google给安卓开发者推出了新型的Map存储集合,ArrayMap和SparseArray等。我们已经分析过了Google推荐数据结构之SparseArray。但是SparseArray对key的类型是有要求的,无法像HashMap那么随意的去存储数据,今天要分析的ArrayMap恰好能解决这个问题。
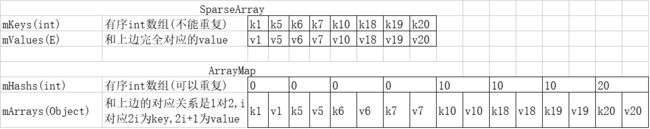
首先大家来看个图表,了解一下其实现原理。
我们假设k1到k20是升序,然后每逢10 hash值是一样的。
看过这个图表后是不是对SparseArray和ArrayMap瞬间清楚了很多呢。
下边我们来细看下ArrayMap。
public final class ArrayMap implements Map {
private static final boolean DEBUG = false;
private static final String TAG = "ArrayMap";
/**
* The minimum amount by which the capacity of a ArrayMap will increase.
* This is tuned to be relatively space-efficient.
*/
private static final int BASE_SIZE = 4;
/**
* Maximum number of entries to have in array caches.
*/
private static final int CACHE_SIZE = 10;
/**
* Special hash array value that indicates the container is immutable.
*/
static final int[] EMPTY_IMMUTABLE_INTS = new int[0];
/**
* @hide Special immutable empty ArrayMap.
*/
public static final ArrayMap EMPTY = new ArrayMap<>(-1);
/**
* Caches of small array objects to avoid spamming garbage. The cache
* Object[] variable is a pointer to a linked list of array objects.
* The first entry in the array is a pointer to the next array in the
* list; the second entry is a pointer to the int[] hash code array for it.
*/
static Object[] mBaseCache;
static int mBaseCacheSize;
static Object[] mTwiceBaseCache;
static int mTwiceBaseCacheSize;
final boolean mIdentityHashCode;
int[] mHashes;
Object[] mArray;
int mSize;
MapCollections mCollections;
}
最重要的put方法。
public V put(K key, V value) {
final int hash;
int index;
if (key == null) {
hash = 0;
index = indexOfNull();
} else {
hash = mIdentityHashCode ? System.identityHashCode(key) : key.hashCode();
index = indexOf(key, hash);
}
if (index >= 0) {
index = (index<<1) + 1;
final V old = (V)mArray[index];
mArray[index] = value;
return old;
}
index = ~index;
if (mSize >= mHashes.length) {
final int n = mSize >= (BASE_SIZE*2) ? (mSize+(mSize>>1))
: (mSize >= BASE_SIZE ? (BASE_SIZE*2) : BASE_SIZE);
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "put: grow from " + mHashes.length + " to " + n);
final int[] ohashes = mHashes;
final Object[] oarray = mArray;
allocArrays(n);
if (mHashes.length > 0) {
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "put: copy 0-" + mSize + " to 0");
System.arraycopy(ohashes, 0, mHashes, 0, ohashes.length);
System.arraycopy(oarray, 0, mArray, 0, oarray.length);
}
freeArrays(ohashes, oarray, mSize);
}
if (index < mSize) {
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "put: move " + index + "-" + (mSize-index)
+ " to " + (index+1));
System.arraycopy(mHashes, index, mHashes, index + 1, mSize - index);
System.arraycopy(mArray, index << 1, mArray, (index + 1) << 1, (mSize - index) << 1);
}
mHashes[index] = hash;
mArray[index<<1] = key;
mArray[(index<<1)+1] = value;
mSize++;
return null;
}
indexOf是所有方法的基本也是核心。是根据key来查找它在mHashes中的位置,然后根据对应关系就可以从mArray取出取出key和value.
int indexOf(Object key, int hash) {
final int N = mSize;
// Important fast case: if nothing is in here, nothing to look for.
if (N == 0) {
return ~0;
}
int index = ContainerHelpers.binarySearch(mHashes, N, hash);
二分查找当前key的hash在mHashes中的位置。
// If the hash code wasn't found, then we have no entry for this key.
if (index < 0) {
return index;
}
// If the key at the returned index matches, that's what we want.
if (key.equals(mArray[index<<1])) {
return index;
}
// Search for a matching key after the index.
int end;
for (end = index + 1; end < N && mHashes[end] == hash; end++) {
if (key.equals(mArray[end << 1])) return end;
}
// Search for a matching key before the index.
for (int i = index - 1; i >= 0 && mHashes[i] == hash; i--) {
if (key.equals(mArray[i << 1])) return i;
}
// Key not found -- return negative value indicating where a
// new entry for this key should go. We use the end of the
// hash chain to reduce the number of array entries that will
// need to be copied when inserting.
return ~end;
}
现在我们再来看下边的方法,就会非常简单。注意mArray的长度是size的2倍,因为key和value同时都在这里边存储。
public V get(Object key) {
final int index = indexOfKey(key);
return index >= 0 ? (V)mArray[(index<<1)+1] : null;
}
/**
* Return the key at the given index in the array.
* @param index The desired index, must be between 0 and {@link #size()}-1.
* @return Returns the key stored at the given index.
*/
public K keyAt(int index) {
return (K)mArray[index << 1];
}
/**
* Return the value at the given index in the array.
* @param index The desired index, must be between 0 and {@link #size()}-1.
* @return Returns the value stored at the given index.
*/
public V valueAt(int index) {
return (V)mArray[(index << 1) + 1];
}
/**
* Set the value at a given index in the array.
* @param index The desired index, must be between 0 and {@link #size()}-1.
* @param value The new value to store at this index.
* @return Returns the previous value at the given index.
*/
public V setValueAt(int index, V value) {
index = (index << 1) + 1;
V old = (V)mArray[index];
mArray[index] = value;
return old;
}
public int indexOfKey(Object key) {
return key == null ? indexOfNull()
: indexOf(key, mIdentityHashCode ? System.identityHashCode(key) : key.hashCode());
}
int indexOfValue(Object value) {
final int N = mSize*2;
final Object[] array = mArray;
if (value == null) {
for (int i=1; i>1;
}
}
} else {
for (int i=1; i>1;
}
}
}
return -1;
}
/**
* Check whether a value exists in the array. This requires a linear search
* through the entire array.
*
* @param value The value to search for.
* @return Returns true if the value exists, else false.
*/
@Override
public boolean containsValue(Object value) {
return indexOfValue(value) >= 0;
}
/**
* Remove an existing key from the array map.
* @param key The key of the mapping to remove.
* @return Returns the value that was stored under the key, or null if there
* was no such key.
*/
@Override
public V remove(Object key) {
final int index = indexOfKey(key);
if (index >= 0) {
return removeAt(index);
}
return null;
}
删除方法
@Override
public V remove(Object key) {
final int index = indexOfKey(key);
if (index >= 0) {
return removeAt(index);
}
return null;
}
/**
* Remove the key/value mapping at the given index.
* @param index The desired index, must be between 0 and {@link #size()}-1.
* @return Returns the value that was stored at this index.
*/
public V removeAt(int index) {
final Object old = mArray[(index << 1) + 1];
if (mSize <= 1) {
// Now empty.
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "remove: shrink from " + mHashes.length + " to 0");
freeArrays(mHashes, mArray, mSize);
mHashes = EmptyArray.INT;
mArray = EmptyArray.OBJECT;
mSize = 0;
} else {
if (mHashes.length > (BASE_SIZE*2) && mSize < mHashes.length/3) {
// Shrunk enough to reduce size of arrays. We don't allow it to
// shrink smaller than (BASE_SIZE*2) to avoid flapping between
// that and BASE_SIZE.
final int n = mSize > (BASE_SIZE*2) ? (mSize + (mSize>>1)) : (BASE_SIZE*2);
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "remove: shrink from " + mHashes.length + " to " + n);
final int[] ohashes = mHashes;
final Object[] oarray = mArray;
allocArrays(n);
mSize--;
if (index > 0) {
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "remove: copy from 0-" + index + " to 0");
System.arraycopy(ohashes, 0, mHashes, 0, index);
System.arraycopy(oarray, 0, mArray, 0, index << 1);
}
if (index < mSize) {
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "remove: copy from " + (index+1) + "-" + mSize
+ " to " + index);
System.arraycopy(ohashes, index + 1, mHashes, index, mSize - index);
System.arraycopy(oarray, (index + 1) << 1, mArray, index << 1,
(mSize - index) << 1);
}
} else {
mSize--;
if (index < mSize) {
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "remove: move " + (index+1) + "-" + mSize
+ " to " + index);
System.arraycopy(mHashes, index + 1, mHashes, index, mSize - index);
System.arraycopy(mArray, (index + 1) << 1, mArray, index << 1,
(mSize - index) << 1);
}
mArray[mSize << 1] = null;
mArray[(mSize << 1) + 1] = null;
}
}
return (V)old;
}
好了,相信看完这篇文章后,大家对Android的特有数据结构有了清晰的理解,希望大家以后在工作中能够合理的使用它们。