使用
spring4.0之后能够很方便的使用spring aop,使用@EnableAspectJAutoProxy开启aop,使用@Aspect注解声明切面。
@Configuration
@ComponentScan
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
public class PerformConfig {
}
public interface Performance {
void perform();
}
@Component
public class PerformanceImpl implements Performance{
@Override
public void perform() {
System.out.println("perform");
}
}
@Aspect
@Component
public class Audience {
@Pointcut("execution(* com.ming.aop.Performance.*(..))")
public void perform(){
}
@Before("perform()")
public void takeSeats() {
System.out.println("perform before take seats");
}
@AfterReturning("perform()")
public void applause() {
System.out.println("CLAP CLAP CLAP");
}
@AfterThrowing("perform()")
public void demandRefund() {
System.out.println("demanding a refund");
}
}
原理解析
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy注解是开启spring aop,@EnableAspectJAutoProxy注解源码如下:
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Import(AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar.class)
public @interface EnableAspectJAutoProxy {
boolean proxyTargetClass() default false;
boolean exposeProxy() default false;
}
通过@Import注解导入bean,在八、spring ioc之@Import解析中讲了@Import三种导入方式,@EnableAspectJAutoProxy是属于动态注册Bean,会调用AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar类的registerBeanDefinitions,registerBeanDefinitions实现逻辑如下:
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(
AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
//注册AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator bean
AopConfigUtils.registerAspectJAnnotationAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(registry);
//根据注解设置属性值
AnnotationAttributes enableAspectJAutoProxy =
AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesFor(importingClassMetadata, EnableAspectJAutoProxy.class);
if (enableAspectJAutoProxy.getBoolean("proxyTargetClass")) {
AopConfigUtils.forceAutoProxyCreatorToUseClassProxying(registry);
}
if (enableAspectJAutoProxy.getBoolean("exposeProxy")) {
AopConfigUtils.forceAutoProxyCreatorToExposeProxy(registry);
}
}
AopConfigUtils.registerAspectJAnnotationAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(registry)调用链比较多,但是主要目的是注册AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator bean,注册这个bean有什么用呢?
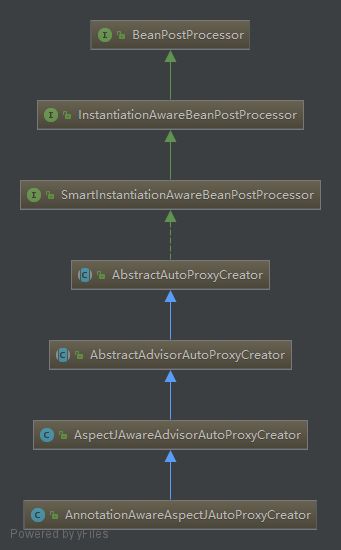
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator类图
由类图可以看出,AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator实现的根接口是BeanPostProcessor,在 二、spring ioc之BeanPostProcessor解析分析了BeanPostProcessor的用法。在bean初始化的时候会调用BeanPostProcessor的postProcessBeforeInitialization和postProcessAfterInitialization方法。
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator驱动器实现逻辑
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator驱动器的实现逻辑主要在父类AbstractAutoProxyCreator中。
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
//前置驱动直接返回bean
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (bean != null) {
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName);
if (!this.earlyProxyReferences.contains(cacheKey)) {
//后置驱动器把逻辑交给了wrapIfNecessary方法
return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);
}
}
return bean;
}
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) {
if (beanName != null && this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) {
return bean;
}
if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(this.advisedBeans.get(cacheKey))) {
return bean;
}
if (isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) || shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName)) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
// Create proxy if we have advice.
//如果存在适合当前bean的增强方法,则创建代理
Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null);
if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE);
//创建代理
Object proxy = createProxy(
bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean));
this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());
return proxy;
}
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
前置驱动器直接返回bean,后置驱动把逻辑交给了wrapIfNecessary方法,wrapIfNecessary主要的逻辑是查找是否存在匹配当前bean的增加方法,如果存在则创建bean。所以接下来主要分析:
- 如何查找匹配的增强器
- 如何创建代理