Prometheus 持久化安装
我们prometheus采用nfs挂载方式来存储数据,同时使用configMap管理配置文件。并且我们将所有的prometheus存储在kube-system
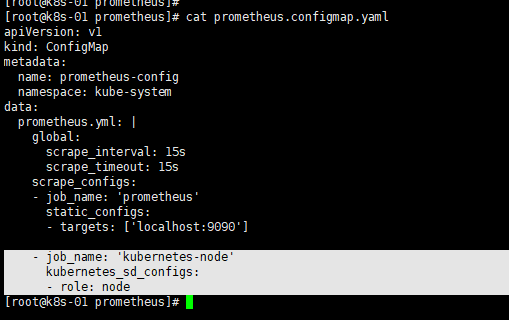
#建议将所有的prometheus yaml文件存在一块 mkdir /opt/prometheus -p && cd /opt/prometheus #生成配置文件 cat >> prometheus.configmap.yaml <<EOF apiVersion: v1 kind: ConfigMap metadata: name: prometheus-config namespace: kube-system data: prometheus.yml: | global: scrape_interval: 15s scrape_timeout: 15s scrape_configs: - job_name: 'prometheus' static_configs: - targets: ['localhost:9090'] EOF # 配置文件解释(这里的configmap实际上就是prometheus的配置) 上面包含了3个模块global、rule_files和scrape_configs 其中global模块控制Prometheus Server的全局配置 scrape_interval:表示prometheus抓取指标数据的频率,默认是15s,我们可以覆盖这个值 evaluation_interval:用来控制评估规则的频率,prometheus使用规则产生新的时间序列数据或者产生警报 rule_files模块制定了规则所在的位置,prometheus可以根据这个配置加载规则,用于生产新的时间序列数据或者报警信息,当前我们没有配置任何规则,后期会添加 scrape_configs用于控制prometheus监控哪些资源。由于prometheus通过http的方式来暴露它本身的监控数据,prometheus也能够监控本身的健康情况。在默认的配置有一个单独的job,叫做prometheus,它采集prometheus服务本身的时间序列数据。这个job包含了一个单独的、静态配置的目标;监听localhost上的9090端口。 prometheus默认会通过目标的/metrics路径采集metrics。所以,默认的job通过URL:http://localhost:9090/metrics采集metrics。收集到时间序列包含prometheus服务本身的状态和性能。如果我们还有其他的资源需要监控,可以直接配置在该模块下即可
然后创建该资源对象:
[root@k8s-01 prometheus]# kubectl apply -f prometheus.configmap.yaml configmap/prometheus-config created
[root@k8s-01 prometheus]# kubectl get configmaps -n kube-system |grep prometheus prometheus-config 1 163m
配置文件创建完成,如果以后我们有新的资源需要被监控,我们只需要将ConfigMap对象更新即可,现在我们开始创建prometheus的Pod资源
[root@k8s-01 prometheus]# cat > prometheus.deploy.yaml <<EOF apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: prometheus namespace: kube-system labels: app: prometheus spec: selector: matchLabels: app: prometheus template: metadata: labels: app: prometheus spec: serviceAccountName: prometheus containers: - image: prom/prometheus:v2.4.3 name: prometheus command: - "/bin/prometheus" args: - "--config.file=/etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml" - "--storage.tsdb.path=/prometheus" - "--storage.tsdb.retention=30d" - "--web.enable-admin-api" # 控制对admin HTTP API的访问,其中包括删除时间序列等功能 - "--web.enable-lifecycle" # 支持热更新,直接执行localhost:9090/-/reload立即生效 ports: - containerPort: 9090 protocol: TCP name: http volumeMounts: - mountPath: "/prometheus" subPath: prometheus name: data - mountPath: "/etc/prometheus" name: config-volume resources: requests: cpu: 100m memory: 512Mi limits: cpu: 100m memory: 512Mi securityContext: runAsUser: 0 volumes: - name: data persistentVolumeClaim: claimName: prometheus - configMap: name: prometheus-config name: config-volume --- apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: namespace: kube-system name: prometheus labels: app: prometheus spec: type: NodePort selector: app: prometheus ports: - name: http port: 9090 EOF
我们在启动程序的时候,除了指定prometheus.yaml(configmap)以外,还通过storage.tsdb.path指定了TSDB数据的存储路径、通过storage.tsdb.rentention设置了保留多长时间的数据,还有下面的web.enable-admin-api参数可以用来开启对admin api的访问权限,参数web.enable-lifecyle用来开启支持热更新,有了这个参数之后,prometheus.yaml(configmap)文件只要更新了,通过执行localhost:9090/-/reload就会立即生效
我们添加了一行securityContext,,其中runAsUser设置为0,这是因为prometheus运行过程中使用的用户是nobody,如果不配置可能会出现权限问题
NFS搭建步骤
for i in k8s-01 k8s-02 k8s-03;do ssh root@$i "yum install nfs-utils rpcbind -y";done 接着我们在任意一台机器上搭建nfs,其他的服务器主要是挂载 我这里使用192.168.0.200 NFS服务器操作如下 mkdir -p /home/kvm systemctl start rpcbind systemctl enable rpcbind systemctl enable nfs echo "/home/kvm *(rw,no_root_squash,sync)" >>/etc/exports 其他k8s节点直接启动rpcbind并且挂载目录就可以 systemctl start rpcbind systemctl enable rpcbind mkdir /data/k8s -p mount -t nfs 10.4.82.138:/home/kvm /data/k8s
prometheus.yaml文件对应的ConfigMap对象通过volume的形式挂载进Pod,这样ConfigMap更新后,对应的pod也会热更新,然后我们在执行上面的reload请求,prometheus配置就生效了。除此之外,对了将时间数据进行持久化,我们将数据目录和一个pvc对象进行了绑定,所以我们需要提前创建pvc对象
[root@k8s-01 prometheus]# cat >prometheus-volume.yaml <<EOF apiVersion: v1 kind: PersistentVolume metadata: name: prometheus spec: capacity: storage: 10Gi accessModes: - ReadWriteOnce persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy: Recycle nfs: server: 192.168.0.200 path: /home/kvm/k8s-vloume --- apiVersion: v1 kind: PersistentVolumeClaim metadata: name: prometheus namespace: kube-system spec: accessModes: - ReadWriteOnce resources: requests: storage: 10Gi EOF #nfs server nfs服务器ip path 挂载点,提前挂在好,确保可以写入
这里通过一个简单的NFS作为存储后端创建一个pv & pvc
[root@k8s-01 prometheus]# kubectl create -f prometheus-volume.yaml persistentvolume/prometheus created persistentvolumeclaim/prometheus created
我们这里还需要创建rbac认证,因为prometheus需要访问k8s集群内部的资源
cat >>prometheus-rbac.yaml <<EOF apiVersion: v1 kind: ServiceAccount metadata: name: prometheus namespace: kube-system --- apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 kind: ClusterRole metadata: name: prometheus rules: - apiGroups: - "" resources: - nodes - services - endpoints - pods - nodes/proxy verbs: - get - list - watch - apiGroups: - "" resources: - configmaps - nodes/metrics verbs: - get - nonResourceURLs: - /metrics verbs: - get --- apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1 kind: ClusterRoleBinding metadata: name: prometheus roleRef: apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io kind: ClusterRole name: prometheus subjects: - kind: ServiceAccount name: prometheus namespace: kube-system EOF
由于我们要获取的资源,在每一个namespace下面都有可能存在,所以我们这里使用的是ClusterRole的资源对象,nonResourceURLs是用来对非资源型metrics进行操作的权限声明
创建rbac文件 [root@k8s-01 prometheus]# kubectl create -f prometheus-rbac.yaml serviceaccount/prometheus created clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/prometheus created clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/prometheus created
我们将ConfigMap volume rbac 创建完毕后,就可以创建prometheus.deploy.yaml了,运行prometheus服务
[root@k8s-01]# kubectl create -f prometheus.deploy.yaml deployment.extensions/prometheus created [root@k8s-01 prometheus]# kubectl get pod -n kube-system |grep prometheus prometheus-847494df74-zbz9v 1/1 Running 0 148m #这里1/1 状态为Running即可
现在我们prometheus服务状态是已经正常了,但是我们在浏览器是无法访问prometheus的 webui服务。那么我们还需要创建一个service
cat >>prometeheus-svc.yaml <<EOF apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: namespace: kube-system name: prometheus labels: app: prometheus spec: type: NodePort selector: app: prometheus ports: - name: http port: 9090 EOF
[root@k8s-01prometheus]# kubectl create -f prometeheus-svc.yaml service/prometheus created [root@k8s-01 prometheus]# kubectl get svc -n kube-system |grep prometheus prometheus NodePort 10.1.183.2509090:30129/TCP 148m
这里定义的端口为3xxxx,我们直接在浏览器上任意节点输入ip+端口即可
我们可以查看一下当前监控规则
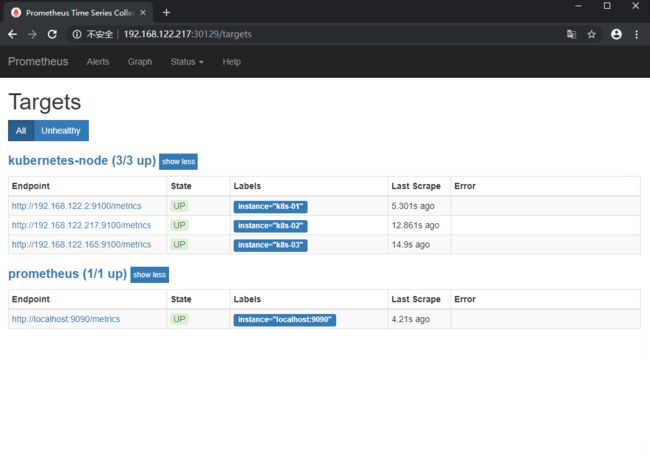
默认prometheus会监控自己
Status-->Targets
我们查看一下数据,是否收集到数据
Prometheus监控Kubernetes 集群节点及应用
对于Kubernetes的集群监控一般我们需要考虑一下几方面
- Kubernetes节点的监控;比如节点的cpu、load、fdisk、memory等指标
- 内部系统组件的状态;比如kube-scheduler、kube-controller-manager、kubedns/coredns等组件的运行状态
- 编排级的metrics;比如Deployment的状态、资源请求、调度和API延迟等数据指标
监控方案
Kubernetes集群的监控方案主要有以下几种方案
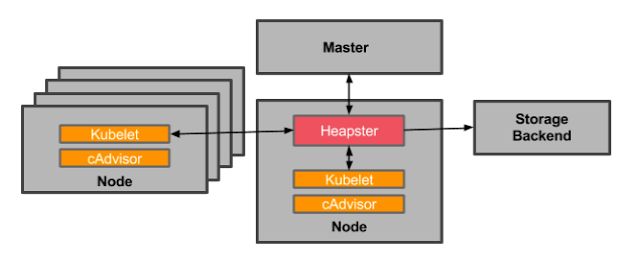
- Heapster:Herapster是一个集群范围的监控和数据聚合工具,以Pod的形式运行在集群中
Kubelet/cAdvisor之外,我们还可以向Heapster添加其他指标源数据,比如kube-state-metrics
Heapster已经被废弃,使用metrics-server代替
- cAvisor:cAdvisor是Google开源的容器资源监控和性能分析工具,它是专门为容器而生,本身也支持Docker容器,Kubernetes中,我们不需要单独去安装,cAdvisor作为kubelet内置的一部分程序可以直接使用
- Kube-state-metrics:通过监听API Server生成有关资源对象的状态指标,比如Deployment、Node、Pod,需要注意的是kube-state-metrics只是简单的提供一个metrics数据,并不会存储这些指标数据,所以我们可以使用Prometheus来抓取这些数据然后存储
- metrics-server:metrics-server也是一个集群范围内的资源数据局和工具,是Heapster的代替品,同样的,metrics-server也只是显示数据,并不提供数据存储服务。
不过kube-state-metrics和metrics-server之前还有很大不同的,二者主要区别如下
1.kube-state-metrics主要关注的是业务相关的一些元数据,比如Deployment、Pod、副本状态等 2.metrics-service主要关注的是资源度量API的实现,比如CPU、文件描述符、内存、请求延时等指标
资源度量API
监控集群节点
首先需要我们监控集群的节点,要监控节点其实我们已经有很多非常成熟的方案了,比如Nagios、Zabbix,甚至可以我们自己收集数据,这里我们通过prometheus来采集节点的监控指标,可以通过node_exporter获取,node_exporter就是抓取用于采集服务器节点的各种运行指标,目前node_exporter几乎支持所有常见的监控点,比如cpu、distats、loadavg、meminfo、netstat等,详细的监控列表可以参考github repo
这里使用DeamonSet控制器来部署该服务,这样每一个节点都会运行一个Pod,如果我们从集群中删除或添加节点后,也会进行自动扩展
[root@k8s-01 prometheus]# cat >>prometheus-node-exporter.yaml<<EOF apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: DaemonSet metadata: name: node-exporter namespace: kube-system labels: name: node-exporter k8s-app: node-exporter spec: selector: matchLabels: name: node-exporter template: metadata: labels: name: node-exporter app: node-exporter spec: hostPID: true hostIPC: true hostNetwork: true containers: - name: node-exporter image: prom/node-exporter:v0.16.0 ports: - containerPort: 9100 resources: requests: cpu: 0.15 securityContext: privileged: true args: - --path.procfs - /host/proc - --path.sysfs - /host/sys - --collector.filesystem.ignored-mount-points - '"^/(sys|proc|dev|host|etc)($|/)"' volumeMounts: - name: dev mountPath: /host/dev - name: proc mountPath: /host/proc - name: sys mountPath: /host/sys - name: rootfs mountPath: /rootfs tolerations: - key: "node-role.kubernetes.io/master" operator: "Exists" effect: "NoSchedule" volumes: - name: proc hostPath: path: /proc - name: dev hostPath: path: /dev - name: sys hostPath: path: /sys - name: rootfs hostPath: path: / EOF
创建node-exporter并检查pod
[root@k8s-01prometheus]# kubectl create -f prometheus-node-exporter.yaml daemonset.extensions/node-exporter created [root@k8s-01 prometheus]# kubectl get pod -n kube-system -o wide|grep node node-exporter-bsdkl 1/1 Running 0 36m 192.168.122.217 k8s-02node-exporter-f8wrt 1/1 Running 0 36m 192.168.122.2 k8s-01 node-exporter-gjhvz 1/1 Running 0 36m 192.168.122.165 k8s-03 #这里我们可以看到,我们有3个节点,在所有的节点上都启动了一个对应Pod进行获取数据
node-exporter.yaml文件说明
由于我们要获取的数据是主机的监控指标数据,而我们的node-exporter是运行在容器中的,所以我们在Pod中需要配置一些Pod的安全策略
hostPID:true hostIPC:true hostNetwork:true #这三个配置主要用于主机的PID namespace、IPC namespace以及主机网络,这里需要注意的是namespace是用于容器隔离的关键技术,这里的namespace和集群中的namespace是两个完全不同的概念
另外我们还需要将主机/dev、/proc、/sys这些目录挂在到容器中,这些因为我们采集的很多节点数据都是通过这些文件来获取系统信息
比如我们在执行top命令可以查看当前cpu使用情况,数据就来源于/proc/stat,使用free命令可以查看当前内存使用情况,其数据来源是/proc/meminfo文件
另外如果是使用kubeadm搭建的,同时需要监控master节点的,则需要添加下方的相应容忍
- key: "node-role.kubernetes.io/master"
operator: "Exists"
effect: "NoSchedule
node-exporter容器相关启动参数
args:
- --path.procfs #配置挂载宿主机(node节点)的路径
- /host/proc
- --path.sysfs #配置挂载宿主机(node节点)的路径
- /host/sys
- --collector.filesystem.ignored-mount-points
- '"^/(sys|proc|dev|host|etc)($|/)"'
在我们的yaml文件中加入了hostNetwork:true会直接将我们的宿主机的9100端口映射出来,从而不需要创建service 在我们的宿主机上就会有一个9100的端口
容器的9100--->映射到宿主机9100
hostNetwork: true
containers:
- name: node-exporter
image: prom/node-exporter:v0.16.0
ports:
- containerPort: 9100
上面我们检查了Pod的运行状态都是正常的,接下来我们要查看一下Pod日志,以及node-exporter中的metrics
使用命令kubectl logs -n 命名空间 node-exporter中Pod名称检查Pod日志是否有额外报错
[root@k8s-01 prometheus]# kubectl logs -n kube-system node-exporter- node-exporter-bsdkl node-exporter-f8wrt node-exporter-gjhvz [root@k8s-01 prometheus]# kubectl logs -n kube-system node-exporter-bsdkl time="2019-12-05T05:50:42Z" level=info msg="Starting node_exporter (version=0.16.0, branch=HEAD, revision=d42bd70f4363dced6b77d8fc311ea57b63387e4f)" source="node_exporter.go:82" time="2019-12-05T05:50:42Z" level=info msg="Build context (go=go1.9.6, user=root@a67a9bc13a69, date=20180515-15:52:42)" source="node_exporter.go:83" time="2019-12-05T05:50:42Z" level=info msg="Enabled collectors:" source="node_exporter.go:90" time="2019-12-05T05:50:42Z" level=info msg=" - arp" source="node_exporter.go:97" time="2019-12-05T05:50:42Z" level=info msg=" - bcache" source="node_exporter.go:97" time="2019-12-05T05:50:42Z" level=info msg=" - bonding" source="node_exporter.go:97" time="2019-12-05T05:50:42Z" level=info msg=" - conntrack" source="node_exporter.go:97" time="2019-12-05T05:50:42Z" level=info msg=" - cpu" source="node_exporter.go:97" time="2019-12-05T05:50:42Z" level=info msg=" - diskstats" source="node_exporter.go:97" time="2019-12-05T05:50:42Z" level=info msg=" - edac" source="node_exporter.go:97" time="2019-12-05T05:50:42Z" level=info msg=" - entropy" source="node_exporter.go:97" time="2019-12-05T05:50:42Z" level=info msg=" - filefd" source="node_exporter.go:97" time="2019-12-05T05:50:42Z" level=info msg=" - filesystem" source="node_exporter.go:97" time="2019-12-05T05:50:42Z" level=info msg=" - hwmon" source="node_exporter.go:97" time="2019-12-05T05:50:42Z" level=info msg=" - infiniband" source="node_exporter.go:97" time="2019-12-05T05:50:42Z" level=info msg=" - ipvs" source="node_exporter.go:97" time="2019-12-05T05:50:42Z" level=info msg=" - loadavg" source="node_exporter.go:97" time="2019-12-05T05:50:42Z" level=info msg=" - mdadm" source="node_exporter.go:97" time="2019-12-05T05:50:42Z" level=info msg=" - meminfo" source="node_exporter.go:97" time="2019-12-05T05:50:42Z" level=info msg=" - netdev" source="node_exporter.go:97" time="2019-12-05T05:50:42Z" level=info msg=" - netstat" source="node_exporter.go:97" time="2019-12-05T05:50:42Z" level=info msg=" - nfs" source="node_exporter.go:97" time="2019-12-05T05:50:42Z" level=info msg=" - nfsd" source="node_exporter.go:97" time="2019-12-05T05:50:42Z" level=info msg=" - sockstat" source="node_exporter.go:97" time="2019-12-05T05:50:42Z" level=info msg=" - stat" source="node_exporter.go:97" time="2019-12-05T05:50:42Z" level=info msg=" - textfile" source="node_exporter.go:97" time="2019-12-05T05:50:42Z" level=info msg=" - time" source="node_exporter.go:97" time="2019-12-05T05:50:42Z" level=info msg=" - timex" source="node_exporter.go:97" time="2019-12-05T05:50:42Z" level=info msg=" - uname" source="node_exporter.go:97" time="2019-12-05T05:50:42Z" level=info msg=" - vmstat" source="node_exporter.go:97" time="2019-12-05T05:50:42Z" level=info msg=" - wifi" source="node_exporter.go:97" time="2019-12-05T05:50:42Z" level=info msg=" - xfs" source="node_exporter.go:97" time="2019-12-05T05:50:42Z" level=info msg=" - zfs" source="node_exporter.go:97" time="2019-12-05T05:50:42Z" level=info msg="Listening on :9100" source="node_exporter.go:111"
#接下来,我们在任意集群节点curl 9100/metrics
[root@k8s-01 prometheus]# curl 127.0.0.1:9100/metrics|head % Total % Received % Xferd Average Speed Time Time Time Current Dload Upload Total Spent Left Speed 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 --:--:-- --:--:-- --:--:-- 0# HELP go_gc_duration_seconds A summary of the GC invocation durations. # TYPE go_gc_duration_seconds summary go_gc_duration_seconds{quantile="0"} 0.000239179 go_gc_duration_seconds{quantile="0.25"} 0.000322674 go_gc_duration_seconds{quantile="0.5"} 0.000361148 go_gc_duration_seconds{quantile="0.75"} 0.000416324 go_gc_duration_seconds{quantile="1"} 0.000513074 go_gc_duration_seconds_sum 0.006654219 go_gc_duration_seconds_count 18 # HELP go_goroutines Number of goroutines that currently exist. 100 64669 100 64669 0 0 2235k 0 --:--:-- --:--:-- --:--:-- 2339k curl: (23) Failed writing body (135 != 15652)
只要metrics可以获取到数据说明node-exporter没有问题
服务发现
我们这里三个节点都运行了node-exporter程序,如果我们通过一个Server来将数据收集在一起,用静态的方式配置到prometheus就会显示一条数据,我们得自己在指标中过滤每个节点的数据,配置比较麻烦。 这里就采用服务发现
在Kubernetes下,Prometheus通过Kubernetes API基础,目前主要支持5种服务发现,分别是node、Server、Pod、Endpoints、Ingress
需要我们在Prometheus配置文件中,添加如下三行
- job_name: 'kubernetes-node' kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: node #通过制定Kubernetes_sd_config的模式为node,prometheus就会自动从Kubernetes中发现所有的node节点并作为当前job监控的目标实例,发现的节点/metrics接口是默认的kubelet的HTTP接口
接下来我们更新配置文件
[root@k8s-01 prometheus]# kubectl apply -f prometheus.configmap.yaml configmap/prometheus-config configured [root@k8s-01 prometheus]# [root@k8s-01 prometheus]# [root@k8s-01 prometheus]# kubectl get svc -n kube-system |grep prometheus prometheus NodePort 10.1.183.2509090:30129/TCP 169m [root@k8s-01 prometheus]# [root@k8s-01 prometheus]# curl -X POST http://10.1.183.250:9090/-/reload #热更新刷新配置(需要等待一小会)
接着访问我们的地址
http://192.168.122.217:30129/targets
这个端口要和service对上
现在我们可以看到已经获取到我们的Node节点的IP,但是由于metrics监听的端口是10250而并不是我们设置的9100,所以提示我们节点属于Down的状态
这里我们就需要使用Prometheus提供的relabel_configs中的replace能力了,relabel可以在Prometheus采集数据之前,通过Target实例的Metadata信息,动态重新写入Label的值。除此之外,我们还能根据Target实例的Metadata信息选择是否采集或者忽略该Target实例。这里使用__address__标签替换10250端口为9100
这里使用正则进行替换端口
- job_name: 'kubernetes-node' kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: node relabel_configs: - source_labels: [__address__] regex: '(.*):10250' replacement: '${1}:9100' target_label: __address__ action: replace
接下来我们更新一下配置
curl的时候可以多更新几次,顺便等待一会
[root@k8s-01 prometheus]# kubectl apply -f prometheus.configmap.yaml configmap/prometheus-config configured [root@k8s-01 prometheus]# curl -X POST http://10.1.183.250:9090/-/reload [root@k8s-01 prometheus]# curl -X POST http://10.1.183.250:9090/-/reload [root@k8s-01 prometheus]#
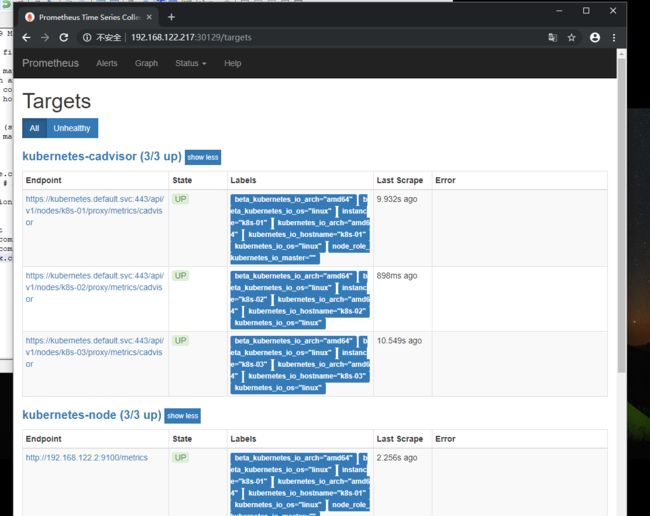
现在在状态就正常了
目前状态已经正常,但是还有一个问题就是我们的采集数据只显示了IP地址,对于我们监控分组分类不是很方便,这里可以通过labelmap这个属性来将Kubernetes的Label标签添加为Prometheus的指标标签
- job_name: 'kubernetes-node' kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: node relabel_configs: - source_labels: [__address__] regex: '(.*):10250' replacement: '${1}:9100' target_label: __address__ action: replace - action: labelmap regex: __meta_kubernetes_node_label_(.+)
添加了一个action为labelmap,正则表达式是__meta_kubernetes_node(.+)的配置,这里的意思就是表达式中匹配的数据也添加到指标数据的Label标签中去。
[root@k8s-01 prometheus]# kubectl apply -f prometheus.configmap.yaml configmap/prometheus-config configured [root@k8s-01 prometheus]# curl -X POST http://10.1.183.250:9090/-/reload [root@k8s-01 prometheus]# curl -X POST http://10.1.183.250:9090/-/reload
实际上就是获取我们的标签
[root@k8s-01 ~]# kubectl get nodes --show-labels NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION LABELS k8s-01 Ready master 30d v1.16.0 beta.kubernetes.io/arch=amd64,beta.kubernetes.io/os=linux,kubernetes.io/arch=amd64,kubernetes.io/hostname=k8s-01,kubernetes.io/os=linux,node-role.kubernetes.io/master= k8s-02 Ready30d v1.16.0 beta.kubernetes.io/arch=amd64,beta.kubernetes.io/os=linux,kubernetes.io/arch=amd64,kubernetes.io/hostname=k8s-02,kubernetes.io/os=linux k8s-03 Ready 30d v1.16.0 beta.kubernetes.io/arch=amd64,beta.kubernetes.io/os=linux,kubernetes.io/arch=amd64,kubernetes.io/hostname=k8s-03,kubernetes.io/os=linux [root@k8s-01 ~]#
对于Kubernetes_sd_configs下面可用的元标签如下
- __meta_kubernetes_node_name: 节点对象的名称
- _meta_kubernetes_node_label: 节点对象中的每个标签
- _meta_kubernetes_node_annotation: 来自节点对象的每个注释
_meta_kubernetes_node_address: 每个节点地址类型的第一个地址(如果存在) 关于kubernetes_sd_configs更多信息可以查看官方文档: kubernetes_sd_config
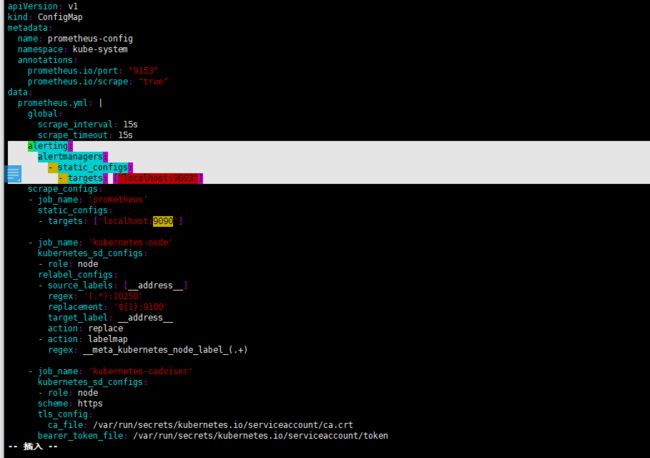
#prometheus configmap 监控完整配置如下,可以直接拷贝 root@k8s-01 prometheus]# cat prometheus.configmap.yaml apiVersion: v1 kind: ConfigMap metadata: name: prometheus-config namespace: kube-system data: prometheus.yml: | global: scrape_interval: 15s scrape_timeout: 15s scrape_configs: - job_name: 'prometheus' static_configs: - targets: ['localhost:9090'] - job_name: 'kubernetes-node' kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: node relabel_configs: - source_labels: [__address__] regex: '(.*):10250' replacement: '${1}:9100' target_label: __address__ action: replace - action: labelmap regex: __meta_kubernetes_node_label_(.+) - job_name: 'kubernetes-cadvisor' kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: node scheme: https tls_config: ca_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/ca.crt bearer_token_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/token relabel_configs: - action: labelmap regex: __meta_kubernetes_node_label_(.+) - target_label: __address__ replacement: kubernetes.default.svc:443 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_node_name] regex: (.+) target_label: __metrics_path__ replacement: /api/v1/nodes/${1}/proxy/metrics/cadvisor
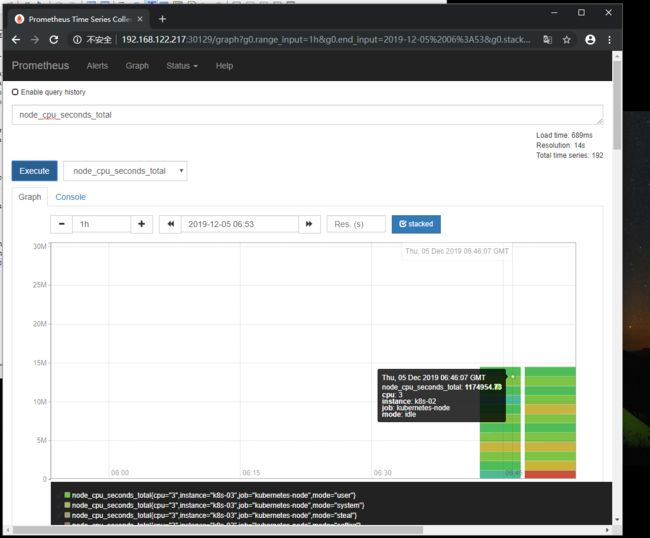
我们还可以去Graph里面看一下数据
我们这里也可以自定义规则
容器监控
cAdvisor是一个容器资源监控工具,包括容器的内存,CPU,网络IO,资源IO等资源,同时提供了一个Web页面用于查看容器的实时运行状态。
cAvisor已经内置在了kubelet组件之中,所以我们不需要单独去安装,cAdvisor的数据路径为/api/v1/nodes//proxy/metrics
action 使用labelkeep或者labeldrop则可以对Target标签进行过滤,仅保留符合过滤条件的标签
- job_name: 'kubernetes-cadvisor' kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: node scheme: https tls_config: ca_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/ca.crt bearer_token_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/token relabel_configs: - action: labelmap regex: __meta_kubernetes_node_label_(.+) - target_label: __address__ replacement: kubernetes.default.svc:443 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_node_name] regex: (.+) target_label: __metrics_path__ replacement: /api/v1/nodes/${1}/proxy/metrics/cadvisor
ls_config配置的证书地址是每个Pod连接apiserver所使用的地址,基本上写死了。并且我们在配置文件添加了一个labelmap标签。在最下面使用了一个正则替换了cAdvisor的一个metrics地址
证书是我们Pod启动的时候kubelet给pod注入的一个证书,所有的pod启动的时候都会有一个ca证书注入进来
如要想要访问apiserver的信息,还需要配置一个token_file
修改完成之后,我们需要configmap并且使用curl进行热更新(过程比较慢,需要等待会)
[root@k8s-01 prometheus]# kubectl apply -f prometheus.configmap.yaml configmap/prometheus-config configured [root@k8s-01 prometheus]# curl -X POST http://10.1.183.250:9090/-/reload [root@k8s-01 prometheus]# curl -X POST http://10.1.183.250:9090/-/reload
现在我们可以到Graph路径下面查询容器的相关数据
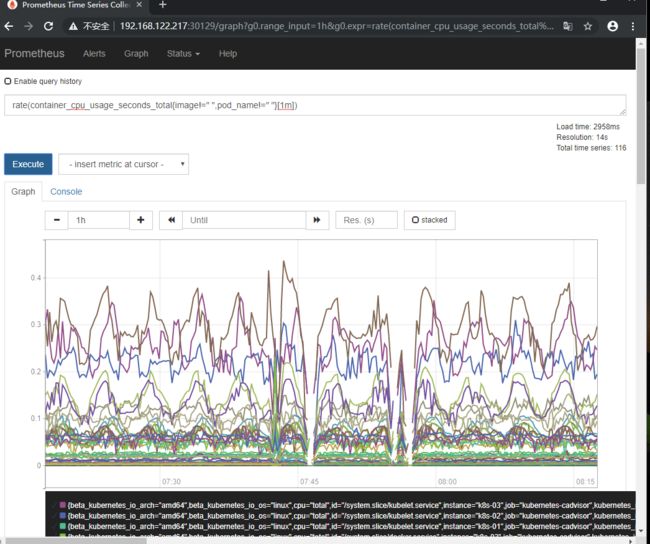
这里演示查询集群中所有Pod的CPU使用情况,查询指标
container_cpu_usage_seconds_total并且查询1分钟之内的数据
这里演示一下使用函数rate和不使用函数的一个过滤功能
container_cpu_usage_seconds_total{image!=" ",pod_name!=" "}
rate(container_cpu_usage_seconds_total{image!=" ",pod_name!=" "}[1m])
执行下方命令,过滤1分钟内的数据
rate(container_cpu_usage_seconds_total{image!=" ",pod_name!=" "}[1m])
还可以使用sum函数,pod在1分钟内的使用率,同时将pod名称打印出来
sum by (pod)(rate(container_cpu_usage_seconds_total{image!=" ", pod_name!=" "}[1m] ))
Api-Service 监控
apiserver作为Kubernetes最核心的组件,它的监控也是非常有必要的,对于apiserver的监控,我们可以直接通过kubernetes的service来获取
[root@k8s-01 prometheus]# kubectl get svc --all-namespaces NAMESPACE NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE default kubernetes ClusterIP 10.1.0.1443/TCP 31d ingress-nginx ingress-nginx ClusterIP 10.1.216.99 80/TCP,443/TCP 24h kube-system kube-dns ClusterIP 10.1.0.10 53/UDP,53/TCP,9153/TCP 30d kube-system kubelet ClusterIP None 10250/TCP 25h kube-system prometheus NodePort 10.1.183.250 9090:30129/TCP 4h38m kubernetes-dashboard dashboard-metrics-scraper ClusterIP 10.1.100.76 8000/TCP 30d kubernetes-dashboard kubernetes-dashboard NodePort 10.1.158.92 443:30001/TCP 30d
上面的service是我们集群的apiserver内部的service的地址,要自动发现service类型的服务,需要使用role为Endpoints的kubernetes_sd_configs (自动发现),我们只需要在configmap里面在添加Endpoints类型的服务发现
- job_name: 'kubernetes-apiserver' kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: endpoints
刷新配置文件
[root@k8s-01 prometheus]# kubectl get svc -n kube-system NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE kube-dns ClusterIP 10.1.0.1053/UDP,53/TCP,9153/TCP 30d kubelet ClusterIP None 10250/TCP 25h prometheus NodePort 10.1.183.250 9090:30129/TCP 4h43m [root@k8s-01 prometheus]# kubectl apply -f prometheus.configmap.yaml configmap/prometheus-config configured [root@k8s-01 prometheus]# curl -X POST http://10.1.183.250:9090/-/reload [root@k8s-01 prometheus]# curl -X POST http://10.1.183.250:9090/-/reload [root@k8s-01 prometheus]#
更新完成后,我们可以看到kubernetes-apiserver下面出现了很多实例,这是因为我们这里使用的Endpoints类型的服务发现,所以prometheus把所有的Endpoints服务都抓取过来了,同样的我们要监控的kubernetes也在列表中。
这里我们使用keep动作,将符合配置的保留下来,例如我们过滤default命名空间下服务名称为kubernetes的元数据,这里可以根据__meta_kubernetes_namespace和__mate_kubertnetes_service_name2个元数据进行relabel
- job_name: kubernetes-apiservers kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: endpoints relabel_configs: - action: keep regex: default;kubernetes;https source_labels: - __meta_kubernetes_namespace - __meta_kubernetes_service_name - __meta_kubernetes_endpoint_port_name scheme: https tls_config: ca_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/ca.crt insecure_skip_verify: true bearer_token_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/token
#参数解释
action: keep #保留哪些标签
regex: default;kubernetes;https #匹配namespace下的default命名空间下的kubernetes service 最后https协议
可以通过`kubectl describe svc kubernetes`查看到
刷新配置
#这个过程比较慢,可能要等几分钟,可以多reload几次
[root@k8s-01 prometheus]# kubectl apply -f prometheus.configmap.yaml configmap/prometheus-config configured [root@k8s-01 prometheus]# curl -X POST http://10.1.183.250:9090/-/reload [root@k8s-01 prometheus]# curl -X POST http://10.1.183.250:9090/-/reload [root@k8s-01 prometheus]# curl -X POST http://10.1.183.250:9090/-/reload [root@k8s-01 prometheus]#
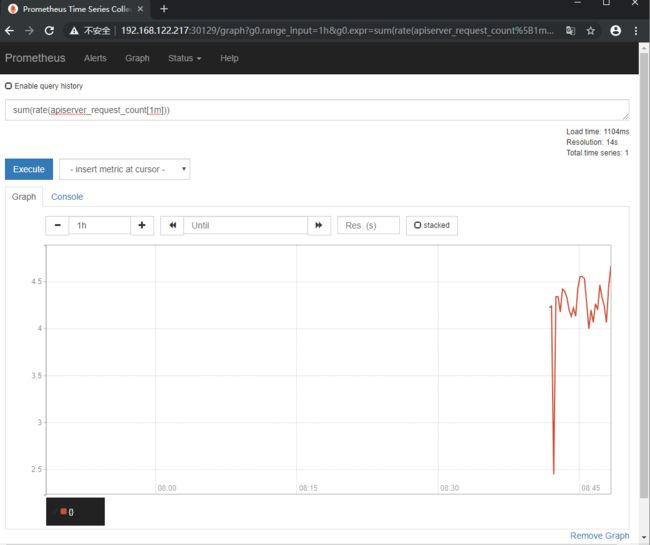
接下来我们还是前往Greph上查看采集到的数据
sum(rate(apiserver_request_count[1m])) #这里使用的promql里面的rate和sun函数,意思是apiserver在1分钟内请求的数
如果我们要监控其他系统组件,比如kube-controller-manager、kube-scheduler的话就需要单独手动创建service,因为apiserver服务默认在default,而其他组件在kube-steam这个namespace下。其中kube-sheduler的指标数据端口为10251,kube-controller-manager对应端口为10252
Service 监控
apiserver实际上是一种特殊的Service,现在配置一个专门发现普通类型的Service
这里我们对service进行过滤,只有在service配置了prometheus.io/scrape: "true"过滤出来
- job_name: 'kubernetes-service-endpoints' kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: endpoints relabel_configs: - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_scrape] action: keep regex: true - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_scheme] action: replace target_label: __scheme__ regex: (https?) - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_path] action: replace target_label: __metrics_path__ regex: (.+) - source_labels: [__address__, __meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_port] action: replace target_label: __address__ regex: ([^:]+)(?::\d+)?;(\d+) replacement: $1:$2 - action: labelmap regex: __meta_kubernetes_service_label_(.+) - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_namespace] action: replace target_label: kubernetes_namespace - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_name] action: replace target_label: kubernetes_name
继续重复步骤,刷新配置
[root@k8s-01 prometheus]# [root@k8s-01 prometheus]# kubectl apply -f prometheus.configmap.yaml configmap/prometheus-config configured [root@k8s-01 prometheus]# curl -X POST http://10.1.183.250:9090/-/reload [root@k8s-01 prometheus]# curl -X POST http://10.1.183.250:9090/-/reload [root@k8s-01 prometheus]#
Serivce自动发现参数说明 (并不是所有创建的service都可以被prometheus发现)
#1.参数解释 relabel_configs: -source_labels:[__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_scrape] action: keep regex: true 保留标签 source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_cheme] 这行配置代表我们只去筛选有__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_scrape的service,只有添加了这个声明才可以自动发现其他service #2.参数解释 - source_labels: [__address__, __meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_port] action: replace target_label: __address__ regex: ([^:]+)(?::\d+)?;(\d+) replacement: $1:$2 #指定一个抓取的端口,有的service可能有多个端口(比如之前的redis)。默认使用的是我们添加是使用kubernetes_service端口 #3.参数解释 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_scheme] action: replace target_label: __scheme__ regex: (https?) #这里如果是https证书类型,我们还需要在添加证书和token
我们可以看到这里的服务的core DNS,为什么那么多service只有coreDNS可以被收集到呢?
上面也说了,我们有过滤条件,只有复合条件的才进行过滤
core DNS serviceYaml 文件包含
true参数,所以会被匹配到
继续重复步骤,刷新配置
[root@k8s-01 prometheus]# [root@k8s-01 prometheus]# kubectl apply -f prometheus.configmap.yaml configmap/prometheus-config configured [root@k8s-01 prometheus]# curl -X POST http://10.1.183.250:9090/-/reload [root@k8s-01 prometheus]# curl -X POST http://10.1.183.250:9090/-/reload [root@k8s-01 prometheus]# curl -X POST http://10.1.183.250:9090/-/reload [root@k8s-01 prometheus]#
当我们再次查看,发现状态完成
Grafana 安装并监控k8s集群
由于Prometheus自带的web Ui图标功能相对较弱,所以一般情况下我们会使用一个第三方的工具来展示这些数据
Grafana介绍
grafana 是一个可视化面包,有着非常漂亮的图片和布局展示,功能齐全的度量仪表盘和图形化编辑器,支持Graphite、Zabbix、InfluxDB、Prometheus、OpenTSDB、Elasticasearch等作为数据源,比Prometheus自带的图标展示功能强大很多,更加灵活,有丰富的插件
我们这里使用deployment持久化安装grafana
cat >>grafana_deployment.yaml <<EOF apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: grafana namespace: kube-system labels: app: grafana k8s-app: grafana spec: selector: matchLabels: k8s-app: grafana app: grafana revisionHistoryLimit: 10 template: metadata: labels: app: grafana k8s-app: grafana spec: containers: - name: grafana image: grafana/grafana:5.3.4 imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent ports: - containerPort: 3000 name: grafana env: - name: GF_SECURITY_ADMIN_USER value: admin - name: GF_SECURITY_ADMIN_PASSWORD value: jiangwenhui readinessProbe: failureThreshold: 10 httpGet: path: /api/health port: 3000 scheme: HTTP initialDelaySeconds: 60 periodSeconds: 10 successThreshold: 1 timeoutSeconds: 30 livenessProbe: failureThreshold: 3 httpGet: path: /api/health port: 3000 scheme: HTTP periodSeconds: 10 successThreshold: 1 timeoutSeconds: 1 resources: limits: cpu: 300m memory: 1024Mi requests: cpu: 300m memory: 1024Mi volumeMounts: - mountPath: /var/lib/grafana subPath: grafana name: storage securityContext: fsGroup: 472 runAsUser: 472 volumes: - name: storage persistentVolumeClaim: claimName: grafana EOF
这里使用了grafana 5.3.4的镜像,添加了监控检查、资源声明,比较重要的变量是GF_SECURITY_ADMIN_USER和GF_SECURITY_ADMIN_PASSWORD为grafana的账号和密码。
由于grafana将dashboard、插件这些数据保留在/var/lib/grafana目录下,所以我们这里需要做持久化,同时要针对这个目录做挂载声明,由于5.3.4版本用户的userid和groupid都有所变化,所以这里添加了一个securityContext设置用户ID
现在我们添加一个pv和pvc用于绑定grafana
cat >>grafana_volume.yaml <<EOF apiVersion: v1 kind: PersistentVolume metadata: name: grafana spec: capacity: storage: 10Gi accessModes: - ReadWriteOnce persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy: Recycle nfs: server: 192.168.0.200 path: /home/kvm/k8s-vloume --- apiVersion: v1 kind: PersistentVolumeClaim metadata: name: grafana namespace: kube-system spec: accessModes: - ReadWriteOnce resources: requests: storage: 10Gi EOF
这里配置依旧使用NFS进行挂载使用
现在我们还需要创建一个service,使用NodePort
cat >>grafana_svc.yaml<<EOF apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: grafana namespace: kube-system labels: app: grafana spec: type: NodePort ports: - port: 3000 selector: app: grafana EOF
由于5.1(可以选择5.1之前的docker镜像,可以避免此类错误)版本后groupid更改,同时我们将/var/lib/grafana挂载到pvc后,目录拥有者可能不是grafana用户,所以我们还需要添加一个Job用于授权目录
cat > grafana_job.yaml <<EOF apiVersion: batch/v1 kind: Job metadata: name: grafana-chown namespace: kube-system spec: template: spec: restartPolicy: Never containers: - name: grafana-chown command: ["chown", "-R", "472:472", "/var/lib/grafana"] image: busybox imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent volumeMounts: - name: storage subPath: grafana mountPath: /var/lib/grafana volumes: - name: storage persistentVolumeClaim: claimName: grafana EOF
这里使用一个busybox镜像将/var/lib/grafana目录修改为权限472
#需要先创建pv和pvc (这里是需要安装顺序来创建) [root@k8s-01 prometheus]# kubectl create -f grafana_volume.yaml persistentvolume/grafana created persistentvolumeclaim/grafana created [root@k8s-01 prometheus]# kubectl create -f grafana_job.yaml job.batch/grafana-chown created [root@k8s-01 prometheus]# kubectl apply -f grafana_deployment.yaml deployment.apps/grafana created [root@k8s-01 prometheus]# kubectl create -f grafana_svc.yaml
创建完成后我们打开grafana的dashboard界面
[root@k8s-01 prometheus]# [root@k8s-01 prometheus]# kubectl get pod,svc -n kube-system |grep grafana pod/grafana-59bd6c446d-4jjnf 1/1 Running 0 7m39s pod/grafana-chown-w562v 0/1 Completed 0 14m service/grafana NodePort 10.1.63.1823000:30636/TCP 13m [root@k8s-01 prometheus]#
然后我们在任意集群中的节点访问端口为30636
这里的集群密码就是上面我们创建deployment里面设置的变量,我这里用户设置为admin密码jiangwenhui
登陆到grafana就显示到了我们的引导界面
登陆到grafana就显示到了我们的引导界面
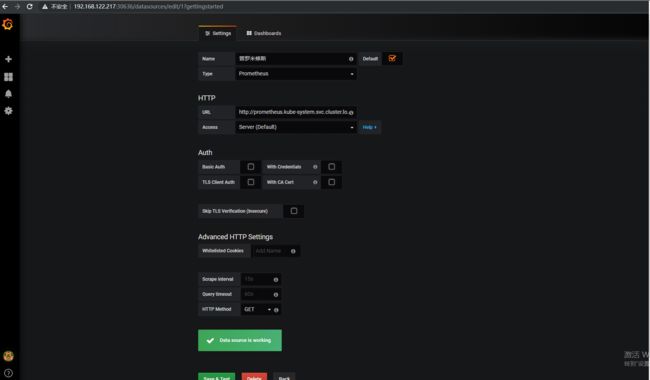
第一次创建grafana需要添加数据源
类型选择prometheus
这里的地址我们填写下面的url
http://prometheus.kube-system.svc.cluster.local:9090
这里的prometheus代表service名称
kube-system代表命名空间
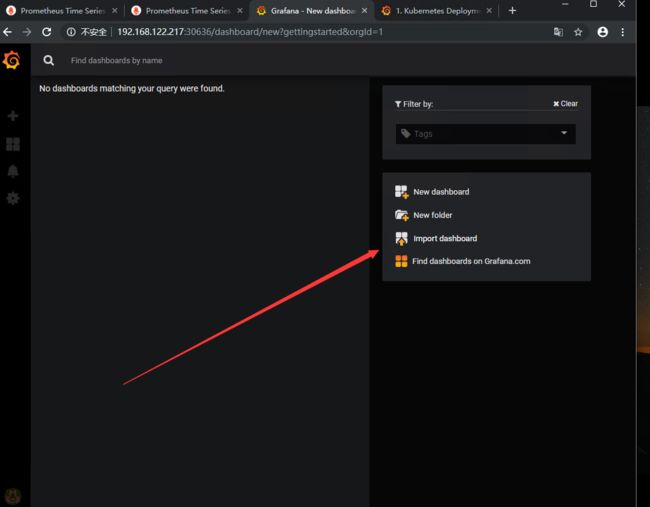
数据源添加完毕后,接下来添加New dashboard
这里我们可以自定义模板,或者可以使用别人写好的模板 (写好的模板后面是需要我们自己修改的)
grafana提供了很多模板,类似和docker镜像仓库一下。导入模板也极其简单。点击上方的Dashboard
这里面的模板都是公共的,可以免费使用
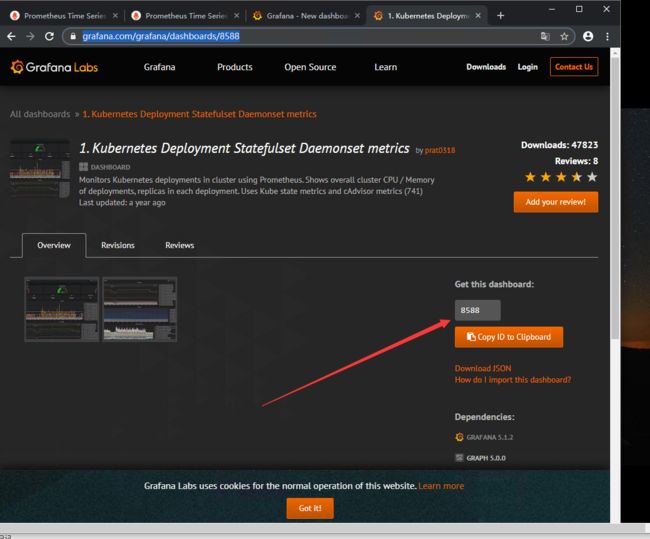
点进去任意一个模板后,我们可以看到ID,复制ID然后在返回grafana
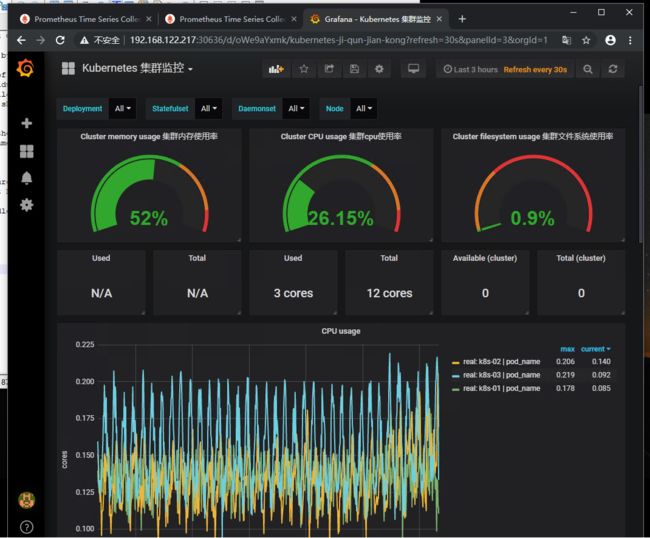
我这里添加一个监控Kubernetes集群。显示整体群集CPU、内存、磁盘使用情况以及单个pod统计信息。
https://grafana.com/grafana/dashboards/8588
点击导入模板
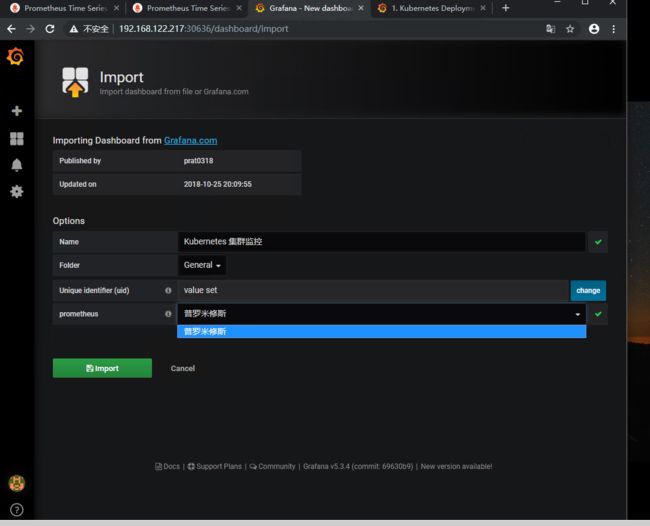
在这里我们输入8588或者url,会自动跳转到配置页面
https://grafana.com/grafana/dashboards/8588
选择好数据源之后,我们在点击Import即可
这里就会将模板8588给我们导入进行
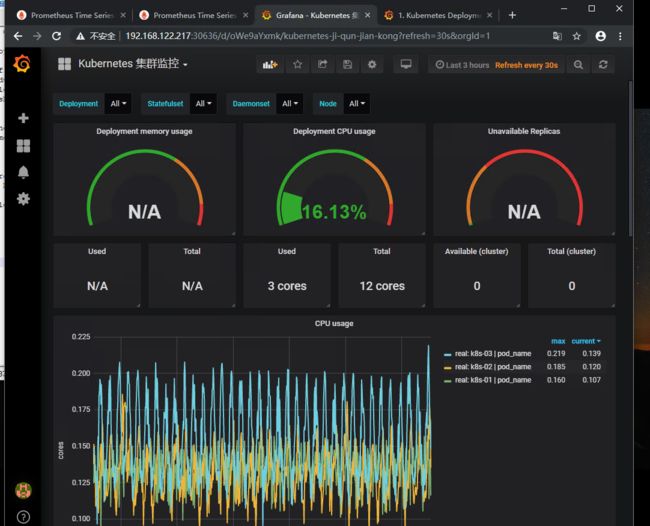
这里就会获取我们prometheus里面的数据了
现在的模板还没有进行保存,我们要点击保存一下
现在就保存下来了
目前我们导入模板之后是无法直接使用滴
这里无法显示是由于模板定义的标签,我们prometheus并没有这个数据元,所以说我们要对模板进行修改!
在修改之前我们先设置一下时区,grafana默认走的是浏览器时区,但是prometheus使用的是
UTC时区
修改默认模板 (我这里使用的是8588模板,下面模板修改请根据我的操作步骤进行操作)
grafana模板修改
前面的步骤必须和我相同,否则这里可能会无法出现值
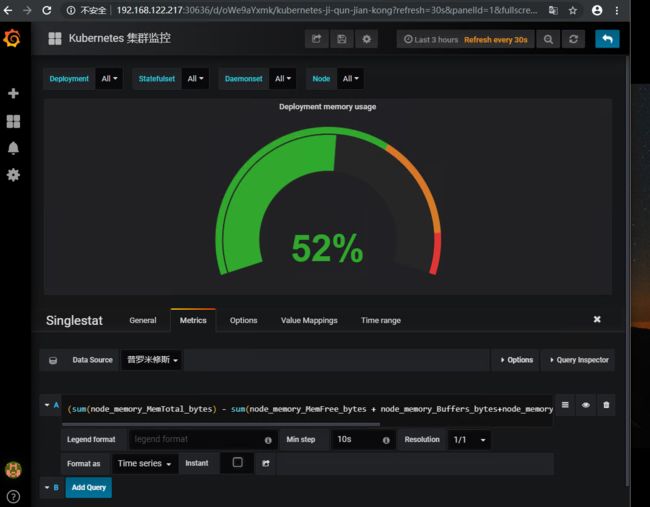
首先我们进行编辑 Cluster memory usage (集群内存使用率)
计算方式就是(整个集群的内存-(整个集群剩余的内存以及Buffer和Cached))/整
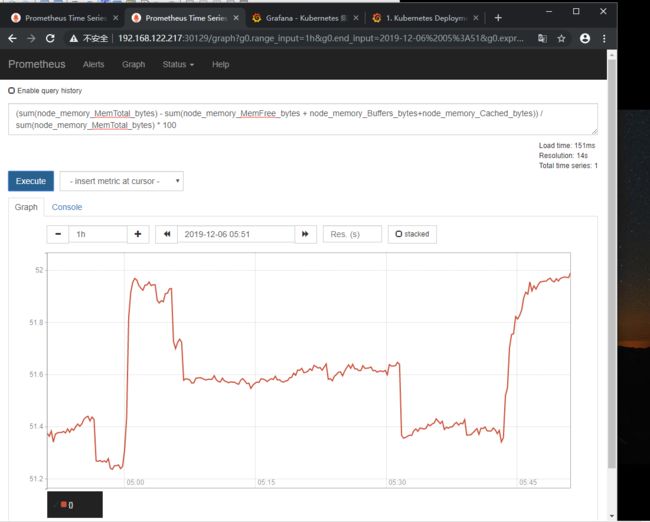
(sum(node_memory_MemTotal_bytes) - sum(node_memory_MemFree_bytes + node_memory_Buffers_bytes+node_memory_Cached_bytes)) / sum(node_memory_MemTotal_bytes) * 100
这里要说明一点,这里填写的是PromSQL,也就是说是可以在prometheus查询到的。 如果查询不到grafana也是会获取不到数据的
这里在prometheus是可以获取到的
Cluster memory usage 配置如下 (集群内存使用率)
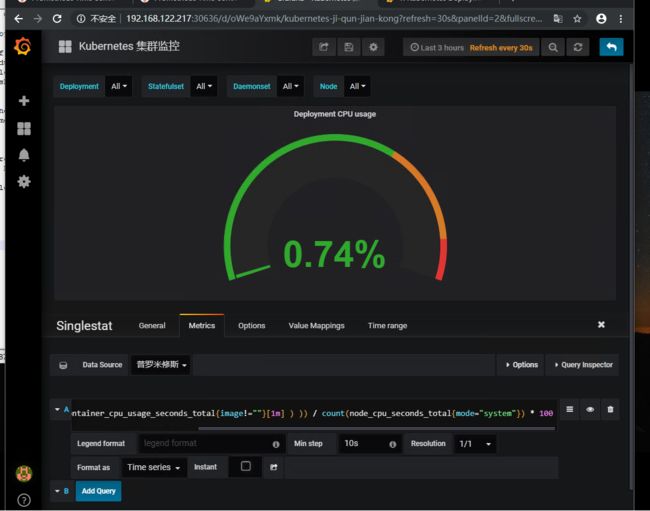
sum(sum by (container_name)( rate(container_cpu_usage_seconds_total{image!=""}[1m] ) )) / count(node_cpu_seconds_total{mode="system"}) * 100
Cluster filesystem usage 集群文件系统使用率
(sum(node_filesystem_size_bytes{device="tmpfs"}) - sum(node_filesystem_free_bytes{device="tmpfs"}) ) / sum(node_filesystem_size_bytes{device="tmpfs"}) * 100
这里我们就获取到数据了
接下来我们配置集群中Pod cpu使用率
sum by (pod)(rate(container_cpu_usage_seconds_total{image!=" ", pod_name!=" "}[1m]))
下面显示的地方配置
{{ pod }}
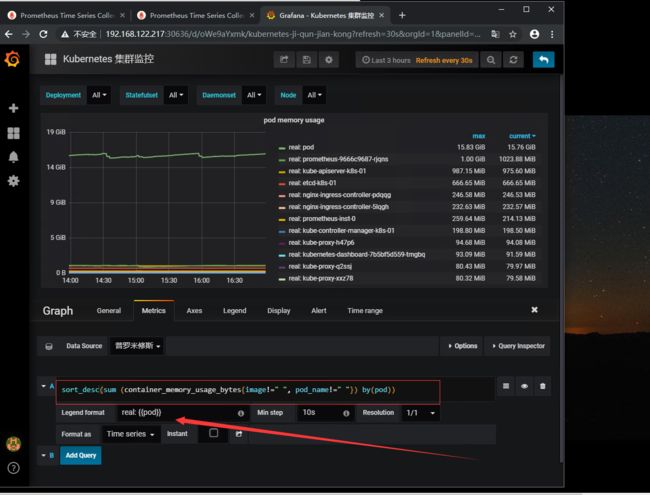
集群pod 内存使用率
sort_desc(sum (container_memory_usage_bytes{image!=" ", pod_name!=" "}) by(pod))
下面显示的名称同样也是{{ pod }}
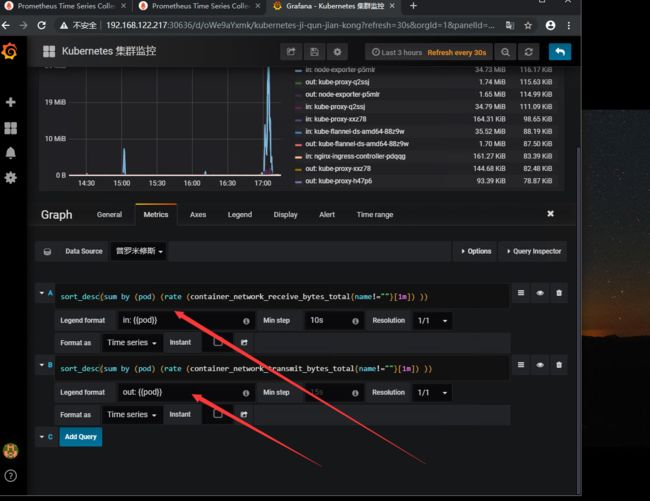
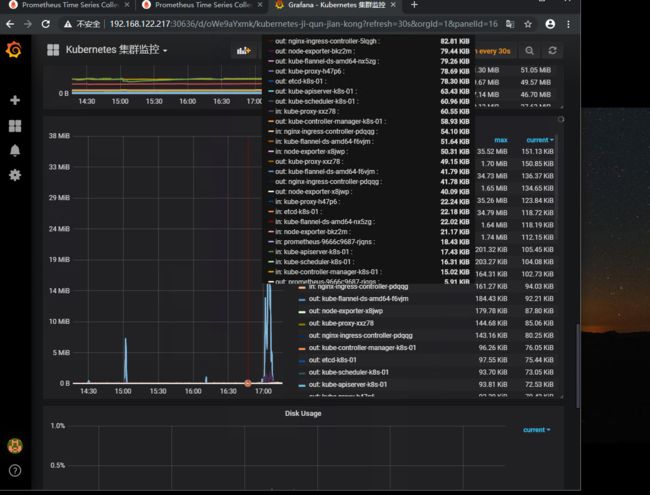
最后我们配置一下Pod 网络监控
1.入口流量 sort_desc(sum by (pod) (rate (container_network_receive_bytes_total{name!=""}[1m]) )) 2.出口流量 sort_desc(sum by (pod) (rate (container_network_transmit_bytes_total{name!=""}[1m]) )) #监控时间为1分钟
效果图如下 记得点击保存
所有的PromSQL都是可以在prometheus获取到数据的!
Prometheus AlertManager 实战
AlerManager 简介
Prometheus包含了一个报警模块,那就是AlertManager,主要用于接受Prometheus发送的告警信息,它支持丰富的告警通知渠道,而且很容易做到告警信息进行去重,降噪,分组等,是一个前卫的告警通知系统
安装 AlerManager
prometheus配置文件官方文档
https://prometheus.io/docs/alerting/configuration/
首先,我们需要先指定配置文件 ,这里我们还是创建一个ConfigMap资源对象
[root@k8s-01 prometheus]# cat >> prometheus-alert-conf.yaml <<EOF apiVersion: v1 kind: ConfigMap metadata: name: alert-config namespace: kube-system data: config.yml: |- global: # 在没有报警的情况下声明为已解决的时间 resolve_timeout: 5m # 配置邮件发送信息 smtp_smarthost: 'smtp.163.com:465' smtp_from: '[email protected]' smtp_auth_username: '[email protected]' smtp_auth_password: '授权密码' smtp_hello: '163.com' smtp_require_tls: false # 所有报警信息进入后的根路由,用来设置报警的分发策略 route: # 这里的标签列表是接收到报警信息后的重新分组标签,例如,接收到的报警信息里面有许多具有 cluster=A 和 alertname=LatncyHigh 这样的标签的报警信息将会批量被聚合到一个分组里面 group_by: ['alertname', 'cluster'] # 当一个新的报警分组被创建后,需要等待至少group_wait时间来初始化通知,这种方式可以确保您能有足够的时间为同一分组来获取多个警报,然后一起触发这个报警信息。 group_wait: 30s # 当第一个报警发送后,等待'group_interval'时间来发送新的一组报警信息。 group_interval: 5m # 如果一个报警信息已经发送成功了,等待'repeat_interval'时间来重新发送他们 repeat_interval: 5m # 默认的receiver:如果一个报警没有被一个route匹配,则发送给默认的接收器 receiver: default # 上面所有的属性都由所有子路由继承,并且可以在每个子路由上进行覆盖。 routes: - receiver: email group_wait: 10s match: team: node receivers: - name: 'default' email_configs: - to: '[email protected]' send_resolved: true - name: 'email' email_configs: - to: '[email protected]' send_resolved: true EOF
授权密码申请,这里以163邮箱为例
我们现在创建alertmanager的配置文件
[root@k8s-01 prometheus]# kubectl create -f prometheus-alert-conf.yaml configmap/alert-config created [root@k8s-01 prometheus]# kubectl get cm -n kube-system NAME DATA AGE alert-config 1 8s coredns 1 37d extension-apiserver-authentication 6 37d kube-flannel-cfg 2 37d kube-proxy 2 37d kubeadm-config 2 37d kubelet-config-1.16 1 37d prometheus-config 1 6d21h [root@k8s-01 prometheus]# #这里已经显示我们创建好的alert-config
现在我们在之前的prometheus pod的yaml文件中添加这个容器
这里我们将上面创建的aler-config这个configmap资源对象volume的形式挂载到/etc/alertmanager目录下去,然后在启动参数中指定--config.file=/etc/alertmanager/config.yml
- name: alermanager image: prom/alertmanager:v0.15.3 imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent args: - "--config.file=/etc/alertmanager/config.yml" - "--storage.path=/alertmanager/data" ports: - containerPort: 9093 name: http volumeMounts: - mountPath: "/etc/alertmanager" name: alertcfg resources: requests: cpu: 100m memory: 256Mi limits: cpu: 200m memory: 1024Mi ... - name: alertcfg configMap: name: alert-config
在0.15版本,alertmanager的WORKDIR发生了变化,变成/etc/alertmanager默认情况下存储路径--storage.path是相对目录data/,因此alertmanager会在我们上面挂载的ConfigMap中去创建这个目录,所以会报错,这里通过--storage.path参数来解决
[root@k8s-01 prometheus]# kubectl apply -f prometheus.deploy.yaml deployment.apps/prometheus configured #更新deployment
查看一下pod启动状态
[root@k8s-01 prometheus]# kubectl get pod -n kube-system |grep prometheus prometheus-65856969cd-29rqf 2/2 Running 1 49s
AlertManager容器启动之后,我们还需要在Prometheus中配置下AlertManager的地址,让Prometheus能够访问AlertManager
alerting: alertmanagers: - static_configs: - targets: ["localhost:9093"]
接下来更新一下Prometheus配置文件
[root@k8s-01 prometheus]# [root@k8s-01 prometheus]# kubectl apply -f prometheus.configmap.yaml configmap/prometheus-config configured [root@k8s-01 prometheus]# kubectl get pod -n kube-system -o wide |grep prometheus prometheus-65856969cd-29rqf 2/2 Running 1 3m58s 10.244.1.70 k8s-02[root@k8s-01 prometheus]# curl -X POST http://10.244.1.70:9090/-/reload
#确保更新配置没有报错(刷新比较慢可以等等)
现在prometheus alertmanager并没有告警的规则,还需要我们添加报警规则
Prometheus 报警规则
上面我们将prometheus和alertmanager进行了关联,但是现在并没有报警规则,所以这里还需要配置一些报警规则。让prometheus触发报警
#首先在prometheus.configmap.yaml文件中添加报警规则,下面的文件就是prometheus报警的规则文件
rule_files:
- /etc/prometheus/rules.yml
报警规则允许基于Prometheus表达式语言来定义报警规则条件,并在出发报警时发送给外部
我们上面已经将
/etc/promtehus进行挂载了,所以这里只需要修改prometheus-configmap就可以了。
rules.yml: |
groups:
- name: test-rule
rules:
- alert: NodeMemoryUsage
expr: (node_memory_MemTotal_bytes - (node_memory_MemFree_bytes+node_memory_Buffers_bytes + node_memory_Cached_bytes)) / node_memory_MemTotal_bytes * 100 > 50
for: 1m
labels:
team: node
annotations:
summary: "{{ $labels.instance }}:High Memory Usage detected"
description: "{{ $labels.instance }}: Memory usage us avive 50% (current value is :: {{ $value }})"
#配置相关参数说明
rules.yml: |
groups:
- name: test-rule
rules: #规则
- alert: NodeMemoryUsage #报警名称(内存报警)
expr: (node_memory_MemTotal_bytes - (node_memory_MemFree_bytes + node_memory_Buffers_bytes + node_memory_Cached_bytes)) / node_memory_MemTotal_bytes * 100 > 50 #规则表达式
for: 1m #等待1分钟执行查询条件
labels:
team: node #当我们触发报警后,带有team=node的标签,并且这里走的是我们alertmanager node标签,这里对应的就是我们的email接收器
annotations: #指定另外一组标签,不会将这个标签当做我们告警的身份标示(不会在我们报警信息里操作)这里主要是用于额外的展示,例如发送给邮件里面>的报警信息
summary: "{{ $labels.instance }}:High Memory Usage detected" #label标签,instance代表节点名称
description: "{{ $labels.instance }}: Memory usage us avive 50% (current value is :: {{ $value }})" #描述:相当于报警信息 $value代表当前值
expr所执行的命令是可以在prometheus上获取到数据的
[root@k8s-01 prometheus]# kubectl apply -f prometheus.configmap.yaml configmap/prometheus-config configured [root@k8s-01 prometheus]# kubectl get pod -n kube-system -o wide |grep prometheus prometheus-65856969cd-29rqf 2/2 Running 1 14m 10.244.1.70 k8s-02[root@k8s-01 prometheus]# curl -X POST http://10.244.1.70:9090/-/reload [root@k8s-01 prometheus]# curl -X POST http://10.244.1.70:9090/-/reload
报警说明
本次报警大概意思是当服务器内存百分比大于80的时候,就进行报警,并且通过labels标签关联team:node (这里team=node是在我们alertmanager里面配置的接收器,默认是default),并且报警内容添加主机和当前内存使用率
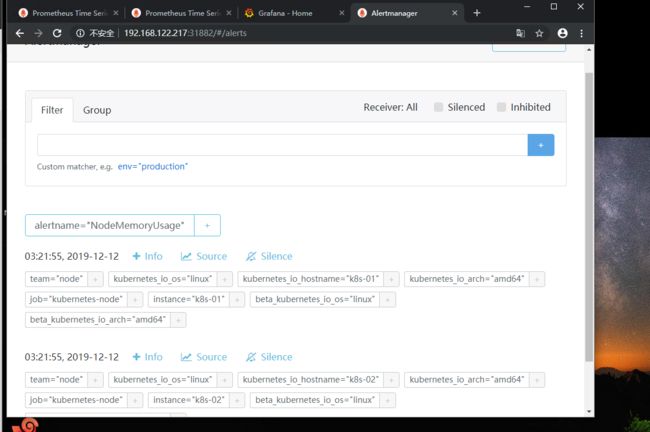
接下来我们访问prometheus,点击alerts,就可以看到我们添加的NodeMemoryUsage
我这里将脚本改成>50
当前值已经大于我们设置的50%,现在已经出发报警
邮件内容如下
alertManager Ui界面
我们可以在邮件内容中看到包含View in AlertManager的链接,这是alertmanager自带的Ui界面。我们可以使用NodePort进行访问
这里需要修改一下prometheus的service
cat >>prometeheus-svc.yaml <<EOF apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: prometheus namespace: kube-system labels: app: prometheus spec: selector: app: prometheus type: NodePort ports: - name: web port: 9090 targetPort: http - name: alertmanager port: 9093 targetPort: 9093 EOF
我们查看一下node-port端口
[root@k8s-01 prometheus]# kubectl get svc -n kube-system |grep prometheus prometheus NodePort 10.1.183.2509090:30129/TCP,9093:31882/TCP 6d23h
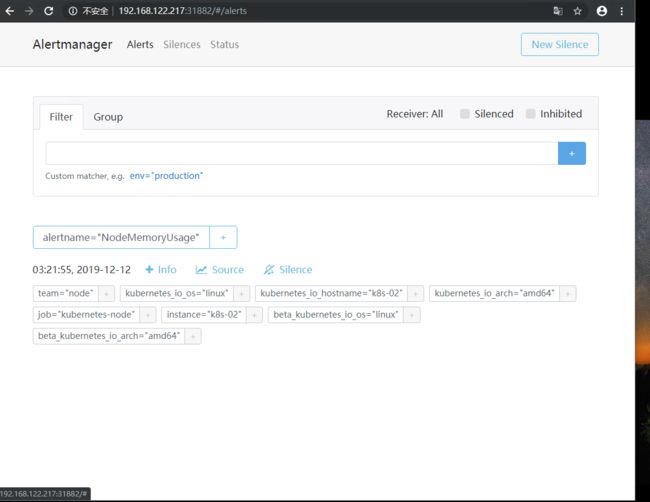
访问alertmanager端口为9093=31882 (集群任一节点访问即可)
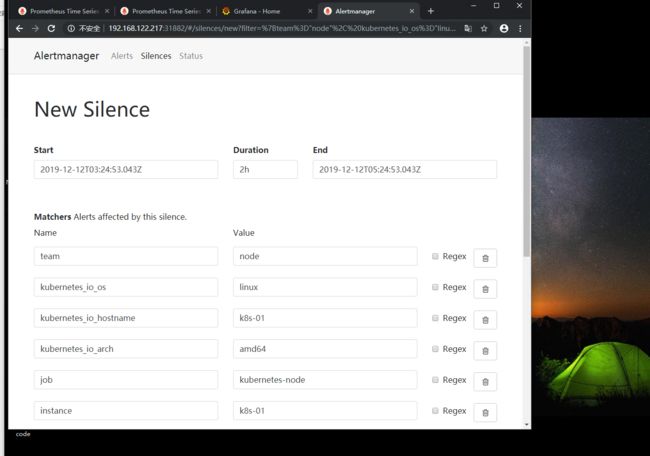
在上面的图片,我们可以看到hostname为k8s-01,02一直在报警,如果不想接收这个IP报警。可以点击Slience
注意Prometheus有8小时时区问题
这时候报警匹配为k8s-01的host,在2个小时内。不进行报警,我们点击创建就可以。在Comment输入提交内容就可以了
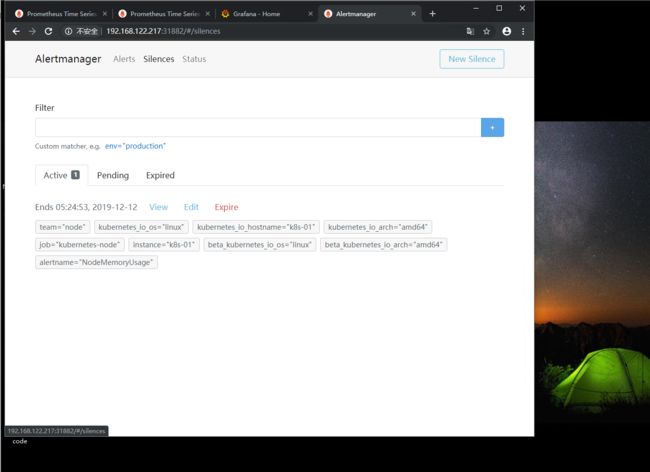
这里可以直接编辑,或者直接让它过期
这里我们已经看不到k8s-01的报警内容了
点击Silences可以看到被禁用的监控