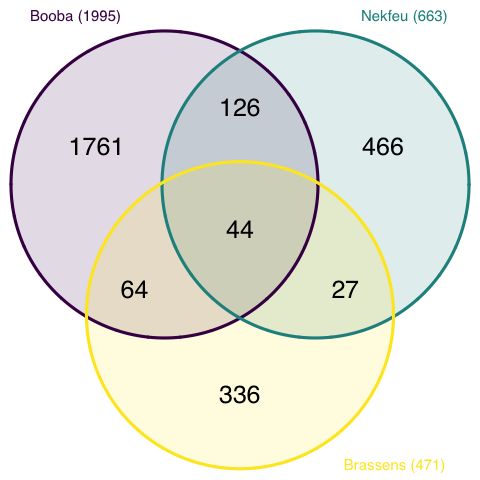
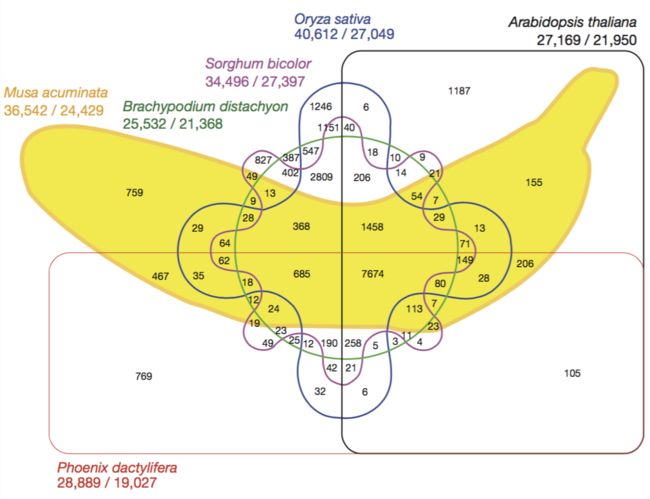
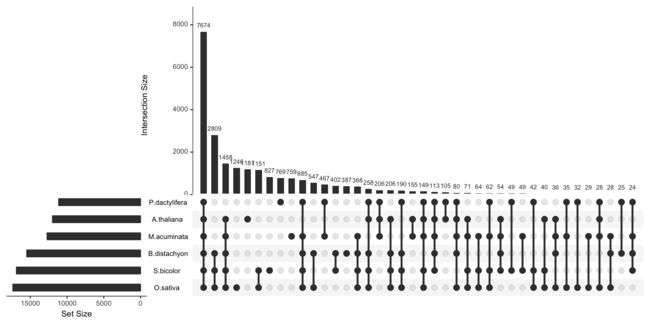
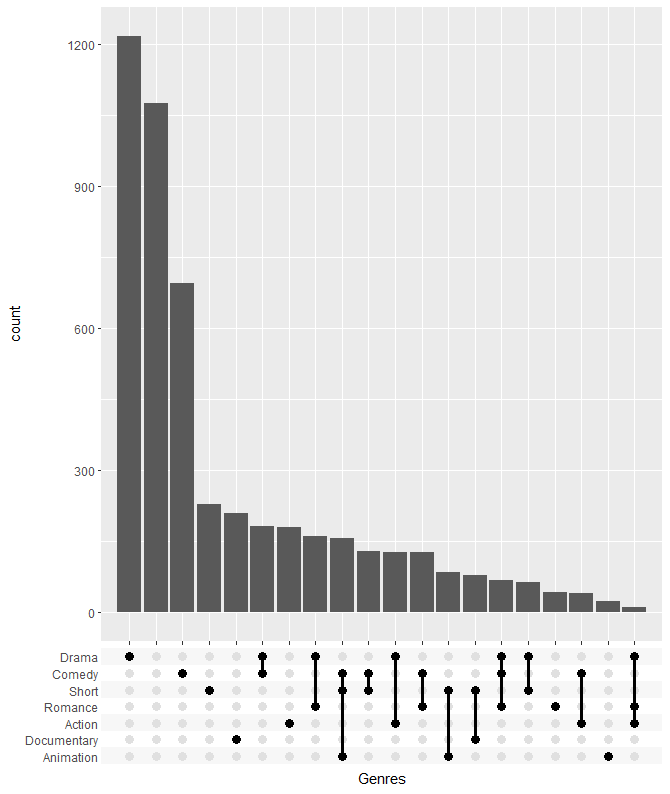
对于不同数据集合的比较的可视化,一般用韦恩图来表示,但是数据集合太多了,就不好看了,反而不容易从图中获得信息了。
三个集合看起来最合适。
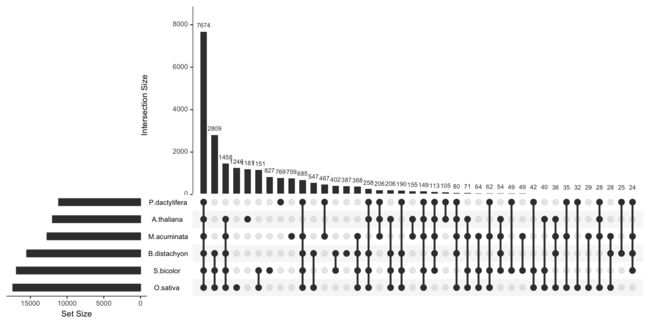
2012年发表的香蕉基因组文章中的韦恩图,已经很美观了,但阅读起来还是比较费劲的。
为了解决过多的数据集合造成的信息混乱问题,UpsetR包应运而生完美解决了这个问题,这个包的使用教程网上也比较多。
今天看见Y叔推荐了ggplot2风格的upset plot——ggupset包,顺便学习一下这个包的使用教程,我这个有点跟风的嫌疑,感谢Y叔的分享。
1.安装ggupset
# Download package from CRAN
> install.packages("ggupset")
# Or get the latest version directly from GitHub
> devtools::install_github("const-ae/ggupset")
2.示例
> library(ggplot2)
> library(tidyverse)
> library(ggupset)
#使用的数据集tidy_movies,IMDB中的电影列表
> tidy_movies
# A tibble: 50,000 x 10
title year length budget rating votes mpaa Genres stars percent_rating
1 Ei ist eine geschissene Gottesgabe, Das 1993 90 NA 8.4 15 "" 1 4.5
2 Hamos sto aigaio 1985 109 NA 5.5 14 "" 1 4.5
3 Mind Benders, The 1963 99 NA 6.4 54 "" 1 0
4 Trop (peu) d'amour 1998 119 NA 4.5 20 "" 1 24.5
5 Crystania no densetsu 1995 85 NA 6.1 25 "" 1 0
6 Totale!, La 1991 102 NA 6.3 210 "" 1 4.5
7 Visiblement je vous aime 1995 100 NA 4.6 7 "" 1 24.5
8 Pang shen feng 1976 85 NA 7.4 8 "" 1 0
9 Not as a Stranger 1955 135 2000000 6.6 223 "" 1 4.5
10 Autobiographia Dimionit 1994 87 NA 7.4 5 "" 1 0
# ... with 49,990 more rows
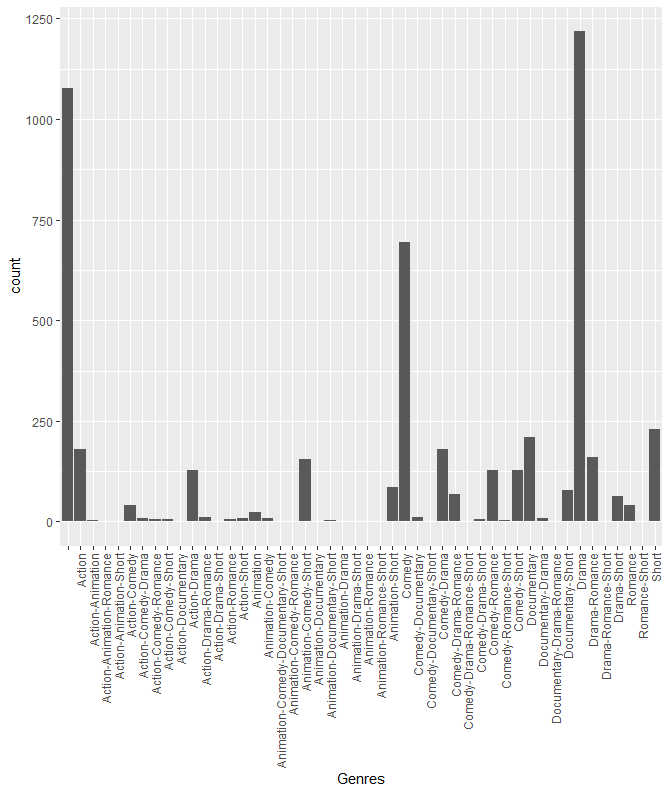
> > tidy_movies %>%
+ distinct(title, year, length, .keep_all=TRUE) %>%
+ ggplot(aes(x=Genres)) +
+ geom_bar() +
+ scale_x_upset(n_intersections = 20)
Warning message:
Removed 100 rows containing non-finite values (stat_count).
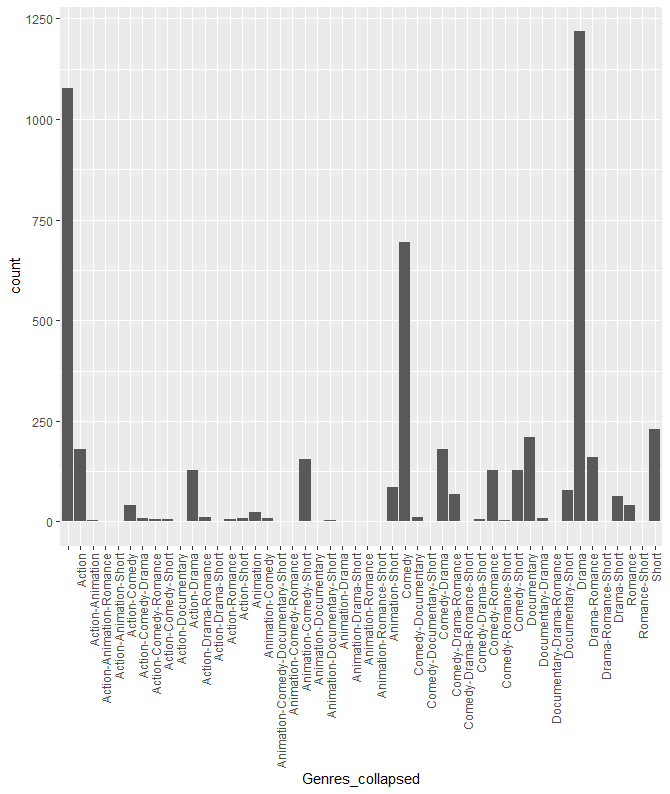
查看更细致的电影分类情况
> tidy_movies %>%
+ distinct(title, year, length, .keep_all=TRUE) %>%
+ mutate(Genres_collapsed = sapply(Genres, function(x) paste0(sort(x), collapse = "-"))) %>%
+ select(title, Genres, Genres_collapsed)
# A tibble: 5,000 x 3
title Genres Genres_collapsed
1 Ei ist eine geschissene Gottesgabe, Das Documentary
2 Hamos sto aigaio Comedy
3 Mind Benders, The ""
4 Trop (peu) d'amour ""
5 Crystania no densetsu Animation
6 Totale!, La Comedy
7 Visiblement je vous aime ""
8 Pang shen feng Action-Animation
9 Not as a Stranger Drama
10 Autobiographia Dimionit Drama
# ... with 4,990 more rows
> tidy_movies %>%
+ distinct(title, year, length, .keep_all=TRUE) %>%
+ mutate(Genres_collapsed = sapply(Genres, function(x) paste0(sort(x), collapse = "-"))) %>%
+ ggplot(aes(x=Genres_collapsed)) +
+ geom_bar() +
+ theme(axis.text.x = element_text(angle=90, hjust=1, vjust=0.5))
根据上述结果,生成新的电影分类方式。
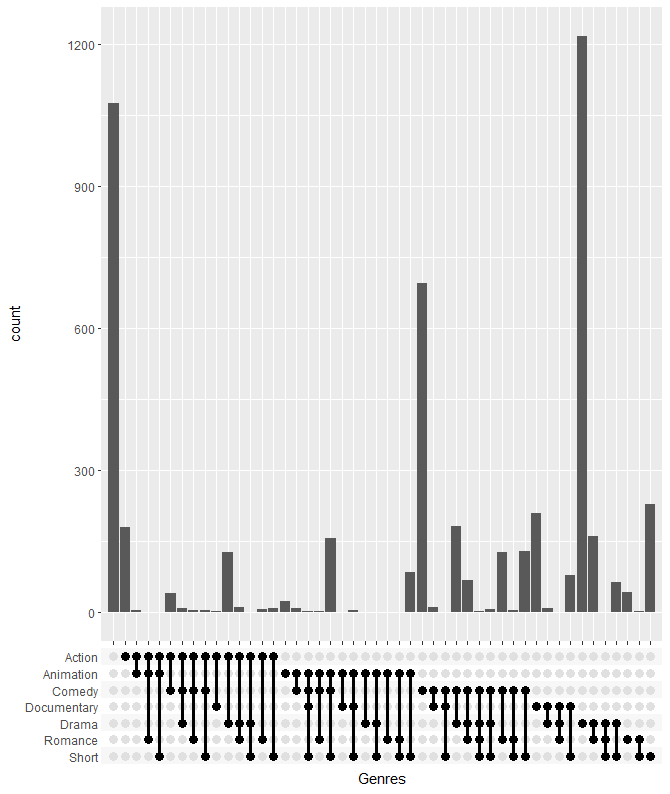
> tidy_movies %>%
+ distinct(title, year, length, .keep_all=TRUE) %>%
+ ggplot(aes(x=Genres)) +
+ geom_bar() +
+ scale_x_mergelist(sep = "-") +
+ theme(axis.text.x = element_text(angle=90, hjust=1, vjust=0.5))
展示不同类型电影之间的关系
> tidy_movies %>%
+ distinct(title, year, length, .keep_all=TRUE) %>%
+ ggplot(aes(x=Genres)) +
+ geom_bar() +
+ scale_x_mergelist(sep = "-") +
+ axis_combmatrix(sep = "-")
不同的图形类型
每种类型电影的总数量
> tidy_movies %>%
+ distinct(title, year, length, .keep_all=TRUE) %>%
+ unnest() %>%
+ mutate(GenreMember=1) %>%
+ spread(Genres, GenreMember, fill=0) %>%
+ as.data.frame() %>%
+ UpSetR::upset(sets = c("Action", "Romance", "Short", "Comedy", "Drama"), keep.order = TRUE)
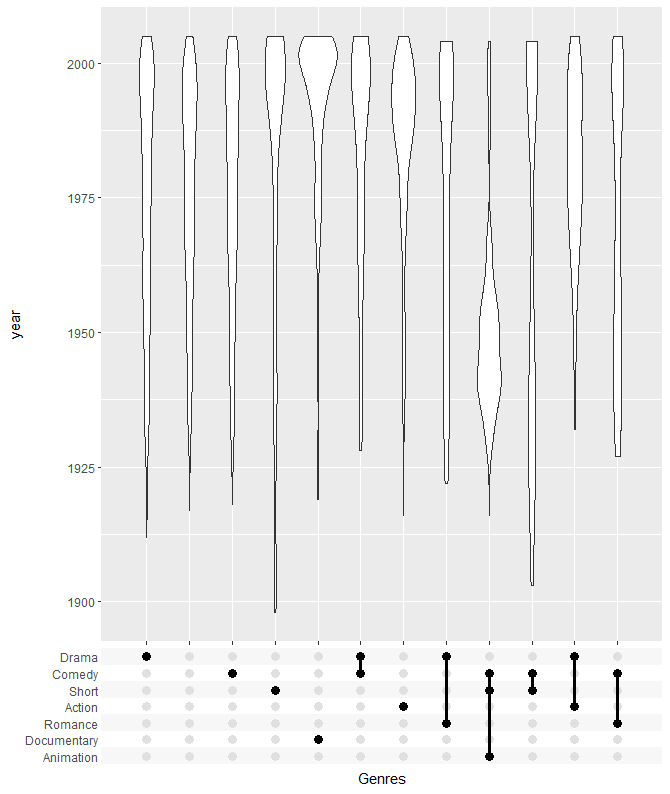
使用小提琴图展示
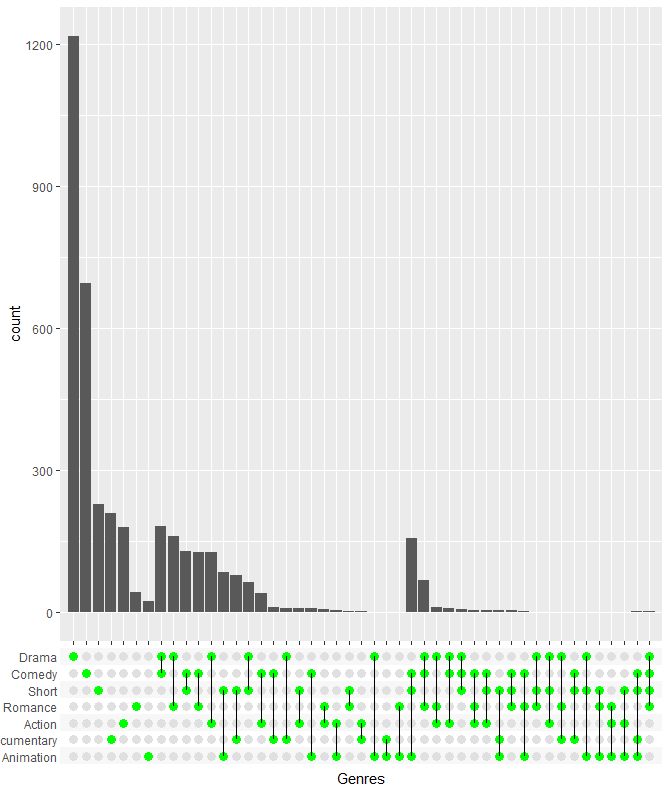
> tidy_movies %>%
+ distinct(title, year, length, .keep_all=TRUE) %>%
+ ggplot(aes(x=Genres, y=year)) +
+ geom_violin() +
+ scale_x_upset(order_by = "freq", n_intersections = 12)
3.更出色的范例
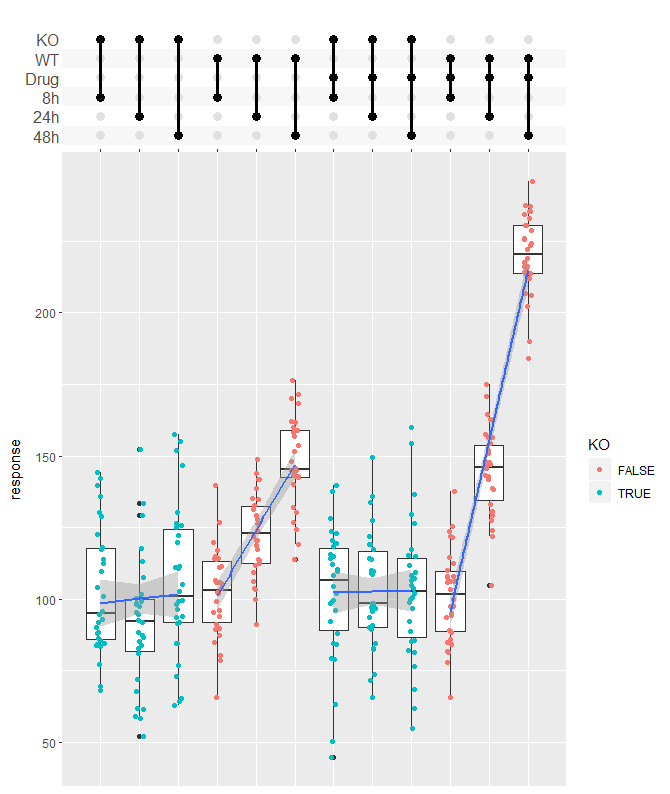
使用箱线图,散点图和拟合曲线展示结果
> df_complex_conditions
# A tibble: 360 x 4
KO DrugA Timepoint response
1 TRUE Yes 8 84.3
2 TRUE Yes 8 105.
3 TRUE Yes 8 79.1
4 TRUE Yes 8 140.
5 TRUE Yes 8 108.
6 TRUE Yes 8 79.5
7 TRUE Yes 8 112.
8 TRUE Yes 8 118.
9 TRUE Yes 8 114.
10 TRUE Yes 8 92.4
# ... with 350 more rows
> df_complex_conditions %>%
+ mutate(Label = pmap(list(KO, DrugA, Timepoint), function(KO, DrugA, Timepoint){
+ c(if(KO) "KO" else "WT", if(DrugA == "Yes") "Drug", paste0(Timepoint, "h"))
+ })) %>%
+ ggplot(aes(x=Label, y=response)) +
+ geom_boxplot() +
+ geom_jitter(aes(color=KO), width=0.1) +
+ geom_smooth(method = "lm", aes(group = paste0(KO, "-", DrugA))) +
+ scale_x_upset(order_by = "degree",
+ sets = c("KO", "WT", "Drug", "8h", "24h", "48h"),
+ position="top", name = "") +
+ theme_combmatrix(combmatrix.label.text = element_text(size=12),
+ combmatrix.label.extra_spacing = 5)
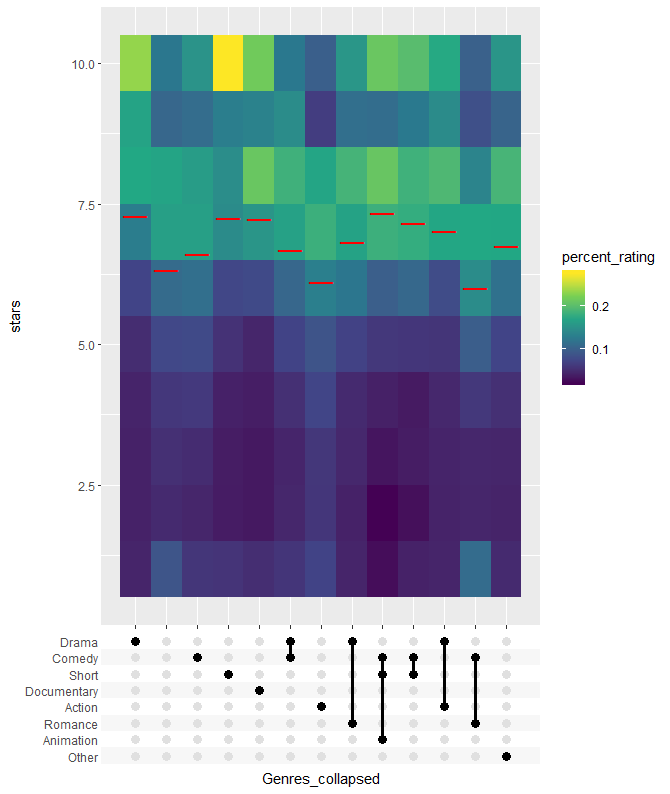
不同类型电影的IMDBD评分情况
> avg_rating <- tidy_movies %>%
+ mutate(Genres_collapsed = sapply(Genres, function(x) paste0(sort(x), collapse="-"))) %>%
+ mutate(Genres_collapsed = fct_lump(fct_infreq(as.factor(Genres_collapsed)), n=12)) %>%
+ group_by(stars, Genres_collapsed) %>%
+ summarize(percent_rating = sum(votes * percent_rating)) %>%
+ group_by(Genres_collapsed) %>%
+ mutate(percent_rating = percent_rating / sum(percent_rating)) %>%
+ arrange(Genres_collapsed)
> avg_rating
# A tibble: 130 x 3
# Groups: Genres_collapsed [13]
stars Genres_collapsed percent_rating
1 1 Drama 0.0437
2 2 Drama 0.0411
3 3 Drama 0.0414
4 4 Drama 0.0433
5 5 Drama 0.0506
6 6 Drama 0.0717
7 7 Drama 0.129
8 8 Drama 0.175
9 9 Drama 0.170
10 10 Drama 0.235
# ... with 120 more rows
# Plot using the combination matrix axis
# the red lines indicate the average rating per genre
> ggplot(avg_rating, aes(x=Genres_collapsed, y=stars, fill=percent_rating)) +
+ geom_tile() +
+ stat_summary_bin(aes(y=percent_rating * stars), fun.y = sum, geom="point",
+ shape="—", color="red", size=6) +
+ axis_combmatrix(sep = "-", levels = c("Drama", "Comedy", "Short",
+ "Documentary", "Action", "Romance", "Animation", "Other")) +
+ scale_fill_viridis_c()
粗略的走了一遍教程,结束!