FDS,全称Flash Data Storage,用来访问芯片内部Flash的。当你需要把数据存储在Flash中,或者读取Flash中的用户数据,或者更新或者删除Flash中的数据,那么FDS模块是你最好的选择。FDS采用文件和记录方式来组织Flash数据,也就是说,真正的数据是放在一条记录中,而多条记录组成一个文件。根据应用的需要,整个系统可以只有一个文件,也可以包含多个文件。文件采用文件ID来标示,文件ID为2个字节(注:不能取值为0xFFFF)。一个文件下面可以放一条记录,也可以放多条记录,记录是通过记录key来标示的,记录key也是2个字节长度(注:不能取值为0x0000)。这里需要注意的是,同一个文件下面的两条或者多条记录他们的key可以是一样的,比如我们可以建立如下文件系统:文件1包含2条记录,文件2包含3条记录,文件2包含2条key为0x0003的记录
注:如果你可以保证一个文件下面所有记录的key都不一样,那么文件系统会变得更简洁一些,尤其在find记录的时候,只会返回一条记录,可以简化很多应用逻辑。如前所述,这个不是强制要求:同一个文件下记录key可以相同。
FDS用法
一般而言,按照如下步骤使用FDS模块:
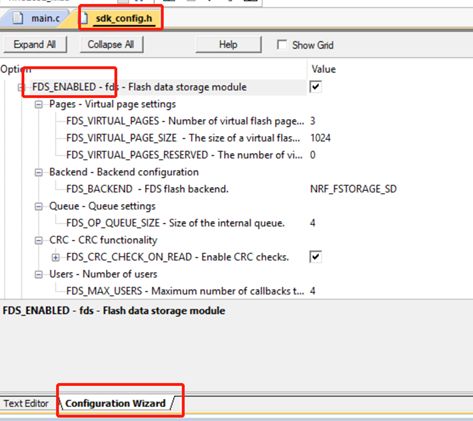
- 修改FDS的默认配置参数,比如总共分配多少Flash空间(默认只分配了8kB Flash空间给用户使用),请到sdk_config.h文件中修改如下默认配置项:
- 通过fds_register注册FDS事件回调函数及通过fds_init初始化FDS模块。FDS模块的初始化,写记录,更新记录,删除记录以及垃圾回收,这些API都是异步的。也就是说调用这些FDS操作的API,只是把相应操作放入队列然后立即返回(队列大小由上述的FDS_OP_QUEUE_SIZE控制),真正的Flash操作结果是通过事件回调函数通知你的。注:现在的FDS模块可以进行多次初始化。示例代码如下所示:
// Simple event handler to handle errors during initialization. static void fds_evt_handler(fds_evt_t const * p_fds_evt) { switch (p_fds_evt->id) { case FDS_EVT_INIT: if (p_fds_evt->result != FDS_SUCCESS) { // Initialization failed. } break; default: break; } } ret_code_t ret = fds_register(fds_evt_handler); if (ret != FDS_SUCCESS) { // Registering of the FDS event handler has failed. } ret_code_t ret = fds_init(); if (ret != FDS_SUCCESS) { // Handle error. }
- 通过fds_record_write创建新的记录,即写记录。注意写记录的时候,必须保证输入参数是全局变量或者static的局部变量,推荐使用全局变量!由于record key可以重复,所以连续调用两次相同的fds_record_write,将生成两条同样key的记录。前面也提及过,fds_record_write是异步的,所以它的返回值为success只是表示操作入队成功,真正的flash操作结果是通过前面注册的fds_evt_handler来通知的。示例代码如下所示:
#define FILE_ID 0x0001 /* The ID of the file to write the records into. */ #define RECORD_KEY_1 0x1111 /* A key for the first record. */ #define RECORD_KEY_2 0x2222 /* A key for the second record. */ static uint32_t const m_deadbeef = 0xDEADBEEF; static char const m_hello[] = "Hello, world!"; fds_record_t record; fds_record_desc_t record_desc; // Set up record. record.file_id = FILE_ID; record.key = RECORD_KEY_1; record.data.p_data = &m_deadbeef; record.data.length_words = 1; /* one word is four bytes. */ ret_code_t rc; rc = fds_record_write(&record_desc, &record); if (rc != FDS_SUCCESS) { /* Handle error. */ } // Set up record. record.file_id = FILE_ID; record.key = RECORD_KEY_2; record.data.p_data = &m_hello; /* The following calculation takes into account any eventual remainder of the division. */ record.data.length_words = (sizeof(m_hello) + 3) / 4; rc = fds_record_write(&record_desc, &record); if (rc != FDS_SUCCESS) { /* Handle error. */ }
- 通过fds_record_open来读记录。读记录之前必须先找到这条记录,这个是通过fds_record_find来实现的,由于同一个文件可以包含多条key相同的记录,所以通过多次调用同一个fds_record_find,可以找到所有相关记录。示例代码如下所示:
#define FILE_ID 0x1111 #define RECORD_KEY 0x2222 fds_flash_record_t flash_record; fds_record_desc_t record_desc; fds_find_token_t ftok; /* It is required to zero the token before first use. */ memset(&ftok, 0x00, sizeof(fds_find_token_t)); /* Loop until all records with the given key and file ID have been found. */ while (fds_record_find(FILE_ID, RECORD_KEY, &record_desc, &ftok) == FDS_SUCCESS) { if (fds_record_open(&record_desc, &flash_record) != FDS_SUCCESS) { /* Handle error. */ } /* Access the record through the flash_record structure. */ /* Close the record when done. */ if (fds_record_close(&record_desc) != FDS_SUCCESS) { /* Handle error. */ } }
- 操作记录,比如fds_record_update,fds_record_delete等,update和delete操作,必须先找到相应记录,然后才能去update或者delete。fds_record_delete不是真得把记录删除,而是将记录标示为无效。而fds_record_update实际包含2步:先找到之前的记录然后将其标记为无效(即delete操作),然后write一条新记录。记住:delete并不会回收Flash空间,无效记录仍然占据着Flash空间,这些无效记录占据着的Flash空间只有经过垃圾回收(fds_gc)才能再次给新记录使用。请注意fds_record_find只会去寻找有效记录,而不会将无效记录返回给用户的。另外,fds_record_ update和fds_record_delete是异步的,所以它们的返回值为success只是表示操作入队成功,真正的flash操作结果是通过前面注册的fds_evt_handler来通知的。示例代码如下所示:
fds_record_desc_t desc = {0};
fds_find_token_t tok = {0};
rc = fds_record_find(CONFIG_FILE, CONFIG_REC_KEY, &desc, &tok);
if (rc == FDS_SUCCESS)
{
/* A config file is in flash. Let's update it. */
fds_flash_record_t config = {0};
/* Open the record and read its contents. */
rc = fds_record_open(&desc, &config);
APP_ERROR_CHECK(rc);
/* Copy the configuration from flash into m_dummy_cfg. */
memcpy(&m_dummy_cfg, config.p_data, sizeof(configuration_t));
NRF_LOG_INFO("Config file found, updating boot count to %d.", m_dummy_cfg.boot_count);
/* Update boot count. */
m_dummy_cfg.boot_count++;
/* Close the record when done reading. */
rc = fds_record_close(&desc);
APP_ERROR_CHECK(rc);
/* Write the updated record to flash. */
rc = fds_record_update(&desc, &m_dummy_record);
if (rc == FDS_ERR_NO_SPACE_IN_FLASH) fds_gc();
else APP_ERROR_CHECK(rc);
} ret_code_t ret = fds_record_delete(&desc); if (ret != FDS_SUCCESS) { /* Error. */ }
- 当Flash不够用时,即FDS写记录或者更新记录操作返回错误FDS_ERR_NO_SPACE_IN_FLASH,请调用垃圾回收函数:fds_gc进行垃圾回收。fds_gc是一个非常耗时的操作过程(请确保操作过程中不会掉电,否则Flash行为未知),它会一个page一个page操作,然后将该page中的有效记录拷贝到swap page,然后擦除该page,并标记该page为swap page,而之前的swap page则变为data page,如此往复,直到把所有page都回收完。只有经过fds_gc后,之前无效记录占据的Flash空间才会释放,这个时候才会有多余的Flash空间给用户去操作。
建议大家直接参考SDK里面自带的fds例子来编写自己的fds应用代码,SDK自带的fds例子所在目录为:SDK安装目录\examples\peripheral\flash_fds (注:从SDK14之后才有fds例子)
理解FDS
FDS作为上层模块,它是通过调用fstorage API来实现自己的功能,fstorage又是通过调用NVMC外设驱动或者softdevice Flash访问API来达到操作Flash的目的,调用关系图如下所示:
当softdevice存在的时候,建议使用nrf_fstorage_sd后端;没有softdevice的时候,请使用nrf_fstorage_nvmc后端。
根据有无bootloader,FDS将操作不同的Flash空间,如下:
当你通过FDS把数据写入Flash中,除了数据本身,FDS还会在这条记录中加入额外的信息:记录头header,一条记录在Flash中完整的格式如下所示:
| 字段 |
大小 |
描述 |
| Record key |
16 bits |
Key that can be used to find the record. The value FDS_RECORD_KEY_DIRTY (0x0000) is reserved by the system to flag records that have been invalidated. See Restrictions on keys and IDs for further restrictions. |
| Data length |
16 bits |
Length of the data that is stored in the record (in 4-byte words). |
| File ID |
16 bits |
ID of the file that the record is associated with. The value FDS_FILE_ID_INVALID (0xFFFF) is used by the system to identify records that have not been written correctly. See Restrictions on keys and IDs for further restrictions. |
| CRC value |
16 bits |
CRC value of the whole record (checks can be enabled by setting the FDS_CRC_ENABLED compile flag, see Configuration). |
| Record ID |
32 bits |
Unique identifier of the record. 注:对用户不可见 |
所以,在计算记录总共占用多少Flash空间的时候,记得一定要把每条记录的header(3个word)也加上。
FDS使用常见问题
大家在使用FDS模块时,经常碰到的问题有如下几种:
- FDS不支持掉电保护,所以在Flash操作过程中出现了掉电,FDS行为将未知
- OTA的时候,新固件的FDS page数目一定要等于老固件的FDS page数,否则将出现不可知行为
- fds_record_write或者fds_record_update后,强烈建议回读该记录,以确保记录的确write或者update成功
- 忘了给参数清0。Nordic提供的API输入参数很多都是结构体变量,这些变量使用之前,记得一定要通过memset先清0。如果忘了清0,就会出现一些匪夷所思的现象。
fds_record_desc_t desc; //= {0}; //错误,忘了清0 fds_find_token_t tok; //= {0}; //错误,忘了清0
- 忘了使用全局变量或者静态局部变量。因为write和update操作都是异步的,所以record.data.p_data必须指向全局变量或者静态局部变量,以保证Flash操作过程中p_data指向的内容不会更改。
- 变量起始地址必须字对齐。Flash操作是以word为单位的,所以要求write和update操作的p_data指向的变量的起始地址必须word对齐,大家可以使用伪汇编指令“__ALIGN(sizeof(uint32_t))”来保证该变量起始地址是word对齐的。
- Update或者delete之前必须先find。fds_record_update或者fds_record_delete会用到参数descriptor,这个descriptor必须是通过fds_record_find返回的。
- 忘了使用fds_gc导致Flash fatal error或者其他奇奇怪怪的问题。当write或者update报FDS_ERR_NO_SPACE_IN_FLASH错误时,记得一定要调用fds_gc。或者当delete record或者update record达到一定次数后,主动调用fds_gc。或者通过查看fds_stat得到dirty record数目达到某个值后,主动调用fds_gc。
- SDK已知问题。每个版本SDK都有或多或少的问题,这些问题都可以在Nordic devzone上查到。比如SDK12.2.0 fds_gc在某些情况下,就会有问题,请参考:https://devzone.nordicsemi.com/question/93241/what-are-sdk-12x0-known-issues/,所以,一般建议大家使用最新版SDK,最新版SDK会把之前发现的问题都修复掉,它的稳定性和可靠性都是最高的。
- 最后再次强调一遍:FDS不支持掉电保护,所以在FDS操作过程中,尤其是垃圾回收过程中,发生了掉电,那么Flash内容将变得不可靠。所以强烈建议大家:在每一次write或者update之后,都把相应记录读出来,跟原始内容进行比对,以确保记录真的写成功或者更新成功了