本文从CSDN上转移过来:
http://blog.csdn.net/mounty_fsc/article/details/51379395
本部分剖析Caffe中Net::Backward()函数,即反向传播计算过程。从LeNet网络角度出发,且调试网络为训练网络,共9层网络。具体网络层信息见 (Caffe,LeNet)初始化训练网络(三) 第2部分
本部分不介绍反向传播算法的理论原理,以下介绍基于对反向传播算法有一定的了解。
1 入口信息
Net::Backward()函数中调用BackwardFromTo函数,从网络最后一层到网络第一层反向调用每个网络层的Backward。
void Net::BackwardFromTo(int start, int end) {
for (int i = start; i >= end; --i) {
if (layer_need_backward_[i]) {
layers_[i]->Backward(
top_vecs_[i], bottom_need_backward_[i], bottom_vecs_[i]);
if (debug_info_) { BackwardDebugInfo(i); }
}
}
}
2 第九层SoftmaxWithLossLayer
2.1 代码分析
代码实现如下:
void SoftmaxWithLossLayer::Backward_gpu(const vector*>& top,
const vector& propagate_down, const vector*>& bottom) {
// bottom_diff shape:64*10
Dtype* bottom_diff = bottom[0]->mutable_gpu_diff();
// prob_data shape:64*10
const Dtype* prob_data = prob_.gpu_data();
// top_data shape:(1)
const Dtype* top_data = top[0]->gpu_data();
// 将Softmax层预测的结果prob复制到bottom_diff中
caffe_gpu_memcpy(prob_.count() * sizeof(Dtype), prob_data, bottom_diff);
// label shape:64*1
const Dtype* label = bottom[1]->gpu_data();
// dim = 640 / 64 = 10
const int dim = prob_.count() / outer_num_;
// nthreads = 64 / 1 = 64
const int nthreads = outer_num_ * inner_num_;
// Since this memory is never used for anything else,
// we use to to avoid allocating new GPU memory.
Dtype* counts = prob_.mutable_gpu_diff();
// 该函数将bottom_diff(此时为每个类的预测概率)对应的正确类别(label)的概率值-1,其他数据没变。见公式推导。
SoftmaxLossBackwardGPU<<>>(nthreads, top_data, label, bottom_diff,
outer_num_, dim, inner_num_, has_ignore_label_, ignore_label_, counts);
// 代码展开开始,代码有修改
__global__ void SoftmaxLossBackwardGPU(...) {
CUDA_KERNEL_LOOP(index, nthreads) {
const int label_value = static_cast(label[index]);
bottom_diff[index * dim + label_value] -= 1;
counts[index] = 1;
}
}
// 代码展开结束
Dtype valid_count = -1;
// 注意为loss的权值,对该权值(一般为1或者0)归一化(除以64)
const Dtype loss_weight = top[0]->cpu_diff()[0] /
get_normalizer(normalization_, valid_count);
caffe_gpu_scal(prob_.count(), loss_weight , bottom_diff);
}
说明:
- SoftmaxWithLossLayer是没有学习参数的(见前向计算(五)) ,因此不需要对该层的参数做调整,只需要计算bottom_diff(理解反向传播算法的链式求导,求bottom_diff对上一层的输出求导,是为了进一步计算调整上一层权值)
- 以上代码核心部分在SoftmaxLossBackwardGPU。该函数将
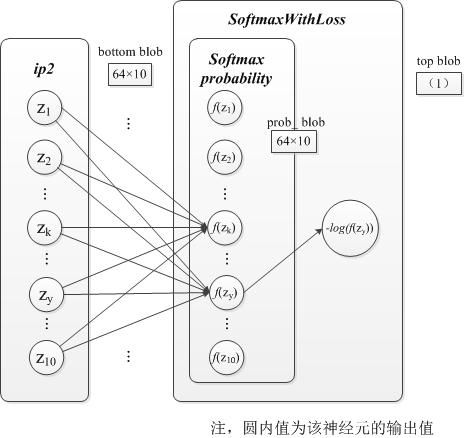
bottom_diff(此时为每个类的预测概率)对应的正确类别(label)的概率值-1,其他数据没变。这里使用前几节的符号系统及图片进行解释。
2.2 公式推导
-
符号系统
设SoftmaxWithLoss层的输入为向量$\mathbf{z}$,即bottom_blob_data,也就是上一层的输出。经过Softmax计算后的输出为向量$\mathbf{f(z)}$,公式为(省略了标准化常量m)$f(z_k)=\frac{e{z_k}}{\sum_in{e{z_i}}}$。最后SoftmaxWithLoss层的输出为$loss=\sumn-\log{f(z_y)}$,$y$为样本的标签。见前向计算(五)。
-
反向推导
把loss展开可得
$$loss=log\sum_in{e{z_i}}-z_y$$
所以$\frac{d loss}{d\mathbf{z}}$结果如下:
$$
\frac{\partial loss}{\partial z_i}=
\left {
\begin{aligned}
& f(z_y)-1,z_i= z_y \
& f(z_i),z_i \ne z_y
\end{aligned}
\right.
$$ -
图示
3 第八层InnerProduct
3.1 代码分析
template
void InnerProductLayer::Backward_gpu(const vector*>& top,
const vector& propagate_down,
const vector*>& bottom) {
//对参数求偏导,top_diff*bottom_data=blobs_diff
if (this->param_propagate_down_[0]) {
const Dtype* top_diff = top[0]->gpu_diff();
const Dtype* bottom_data = bottom[0]->gpu_data();
// Gradient with respect to weight
caffe_gpu_gemm(CblasTrans, CblasNoTrans, N_, K_, M_, (Dtype)1.,
top_diff, bottom_data, (Dtype)1., this->blobs_[0]->mutable_gpu_diff());
}
// 对偏置求偏导top_diff*bias=blobs_diff
if (bias_term_ && this->param_propagate_down_[1]) {
const Dtype* top_diff = top[0]->gpu_diff();
// Gradient with respect to bias
caffe_gpu_gemv(CblasTrans, M_, N_, (Dtype)1., top_diff,
bias_multiplier_.gpu_data(), (Dtype)1.,
this->blobs_[1]->mutable_gpu_diff());
}
//对上一层输出求偏导top_diff*blobs_data=bottom_diff
if (propagate_down[0]) {
const Dtype* top_diff = top[0]->gpu_diff();
// Gradient with respect to bottom data
caffe_gpu_gemm(CblasNoTrans, CblasNoTrans, M_, K_, N_, (Dtype)1.,
top_diff, this->blobs_[0]->gpu_data(), (Dtype)0.,
bottom[0]->mutable_gpu_diff());
}
}
3.2 公式推导
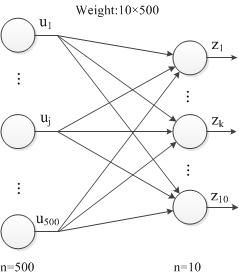
如图,当前层ip2层的输入为$\mathbf{z}$,上一层的输入为$\mathbf{u}$。
1. 对上一层输出求偏导
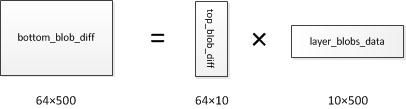
$\frac{\partial loss}{\partial u_j}$存放在ip2层的bottom_blob_diff(64500)中,计算公式如下,其中$\frac{\partial loss}{\partial z_k}$存放在top_blob_diff(6410)中:
$$
\frac{\partial z_k}{\partial u_j} = \frac{\sum_j^{100}{w_{kj}u_j}}{\partial u_j}=w_{kj}
$$
$$
\frac{\partial loss}{\partial u_j}=\sum_k^{n=10}{\frac{\partial loss}{\partial z_k}\frac{\partial z_k}{\partial u_j}}=\sum_k^{n=10}{\frac{\partial loss}{\partial z_k}w_{kj}}
$$
写成向量的形式为:
$$
\frac{\partial loss}{\partial u_j}=\frac{\partial loss}{\partial \mathbf{z^T}} \cdot \mathbf{w_{j}}
$$
进一步,写成矩阵的形式,其中$\mathbf{u}$为500维,$\mathbf{z}$为10维,$\mathbf{W}$为$10 \times 500$:
$$
\frac{\partial loss}{\partial \mathbf{u^T}}=\frac{\partial loss}{\partial \mathbf{z^T}} \cdot \mathbf{W}
$$
再进一步,考虑到一个batch有64个样本,表达式可以写成如下形式,其中$\mathbf{U}$为$64 \times 500$;$\mathbf{Z}$为$64 \times 10$;$\mathbf{W}$为$10 \times 500$:
$$
\frac{\partial loss}{\partial \mathbf{U}}=\frac{\partial loss}{\partial \mathbf{Z}} \cdot \mathbf{W}
$$
2. 对参数求偏导
$$
\frac{\partial loss}{\partial w_{kj}}=\frac{\partial loss}{\partial z_k}\frac{\partial z_k}{\partial w_{kj}}=\frac{\partial loss}{\partial z_k} u_{j}
$$
写成向量的形式有:
$$
\frac{\partial loss}{\partial \mathbf{w_{j}}}=\frac{\partial loss}{\partial \mathbf{z}} u_{j}
$$
进一步,可以写成矩阵形式,其中$\mathbf{W}$为$10 \times 500$;$\mathbf{z}$为10维;$\mathbf{u}$为500维。
$$
\frac{\partial loss}{\partial \mathbf{W}}=\frac{\partial loss}{\partial \mathbf{z}} \mathbf{u^T}
$$
再进一步,考虑到一个batch有64个样本,表达式可以写成如下形式,其中$\mathbf{W}$为$10 \times 500$;$\mathbf{Z}$为$64 \times 10$;$\mathbf{U}$为$64 \times 500$:
$$
\frac{\partial loss}{\partial \mathbf{W}}=\frac{\partial loss}{\partial \mathbf{Z^T}} \cdot \mathbf{U}
$$
4 第七层ReLU
4.1 代码分析
cpu代码分析如下,注,该层没有参数,只需对输入求导
void ReLULayer::Backward_cpu(const vector*>& top,
const vector& propagate_down,
const vector*>& bottom) {
if (propagate_down[0]) {
const Dtype* bottom_data = bottom[0]->cpu_data();
const Dtype* top_diff = top[0]->cpu_diff();
Dtype* bottom_diff = bottom[0]->mutable_cpu_diff();
const int count = bottom[0]->count();
//见公式推导
Dtype negative_slope = this->layer_param_.relu_param().negative_slope();
for (int i = 0; i < count; ++i) {
bottom_diff[i] = top_diff[i] * ((bottom_data[i] > 0)
+ negative_slope * (bottom_data[i] <= 0));
}
}
}
4.2 公式推导
设输入向量为$\mathbf{bottom_data}$,输出向量为$\mathbf{top_data}$,ReLU层公式为
$$top_data_i=
\left {
\begin{aligned}
& bottom_data_i & bottom_data_i \gt 0 \
& bottom_data_i*slope & bottom_data_i \le 0
\end{aligned}
\right .
$$所以,loss对输入的偏导为:
$$
\frac{\partial loss}{\partial bottom_data_i}=\frac{\partial loss}{\partial top_data_i} \cdot \frac{\partial top_data_i}{\partial bottom_data_i} \
= \left {
\begin{aligned}
& top_diff_i & bottom_data_i \gt 0\
& top_diff_i * slope & bottom_data_i \le 0
\end{aligned}
\right .
$$
5 第五层Pooling
5.1 代码分析
Maxpooling的cpu代码分析如下,注,该层没有参数,只需对输入求导
void PoolingLayer::Backward_cpu(const vector*>& top,
const vector& propagate_down, const vector*>& bottom) {
const Dtype* top_diff = top[0]->cpu_diff();
Dtype* bottom_diff = bottom[0]->mutable_cpu_diff();
// bottom_diff初始化置0
caffe_set(bottom[0]->count(), Dtype(0), bottom_diff);
const int* mask = NULL; // suppress warnings about uninitialized variables
...
// 在前向计算时max_idx中保存了top_data中的点是有bottom_data中的点得来的在该feature map中的坐标
mask = max_idx_.cpu_data();
// 主循环,按(N,C,H,W)方式便利top_data中每个点
for (int n = 0; n < top[0]->num(); ++n) {
for (int c = 0; c < channels_; ++c) {
for (int ph = 0; ph < pooled_height_; ++ph) {
for (int pw = 0; pw < pooled_width_; ++pw) {
const int index = ph * pooled_width_ + pw;
const int bottom_index = mask[index];
// 见公式推导
bottom_diff[bottom_index] += top_diff[index];
}
}
bottom_diff += bottom[0]->offset(0, 1);
top_diff += top[0]->offset(0, 1);
mask += top[0]->offset(0, 1);
}
}
}
5.2 公式推导
由图可知,maxpooling层是非线性变换,但有输入与输出的关系可线性表达为$bottom_data_j=top_data_i$(所以需要前向计算时需要记录索引i到索引j的映射max_idx_.
链式求导有:
$$
bottom_diff_j = \frac{\partial loss}{\partial bottom_data_j}=\frac{\partial loss}{\partial top_data_i} \cdot \frac{\partial top_data_i}{\partial bottom_data_j} \= top_diff_i \cdot 1(注意下标)
$$
6 第四层Convolution
void ConvolutionLayer::Backward_cpu(const vector*>& top,
const vector& propagate_down, const vector*>& bottom) {
const Dtype* weight = this->blobs_[0]->cpu_data();
Dtype* weight_diff = this->blobs_[0]->mutable_cpu_diff();
for (int i = 0; i < top.size(); ++i) {
const Dtype* top_diff = top[i]->cpu_diff();
const Dtype* bottom_data = bottom[i]->cpu_data();
Dtype* bottom_diff = bottom[i]->mutable_cpu_diff();
// Bias gradient, if necessary.
if (this->bias_term_ && this->param_propagate_down_[1]) {
Dtype* bias_diff = this->blobs_[1]->mutable_cpu_diff();
// 对于每个Batch中的样本,计算偏执的偏导
for (int n = 0; n < this->num_; ++n) {
this->backward_cpu_bias(bias_diff, top_diff + n * this->top_dim_);
}
}
if (this->param_propagate_down_[0] || propagate_down[i]) {
// 对于每个Batch中的样本,关于权值及输入求导部分代码展开了函数(非可运行代码)
for (int n = 0; n < this->num_; ++n) {
// gradient w.r.t. weight. Note that we will accumulate diffs.
//top_diff(50*64) * bottom_data(500*64,Transpose) = weight_diff(50*500)
caffe_cpu_gemm(CblasNoTrans, CblasTrans, conv_out_channels_ / group_,
kernel_dim_, conv_out_spatial_dim_,
(Dtype)1., top_diff + n * this->top_dim_, bottom_data + n * this->bottom_dim_,
(Dtype)1., weight_diff);
// gradient w.r.t. bottom data, if necessary.
// weight(50*500,Transpose) * top_diff(50*64) = bottom_diff(500*64)
caffe_cpu_gemm(CblasTrans, CblasNoTrans, kernel_dim_,
conv_out_spatial_dim_, conv_out_channels_ ,
(Dtype)1., weight, top_diff + n * this->top_dim_,
(Dtype)0., bottom_diff + n * this->bottom_dim_);
}
}
}
}
说明:
- 第四层的bottom维度$(N,C,H,W)=(64,20,12,12)$,top的维度bottom维度$(N,C,H,W)=(64,50,8,8)$,由于每个样本单独处理,所以只需要关注$(C,H,W)$的维度,分别为$(20,12,12)$和$(50,8,8)$
- 根据(Caffe)卷积的实现,该层可以写成矩阵相乘的形式$Weight_data \times Bottom_data^T = Top_data$
- $Weight_data$的维度为$C_{out} \times (CKK)=50 \times 500$
- $Bottom_data$的维度为$(HW) \times (CKK)=64 \times 500$,$64$为$88$个卷积核的位置,$500=CKK=2055$
- $Top_data$的维度为$64 \times 50$
- 写成矩阵表示后,从某种角度上与全连接从(也是表示成矩阵相乘)相同,因此,可以借鉴全连接层的推导。