1.改变日历打印程序,让每周从周日开始。同时让它在结尾新打印一行(并且只新打印一行)。
01题参考答案:
package com.example;
import java.time.LocalDate;
public class LearnJava {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
System.out.println(" Mon Tue Wed Thu Fri Sat Sun");
final int month = 11;
LocalDate date = LocalDate.of(2017, month, 1);
final int dayOfWeek = date.getDayOfWeek().getValue();
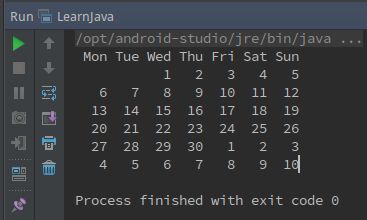
for (int i=1; i01题输出效果:
2.思考一下 Scanner 类的 nextInt 方法。它是访问器方法还是修改器方法?为什么?那 Random 类的 nextInt 方法呢?
02题参考答案(个人理解):
Scanner 类的 nextInt 方法是修改器方法,因为它改变了 Scanner 类的状态,使其读取下一个输入。Random 类的 nextInt 方法是访问器方法,因为它只是用来返回随机整数,而不会改变 Random 类的状态。
3.你曾经写过返回值不为 void 的修改器方法吗?你曾有写过返回值为 void 的访问器方法吗?可能的话给个例子。
03题参考答案:
package com.example;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class LearnJava {
private static ArrayList s_strings;
// 静态初始化块
static {
s_strings = new ArrayList<>();
s_strings.add("Mon");
s_strings.add("Tue");
s_strings.add("Wed");
s_strings.add("Thu");
s_strings.add("Fri");
}
// 返回值为 void 的访问器方法
public void printWeekdays() {
for (String string : s_strings) {
System.out.printf("%4s", string);
}
System.out.println();
}
// 返回值不为 void 的修改器方法
public boolean addSaturday() {
if (s_strings.size() >= 5) {
s_strings.add(5, "Sat");
return true;
}
return false;
}
// 返回值不为 void 的修改器方法
public boolean addSunday() {
if (s_strings.size() >= 6) {
s_strings.add(6, "Sun");
return true;
}
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
LearnJava learnJava = new LearnJava();
learnJava.printWeekdays();
learnJava.addSaturday();
learnJava.printWeekdays();
learnJava.addSunday();
learnJava.printWeekdays();
}
}
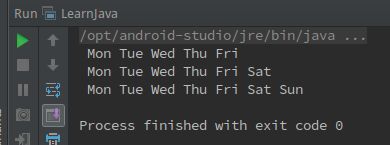
03题输出效果:
4.为什么不能实现一个可以交换两个 int 变量内容的 Java 方法,但是却可以编写一个交换两个 IntHolder 对象内容的方法?(在 API 文档中查询这个比较晦涩的 IntHolder 类。)你能交换连个 Integer 对象的内容吗?
04题参考答案:
在 Java 中,所有参数 —— 对象引用以及基本类型值 —— 都是值传递。因此,不可能写出一个方法,将对象引用修改为其他东西。我们可以查看以下的实现,就能够理解为何要借助 IntHolder 类来实现两个 Integer 变量值的交换了:
package com.example;
import org.omg.CORBA.IntHolder;
public class LearnJava {
private Integer s_integer_a = 1;
private Integer s_integer_b = 2;
public void printIntegerA_B() {
System.out.println(s_integer_a + " " + s_integer_b);
}
public void swapIntegerA_B() {
int temp = s_integer_a;
s_integer_a = s_integer_b;
s_integer_b = temp;
}
public void swapIntegerA_B(Integer a, Integer b) {
int temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
public void swapIntegerA_B(IntHolder a, IntHolder b) {
int temp = a.value;
a.value = b.value;
b.value = temp;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
LearnJava learnJava = new LearnJava();
learnJava.printIntegerA_B();
learnJava.swapIntegerA_B();
learnJava.printIntegerA_B();
Integer a = 3;
Integer b = 4;
System.out.println(a + " " + b);
learnJava.swapIntegerA_B(a, b);
System.out.println(a + " " + b);
IntHolder c = new IntHolder(5);
IntHolder d = new IntHolder(6);
System.out.println(c.value + " " + d.value);
learnJava.swapIntegerA_B(c, d);
System.out.println(c.value + " " + d.value);
}
}
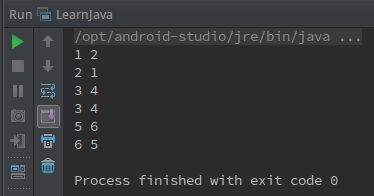
04题输出效果:
5.实现一个描述平面上点的不可能修改的 Point 类。提供一个设置具体点的构造函数、一个设置为原点的无参数构造函数,以及方法 getX、getY、translate 和 scale。translate 方法根据给定量在 x 和 y 方向上移动该点。scale 方法根据给定因子在坐标系按比例变化。实现这些方法以便它们将新的 Point 对象作为结果返回。例如:
Point p = new Point(3, 4).translate(1, 3).scale(0.5);
应该设置 p 为坐标系上为(2, 3.5)的点。
05题参考答案:
package com.example;
public class LearnJava {
public static class Point {
private double x;
private double y;
public Point(double x, double y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public Point() {
this(0, 0);
}
public double getX() {
return x;
}
public double getY() {
return y;
}
public Point translate(double x, double y) {
return new Point(this.x + x, this.y + y);
}
public Point scale(double s) {
return new Point(this.x * s, this.y * s);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Point p = new Point(3, 4).translate(1, 3).scale(0.5);
System.out.println("the point is: (" + p.getX() + "," + p.getY() + ")");
}
}
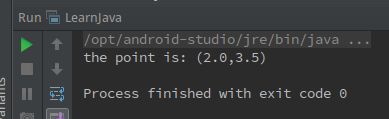
05题输出效果:
6.重复前面的练习5,但是使得 translate 和 scale 方法变成修改器方法。
06题参考答案:
package com.example;
public class LearnJava {
public static class Point {
private double x;
private double y;
public Point(double x, double y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public Point() {
this(0, 0);
}
public double getX() {
return x;
}
public double getY() {
return y;
}
public Point translate(double x, double y) {
return new Point(this.x + x, this.y + y);
}
public Point scale(double s) {
return new Point(this.x * s, this.y * s);
}
public void setTranslate(double x, double y) {
this.x += x;
this.y += y;
}
public void setScale(double s) {
this.x *= s;
this.y *= s;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Point p = new Point(3, 4).translate(1, 3).scale(0.5);
System.out.println("the point is: (" + p.getX() + "," + p.getY() + ")");
p = new Point(3, 4);
p.setTranslate(1, 3);
p.setScale(0.5);
System.out.println("the point is: (" + p.getX() + "," + p.getY() + ")");
}
}
06题输出效果:
7.给前面两个版本的 Point 类添加 javadoc 注释。
07题参考答案:
package com.example;
public class LearnJava {
/**
* 一个 Point 对象代表一个坐标点
* 坐标点中包含该坐标对应的横坐标的值 x 以及纵坐标的值 y
* @author ZhaoDongshuang
* @version 1.0
*/
public static class Point {
private double x;
private double y;
/**
* 使用给定的 x 和 y 值构造一个坐标点对象
* @param x 横坐标的值
* @param y 纵坐标的值
*/
public Point(double x, double y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
/**
* 使用原点坐标构造一个坐标点对象
*/
public Point() {
this(0, 0);
}
/**
* 获取横坐标的值
* @return 返回 double 类型的横坐标的值
*/
public double getX() {
return x;
}
/**
* 获取纵坐标的值
* @return 返回 double 类型的纵坐标的值
*/
public double getY() {
return y;
}
/**
* 获取相对原坐标点移动之后的坐标点,该方法不改变原有坐标点的状态
* @param x 横坐标的移动量
* @param y 纵坐标的移动量
* @return 返回移动之后的坐标点
*/
public Point translate(double x, double y) {
return new Point(this.x + x, this.y + y);
}
/**
* 获取相对原坐标点缩放之后的坐标点,该方法不改变原有坐标点的状态
* @param s 缩放因子
* @return 返回缩放之后的坐标点
*/
public Point scale(double s) {
return new Point(this.x * s, this.y * s);
}
/**
* 将坐标点按照给定的横纵坐标值进行移动
* @param x 横坐标的移动量
* @param y 纵坐标的移动量
*/
public void setTranslate(double x, double y) {
this.x += x;
this.y += y;
}
/**
* 将坐标点按照给定的缩放因子值进行缩放
* @param s 缩放因子
*/
public void setScale(double s) {
this.x *= s;
this.y *= s;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Point p = new Point(3, 4).translate(1, 3).scale(0.5);
System.out.println("the point is: (" + p.getX() + "," + p.getY() + ")");
p = new Point(3, 4);
p.setTranslate(1, 3);
p.setScale(0.5);
System.out.println("the point is: (" + p.getX() + "," + p.getY() + ")");
}
}
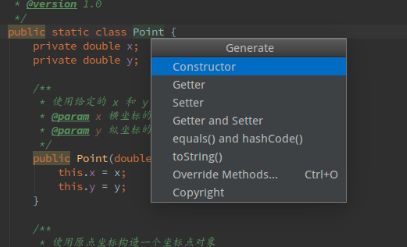
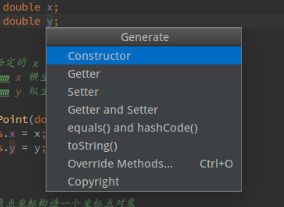
8.在前面的练习中,提供的 Point 类的这些构造函数和 getter 方法有些重复。大多数 IDE 为编写样板代码都提供了快捷方式。你的 IDE 都提供了哪些?
Android Studio 中在光标选中构造函数,键盘快捷键 “alt+insert”,显示构造函数的快速构建方法如下:
Android Studio 中在光标选中某个变量,键盘快捷键 “alt+insert”,显示变量的快速构建方法如下:
9.实现一个 Car 类,模拟汽车沿着 x 轴移动,随着移动消耗燃油。提供一个按照给定英里数驱动汽车的方法、给汽车燃料箱添加给定加仑(燃油)的方法,以及获取原点到油位的当前距离的方法。在构造函数中指定燃料效率(单位为每加仑多少英里)。Car 类应该是不可修改类吗?为什么或者为什么不应该?
09题参考答案:
package com.example;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.math.RoundingMode;
public class LearnJava {
public static class Car {
private BigDecimal burningPower;
private BigDecimal oilVolume;
private BigDecimal miles;
public Car(BigDecimal burningPower, BigDecimal oilVolume, BigDecimal miles) {
this.burningPower = burningPower;
this.oilVolume = oilVolume;
this.miles = miles;
}
public Car(BigDecimal burningPower, BigDecimal oilVolume) {
this(burningPower, oilVolume, new BigDecimal(0));
}
public Car(BigDecimal burningPower) {
this(burningPower, new BigDecimal(0), new BigDecimal(0));
}
public void move(BigDecimal miles) {
if (oilVolume.compareTo(miles.divide(burningPower,
RoundingMode.UP)) == 1) {
this.miles = this.miles.add(miles);
} else {
this.miles = this.miles.add(oilVolume.multiply(burningPower));
}
}
public void addOil(BigDecimal oilVolume) {
this.oilVolume = this.oilVolume.add(oilVolume);
}
public BigDecimal getMiles() {
return miles;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 使用下面第一种方式的 2.3 初始化 BigDecimal,其值将变成 2.2999999999999998,
// 所以建议使用第二种方式赋值
// method 1
// Car car = new Car(new BigDecimal(2.3), new BigDecimal(100));
// method 2
Car car = new Car(new BigDecimal("2.3"), new BigDecimal(100));
car.move(new BigDecimal(200));
System.out.println("Current move miles: " + car.getMiles().toString());
}
}
09题输出效果:
虽然我们想要这台车开个 400 英里,但是在当前的燃烧率和油量下,最多只能开到 230 英里。
10.在 RandomNumbers 类中,提供两个静态方法 randomElement,从数组或者整数数组列表中获得随机元素。(如果数组或者数组列表为空,则返回 0。)为什么不能使这两个方法成为 int [] 或 ArrayList
10题参考答案:
package com.example;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Random;
public class LearnJava {
static class RandomNumbers {
private static Random s_random;
static {
s_random = new Random();
s_random.setSeed(System.currentTimeMillis());
}
public static Object randomElement(ArrayList arrayList) {
if (arrayList.size() == 0) {
return 0;
}
return arrayList.get(Math.abs(s_random.nextInt())%(arrayList.size() - 1));
}
// public static Object randomElement(Integer[] arrayList) {
// return randomElement(new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(arrayList)));
// }
public static Object randomElement(int[] arrayList) {
ArrayList intList = new ArrayList<>();
for (Integer i : arrayList) {
intList.add(i);
}
return randomElement(intList);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList integers = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i=0; i<100; ++i) {
integers.add(i);
}
System.out.println(RandomNumbers.randomElement(integers).toString());
int[] arrays = new int[100];
for (int i=0; i<100; ++i) {
arrays[i] = i;
}
System.out.println(RandomNumbers.randomElement(arrays).toString());
}
}
10题输出效果:
为什么不能使这两个方法成为 int [] 或 ArrayList
这是因为在 Java 中,基本类型不是类。无法创建其对象,即无法实现通过对象对方法的调用。
11.对 System 和 LocalDate 类使用静态导入,重写 Cal 类。
11题参考答案:
package com.example;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import static java.time.LocalDate.of;
public class LearnJava {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
System.out.println(" Mon Tue Wed Thu Fri Sat Sun");
final int month = 11;
LocalDate date = of(2017, month, 1);
final int dayOfWeek = date.getDayOfWeek().getValue();
for (int i=1; i11题输出效果:
11题的示例中,我只是使用了 of 这个静态方法,因此,就仅仅改动了两行代码
import static java.time.LocalDate.of;
//...
LocalDate date = of(2017, month, 1);
12.创建一个 HelloWorld.java 文件,它在包 ch01.sec01 中声明了 HelloWorld 类。把它放在某个目录,但不在 ch01/sec01 子目录。从存放文件的那个目录运行 javac HelloWorld.java。你会得到类文件吗?类文件存放在哪里?接着运行 java HelloWorld 会发生什么?为什么?(提示:运行 javap HelloWorld 并研究告警信息。)最后,为什么 javac -d . HelloWorld.java 更好?
12题参考答案:
会得到类文件,文件存放在 HelloWorld.java 所在的目录
运行
java HelloWorld
会提示错误:
错误: 找不到或无法加载主类 HelloWorld
通过运行
javap HelloWorld
我们可以知道这是因为:
警告: 二进制文件HelloWorld包含ch01.sec01.LearnJava
也就是无法正确的找到相应的文件。
而使用
javac -d . HelloWorld.java
的好处是,class 文件会产生在单独的目录中,不会搞乱代码树,并且 class 文件也有正确的子目录结构。
运行完
javac -d . HelloWorld.java
再执行
java ch01.sec01.LearnJava
就可以得到正常的输出了。
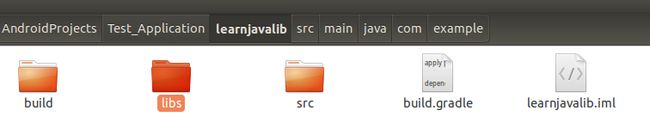
13.从 http://opencsv.sourceforge.net 下载 OpenCSV 的 JAR 文件。写个有 main 方法的类,读取你选择的 CSV 文件并打印部分内容。OpenCSV 网站上有示例代码。我们还未学习处理异常。先用下面的内容作为 main 方法头:
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
这个练习的目的不是让我们用 CSV 文件做些有用的事情,而是练习如何使用交付为 JAR 文件格式的类库。
13题参考答案:
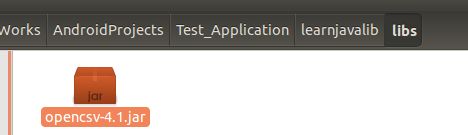
在 Android Studio 中,我们将下载的 jar 包,放到 libs 目录中:
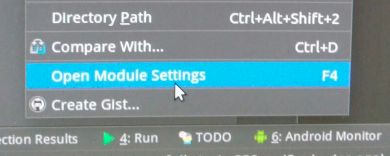
在 Android Studio 中,选择需要加入 JAR 包的 java module,点击鼠标右键:
选择 “Open Module Settings” 选项:
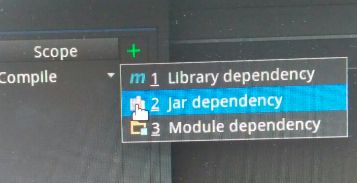
点击新弹出的窗口的右侧的 “+” 符号,选择 “jar dependency” 选项:
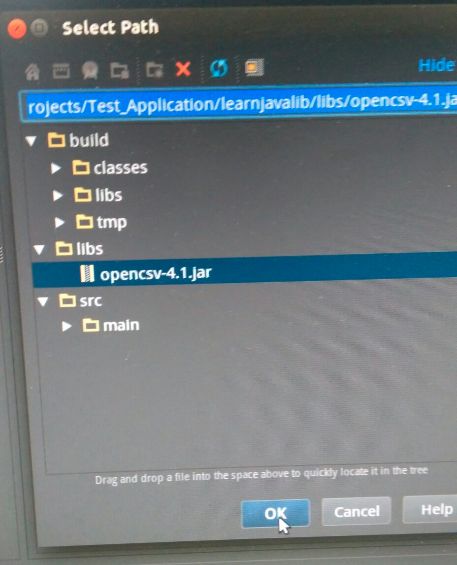
在弹出的窗口中选择我们刚刚放到 libs 中的 JAR 包:
下面是测试代码(其实不好用),只是我们可以引用 JAR 包中的方法了。
package com.example;
import com.opencsv.CSVReader;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.util.List;
public class LearnJava {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
CSVReader reader = new CSVReader(
new FileReader("/home/toby/SampleCSVFile_10600kb.csv"));
List myEntries = reader.readAll();
}
}
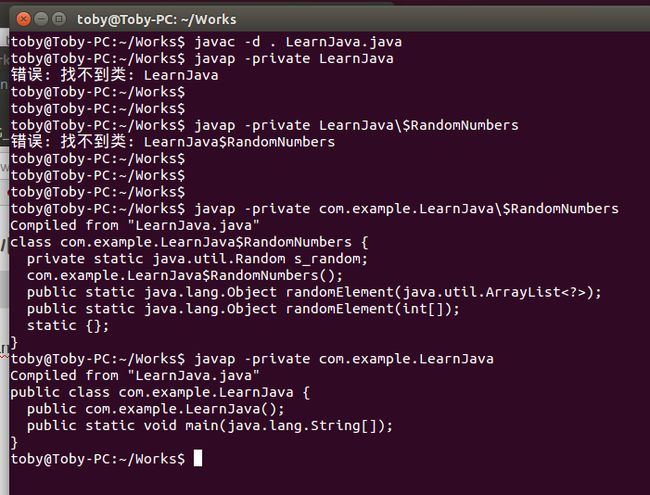
14.编译 Network 类。注意内部类文件被命名为 Network$Member.class。使用 javap 程序检查生成的代码。命令
javap -private Classname
显示方法和实例变量。你在哪里看到外部类的引用?(在 Linux/Mac OS X 系统上,运行 javap 时,在 $ 符号前你需要输入 “\”。)
14题参考答案:
我没有编译 Network 类,而是将第10题的例子编译了一下:
package com.example;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Random;
public class LearnJava {
static class RandomNumbers {
private static Random s_random;
static {
s_random = new Random();
s_random.setSeed(System.currentTimeMillis());
}
public static Object randomElement(ArrayList arrayList) {
if (arrayList.size() == 0) {
return 0;
}
return arrayList.get(Math.abs(s_random.nextInt())%(arrayList.size() - 1));
}
// public static Object randomElement(Integer[] arrayList) {
// return randomElement(new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(arrayList)));
// }
public static Object randomElement(int[] arrayList) {
ArrayList intList = new ArrayList<>();
for (Integer i : arrayList) {
intList.add(i);
}
return randomElement(intList);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList integers = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i=0; i<100; ++i) {
integers.add(i);
}
System.out.println(RandomNumbers.randomElement(integers).toString());
int[] arrays = new int[100];
for (int i=0; i<100; ++i) {
arrays[i] = i;
}
System.out.println(RandomNumbers.randomElement(arrays).toString());
}
}
对上述代码所在的类文件 LearnJava.java 运行:
javac -d . LearnJava.java
之后14题测试的效果如下:
15.完整实现 2.6.1 节中的 Invoice 类。提供一个打印 invoice 的方法,以及构造并打印示例 invoice 的演示程序。
15题参考答案:
package com.example;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class LearnJava {
static class Invoice {
public static class Item {
String description;
int quantity;
double unitPrice;
public Item() {
this("", 0, 0);
}
public Item(String description, int quantity, double unitPrice) {
this.description = description;
this.quantity = quantity;
this.unitPrice = unitPrice;
}
double price() {
return quantity * unitPrice;
}
}
private ArrayList- items = new ArrayList<>();
public void addItem(String description, int quantity, double unitPrice) {
Item newItem = new Item();
newItem.description = description;
newItem.quantity = quantity;
newItem.unitPrice = unitPrice;
items.add(newItem);
}
public void addItem(Item item) {
items.add(item);
}
public void printInvoice() {
for (Item item : items) {
System.out.print("description: " + item.description + ", ");
System.out.print("quantity: " + item.quantity + ", ");
System.out.println("unitPrice: " + item.unitPrice);
}
}
}
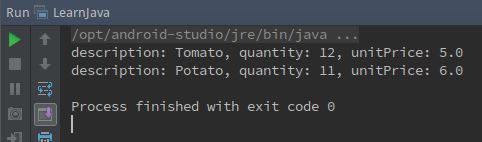
public static void main(String[] args) {
Invoice invoice = new Invoice();
invoice.addItem("Tomato", 12, 5);
Invoice.Item item0 = new Invoice.Item("Potato", 11, 6);
invoice.addItem(item0);
invoice.printInvoice();
}
}
15题输出效果:
16.实现一个 Queue 类 —— 一个无边界的字符串队列,分别提供在末尾添加字符串的 add 方法和从队列头部进行删除的 remove 方法。将元素存储成链表节点。创建一个嵌套类 Node。Node 类应该是静态类或不应该是静态类吗?
16题参考答案:
静态嵌套类没有外部类的引用。当嵌套类的实例不需要知道它属于外部类的哪个实例时,使用静态嵌套类。只有当这种信息重要时,才使用内部类。
对于这个队列来说因为 Node 无需访问 Queue 的成员或者方法,所以,Node 可以是静态的嵌套类。
package com.example;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class LearnJava {
static class Queue {
private ArrayList nodes = new ArrayList<>();
public static class Node {
public String getContent() {
return content;
}
private String content;
public Node() {
this.content = "";
}
public Node(String content) {
this.content = content;
}
}
public int size() {
return nodes.size();
}
public void add(String value) {
Node node = new Node(value);
nodes.add(node);
}
public void remove() {
if (nodes.size() > 0) {
nodes.remove(0);
}
}
public void printValue(int i) {
if (i>=0 && i < nodes.size()) {
System.out.println(nodes.get(i).getContent());
} else {
System.out.println();
}
}
}
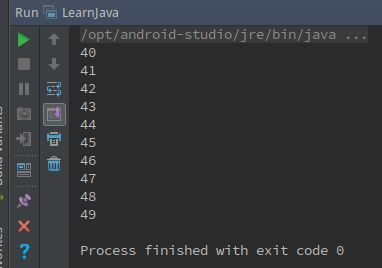
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue queue = new Queue();
for (int i=0; i<50; ++i) {
queue.add(String.valueOf(i));
}
int i = 40;
while (i>0) {
queue.remove();
--i;
}
for (i=0; i 16题输出效果:
17.提供一个 iterator —— 依次产生队列元素的对象 —— 就是上一道练习题中的队列。将 Interator 作为拥有 next 和 hasNext 方法的嵌套类。给 Queue 类提供 iterator() 方法,该方法产生 Queue.Iterator。Iterator 应该是静态类或不应该是静态类吗?
17题参考答案:
Iterator 不应该是静态嵌套类,因为它需要访问外部类的非静态成员。
package com.example;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class LearnJava {
static class Queue {
private ArrayList nodes = new ArrayList<>();
public static class Node {
public String getContent() {
return content;
}
private String content;
public Node() {
this.content = "";
}
public Node(String content) {
this.content = content;
}
}
public class Iterator {
private int i = -1;
public Iterator() {
i = -1;
}
public Iterator(int i) {
this.i = i;
}
public Node next() {
return nodes.get(++i);
}
public boolean hasNext() {
return (i+1) < nodes.size();
}
}
public int size() {
return nodes.size();
}
public void add(String value) {
Node node = new Node(value);
nodes.add(node);
}
public void remove() {
if (nodes.size() > 0) {
nodes.remove(0);
}
}
public void printValue(int i) {
if (i>=0 && i < nodes.size()) {
System.out.println(nodes.get(i).getContent());
} else {
System.out.println();
}
}
public Iterator iterator() {
return new Iterator(-1);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue queue = new Queue();
for (int i=0; i<50; ++i) {
queue.add(String.valueOf(i));
}
int i = 40;
while (i>0) {
queue.remove();
--i;
}
Queue.Iterator iterator = queue.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Queue.Node node = iterator.next();
System.out.println(node.getContent());
}
}
}
17题输出效果: