1. RNN+CRF:
过去的方法主要分为两类:
第一种:从一个seed集合,使用句法规则和aspect及opinion之间的关联来积累aspect terms和opinion terms。但是这种方法很依赖与手动定义的规则,并且严格遵循特定的词性规则,例如opinion词是形容词。
第二种:sequence labeling classifier,例如CRFs和HMMs,使用feature engineering,词典和有标注的数据集。This approach requires extensive efforts for designinghand-crafted features, and only combines features linearly when a CRF/HMM isapplied
使用深度学习进行情感分析的方法分为两类:一类是句子级别的情感预测,一类是phrase/word-level情感预测。
2. Sentiment Analysis 分为以下三步
1)Tokenization符号化的特征 2)Feature Extraction词语或句子级别的特征 3)Classification using different classifiers,分类器例如:Naïve Bayes,MaxEnt,SVM
例文:Sentiment Classification using Machine Learning Techniqueshttp://www.ijsr.net/archive/v5i4/NOV162724.pdf
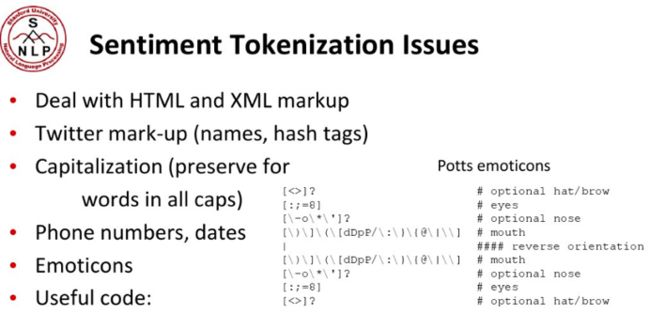
1)Tokenization符号化的信息包括如下类别,表情或者电话号码,日期等等
2)特征提取
问题1:只使用形容词还是所有词都使用?所有词更好
I didn’t like this movie---I really like this movie
问题2:否定词如何处理?
给否定词后和下一个标点符号之间的词前面加NOT_
didn’t like this movie, but I
---》 didn’t NOT_likeNOT_this NOT_movie, but I
3. Aspect sentiment classification
主要有两种方法:有监督学习和基于词典(lexicon-based)的方法
1)有监督学习:
已知aspect,关键问题就是如何确定每个sentiment的scope。主流方法是使用依存关系,根据依存关系给特征加权重。
2)基于词典的方法
sentiment shifters:有一些词会更改情感的极性,例如not, never, none, nobody, nowhere, neither。
but-clauses:“Car-x is great, but Car-y is better.”
除了以上方法,有很多情感是隐性表示的,难提取的,也可以使用Basic rules ofopinions
Liu Bing:BNF form
P和PO代表两种positive sentiment expressions。P代表atomic positive expression,一个词或一个短语。PO代表更复杂的表达。sentiment_shifter N和sentiment_shifter NE代表negation
4. Aspect Extraction 主要有四种方法:
1)频繁出现的名词和名词短语
改进:去除可能不是aspect的名词短语
对每个名词短语计算PMI(pointwise
mutual information) score,该短语与其相关的短语之间的,meronymy discriminators(关系鉴别器)
例如camera类中可能会包括”of camera”, “camera has”, “camera comes with”等,公式中a是candidate aspect,d是discriminator。如果candidate aspect a的PMI值很低,那么可能是因为a和d同时出现的频率很低。
2)通过分析opinion和target的关系,如果opinion已知,sentiment words往往比较容易知道。依存关系
3)有监督的学习方法
sequential learning(or sequential labeling),HMM或CRF
另一种:
首先使用依存树找到aspect和opinion word对,然后使用树结构的分类方法来学习,aspect从得分最高的pair得到。
4)主题模型
两种基本的方法:pLSA和LDA
Topic modeling is an unsupervised learning method thatassumes each document consists of a mixture of topics and each topic is aprobability distribution over words
Theoutput of topic modeling is a set of word clusters. Each cluster forms a topicand is a probability distribution over words in the document collection
Joint sentiment/topic model forsentiment analysis
http://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/9902/8b156a3a996914203bca7308ac339e708751.pdf
Sentiment analysis with global topicsand local dependency
http://www.cs.huji.ac.il/~jeff/aaai10/02/AAAI10-242.pdf
5. 深度学习的aspect level情感分析
1)分类问题:
Given a sentence and a target mention, the task calls forinferring the sentiment polarity (e.g. positive, negative, neutral) of thesentence towards the target.
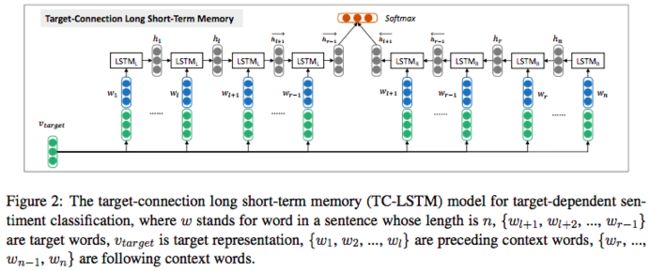
Effective LSTMs for Target-dependentsentiment classification
链接:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1512.01100.pdf
Aspectlevel sentiment classification with deep memory network
论文链接:http://wing.comp.nus.edu.sg/~antho/D/D16/D16-1021.pdf
Given a sentence s = {w1, w2, ..., wi ,
...wn} consisting of n words and an aspect word wi occurring in sentence s文中只考虑了单个aspect的情况
2)序列标注问题:标注出sentiment和aspect