结果
NeiMaEr : 内马尔
MeiXi : 梅西
CLuo : C罗
BuFeng : 布冯
参考文章:
TreeMap
红黑树(一)之 原理和算法详细介绍
Comparable和Comparator的区别