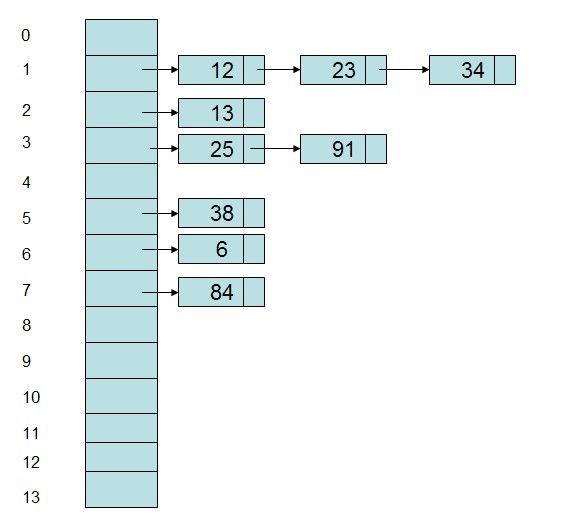
本文基于JDK1.7分析
1.数据结构
数据结构中可以用数组和链表存储数据,它们各有利弊。
数组:数组存储区间是连续的,空间复杂度大。它的特点是寻址容易,插入删除困难。
链表:链表存储区间离散,空间复杂度小。它的特点是寻址困难,插入删除容易。
哈希表:根据关键码值(Key value)而直接进行访问的数据结构。它的主干是数组,既满足了数据查找,同时也不会占用很多空间。
哈希冲突:当我们对某个元素进行哈希运算,得到一个存储地址,然后要进行插入的时候,发现已经被其他元素占用了,这就是哈希冲突。哈希冲突的解决方案有很多种:开放地址法、链地址法。HashMap所采用的处理方法就是链地址法。
链地址法:采用数组和链表相结合的办法,将Hash地址相同的记录存储在一张线性表中,而每张表的表头的序号即为计算得到的Hash地址。可以看下图:
2.实现原理
HashMap的内部是一个HashMapEntry的 table数组,HashMapEntry是HashMap的基本组成单元,每一个HashMapEntry包含一个key-value键值对。
// 初始值为一个空数组
transient HashMapEntry[] table = (HashMapEntry[]) EMPTY_TABLE;
transient 关键字的作用:被它修饰的变量不再能被序列化。
再看下HashMapEntry这个类,是HashMap的静态内部类。
static class HashMapEntry implements Map.Entry {
final K key;
V value;
// 存储指向下一个HashMapEntry的引用,单链表结构
HashMapEntry next;
// 对key进行hash运算后的结果
int hash;
/**
* Creates new entry.
*/
HashMapEntry(int h, K k, V v, HashMapEntry n) {
value = v;
next = n;
key = k;
hash = h;
}
...
}
所以,HashMap由数组+链表组成的,数组是HashMap的主体,链表则是为了解决哈希冲突。
HashMap的构造方法有4个,看一下主要的一个
/**
* Constructs an empty HashMap with the specified initial
* capacity and load factor.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity
* @param loadFactor the load factor
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is negative
* or the load factor is nonpositive
*/
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
// 校验初始容量,控制大小在4~MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30之间
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " +
initialCapacity);
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
} else if (initialCapacity < DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY) {
initialCapacity = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY;
}
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor);
// Android-Note: We always use the default load factor of 0.75f.
// This might appear wrong but it's just awkward design. We always call
// inflateTable() when table == EMPTY_TABLE. That method will take "threshold"
// to mean "capacity" and then replace it with the real threshold (i.e, multiplied with
// the load factor).
threshold = initialCapacity;
// 空方法,子类有实现
init();
}
再来看下存数据的过程
public V put(K key, V value) {
// 如果是空数组,创建一个一定大小的数组
if (table == EMPTY_TABLE) {
inflateTable(threshold);
}
// 正对key为null单独处理,存储到数组的第0个位置
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
// 对key进行hash运算
int hash = sun.misc.Hashing.singleWordWangJenkinsHash(key);
// 获取在数组中的位置
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
// 遍历链表
for (HashMapEntry e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
// key相同则覆盖,返回了之前的值
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
// 新增一个HashMapEntry
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
}
先看下inflateTable方法
private void inflateTable(int toSize) {
// 得到一个大于阈值threshold的2的次方数的容量
// Find a power of 2 >= toSize
int capacity = roundUpToPowerOf2(toSize);
// Android-changed: Replace usage of Math.min() here because this method is
// called from the of runtime, at which point the native libraries
// needed by Float.* might not be loaded.
// 控制thresholdFloat 最大值,为容量*负载因子与最大容量+1的最小值
float thresholdFloat = capacity * loadFactor;
if (thresholdFloat > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1) {
thresholdFloat = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1;
}
// 为threshold赋值
threshold = (int) thresholdFloat;
table = new HashMapEntry[capacity];
}
再看putForNullKey这个方法
private V putForNullKey(V value) {
// 遍历了数组0位置的HashEntry
for (HashMapEntry e = table[0]; e != null; e = e.next) {
if (e.key == null) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
addEntry(0, null, value, 0);
return null;
}
再看indexFor方法,这里因为length是2的倍数,所以h & (length-1) = h%length,那么用位运算计算效率会高一些
static int indexFor(int h, int length) {
// assert Integer.bitCount(length) == 1 : "length must be a non-zero power of 2";
return h & (length-1);
}
再来看addEntry方法
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
// 当长度要超过阈值同时发生哈希冲突时,对数组扩容
if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) {
resize(2 * table.length);
hash = (null != key) ? sun.misc.Hashing.singleWordWangJenkinsHash(key) : 0;
// 计算新的数组下标
bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length);
}
createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex);
}
继续看resize方法,它将HashMap的容量扩大为两倍
void resize(int newCapacity) {
HashMapEntry[] oldTable = table;
int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;
// 极值判断
if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return;
}
HashMapEntry[] newTable = new HashMapEntry[newCapacity];
// 将旧数组的值重新计算位置后加入到新的数组
transfer(newTable);
table = newTable;
threshold = (int)Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1);
}
void transfer(HashMapEntry[] newTable) {
int newCapacity = newTable.length;
// 遍历旧数组,重新计算下标,加入到新数组中
for (HashMapEntry e : table) {
while(null != e) {
HashMapEntry next = e.next;
int i = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity);
e.next = newTable[i];
newTable[i] = e;
e = next;
}
}
}
这里有一个疑问,为什么HashMap的初始容量以及后续的扩容都是2的n次方?
我们来一个计算:
假设数组长度是15,计算过的hash值分别是8和9
h & (length-1) h (length-1)
8&(15-1) 0100 & 1110 = 0100
9&(15-1) 0101 & 1110 = 0100
8和9计算出来的结果相同,所以会定位到数组的同一个位置上去,产生哈希碰撞,8和9会被放到数组的同一个位置上形成链表,查询的时候会遍历链表,降低效率。而且当长度是15时候,&运算后,最后一位永远是0,所以0001,0011,0101,1001,1011,0111,1101这几个位置永远都不能存放元素了,空间浪费相当大,数组可以使用的位置比数组长度小了很多,这意味着进一步增加了碰撞的几率,减慢了查询的效率!
再来计算下数组长度是16的
h & (length-1) h (length-1)
8&(15-1) 0100 & 1111 = 0100
9&(15-1) 0101 & 1111 = 0101
当数组长度为16时,即为2的n次方时,2n-1得到的二进制数的每个位上的值都为1,这使得在低位上&时,得到的和原hash的低位相同,加之hash(int h)方法对key的hashCode的进一步优化,加入了高位计算,就使得只有相同的hash值的两个值才会被放到数组中的同一个位置上形成链表。
再来看下取数据的过程
public V get(Object key) {
// 针对key为null值,到数组的第0个位置取值
if (key == null)
return getForNullKey();
Entry entry = getEntry(key);
return null == entry ? null : entry.getValue();
}
private V getForNullKey() {
if (size == 0) {
return null;
}
for (HashMapEntry e = table[0]; e != null; e = e.next) {
if (e.key == null)
return e.value;
}
return null;
}
再看下getEntry方法,得到key对应的Entry
final Entry getEntry(Object key) {
if (size == 0) {
return null;
}
// 计算hash值
int hash = (key == null) ? 0 : sun.misc.Hashing.singleWordWangJenkinsHash(key);
// 得到数组下标,遍历链表,找到key相等的
for (HashMapEntry e = table[indexFor(hash, table.length)];
e != null;
e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
}
return null;
}
参考
HashMap实现原理及源码分析
HashMap扩容机制、线程安全