女神镇楼
我们都知道图像美白大致有三种情况
- 自己图片处理算法(操作具体的像素点)
- 第三方开源库(GPUImage。 openCV等等)
- 第三方框架(闭源,收费)(face++,百度图像处理框架等等)
今天我们就讲解一下图片处理算法美白,请看简单的效果图
美白前
美白后
人物虽然丑了点,但是我们不要注意这个细节,哈哈哈哈。
书接正文
我们创建一个image处理类ImageUtils,里面有一个返回处理过后image的方法+ (UIImage*)imageProcess:(UIImage*)image
第一步
首先我们需要先确定图片的大小,获取图片大小有两种方式
-
image.size.width,image.size.height -
CGImageGetWidth,CGImageGetHeight
CGImageRef是基于像素的矩阵,每个点都对应了图片中点的像素信息。CGImageRef是定义在QuartzCore框架中的一个结构体指针,用C语言编写。更加详细的解析,请看iOS中使用像素位图(CGImageRef)对图片进行处理
获取代码
CGImageRef imageFef = image.CGImage;
NSUInteger width = CGImageGetWidth(imageFef);
NSUInteger height = CGImageGetHeight(imageFef);
第二步:开辟颜色内存空间
开辟内存空间的目的就是:让我们可以获取内存空间的指针,然后根据指针找到像素点,操作像素点
创建颜色空间有两种
- 灰色颜色空间
- 彩色颜色空间
灰色颜色空间没办法进行美白,只有彩色内存空间才能根据RGB值的改变,来增加美白功能
代码
CGColorSpaceRef colorSpaceRef = CGColorSpaceCreateDeviceRGB();
第三步:创建图片上下文
这是创建图片上下文的方法,下面我们来解释一下各个参数的意义
参数1
我们看第一个参数可知,这是一个指针,我们需要放置一个指针。
图片其实就是一个像素数组,他是一块内存空间,指针指向像素数组的首地址(c/c++语言语法)
图片使用像素数组组成===》由每一个像素组成===》ARGB组成==》每一个分量组成(每一个分量大小:8位)
也就意味着一个像素点最大的大小(4*8=32)
例如:一个像素点组成(ARGB。RGB。R,G,B, BG)
我们不知道图片每一个像素点的大小是多大,所以采用最大的
代码
UInt32 *inputPixels = (UInt32*)calloc(width * height, sizeof(UInt32));
参数2:宽
参数3:高
参数4:每一个像素点,每一个分量的大小(固定式:8位)
参数5:每一行占用的内存大小
1、计算每一个像素点的大小(大小ARGB 4*8 ==》没8位=1字节 ==》4字节)
2、每一行的大小 = 像素点 * 宽 = 4 * width
参数6:颜色空间
参数7:是否有透明度
bitmapInfo : 指定bitmap是否包含alpha通道,像素中alpha通道的相对位置,像素组件是整形还是浮点型等信息的字符串
CGImageAlphaInfo结构体
typedef CF_ENUM(uint32_t, CGImageAlphaInfo) {
kCGImageAlphaNone, /* For example, RGB. /
kCGImageAlphaPremultipliedLast, / For example, premultiplied RGBA /
kCGImageAlphaPremultipliedFirst, / For example, premultiplied ARGB /
kCGImageAlphaLast, / For example, non-premultiplied RGBA /
kCGImageAlphaFirst, / For example, non-premultiplied ARGB /
kCGImageAlphaNoneSkipLast, / For example, RBGX. /
kCGImageAlphaNoneSkipFirst, / For example, XRGB. /
kCGImageAlphaOnly / No color data, alpha data only */
};
代码
UInt32 *inputPixels = (UInt32*)calloc(width * height, sizeof(UInt32));
CGContextRef contextRef = CGBitmapContextCreate(inputPixels, width, height, 8, 4 * width, colorSpaceRef, kCGBitmapByteOrderDefault|kCGImageAlphaPremultipliedLast);
第四步:根据上下文绘制美白图片
代码
CGContextDrawImage(contextRef, CGRectMake(0, 0, width, height), imageFef);
第五步:开始美白
美白的原理:操作像素点 ==》 操作分量 ==》 修改分量值(增或减少)
我们知道:美白处理其实就是增加RGB的各个值
0-255变化的趋势是什么?越来越白
我们循环便利像素点,把每一个像素点的值都增加,结果就会出现美白效果。
在使用之前我们需要了解两个概念:&,>>
不知道的同学可以参考这篇文章
首先我们定义了一些宏
#define MaskB(x) ((x) & 0xFF)
#define R(x) (MaskB(x))
#define G(x) (MaskB(x >> 8))
#define B(x) (MaskB(x >> 16))
#define A(x) (MaskB(x >> 24))
#define RGBA(r,g,b,a) (MaskB(r) | MaskB(g)<<8 | MaskB(b) << 16 | MaskB(a) << 24)
我们先讨论一些怎么获取RGB中的R,其他的都是一样的。
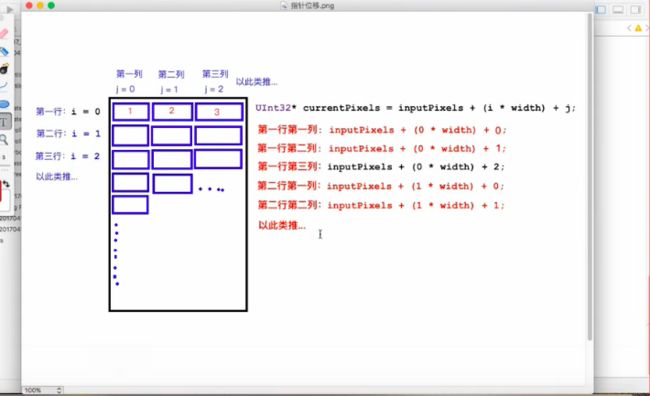
我们知道,像素点是一排一排的向下的,示意图
我们首先获取当前图片的像素点-->指针位移 inputPixels数组的首地址,不会变。
UInt32 *currnetPixels = inputPixels + (i * width) + j;然后获取我们像素点对应的颜色值(*取值 &取地址)
UInt32 color = *currnetPixels;最后获取
R,G,B的值。
color 转化为二进制
进行逻辑规则运算(&:同为1 不同为0)
color = 111111 0011001 00010101 001000 (A R G B),
代码如下
//循环便利图片像素点
for (int i = 0; i < height; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < width; j++) {
//获取当前图片的像素点 -->指针位移 inputPixels数组的首地址,不会变
UInt32 *currnetPixels = inputPixels + (i * width) + j;
//获取我们像素点对应的颜色值(*取值 &取地址)
UInt32 color = *currnetPixels;
// NSLog(@"====%d====",color);
UInt32 thisR,thisG,thisB,thisA;
//定义亮度
int lumi = 50;
//如何获取
//获取红色分量值(R)
/*
原理:
已知:color = 4290822858
0xFF 转化为二进制
color 转化为二进制
进行逻辑规则运算(&:同为1 不同为0)
color = 111111 0011001 00010101 001000 (A R G B)
*/
thisR = R(color);
thisR = thisR + lumi;
thisR = thisR > 255 ? 255 : thisR;
// NSLog(@"红色值:%d",thisR);
//获取绿色分量值
/*
第一步:进行`为`运算,向右移动8位
第二部:获取G的值,进行逻辑运算(&)
color = 111111 0011001 00010101 001000 (A R G B)
第三部:
*/
thisG = G(color);
thisG = thisG + lumi;
thisG = thisG > 255 ? 255 : thisG;
thisB = B(color);
thisB = thisB + lumi;
thisB = thisB > 255 ? 255 : thisB;
thisA = A(color);
//修改像素点的值
*currnetPixels = RGBA(thisR, thisG, thisB, thisA);
}
}
第六步:创建UIImage
代码
CGImageRef newImageRef = CGBitmapContextCreateImage(contextRef);
UIImage *newImage = [UIImage imageWithCGImage:newImageRef];
第七步:释放内存
CGColorSpaceRelease(colorSpaceRef);
CGContextRelease(contextRef);
CGImageRelease(newImageRef);
free(inputPixels);
完整代码
+ (UIImage*)imageProcess:(UIImage*)image{
//第一步:确定图片的大小
CGImageRef imageFef = image.CGImage;
NSUInteger width = CGImageGetWidth(imageFef);
NSUInteger height = CGImageGetHeight(imageFef);
第二部:创建颜色空间(开辟内存空间,目的:操作像素点)
CGColorSpaceRef colorSpaceRef = CGColorSpaceCreateDeviceRGB();
//第三部:创建图片上下文
UInt32 *inputPixels = (UInt32*)calloc(width * height, sizeof(UInt32));
CGContextRef contextRef = CGBitmapContextCreate(inputPixels, width, height, 8, 4 * width, colorSpaceRef, kCGBitmapByteOrderDefault|kCGImageAlphaPremultipliedLast);
//第四步:根据上下文绘制美白图片
CGContextDrawImage(contextRef, CGRectMake(0, 0, width, height), imageFef);
//第五部:正式开始美白
//循环便利图片像素点
for (int i = 0; i < height; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < width; j++) {
//获取当前图片的像素点 -->指针位移 inputPixels数组的首地址,不会变
UInt32 *currnetPixels = inputPixels + (i * width) + j;
//获取我们像素点对应的颜色值(*取值 &取地址)
UInt32 color = *currnetPixels;
// NSLog(@"====%d====",color);
UInt32 thisR,thisG,thisB,thisA;
//定义亮度
int lumi = 50;
//如何获取
//获取红色分量值(R)
thisR = R(color);
thisR = thisR + lumi;
thisR = thisR > 255 ? 255 : thisR;
// NSLog(@"红色值:%d",thisR);
//获取绿色分量值
thisG = G(color);
thisG = thisG + lumi;
thisG = thisG > 255 ? 255 : thisG;
thisB = B(color);
thisB = thisB + lumi;
thisB = thisB > 255 ? 255 : thisB;
thisA = A(color);
//修改像素点的值
*currnetPixels = RGBA(thisR, thisG, thisB, thisA);
}
}
//创建UIImage
CGImageRef newImageRef = CGBitmapContextCreateImage(contextRef);
UIImage *newImage = [UIImage imageWithCGImage:newImageRef];
//第七步:释放内存
CGColorSpaceRelease(colorSpaceRef);
CGContextRelease(contextRef);
CGImageRelease(newImageRef);
free(inputPixels);
return newImage;
}