typora-copy-images-to: ipic
[TOC]
配置环境
首先检查你的python版本:
$ python3 -V
Python 3.6.3
安装aiohttp:
$ pip3 install aiohttp
查看aiohttp版本号:
$ python3 -c 'import aiohttp; print(aiohttp.__version__)'
3.0.7
项目结构与其他基于python的web项目非常相似:
.
├── README.rst
└── polls
├── Makefile
├── README.rst
├── aiohttpdemo_polls
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── __main__.py
│ ├── db.py
│ ├── main.py
│ ├── routes.py
│ ├── templates
│ ├── utils.py
│ └── views.py
├── config
│ └── polls.yaml
├── images
│ └── example.png
├── setup.py
├── sql
│ ├── create_tables.sql
│ ├── install.sh
│ └── sample_data.sql
└── static
└── style.css
开始第一个aiohttp应用
这个教程基于Django的投票应用教程。
应用
所有的aiohttp服务器都围绕aiohttp.web.Application实例来构建。用于注册startup/cleanup信号,以及连接路由等。
创建一个项目:
vote
├── config
│ └── __init__.py
├── models
│ └── __init__.py
├── static
├── template
└── application
└── __init__.py
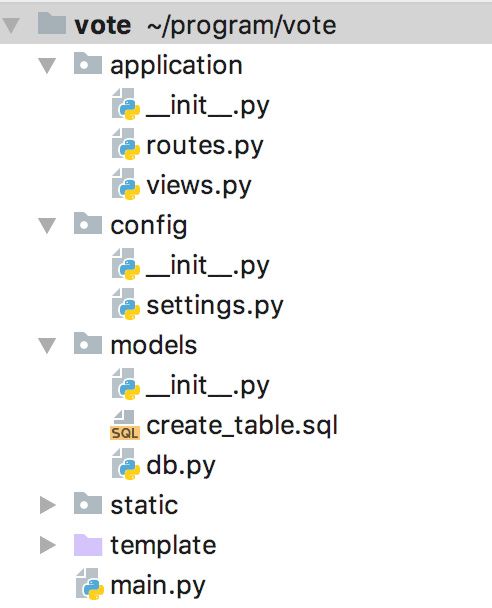
目录vote下面分别创建了config、models、application、static、template。
这里我使用pycharm开发,图示如下:
创建一个应用:
from aiohttp import web
app = web.Application()
web.run_app(app, host='0.0.0.0', port=9000)
保存于vote/main.py并启动服务器:
$ python3 /Users/junxi/program/vote/main.py
这里的vote是项目的根目录。
你将在命令行中看到如下输出:
======== Running on http://0.0.0.0:9000 ========
(Press CTRL+C to quit)
在浏览器中打开http://localhost:9000/或者使用命令
$ curl -X GET http://localhost:9000
不过,对于全部请求现在只会返回404: Not Found,让我们创建一个路由和视图来展示一些更有意义的东西。
视图
让我们从第一个视图开始。创建application/views.py并加入如下代码:
from aiohttp import web
async def hello(request):
return web.Response(text='Hello Aiohttp!')
现在我们应该为这个 index 视图创建一个路由。 将如下代码写入 application/routes.py (分离视图,路由,模型是种很好的做法。 因为你可能拥有很多这些组件,放在不同的地方可以方便地管理代码):
from .views import hello
def setup_routes(app):
app.router.add_get('/hello', hello)
此外,我们应该在某个地方调用 setup_routes 函数,最好是在 main.py 中调用它:
from aiohttp import web
from application.routes import setup_routes
app = web.Application()
setup_routes(app)
web.run_app(app, host='0.0.0.0', port=9000)
再次启动服务器. 现在我们打开浏览器就可以看见:
$ curl -X GET localhost:9000/hello
Hello Aiohttp!
工作目录应该是像下面这样:
vote
├── application
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── routes.py
│ └── views.py
├── config
│ ├── __init__.py
│ └── settings.py
├── main.py
├── models
│ ├── __init__.py
├── static
└── template
配置文件
aiohttp 的配置是不可知的。 这意味着这个库不需要任何配置方法,并且也没有内置支持任何配置模式。
但是请考虑下面这些事实:
99% 的服务器都有配置文件.
每个产品(除了像 Django 和 Flask 等基于 Python 的解决方案外)都不将配置文件写入源代码。
比如 Nginx 默认将自己的配置文件存储在
/etc/nginx文件夹下。Mongo 将配置文件存为
/etc/mongodb.conf。验证配置文件是个好主意,充分的检查可以在产品部署时避免许多愚蠢的错误。
因此,我们 建议 使用以下方法:
- 将配置存为
yaml文件(json或ini格式也不错,但是yaml格式是最好的).- 从预定位置加载
yaml配置。例如./config/app_cfg.yaml,/etc/app_cfg.yaml。- 保持可以通过命令行参数覆盖配置文件的能力。例如
./run_app --config=/opt/config/app_cfg.yaml。- 对于加载的字典应用严格的检查。 trafaret, colander or JSON schema 是这类型工作的好候选。
加载配置并在应用中读取:
# load config from yaml file in current dir
conf = load_config(str(pathlib.Path('.') / 'config' / 'settings.yaml'))
app['config'] = conf
或者使用py文件当作配置文件:
├── config
│ ├── __init__.py
│ └── settings.py
构建数据库
数据库模式
操作MySQL数据库的工具,之前django项目一直使用本身自带的orm,tornado项目使用的torndb.py。其他项目则使用的pymysql库,pymysql库的用法在这里。
本文使用MySQL数据库和aiomysql这个异步操作MySQL的库。
安装aiomysql
需要依赖pymysql
$ pip3 install pymysql
$ pip3 install aiomysql
我们使用 aiomysql 来描述数据库模式。
aiomysql官网连接示例
import asyncio
from aiomysql import create_pool
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
async def go():
async with create_pool(host='127.0.0.1', port=3306,
user='root', password='',
db='mysql', loop=loop) as pool:
async with pool.get() as conn:
async with conn.cursor() as cur:
await cur.execute("SELECT 42;")
value = await cur.fetchone()
print(value)
loop.run_until_complete(go())
aiomysql官网连接池示例
import asyncio
import aiomysql
async def test_example(loop):
pool = await aiomysql.create_pool(host='127.0.0.1', port=3306,
user='root', password='',
db='mysql', loop=loop)
async with pool.acquire() as conn:
async with conn.cursor() as cur:
await cur.execute("SELECT 42;")
print(cur.description)
(r,) = await cur.fetchone()
assert r == 42
pool.close()
await pool.wait_closed()
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
loop.run_until_complete(test_example(loop))
SQLAlchemy可选集成的示例
这里不使用sqlalchemy这个orm,原因:迁移功能不怎么好使,用惯了django的orm,感觉别的不咋好用。写原生sql练习自己的原生sql编写能力。
import asyncio
import sqlalchemy as sa
from aiomysql.sa import create_engine
metadata = sa.MetaData()
tbl = sa.Table('tbl', metadata,
sa.Column('id', sa.Integer, primary_key=True),
sa.Column('val', sa.String(255)))
async def go(loop):
engine = await create_engine(user='root', db='test_pymysql',
host='127.0.0.1', password='', loop=loop)
async with engine.acquire() as conn:
await conn.execute(tbl.insert().values(val='abc'))
await conn.execute(tbl.insert().values(val='xyz'))
async for row in conn.execute(tbl.select()):
print(row.id, row.val)
engine.close()
await engine.wait_closed()
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
loop.run_until_complete(go(loop))
创建数据库表
查看mysql版本
$ mysql --version
/usr/local/mysql/bin/mysql Ver 14.14 Distrib 5.7.20, for macos10.12 (x86_64) using EditLine wrapper
创建一个数据库vote,并增加授权用户
$ mysql -uroot -p123456
mysql> CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS vote CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci;
mysql> grant all on vote.* to vote identified by '123456';
创建表user
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `user`(
`id` INT(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '用户ID',
`delete_flag` tinyint(1) NOT NULL DEFAULT 0 COMMENT '删除标志',
`name` VARCHAR(40) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NOT NULL COMMENT '昵称',
`phone` VARCHAR(11) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NOT NULL COMMENT '电话',
`email` VARCHAR(40) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NOT NULL COMMENT '邮箱',
`password` VARCHAR(16) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NOT NULL COMMENT '密码',
`create_time` datetime NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '创建时间',
PRIMARY KEY ( `id` ),
INDEX `email` (`email`) USING BTREE,
INDEX `phone` (`phone`) USING BTREE
)
ENGINE=InnoDB
DEFAULT CHARACTER SET=utf8 COLLATE=utf8_general_ci
ROW_FORMAT=DYNAMIC
;
查看user表结构
+-------------+-------------+------+-----+-------------------+----------------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+-------------+-------------+------+-----+-------------------+----------------+
| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment |
| delete_flag | tinyint(1) | NO | | 0 | |
| name | varchar(40) | NO | | NULL | |
| phone | varchar(11) | NO | MUL | NULL | |
| email | varchar(40) | NO | MUL | NULL | |
| password | varchar(16) | NO | | NULL | |
| create_time | datetime | NO | | CURRENT_TIMESTAMP | |
+-------------+-------------+------+-----+-------------------+----------------+
创建表question
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `question`(
`id` INT(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '问题ID',
`delete_flag` tinyint(1) NOT NULL DEFAULT 0 COMMENT '删除标志',
`user_id` INT(11) NOT NULL COMMENT '用户ID',
`question_text` VARCHAR(200) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NOT NULL COMMENT '问题内容',
`create_time` datetime NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '创建时间',
PRIMARY KEY ( `id` ),
FOREIGN KEY (`user_id`) REFERENCES `user` (`id`) ON DELETE RESTRICT ON UPDATE RESTRICT,
INDEX `user_id` (`user_id`) USING BTREE
)
ENGINE=InnoDB
DEFAULT CHARACTER SET=utf8 COLLATE=utf8_general_ci
ROW_FORMAT=DYNAMIC
;
查看question表结构
+---------------+--------------+------+-----+-------------------+----------------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+---------------+--------------+------+-----+-------------------+----------------+
| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment |
| delete_flag | tinyint(1) | NO | | 0 | |
| user_id | int(11) | NO | MUL | NULL | |
| question_text | varchar(200) | NO | | NULL | |
| create_time | datetime | NO | | CURRENT_TIMESTAMP | |
+---------------+--------------+------+-----+-------------------+----------------+
创建表choice
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `choice`(
`id` INT(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '选择ID',
`delete_flag` tinyint(1) NOT NULL DEFAULT 0 COMMENT '删除标志',
`choice_text` VARCHAR(200) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '选择内容',
`votes` INT(11) NOT NULL COMMENT '得票数',
`question_id` INT(11) NOT NULL COMMENT '问题ID',
`create_time` datetime NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '创建时间',
PRIMARY KEY ( `id` ),
FOREIGN KEY (`question_id`) REFERENCES `question` (`id`) ON DELETE RESTRICT ON UPDATE RESTRICT,
INDEX `question_id` (`question_id`) USING BTREE
)
ENGINE=InnoDB
DEFAULT CHARACTER SET=utf8 COLLATE=utf8_general_ci
ROW_FORMAT=DYNAMIC
;
查看choice表结构
+-------------+--------------+------+-----+-------------------+----------------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+-------------+--------------+------+-----+-------------------+----------------+
| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment |
| delete_flag | tinyint(1) | NO | | 0 | |
| choice_text | varchar(200) | YES | | NULL | |
| votes | int(11) | NO | | NULL | |
| question_id | int(11) | NO | MUL | NULL | |
| create_time | datetime | NO | | CURRENT_TIMESTAMP | |
+-------------+--------------+------+-----+-------------------+----------------+
创建连接池
我们需要创建一个全局的连接池,每个HTTP请求都可以从连接池中直接获取数据库连接。使用连接池的好处是不必频繁地打开和关闭数据库连接,而是能复用就尽量复用。
缺省情况下将编码设置为utf8,自动提交事务:
async def create_pool(loop, **kw):
"""定义mysql全局连接池"""
logging.info('create database connection pool...')
global _mysql_pool
_mysql_pool = await aiomysql.create_pool(host=DATABASES['host'], port=DATABASES['port'], user=DATABASES['user'],
password=DATABASES['password'], db=DATABASES['db'], loop=loop,
charset=kw.get('charset', 'utf8'), autocommit=kw.get('autocommit', True),
maxsize=kw.get('maxsize', 10), minsize=kw.get('minsize', 1))
return _mysql_pool
封装增删改查
Web App里面有很多地方都要访问数据库。访问数据库需要创建数据库连接、游标对象,然后执行SQL语句,最后处理异常,清理资源。这些访问数据库的代码如果分散到各个函数中,势必无法维护,也不利于代码复用。
所以,我们要首先把常用的SELECT、INSERT、UPDATE和DELETE操作用函数封装起来。
由于Web框架使用了基于asyncio的aiohttp,这是基于协程的异步模型。在协程中,不能调用普通的同步IO操作,因为所有用户都是由一个线程服务的,协程的执行速度必须非常快,才能处理大量用户的请求。而耗时的IO操作不能在协程中以同步的方式调用,否则,等待一个IO操作时,系统无法响应任何其他用户。
这就是异步编程的一个原则:一旦决定使用异步,则系统每一层都必须是异步,“开弓没有回头箭”。
幸运的是aiomysql为MySQL数据库提供了异步IO的驱动。
要执行SELECT语句,我们用select函数执行,需要传入SQL语句和SQL参数:
async def fetchone(sql, args=(), size=None):
"""封装select,查询单个,返回数据为字典"""
log(sql, args)
async with _mysql_pool.acquire() as conn:
async with conn.cursor(aiomysql.DictCursor) as cur:
await cur.execute(sql, args)
rs = await cur.fetchone()
return rs
async def select(sql, args=(), size=None):
"""封装select,查询多个,返回数据为列表"""
log(sql, args)
async with _mysql_pool.acquire() as conn:
async with conn.cursor(aiomysql.DictCursor) as cur:
await cur.execute(sql, args)
if size:
rs = await cur.fetchmany(size)
else:
rs = await cur.fetchall()
logging.info('rows returned: %s' % len(rs))
return rs
注意要始终坚持使用带参数的SQL,而不是自己拼接SQL字符串,这样可以防止SQL注入攻击。
注意到yield from将调用一个子协程(也就是在一个协程中调用另一个协程)并直接获得子协程的返回结果。
如果传入size参数,就通过fetchmany()获取最多指定数量的记录,否则,通过fetchall()获取所有记录。
Insert, Update, Delete
要执行INSERT、UPDATE、DELETE语句,可以定义一个通用的execute()函数,因为这3种SQL的执行都需要相同的参数,以及返回一个整数表示影响的行数:
async def execute(sql, args=()):
"""封装insert, delete, update"""
log(sql, args)
async with _mysql_pool.acquire() as conn:
async with conn.cursor() as cur:
try:
await cur.execute(sql, args)
except BaseException:
await conn.rollback()
return
else:
affected = cur.rowcount
return affected
execute()函数和select()函数所不同的是,cursor对象不返回结果集,而是通过rowcount返回结果数。
这三个函数定义在models文件夹下的db.py中(db.py是新创建的文件):
完整代码如下:
import logging
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
import aiomysql
import aioredis
from config.settings import DATABASES, CACHES
def log(sql, args=()):
logging.info('SQL: %s' % sql, *args)
async def create_pool(loop, **kw):
"""定义mysql全局连接池"""
logging.info('create database connection pool...')
global _mysql_pool
_mysql_pool = await aiomysql.create_pool(host=DATABASES['host'], port=DATABASES['port'], user=DATABASES['user'],
password=DATABASES['password'], db=DATABASES['db'], loop=loop,
charset=kw.get('charset', 'utf8'), autocommit=kw.get('autocommit', True),
maxsize=kw.get('maxsize', 10), minsize=kw.get('minsize', 1))
return _mysql_pool
async def fetchone(sql, args=(), size=None):
"""封装select,查询单个,返回数据为字典"""
log(sql, args)
async with _mysql_pool.acquire() as conn:
async with conn.cursor(aiomysql.DictCursor) as cur:
await cur.execute(sql, args)
rs = await cur.fetchone()
return rs
async def select(sql, args=(), size=None):
"""封装select,查询多个,返回数据为列表"""
log(sql, args)
async with _mysql_pool.acquire() as conn:
async with conn.cursor(aiomysql.DictCursor) as cur:
await cur.execute(sql, args)
if size:
rs = await cur.fetchmany(size)
else:
rs = await cur.fetchall()
logging.info('rows returned: %s' % len(rs))
return rs
async def execute(sql, args=()):
"""封装insert, delete, update"""
log(sql, args)
async with _mysql_pool.acquire() as conn:
async with conn.cursor() as cur:
try:
await cur.execute(sql, args)
except BaseException:
await conn.rollback()
return
else:
affected = cur.rowcount
return affected
把执行SQL的函数导入到models/init.py文件中,方便别的模块引用:
from .db import *
__all__ = ['create_pool', 'select', 'execute', 'fetchone']
把我们创建表的sql语句保存到models/create_table.sql文件中:
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `user`(
`id` INT(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '用户ID',
`delete_flag` tinyint(1) NOT NULL DEFAULT 0 COMMENT '删除标志',
`name` VARCHAR(40) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NOT NULL COMMENT '昵称',
`phone` VARCHAR(11) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NOT NULL COMMENT '电话',
`email` VARCHAR(40) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NOT NULL COMMENT '邮箱',
`password` VARCHAR(16) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NOT NULL COMMENT '密码',
`create_time` datetime NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '创建时间',
PRIMARY KEY ( `id` ),
INDEX `email` (`email`) USING BTREE,
INDEX `phone` (`phone`) USING BTREE
)
ENGINE=InnoDB
DEFAULT CHARACTER SET=utf8 COLLATE=utf8_general_ci
ROW_FORMAT=DYNAMIC
;
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `question`(
`id` INT(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '问题ID',
`delete_flag` tinyint(1) NOT NULL DEFAULT 0 COMMENT '删除标志',
`user_id` INT(11) NOT NULL COMMENT '用户ID',
`question_text` VARCHAR(200) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NOT NULL COMMENT '问题内容',
`create_time` datetime NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '创建时间',
PRIMARY KEY ( `id` ),
FOREIGN KEY (`user_id`) REFERENCES `user` (`id`) ON DELETE RESTRICT ON UPDATE RESTRICT,
INDEX `user_id` (`user_id`) USING BTREE
)
ENGINE=InnoDB
DEFAULT CHARACTER SET=utf8 COLLATE=utf8_general_ci
ROW_FORMAT=DYNAMIC
;
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `choice`(
`id` INT(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '选择ID',
`delete_flag` tinyint(1) NOT NULL DEFAULT 0 COMMENT '删除标志',
`choice_text` VARCHAR(200) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '选择内容',
`votes` INT(11) NOT NULL COMMENT '得票数',
`question_id` INT(11) NOT NULL COMMENT '问题ID',
`create_time` datetime NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '创建时间',
PRIMARY KEY ( `id` ),
FOREIGN KEY (`question_id`) REFERENCES `question` (`id`) ON DELETE RESTRICT ON UPDATE RESTRICT,
INDEX `question_id` (`question_id`) USING BTREE
)
ENGINE=InnoDB
DEFAULT CHARACTER SET=utf8 COLLATE=utf8_general_ci
ROW_FORMAT=DYNAMIC
;
models目录结构:
models/
├── __init__.py
└── db.py
编写配置文件
之前我们说过的配置文件,我使用py文件当作配置文件,conf/settings.py内容如下:
DATABASES = {
'engine': 'mysql',
'db': 'vote',
'user': 'vote',
'password': '123456',
'host': 'localhost',
'port': 3306,
}
插入模拟数据
INSERT INTO user(name, phone, email, password) VALUES('露西', '16666666661', '[email protected]', '123456'), ('南希', '16666666662', '[email protected]', '123456'), ('雪灵', '16666666663', '[email protected]', '123456');
INSERT INTO question(question_text, user_id) VALUES('最受欢迎的计算机语言?', 1), ('最受欢迎的水果?', 2), ('男人最喜欢女人什么地方?', 3);
INSERT INTO choice(choice_text, question_id, votes) VALUES('python', 1, 3), ('java', 1, 2), ('go', 1, 1);
INSERT INTO choice(choice_text, question_id, votes) VALUES('香蕉', 2, 3), ('苹果', 2, 2), ('草莓', 2, 1);
INSERT INTO choice(choice_text, question_id, votes) VALUES('漂亮脸蛋', 3, 3), ('大胸', 3, 2), ('大长腿', 3, 1);
基础视图类
aiohttp.web提供django风格的基础试图类。
你可以从 View 类中继承,并自定义http请求的处理方法:
from aiohttp import web
from models import select
import json
import datetime
import decimal
class RewriteJsonEncoder(json.JSONEncoder):
"""重写json类,为了解决datetime类型的数据无法被json格式化"""
def default(self, obj):
if isinstance(obj, datetime.datetime):
return obj.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')
elif isinstance(obj, datetime.date):
return obj.strftime("%Y-%m-%d")
elif isinstance(obj, decimal.Decimal):
return str(obj)
elif hasattr(obj, 'isoformat'):
# 处理日期类型
return obj.isoformat()
else:
return json.JSONEncoder.default(self, obj)
def json_dumps(obj):
return json.dumps(obj, cls=RewriteJsonEncoder)
async def hello(request):
return web.Response(text='Hello Aiohttp!')
class QuestionChoices(web.View):
"""查看一个问题的可选答案"""
async def get(self):
question_id = self.request.match_info.get('question_id')
result = await select(self.request.app['db'], 'select * from choice where question_id = %s', (question_id,))
return web.json_response(data=result, dumps=json_dumps)
定义路由:
from .views import hello, QuestionChoices
def setup_routes(app):
app.router.add_get('/hello', hello, name='hello')
app.router.add_route('*', '/question/{question_id}/choice', QuestionChoices)
打开浏览器或输入下面命令访问:
$ curl -X GET http://127.0.0.1:9000/question/1/choice
[{"id": 1, "delete_flag": 0, "choice_text": "python", "votes": 3, "question_id": 1, "create_time": "2018-04-15 19:47:16"}, {"id": 2, "delete_flag": 0, "choice_text": "java", "votes": 2, "question_id": 1, "create_time": "2018-04-15 19:47:16"}, {"id": 3, "delete_flag": 0, "choice_text": "go", "votes": 1, "question_id": 1, "create_time": "2018-04-15 19:47:16"}]j
之前使用django比较多,个人喜欢使用类视图。
装饰器视图
路由装饰器有点像Flask风格:
routes = web.RouteTableDef()
@routes.get('/get')
async def handle_get(request):
...
@routes.post('/post')
async def handle_post(request):
...
app.router.add_routes(routes)
首先是要创建一个 aiohttp.web.RouteTableDef 对象。
该对象是一个类列表对象,额外提供aiohttp.web.RouteTableDef.get(),aiohttp.web.RouteTableDef.post()这些装饰器来注册路由。
最后调用add_routes()添加到应用的路由里。
静态文件
处理静态文件( 图片,JavaScripts, CSS文件等)最好的方法是使用反向代理,像是nginx或CDN服务。
但就开发来说,aiohttp服务器本身可以很方便的处理静态文件。
只需要通过 UrlDispatcher.add_static()注册个新的静态路由即可:
app.router.add_static('/static', path_to_static_folder)
当访问静态文件的目录时,默认服务器会返回 HTTP/403 Forbidden(禁止访问)。 使用show_index并将其设置为True可以显示出索引:
app.router.add_static('/static', path_to_static_folder, show_index=True)
当从静态文件目录访问一个符号链接(软链接)时,默认服务器会响应 HTTP/404 Not Found(未找到)。使用follow_symlinks并将其设置为True可以让服务器使用符号链接:
app.router.add_static('/static', path_to_static_folder, follow_symlinks=True)
如果你想允许缓存清除,使用append_version并设为True。
缓存清除会对资源文件像JavaScript 和 CSS文件等的文件名上添加一个hash后的版本。这样的好处是我们可以让浏览器无限期缓存这些文件而不用担心这些文件是否发布了新版本。
app.router.add_static('/static', path_to_static_folder, append_version=True)
这里我们添加一个静态文件的路由
首先在配置文件conf/settings.py中指定项目、静态文件、模版HTML路径:
BASE_DIR = os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))) # 项目路径
STATIC_DIR = os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'static') # 静态文件路径
TEMPLATE_DIR = os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'template') # 模版HTML路径
接下里在application/routes.py文件中添加一个静态文件路由:
def setup_static_routes(app):
app.router.add_static('/static/', path=STATIC_DIR, name='static')
下载uikit的静态文件到static目录下:
static
├── css
│ ├── uikit-rtl.css
│ ├── uikit-rtl.min.css
│ ├── uikit.css
│ └── uikit.min.css
└── js
├── uikit-icons.js
├── uikit-icons.min.js
├── uikit.js
└── uikit.min.js
把添加静态路由的函数添加到application/main.py文件的init函数中:
async def init(loop):
mysql_pool = await create_pool(loop)
app = web.Application(loop=loop)
app['db'] = mysql_pool
setup_routes(app)
setup_static_routes(app)
return app
重启服务器访问http://127.0.0.1:9000/static/js/bootstrap.js
$ curl -X GET http://127.0.0.1:9000/static/js/bootstrap.js
/*!
* Bootstrap v4.0.0 (https://getbootstrap.com)
* Copyright 2011-2018 The Bootstrap Authors (https://github.com/twbs/bootstrap/graphs/contributors)
* Licensed under MIT (https://github.com/twbs/bootstrap/blob/master/LICENSE)
*/
。。。。。
。。。。。
可以正常访问,静态路由已经添加成功了。
模版
aiohttp.web并不直接提供模板读取,不过可以使用第三方库 aiohttp_jinja2,该库是由aiohttp作者维护的。
使用起来也很简单。首先我们用aiohttp_jinja2.setup()来设置下jinja2环境。
安装aiohttp_jinja2:
$ pip3 install aiohttp_jinja2
在application/routes.py文件中添加一个模版文件路由:
from config.settings import STATIC_DIR, TEMPLATE_DIR
def setup_template_routes(app):
aiohttp_jinja2.setup(app, loader=jinja2.FileSystemLoader(TEMPLATE_DIR))
把添加模版路由的函数添加到vote/main.py文件的init函数中:
from application.routes import setup_routes, setup_static_routes, setup_template_routes
async def init(loop):
mysql_pool = await create_pool(loop)
app = web.Application(loop=loop)
app['db'] = mysql_pool
setup_routes(app)
setup_static_routes(app)
setup_template_routes(app)
return app
增加pycharm普通项目对jinja2模版的支持,编辑.idea/vote.iml,在component标签的同级添加如下内容:
新建一个模版HTML文件保存到template/index.html中,内容如下:
{% block title %}
首页
{% endblock %}
{% block content %}
{% endblock %}
新建注册页面保存到template/register.html中,内容如下:
{% extends "index.html" %}
{% block title %}
注册
{% endblock %}
{% block content %}
{% endblock %}
页面用到了jinja2模版的语法。
创建视图函数用来访问这个模版文件:
@aiohttp_jinja2.template('index.html')
async def index(request):
return
@aiohttp_jinja2.template('register.html')
async def register(request):
return
创建与之对应的路由:
def setup_routes(app):
app.router.add_get('/hello', hello, name='hello')
app.router.add_get('/', index, name='index')
app.router.add_get('/register', register, name='register')
app.router.add_route('*', '/question/{question_id}/choice', QuestionChoices, name='QuestionChoices')
重启服务器,浏览器访问http://127.0.0.1:9000
浏览器访问http://127.0.0.1:9000/register
调试工具箱
开发aiohttp.web应用项目时,aiohttp_debugtoolbar是非常好用的一个调试工具。
可使用pip进行安装:
$ pip3 install aiohttp_debugtoolbar
之后将aiohttp_debugtoolbar中间件添加到aiohttp.web.Applicaiton中并调用aiohttp_debugtoolbar.setup()来部署:
import aiohttp_debugtoolbar
from aiohttp_debugtoolbar import toolbar_middleware_factory
app = web.Application(middlewares=[toolbar_middleware_factory])
aiohttp_debugtoolbar.setup(app)
这里是我们的配置:
import asyncio
import aiohttp_debugtoolbar
from aiohttp import web
from application.routes import setup_routes, setup_static_routes, setup_template_routes
from models import create_pool
from aiohttp_debugtoolbar import toolbar_middleware_factory
async def init(loop):
mysql_pool = await create_pool(loop)
app = web.Application(loop=loop, middlewares=[toolbar_middleware_factory])
app['db'] = mysql_pool
aiohttp_debugtoolbar.setup(app)
setup_routes(app)
setup_static_routes(app)
setup_template_routes(app)
return app
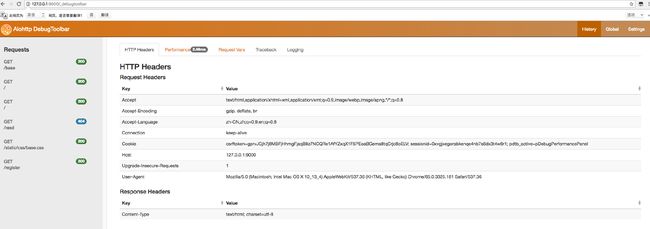
浏览器输入地址http://127.0.0.1:9000/_debugtoolbar可以看到如下页面:
开发工具
aiohttp-devtools提供几个简化开发的小工具。
可以使用pip安装:
$ pip3 install aiohttp-devtools
* ``runserver`` 提供自动重载,实时重载,静态文件服务和aiohttp_debugtoolbar_integration。
* ``start`` 是一个帮助做繁杂且必须的创建'aiohttp.web'应用的命令。
这是我们的项目启动的例子:
$ adev runserver -v main.py --app-factory init -p 9000 --debug-toolbar --host localhost
这个adev着实难用,我们定义的init函数是个协程函数,但是它命令--app-factory要求必须是个普通函数,并且返回一个aiohttp.web.Application。由于我们要使用数据库连接池,必须使用await协程语法。所以我放弃使用这个东西了。
创建和运行本地应用的文档和指南请看aiohttp-devtools。
下面准备编写注册、登录的逻辑了,这里先使用session会话机制。以后使用oauth2.0的token认证机制。
处理session会话
你经常想要一个可以通过请求存储用户数据的仓库。一般简称为会话。
aiohttp.web没有内置会话,不过你可以使用第三方库aiohttp_session来提供会话支持。
官网例子:
import asyncio
import aioredis
import time
from aiohttp import web
from aiohttp_session import setup, get_session
from aiohttp_session.redis_storage import RedisStorage
async def handler(request):
session = await get_session(request)
last_visit = session['last_visit'] if 'last_visit' in session else None
session['last_visit'] = time.time()
text = 'Last visited: {}'.format(last_visit)
return web.Response(text=text)
async def make_redis_pool():
redis_address = ('127.0.0.1', '6379')
return await aioredis.create_redis_pool(redis_address, timeout=1)
def make_app():
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
redis_pool = loop.run_until_complete(make_redis_pool())
storage = RedisStorage(redis_pool)
async def dispose_redis_pool(app):
redis_pool.close()
await redis_pool.wait_closed()
app = web.Application()
setup(app, storage)
app.on_cleanup.append(dispose_redis_pool)
app.router.add_get('/', handler)
return app
web.run_app(make_app())
安装aiohttp_session:
$ pip3 install aiohttp_session
session存储使用redis,这里使用aioredis连接redis。
安装aioredis:
$ pip3 install aioredis
创建redis全局连接池与redis命令简单封装,编辑models/db.py:
import aioredis
from config.settings import DATABASES, CACHES
async def create_redis_pool(loop):
"""定义redis全局连接池"""
logging.info('create redis connection pool...')
global _reids_pool
_reids_pool = await aioredis.create_pool(address=CACHES['address'], db=CACHES['db'], password=CACHES['password'],
minsize=CACHES['minsize'], maxsize=CACHES['maxsize'], loop=loop)
return _reids_pool
async def cache_set(*args, **kwargs):
"""redis set 命令封装"""
with await aioredis.commands.Redis(_reids_pool) as redis:
await redis.set(*args, **kwargs)
async def cache_get(*args, **kwargs):
"""redis get 命令封装"""
with await aioredis.commands.Redis(_reids_pool) as redis:
return await redis.get(*args, **kwargs)
async def cache_del(*args, **kwargs):
"""redis del 命令封装"""
with await aioredis.commands.Redis(_reids_pool) as redis:
return await redis.delete(*args, **kwargs)
CACHES在我们config/settings.py里面定义:
CACHES = {
'engine': 'redis',
'address': ('localhost', 6379),
'password': None,
'db': None,
'minsize': 1,
'maxsize': 10
}
把执行redis命令的函数导入到models/init.py文件中,方便别的模块引用:
from .db import *
__all__ = ['create_pool', 'select', 'execute', 'fetchone', 'create_redis_pool', 'cache_set', 'cache_get', 'cache_del']
注册页面:
{% extends "index.html" %}
{% block title %}
注册
{% endblock %}
{% block head_js %}
{% endblock %}
{% block content %}
{% endblock %}
注册视图函数:
class Register(web.View):
"""a view handler for register page"""
@aiohttp_jinja2.template('register.html')
async def get(self):
return
async def post(self):
data = await self.request.post()
user = await fetchone('select id from user where email = %s or phone = %s', (data.get('email'), data.get('phone')))
# print(await self.request.multipart())
if user:
msg = {'error_code': 20001, 'error_msg': 'The email or phone has been registered'}
else:
params = (data.get('name'), data.get('email'), data.get('phone'), data.get('password'))
result = await fetchone('INSERT INTO user(name, email, phone, password) VALUES(%s, %s, %s, %s)', params)
if result:
msg = {'error_code': 0, 'error_msg': 'ok'}
else:
msg = {'error_code': 20002, 'error_msg': 'Please try again if registration fails'}
# return web.json_response(data=msg, dumps=json_dumps)
return web.json_response(data=msg, dumps=json_dumps)
登录页面:
{% extends "index.html" %}
{% block title %}
登录
{% endblock %}
{% block head_js %}
{% endblock %}
{% block content %}
{% endblock %}
{% block bottom_js %}
{% endblock %}
登录视图函数:
class Login(web.View):
"""a view handler for login page"""
async def get(self):
return aiohttp_jinja2.render_template('login.html', self.request, locals())
async def post(self):
data = await self.request.post()
account = data.get('account')
password = data.get('password')
columns = 'id, name, email, phone, password'
if len(account) == 11 and re.match(r'^1[35678]\d{9}', account):
user = await fetchone('select {} from user where phone = %s'.format(columns), (account,))
elif re.match(r'^[\w-]+(\.[\w-]+)*@[\w-]+(\.[\w-]+)+$', account):
user = await fetchone('select {} from user where email = %s'.format(columns), (account,))
else:
msg = {'error_code': 20003, 'error_msg': 'User does not exists'}
return aiohttp_jinja2.render_template('login.html', self.request, locals())
if password != user.get('password'):
msg = {'error_code': 20004, 'error_msg': 'Password mismatch'}
return aiohttp_jinja2.render_template('login.html', self.request, locals())
session = await get_session(self.request)
session['uid'] = user.get('id')
# sessionid = session.identity
return web.Response(status=302, headers={'location': '/'})
给首页视图函数增加个验证登录到装饰器:
from aiohttp_session import get_session
from functools import wraps
def login_required(func): # 用户登录状态校验
"""This function applies only to class views."""
@wraps(func)
async def inner(cls, *args, **kwargs):
session = await get_session(cls.request)
uid = session.get("uid")
if uid:
user = await fetchone('select id, name, email, phone from user where id = %s', (uid,))
cls.request.app.userdata = user
return await func(cls, *args, **kwargs)
else:
return web.Response(status=302, headers={'location': '/login'})
return inner
class Index(web.View):
"""a view handler for home page"""
@login_required
async def get(self):
# response.headers['Content-Language'] = 'utf-8'
return aiohttp_jinja2.render_template('index.html', self.request, locals())
这里我把视图处理函数全部改为类视图方式编写了。
增加路由:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# _*_ coding:utf-8 _*_
__author__ = 'junxi'
import aiohttp_jinja2
import jinja2
import uuid
from application.views import Hello, Index, Register, Login, QuestionChoices, Questions, hash_sha256
from config.settings import STATIC_DIR, TEMPLATE_DIR
from aiohttp_session import setup
from aiohttp_session.redis_storage import RedisStorage
def setup_session(app, redis_pool):
storage = RedisStorage(redis_pool=redis_pool, cookie_name='sessionid', key_factory=lambda: hash_sha256(uuid.uuid4().hex))
setup(app, storage)
def setup_routes(app):
app.router.add_view('/hello', Hello, name='Hello')
app.router.add_view('', Index, name='Index')
app.router.add_view('/register', Register, name='Register')
app.router.add_view('/login', Login, name='Login')
app.router.add_view('/questions/{question_id}/choice', QuestionChoices, name='QuestionChoices'
main.py增加session处理:
async def init(loop):
mysql_pool = await create_pool(loop)
redis_pool = await create_redis_pool(loop)
# app = web.Application(loop=loop, middlewares=[toolbar_middleware_factory])
# aiohttp_debugtoolbar.setup(app)
async def dispose_mysql_pool():
mysql_pool.close()
await mysql_pool.wait_closed()
async def dispose_redis_pool():
redis_pool.close()
await redis_pool.wait_closed()
async def dispose_pool(app):
await dispose_mysql_pool()
await dispose_redis_pool()
app = web.Application(loop=loop)
setup_session(app, redis_pool)
setup_routes(app)
setup_static_routes(app)
setup_template_routes(app)
app.on_cleanup.append(dispose_pool)
return app
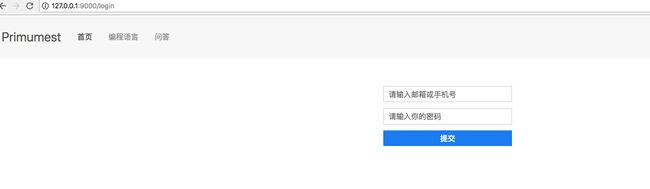
重新启动服务器,输入地址http://127.0.0.1:9000/ , 会跳转到登录页面:
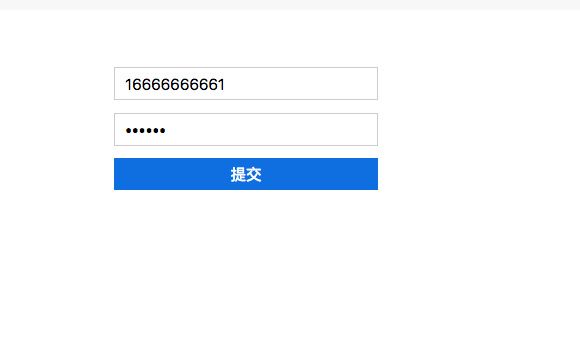
输入账号密码登录:
跳转到首页,可以看到右上角显示昵称,已经登录成功了。
增加问答页面:
{% extends "index.html" %}
{% block title %}
问答
{% endblock %}
{% block head_js %}
{% endblock %}
{% block content %}
{% for question in questions %}
{{ question.question_text }}
{% for i in question.question_choice|choice_split %}
{% endfor %}
{% endfor %}
{% endblock %}
{% block bottom_js %}
{% endblock %}
增加问答视图函数:
class Questions(web.View):
"""a view handler for look at all questions"""
@login_required
async def get(self):
questions = await select('select q.id as qid, q.question_text, (select group_concat(concat_ws("|", c.id, c.choice_text)) from choice c where c.question_id = q.id) as question_choice from question q;')
return aiohttp_jinja2.render_template('questions.html', self.request, locals())
增加路由以及我们自定义的jinja2模版上下文处理函数:
import aiohttp_jinja2
import jinja2
import uuid
from application.views import Hello, Index, Register, Login, QuestionChoices, Questions, hash_sha256
from config.settings import STATIC_DIR, TEMPLATE_DIR
from aiohttp_session import setup
from aiohttp_session.redis_storage import RedisStorage
def setup_session(app, redis_pool):
storage = RedisStorage(redis_pool=redis_pool, cookie_name='sessionid', key_factory=lambda: hash_sha256(uuid.uuid4().hex))
setup(app, storage)
def setup_routes(app):
app.router.add_view('/hello', Hello, name='Hello')
app.router.add_view('', Index, name='Index')
app.router.add_view('/register', Register, name='Register')
app.router.add_view('/login', Login, name='Login')
app.router.add_view('/questions/{question_id}/choice', QuestionChoices, name='QuestionChoices')
app.router.add_view('/questions', Questions, name='Questions')
def setup_static_routes(app):
app.router.add_static('/static/', path=STATIC_DIR, name='static')
def setup_template_routes(app):
aiohttp_jinja2.setup(app, filters={'choice_split': choice_split}, loader=jinja2.FileSystemLoader(TEMPLATE_DIR))
def choice_split(choices):
for i in choices.split(','):
single = i.split('|')
yield single
重启服务后查看问答页面http://127.0.0.1:9000/questions
项目展示
这是完整代码。
supervisor部署项目
安装supervisor:
mkdir ~/supervisor
cd ~/supervisor/
wget https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/44/60/698e54b4a4a9b956b2d709b4b7b676119c833d811d53ee2500f1b5e96dc3/supervisor-3.3.4.tar.gz
tar zxf supervisor-3.3.4.tar.gz
cd supervisor-3.3.4
sudo python setup.py install
supervisord -v
生成配置文件:
$ echo_supervisord_conf > supervisord.conf
启动:
$ supervisord -c supervisord.conf
查看 supervisord 是否在运行:
$ ps aux|grep supervisord
junxi 5064 0.0 0.0 4267768 900 s000 S+ 10:37上午 0:00.00 grep --color supervisord
junxi 5059 0.0 0.0 4344312 2196 ?? Ss 10:37上午 0:00.01 /usr/bin/python /usr/local/bin/supervisord -c supervisord.conf
打开配置文件:
vim supervisord.conf
创建aio目录:
mkdir aio
在配置文件底部,配置include
[include]
files = aio/*.conf
其他参数配置:
# grep -Ev '^;|^$' supervisord.conf
[unix_http_server]
file=/var/log/supervisor/supervisor.sock ; the path to the socket file
[inet_http_server] ; inet (TCP) server disabled by default
port=127.0.0.1:9001 ; ip_address:port specifier, *:port for all iface
username=user ; default is no username (open server)
password=123 ; default is no password (open server)
[supervisord]
logfile=/var/log/supervisor/supervisord.log ; main log file; default $CWD/supervisord.log
logfile_maxbytes=50MB ; max main logfile bytes b4 rotation; default 50MB
logfile_backups=10 ; # of main logfile backups; 0 means none, default 10
loglevel=info ; log level; default info; others: debug,warn,trace
pidfile=/var/log/supervisor/supervisord.pid ; supervisord pidfile; default supervisord.pid
nodaemon=false ; start in foreground if true; default false
minfds=1024 ; min. avail startup file descriptors; default 1024
minprocs=200 ; min. avail process descriptors;default 200
childlogdir=/var/log/supervisor ; 'AUTO' child log dir, default $TEMP
[include]
files = /Users/junxi/supervisor/aio/*.conf
在aio文件夹下新建vote.conf文件用于启动我们的vote项目,内容如下:
# vim aio/vote.conf
[program:vote]
numprocs = 4
numprocs_start = 1
process_name = vote_910%(process_num)s
command=python3 /Users/junxi/program/vote/main.py --port=910%(process_num)s
directory=/Users/junxi/program/vote
autostart=true
autorestart=true
redirect_stderr=true
stdout_logfile=/var/log/vote/access.log
loglevel=info
创建存放日志的文件夹:
$ sudo mkdir /var/log/supervisor
$ sudo chown -R junxi:admin /var/log/supervisor
$ sudo mkdir /var/log/vote/
$ sudo chown -R junxi:admin /var/log/vote/
重启supervisor:
$ kill -Hup `ps -ef|grep supervisord|awk 'NR==1{print $2}'`
或者手动找到pid重启。
使用客户端supervisorctl管理进程的启动
连接到服务端:
$ supervisorctl -c supervisord.conf
输入默认的账户user,密码123进入命令行。
查看状态:
supervisor> help
default commands (type help ):
=====================================
add exit open reload restart start tail
avail fg pid remove shutdown status update
clear maintail quit reread signal stop version
supervisor> status
vote:vote_9101 STOPPED Apr 17 11:00 PM
vote:vote_9102 STOPPED Apr 17 11:00 PM
vote:vote_9103 STOPPED Apr 17 11:00 PM
vote:vote_9104
启动vote:
supervisor> start all
vote:vote_9101: started
vote:vote_9102: started
vote:vote_9103: started
vote:vote_9104: started
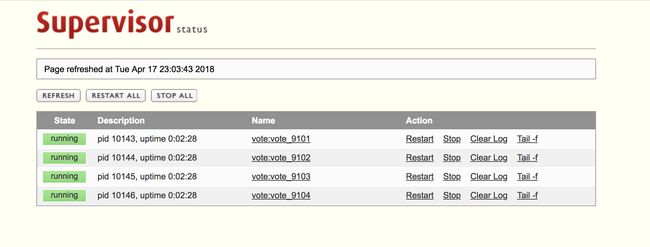
浏览器输入 http://127.0.0.1:9001/ 打开web页面查看supervisor状态,就是我们配置文件中的inet_http_server。
浏览器输入4个端口(分别为9101、9102、9103、9104)分别进行访问测试:
然后再使用nginx做个负载均衡:
proxy_next_upstream error;
upstream votes {
server 127.0.0.1:9101;
server 127.0.0.1:9102;
server 127.0.0.1:9103;
server 127.0.0.1:9104;
}
server {
listen 8008;
server_name localhost;
access_log /var/log/nginx/vote/access.log;
error_log /var/log/nginx/vote/error.log;
proxy_read_timeout 200;
location /static/ {
alias /Users/junxi/program/vote/static/;
}
location / {
proxy_pass_header Server;
proxy_set_header Host $http_host;
proxy_redirect off;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Scheme $scheme;
proxy_pass http://votes;
}
}
别忘了设置Nginx的worker_rlimit_nofile、worker_connections、worker_processes。
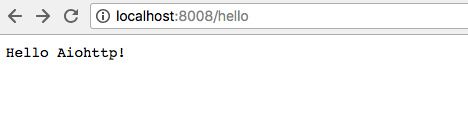
访问http://localhost:8008/hello
Nice。
先写到这里了。