标准输入输出流:System类中的字段--in,out。各代表了系统标准的输入和输出设备。
默认输入设备是键盘,输出设备是显示器。
System.in的类是InputStream;System.out的类型是PrintStream--OutputStream的子类FilterOutputStream的子类。
通过System类的setIn,setOut方法对默认设备进行改变:System.setIn(new FileInputStream("1.txt"))将源改成文件1.txt。System.setOut(new FileInputStream("1.txt"))将目的改成2.txt。
/*
* 读取一个键盘录入的数据,并打印在控制台上。
*
* 键盘本身就是一个标准的输入设备。
* 对于java而言,对于这种输入设备都有对应的对象。
*
*
*/
public class ReadKey {
/**
* @param args
* @throws IOException
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// readKey();
// System.out.println((int)'\r');
// System.out.println((int)'\n');
readKey2();
}
public static void readKey2() throws IOException {
/*
* 获取用户键盘录入的数据,
* 并将数据变成大写显示在控制台上,
* 如果用户输入的是over,结束键盘录入。
*
* 思路:
* 1,因为键盘录入只读取一个字节,要判断是否是over,
* 需要将读取到的字节拼成字符串。
* 2,那就需要一个容器。StringBuilder.
* 3,在用户回车之前将录入的数据变成字符串判断即可。
*
*/
//1,创建容器。
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
//2,获取键盘读取流。
InputStream in = System.in;
//3,定义变量记录读取到的字节,并循环获取。
int ch = 0;
while((ch=in.read())!=-1){
// 在存储之前需要判断是否是换行标记 ,因为换行标记不存储。
if(ch=='\r')
continue;
if(ch=='\n'){
String temp = sb.toString();
if("over".equals(temp))
break;
System.out.println(temp.toUpperCase());
sb.delete(0, sb.length());
}
else
//将读取到的字节存储到StringBuilder中。
sb.append((char)ch);
// System.out.println(ch);
}
}
public static void readKey() throws IOException {
InputStream in = System.in;
int ch = in.read();//阻塞式方法。
System.out.println(ch);
int ch1 = in.read();//阻塞式方法。
System.out.println(ch1);
int ch2 = in.read();//阻塞式方法。
System.out.println(ch2);
// in.close();
// InputStream in2 = System.in;
// int ch3 = in2.read();
}
}
转换流:InputStreamReader,OutputStream--字符流与字节流之间的桥梁,方便了字符流与字节流之间的操作。
应用:字节流中的数据都是字符时,转成字符流操作更高效。
流的操作规律:
1,明确源和目的:
源:InputStream,Reader
目的:OutputStream,Writer
2,明确是否是纯文本:
是:Reader,Writer
否:InputStream,OutputStream
3,明确具体设备:
硬盘:File
键盘:System.in或者out
内存:数组
网络:Socket流
4,是否需要额外功能:
高效:buffer
转换:InputStreamReader,OutputStream
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//字节流。
InputStream in = System.in;
// int ch = in.read();
// System.out.println(ch);
// int ch1 = in.read();
// System.out.println(ch1);
//将字节转成字符的桥梁。装换流。
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(in);
// int ch = isr.read();
// System.out.println((char)ch);
//字符流。
BufferedReader bufr = new BufferedReader(isr);
OutputStream out = System.out;
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(out);
BufferedWriter bufw = new BufferedWriter(osw);
String line = null;
while((line=bufr.readLine())!=null){
if("over".equals(line))
break;
// System.out.println(line.toUpperCase());
// osw.write(line.toUpperCase()+"\r\n");
// osw.flush();
bufw.write(line.toUpperCase());
bufw.newLine();
bufw.flush();
}
}
}
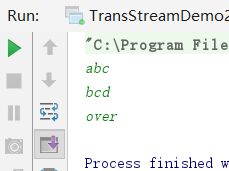
public class TransStreamDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*
需求:将键盘录入的数据写入到一个文件中。
*/
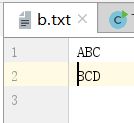
BufferedReader bufr = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
BufferedWriter bufw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("b.txt")));
String line = null;
while((line=bufr.readLine())!=null){
if("over".equals(line))
break;
bufw.write(line.toUpperCase());
bufw.newLine();
bufw.flush();
}
}
}
public class TransStreamDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
readText_2();
}
public static void readText_2() throws IOException, FileNotFoundException {
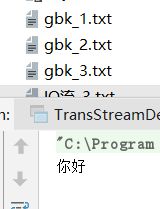
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("gbk_1.txt"),"gbk");
char[] buf = new char[10];
int len = isr.read(buf);
String str = new String(buf,0,len);
System.out.println(str);
isr.close();
}
public static void readText_1() throws IOException {
FileReader fr = new FileReader("gbk_1.txt");
char[] buf = new char[10];
int len = fr.read(buf);
String str = new String(buf,0,len);
System.out.println(str);
fr.close();
}
public static void writeText_3() throws IOException {
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("u8_1.txt"),"UTF-8");
osw.write("你好");
osw.close();
}
public static void writeText_2() throws IOException {
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("gbk_3.txt"),"GBK");
// OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("gbk_3.txt"),"GBK");
// FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("gbk_1.txt");
/*
* 这两句代码的功能是等同的。
* FileWriter:其实就是转换流指定了本机默认码表的体现。而且这个转换流的子类对象,可以方便操作文本文件。
* 简单说:操作文件的字节流+本机默认的编码表。
* 这是按照默认码表来操作文件的便捷类。
*
* 如果操作文本文件需要明确具体的编码。FileWriter就不行了。必须用转换流。
*
*/
osw.write("你好");
osw.close();
}
public static void writeText_1() throws IOException {
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("gbk_1.txt");
fw.write("你好");
fw.close();
}
}
File类:用来将文件或者文件夹封装成对象,对文件与文件夹的属性信息进行操作。File对象可以作为参数传递给流的构造函数。
public static void constructorDemo() {
//可以将一个已存在的,或者不存在的文件或者目录封装成file对象。
File f1 = new File("c:\\a.txt");
File f2 = new File("c:\\","a.txt");
File f = new File("c:\\");
File f3 = new File(f,"a.txt");
File f4 = new File("c:"+File.separator+"abc"+File.separator+"a.txt");
System.out.println(f4);
}
Filter(过滤器):可以筛选自已想要的文件名。
public class FilterByHidden implements FileFilter {
@Override
public boolean accept(File pathname) {
return !pathname.isHidden();
}
}
public class FilterByJava implements FilenameFilter {
@Override
public boolean accept(File dir, String name) {
// System.out.println(dir+"---"+name);
return name.endsWith(".txt");
}
}
public class SuffixFilter implements FilenameFilter {
private String suffix ;
public SuffixFilter(String suffix) {
super();
this.suffix = suffix;
}
@Override
public boolean accept(File dir, String name) {
return name.endsWith(suffix);
}
}
public class FileListDemo {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
listDemo_2();
}
public static void listDemo_3() {
File dir = new File("c:\\");
File[] files = dir.listFiles(new FilterByHidden());
for(File file : files){
System.out.println(file);
}
}
public static void listDemo_2() {
File dir = new File("c:\\");
String[] names = dir.list(new SuffixFilter(".txt"));
for(String name : names){
System.out.println(name);
}
}
public static void listDemo() {
File file = new File("c:\\");
/*
* 获取当前目录下的文件以及文件夹的名称,包含隐藏文件。
* 调用list方法的File对象中封装的必须是目录。
* 否则会发生NullPointerException
* 如果访问的系统级目录也会发生空指针异常。
*
* 如果目录存在但是没有内容,会返回一个数组,但是长度为0.
*
*/
String[] names = file.list();
System.out.println(names.length);
for(String name : names){
System.out.println(name);
}
}
}
File对象的常见方法。
1,获取。
1.1 获取文件名称。
1.2 获取文件路径。
1.3 获取文件大小。
1.4 获取文件修改时间。
2,创建与删除。
3,判断。
4, 重命名
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
getDemo();
createAndDeleteDemo();
isDemo();
renameToDemo();
listRootsDemo();
}
public static void listRootsDemo() {
File file = new File("d:\\");
System.out.println("getFreeSpace:"+file.getFreeSpace());
System.out.println("getTotalSpace:"+file.getTotalSpace());
System.out.println("getUsableSpace:"+file.getUsableSpace());
// File[] files = File.listRoots();
// for(File file : files){
// System.out.println(file);
// }
}
public static void renameToDemo() {
File f1 = new File("c:\\9.mp3");
File f2 = new File("d:\\aa.mp3");
boolean b = f1.renameTo(f2);
System.out.println("b="+b);
}
public static void isDemo() throws IOException{
File f = new File("aaa");
// f.mkdir();
f.createNewFile();
// boolean b = f.exists();
// System.out.println("b="+b);
// 最好先判断是否存在。
System.out.println(f.isFile());
System.out.println(f.isDirectory());
}
public static void createAndDeleteDemo() throws IOException {
File dir = new File("abc\\q\\e\\c\\z\\r\\w\\y\\f\\e\\g\\s");
// boolean b = dir.mkdir();//make directory
// System.out.println("b="+b);
// dir.mkdirs();//创建多级目录
System.out.println(dir.delete());
// System.out.println(dir.delete());
// 文件的创建和删除。
// File file = new File("file.txt");
/*
* 和输出流不一样,如果文件不存在,则创建,如果文件存在,则不创建。
*
*/
// boolean b = file.createNewFile();
// System.out.println("b="+b);
// boolean b = file.delete();
// System.out.println("b="+b);
}
public static void getDemo(){
// File file = new File("E:\\java0331\\day22e\\a.txt");
File file = new File("a.txt");
String name = file.getName();
String absPath = file.getAbsolutePath();//绝对路径。
String path = file.getPath();
long len = file.length();
long time = file.lastModified();
Date date = new Date(time);
DateFormat dateFormat = DateFormat.getDateTimeInstance(DateFormat.LONG,DateFormat.LONG);
String str_time = dateFormat.format(date);
System.out.println("parent:"+file.getParent());
System.out.println("name:"+name);
System.out.println("absPath:"+absPath);
System.out.println("path:"+path);
System.out.println("len:"+len);
System.out.println("time:"+time);
System.out.println("str_time:"+str_time);
}
}
递归:函数自身直接或间接的调用到了自身。
注意:
1,递归一定明确条件,否则容易栈溢出。
2,注意递归的次数。
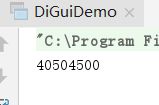
public class DiGuiDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// show();
// toBin(6);
int sum = getSum(9000);
System.out.println(sum);
}
public static int getSum(int num){
int x = 9;
if(num==1)
return 1;
return num+getSum(num-1);
}
public static void toBin(int num){
if(num>0){
toBin(num/2);
System.out.println(num%2);
}
}
/*
public static void show(){
method();
}
public static void method(){
show();
}
*/
}
深度遍历:对列出指定目录所有内容(包含子目录的内容)。
public class FileTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File dir = new File("e:\\demodir");
listAll(dir,0);
}
public static void listAll(File dir,int level) {
System.out.println(getSpace(level)+dir.getName());
//获取指定目录下当前的所有文件夹或者文件对象
level++;
File[] files = dir.listFiles();
for(int x=0; x深度遍历:删除一个带内容的目录(从里往外删)。
public class RemoveDirTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File dir = new File("e:\\demodir");
// dir.delete();
removeDir(dir);
}
public static void removeDir(File dir) {
File[] files = dir.listFiles();
for(File file : files){
if(file.isDirectory()){
removeDir(file);
}else{
System.out.println(file+":"+file.delete());
}
}
System.out.println(dir+":"+dir.delete());
}
}
Properties集合:
1,该集合中的键和值都是字符串类型。
2,集合中的数据可以保存到流中,或从流获取。
3,通常该集合用于操作以键值对形式存在的配置文件。
public class PropertiesDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*
* Map
* |--Hashtable
* |--Properties:
*
* Properties集合:
* 特点:
* 1,该集合中的键和值都是字符串类型。
* 2,集合中的数据可以保存到流中,或者从流获取。
*
* 通常该集合用于操作以键值对形式存在的配置文件。
*
*
*/
// methodDemo_4();
// myLoad();
test();
}
//对已有的配置文件中的信息进行修改。
/*
* 读取这个文件。
* 并将这个文件中的键值数据存储到集合中。
* 在通过集合对数据进行修改。
* 在通过流将修改后的数据存储到文件中。
*/
public static void test() throws IOException{
//读取这个文件。
File file = new File("info.txt");
if(!file.exists()){
file.createNewFile();
}
FileReader fr = new FileReader(file);
//创建集合存储配置信息。
Properties prop = new Properties();
//将流中信息存储到集合中。
prop.load(fr);
prop.setProperty("wangwu", "16");
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(file);
prop.store(fw,"");
// prop.list(System.out);
fw.close();
fr.close();
}
//模拟一下load方法。
public static void myLoad() throws IOException{
Properties prop = new Properties();
BufferedReader bufr = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("info.txt"));
String line = null;
while((line=bufr.readLine())!=null){
if(line.startsWith("#"))
continue;
String[] arr = line.split("=");
// System.out.println(arr[0]+"::"+arr[1]);
prop.setProperty(arr[0], arr[1]);
}
prop.list(System.out);
bufr.close();
}
public static void methodDemo_4() throws IOException {
Properties prop = new Properties();
//集合中的数据来自于一个文件。
//注意;必须要保证该文件中的数据是键值对。
//需要使用到读取流。
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("info.txt");
//使用load方法。
prop.load(fis);
prop.list(System.out);
}
public static void methodDemo_3() throws IOException {
Properties prop = new Properties();
//存储元素。
prop.setProperty("zhangsan","30");
prop.setProperty("lisi","31");
prop.setProperty("wangwu","36");
prop.setProperty("zhaoliu","20");
//想要将这些集合中的字符串键值信息持久化存储到文件中。
//需要关联输出流。
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("info.txt");
//将集合中数据存储到文件中,使用store方法。
prop.store(fos, "info");
fos.close();
}
/**
* 演示Properties集合和流对象相结合的功能。
*/
public static void methodDemo_2(){
Properties prop = new Properties();
//存储元素。
// prop.setProperty("zhangsan","30");
// prop.setProperty("lisi","31");
// prop.setProperty("wangwu","36");
// prop.setProperty("zhaoliu","20");
prop = System.getProperties();
prop.list(System.out);
}
/*
* Properties集合的存和取。
*/
public static void propertiesDemo(){
//创建一个Properties集合。
Properties prop = new Properties();
//存储元素。
prop.setProperty("zhangsan","30");
prop.setProperty("lisi","31");
prop.setProperty("wangwu","36");
prop.setProperty("zhaoliu","20");
//修改元素。
prop.setProperty("wangwu","26");
//取出所有元素。
Set names = prop.stringPropertyNames();
for(String name : names){
String value = prop.getProperty(name);
System.out.println(name+":"+value);
}
}
}
/*
* 定义功能,获取一个应用程序运行的次数,如果超过5次,给出使用次数已到请注册的提示。并不要在运行程序。
*
* 思路:
* 1,应该有计数器。
* 每次程序启动都需要计数一次,并且是在原有的次数上进行计数。
* 2,计数器就是一个变量。 突然冒出一想法,程序启动时候进行计数,计数器必须存在于内存并进行运算。
* 可是程序一结束,计数器消失了。那么再次启动该程序,计数器又重新被初始化了。
* 而我们需要多次启动同一个应用程序,使用的是同一个计数器。
* 这就需要计数器的生命周期变长,从内存存储到硬盘文件中。
*
* 3,如何使用这个计数器呢?
* 首先,程序启动时,应该先读取这个用于记录计数器信息的配置文件。
* 获取上一次计数器次数。 并进行试用次数的判断。
* 其次,对该次数进行自增,并自增后的次数重新存储到配置文件中。
*
*
* 4,文件中的信息该如何进行存储并体现。
* 直接存储次数值可以,但是不明确该数据的含义。 所以起名字就变得很重要。
* 这就有了名字和值的对应,所以可以使用键值对。
* 可是映射关系map集合搞定,又需要读取硬盘上的数据,所以map+io = Properties.
*
*
*
*/
public class PropertiesTest {
/**
* @param args
* @throws IOException
* @throws Exception
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
getAppCount();
}
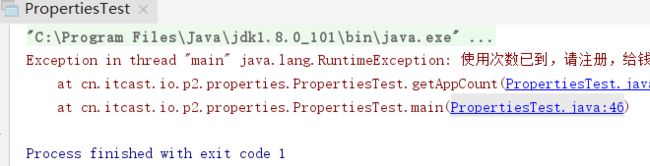
public static void getAppCount() throws IOException{
//将配置文件封装成File对象。
File confile = new File("count.properties");
if(!confile.exists()){
confile.createNewFile();
}
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(confile);
Properties prop = new Properties();
prop.load(fis);
//从集合中通过键获取次数。
String value = prop.getProperty("time");
//定义计数器。记录获取到的次数。
int count =0;
if(value!=null){
count = Integer.parseInt(value);
if(count>=5){
// System.out.println("使用次数已到,请注册,给钱!");
// return;
throw new RuntimeException("使用次数已到,请注册,给钱!");
}
}
count++;
//将改变后的次数重新存储到集合中。
prop.setProperty("time", count+"");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(confile);
prop.store(fos, "");
fos.close();
fis.close();
}
}
获取指定目录下,指定扩展名的文件(包含子目录中的),并将这些文件的绝对路径写入到一个文本文件中。
/*
*
* 获取指定目录下,指定扩展名的文件(包含子目录中的)
* 这些文件的绝对路径写入到一个文本文件中。
*
* 简单说,就是建立一个指定扩展名的文件的列表。
*
* 思路:
* 1,必须进行深度遍历。
* 2,要在遍历的过程中进行过滤。将符合条件的内容都存储到容器中。
* 3,对容器中的内容进行遍历并将绝对路径写入到文件中。
*
*
*/
public class Test {
/**
* @param args
* @throws IOException
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
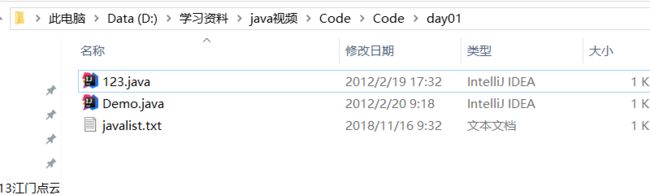
File dir = new File("d:\\学习资料\\java视频\\Code\\Code\\day01");//将javalist.txt放到这个文件夹下
FilenameFilter filter = new FilenameFilter(){
@Override
public boolean accept(File dir, String name) {
return name.endsWith(".java");
}
};
List list = new ArrayList();
getFiles(dir,filter,list);
File destFile = new File(dir,"javalist.txt");
write2File(list,destFile);
}
/**
* 对指定目录中的内容进行深度遍历,并按照指定过滤器,进行过滤,
* 将过滤后的内容存储到指定容器List中。
* @param dir
* @param filter
* @param list
*/
public static void getFiles(File dir,FilenameFilter filter,List list){
File[] files = dir.listFiles();
for(File file : files){
if(file.isDirectory()){
//递归啦!
getFiles(file,filter,list);
}else{
//对遍历到的文件进行过滤器的过滤。将符合条件File对象,存储到List集合中。
if(filter.accept(dir, file.getName())){
list.add(file);
}
}
}
}
public static void write2File(List list,File destFile)throws IOException{
BufferedWriter bufw = null;
try {
bufw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(destFile));
for(File file : list){
bufw.write(file.getAbsolutePath());
bufw.newLine();
bufw.flush();
}
} /*catch(IOException e){
throw new RuntimeException("写入失败");
}*/finally{
if(bufw!=null)
try {
bufw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("关闭失败");
}
}
}
}