__阿里巴巴长期招聘Java研发工程师p6,p7,p8等上不封顶级别,有意向的可以发简历给我,注明想去的部门和工作地点:[email protected]__
__欢迎关注微信公众号:技术原始积累 获取更多技术干货__
# 一、前言
评价一个框架是否是优秀的,其中必有一点是该框架是否留足了可扩展的接口。我们在实际做项目中很多情况下就是基于某某框架,然后在这个框架留出的扩展接口上进行业务开发,所以很有必要对这些框架留出了哪些扩展点,这些扩展点是干啥用的有个心知肚明的了解。本文针对作者项目中用到的tomcat,spring扩展点进行记录,作为记录笔记,以便查找。
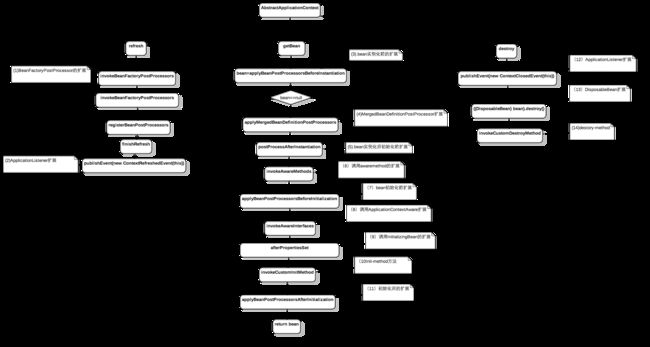
# 二、常用扩展其中Spring框架扩展调用链路图:
(1).refresh(),是spring解析xml配置文件,收集bean定义阶段。
(2).getBean(),是容器启动后从IOC获取bean过程.
(3).destory()是IOC容器销毁阶段
## 2.1 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
public interface BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor extends BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
/* 在bean注册到ioc后创建实例前修改bean定义或者新增bean注册,这个是在context的refresh方法调用 */ void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) throws BeansException;
}
(1)在bean注册到ioc后创建实例前修改bean定义或者新增bean注册,这个是在context的refresh方法调用,
## 2.2 ApplicationListener
public interface ApplicationListenerextends EventListener {
/** * 处理 application event. * @param event the event to respond to */
void onApplicationEvent(E event)
;}
例如下面捕获的事件是当IOC容器refresh后触发的事件,当你需要在IOC容器启动后做一些事情的时候,你可以实现这个接口做些事情。
public class ServiceProviderRegister implements ApplicationListener{
@Override public void onApplicationEvent(ContextRefreshedEvent event) {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = event.getApplicationContext();
}}
例如webx中WebxComponentsLoader 在rootIOC refresh后会通过onApplicationEvent初始化一些东西 initWebxConfiguration();
initInternalRequestHandler();
initRequestContexts();
## 2.3 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
实现该接口并注入IOC容器中,可以对IOC中的bean在实例化前和后dosomething。对应(3),(5)。
public interface InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor extends BeanPostProcessor {
//(1)在bean实例化前doSomething Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(ClassbeanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException;
//(2)在bean实例化后,初始化前doSomething boolean postProcessAfterInstantiation(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException;}
(1)、bean实例化前做一些事情,比如获取类和方法上面的注解,由于实例化后的bean一般都被增强过,增强后的bean不能直接获取注解信息,要使用AopUtils工具获取target则获取注解,
(2)、bean实例化后做一些事情(目前没有应用案例)。
## 2.4 MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor
实现该接口并注入IOC容器中,可以对IOC中的bean定义dosomething。
Javapublic interface MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor extends BeanPostProcessor {
//对bean定义进行修改
void postProcessMergedBeanDefinition(RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition, ClassbeanType, String beanName);
}
例如AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor类解析autowired注解就是通过该方法:
Java public void postProcessMergedBeanDefinition(RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition, ClassbeanType, String beanName) {
if (beanType != null) {
InjectionMetadata metadata = findAutowiringMetadata(beanName, beanType, null); metadata.checkConfigMembers(beanDefinition); } }
## 2.5 AwareMethods
对应流程图步骤(6)
javapublic interface BeanNameAware extends Aware {
/** * 获取bean在IOC容器中名字 */
void setBeanName(String name);}
(1)、如果你需要获取自己的bean在IOC容器中的名字则可以实现该接口。
javapublic interface BeanClassLoaderAware extends Aware {
/** * 获取加载当前bean的类加载器 */
void setBeanClassLoader(ClassLoader classLoader);}
(2)、如果你想要知道自己的bean是那个类加载加载的则可以实现该接口
javapublic interface BeanFactoryAware extends Aware {
/** * 获取当前bean所在的IOC容器 */
void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException;}
(3)、如果你想要知道自己的bean在那个容器,则可实现该接口
## 2.6 BeanPostProcessor
实现该接口并注入IOC容器中,可以对IOC中的bean在初始化前和后dosomething,对应流程图(7,(11)public interface BeanPostProcessor {
//afterPropertiesSet前执行
Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException;
//init-method后执行
Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException;}
## 2.7、InitializingBean,DisposableBean,Init-method,Destroy-method
对应流程图步骤(9),(13),(10),(14)
javapublic interface InitializingBean {
//(1)set属性设置后,init方法前调用
void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception;}
public interface DisposableBean {
//(2)destruction bean的时候调用,在Destroy-method之前调用
void destroy() throws Exception;}
(1)、如果你需要在自己的bean属性设置后做件事情那么该bean就可以实现InitializingBean,这个在开源和中间件代码里随处可见
(2)、如果你需要在自己的bean被销毁前做一件事情,比如回收资源,那么可以实现DisposableBean方法,例如SimpleThreadPoolTaskExecutor实现了该方法在线程池销毁时候决定是不是等当前线程池中线程执行完后在销毁。
## 2.8、 ApplicationContextAware
实现该接口并把实现bean注入容器,则可以获取Spring IOC的容器上下文。对应流程图(8)
public interface ApplicationContextAware extends Aware {
//用来获取Spring IOC容器上下文
void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException;}
那么拿到容器上下文可以做啥那?可以看下ApplicationContext这个接口里面的接口函数就知道了,下面列下常用的功能
(1)、getBean(String name)获取当前容器中所有的bean,当我们在线程中要使用容器中的bean时候可以使用这种方式。
(2)、如果是WebApplicationContext则还可以调用getServletContext获取应用唯一的servletcontext.
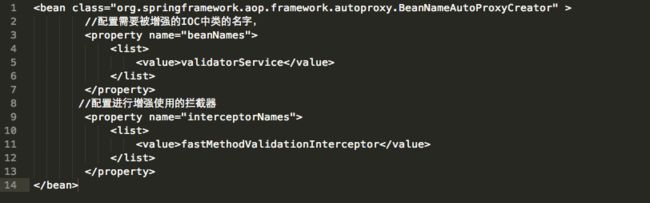
## 2.9 BeanNameAutoProxyCreator
该类是个实现类,一般在这个类的postProcessAfterInitialization方法内对类进行代理增强,该类特殊在于可以指定对IOC容器内的某些名字的类进行增强,并且可以指定增强需要的拦截器,集团内比较牛逼的校验框架fastvalidator 就是使用这个类对需要校验的类进行增强,具体配置如下:
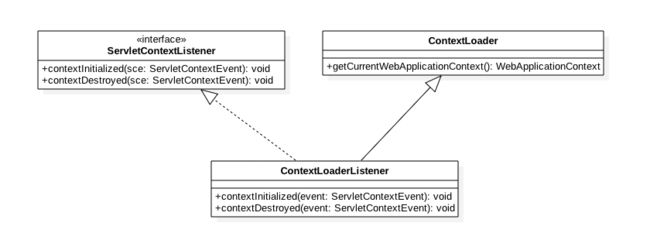
## 2.10 ContextLoaderListener
该listener一般用来启动Spring容器或者框架的根容器,例如webx框架的WebxContextLoaderListener就是继承该类,实现了webx框架到tomcat容器的衔接点,而springmvc则通过在listener启动一个IOC来管理bean。
该类主要方法为:
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext()); }
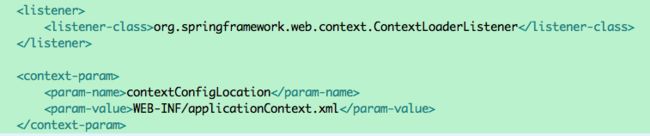
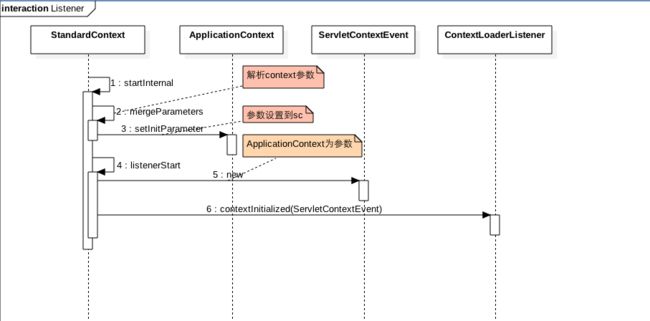
首先ContextLoaderListener一般是在web.xml里面配置:
其中contextConfigLocation配置的就是要ContextLoaderListener把哪些bean注入ioc容器。那么配置的全局的contextConfigLocation怎么在ContextLoaderListener中获取的?这就需要看下tomcat的代码时序图:
从时序图知道listener中contextInitialized函数的参数event就是ServletContextEvent,而event.getServletContext()就是全应用唯一的ApplicationContext,而ApplicationContext中则保存了web.xml里面所有的context-param参数。那么使用listener创建spring容器注入bean后,如何从里面获取bean那:ContextLoader.getCurrentWebApplicationContext().getBean(name);ContextLoaderListener继承自ContextLoader,那为何ContextLoader就能拿到容器上下文那:
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) { initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
}
public WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
... // 这里创建容器上下文
if (this.context == null) {
this.context = createWebApplicationContext(servletContext); }
// 刷新容器,加载bean ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) this.context;
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext);
// 设置容器上下文
if (ccl == ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader()) {
currentContext = this.context; }
else if (ccl != null) {
currentContextPerThread.put(ccl, this.context); } }
protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac, ServletContext sc) {
//设置应用全局唯一的applicationcontext到容器上下文中
wac.setServletContext(sc);
//来获取web.xml里面的context-param
String configLocationParam = sc.getInitParameter(CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM);
if (configLocationParam != null) { wac.setConfigLocation(configLocationParam); } ConfigurableEnvironment env = wac.getEnvironment();
if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) {
((ConfigurableWebEnvironment) env).initPropertySources(sc, null); }
customizeContext(sc, wac);
//刷新容器,注入bean到ioc
wac.refresh();}
public static WebApplicationContext getCurrentWebApplicationContext() {
ClassLoader ccl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
if (ccl != null) {
WebApplicationContext ccpt = currentContextPerThread.get(ccl);
if (ccpt != null) { return ccpt; } }
return currentContext; }
延伸一下,其实和listener一样,servlet的init函数里面的ServletConfig.ServletContext()获取的也是应用全局唯一的applicationcontext,filter的init函数里面的FilterConfig.ServletContext()获取的也是。
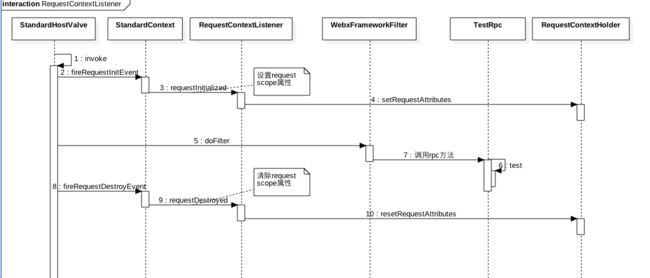
## 2.11 RequestContextListenerspring
中配置bean的作用域时候我们一般配置的都是Singleton,但是有些业务场景则需要三个web作用域,分别为request、session和global session,如果你想让你Spring容器里的某个bean拥有web的某种作用域,则除了需要bean级上配置相应的scope属性,还必须在web.xml里面配置如下:org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestContextListener
那么这个listener调用逻辑如何那,如下:
bean需要声明为RequestScope的情况其实蛮多的,比如pvgInfo,在ssovalve里面根据不同登陆人设置登陆人信息,然后在业务代码里面获取,使用参考文章https://www.atatech.org/articles/76701 。的第四章# 三、
总结本文只是作者目前遇到过的扩展点,当然这些开源框架扩展点肯定不止这些,有知道其他扩展点的童鞋可以在本帖留言,留下宝贵的意义,共同学习。
__阿里巴巴长期招聘Java研发工程师p6,p7,p8等上不封顶级别,有意向的可以发简历给我,注明想去的部门和工作地点:[email protected]__
__欢迎关注微信公众号:技术原始积累 获取更多技术干货__