题目
给定一个二叉树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。
百度百科中最近公共祖先的定义为:“对于有根树 T 的两个结点 p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个结点 x,满足 x 是 p、q 的祖先且 x 的深度尽可能大(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先)。”
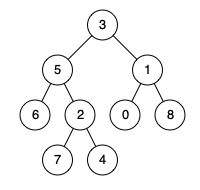
例如,给定如下二叉树: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4]
示例 1:
输入: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 1
输出: 3
解释: 节点 5 和节点 1 的最近公共祖先是节点 3。
示例 2:
输入: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 4
输出: 5
解释: 节点 5 和节点 4 的最近公共祖先是节点 5。因为根据定义最近公共祖先节点可以为节点本身。
说明:
- 所有节点的值都是唯一的。
- p、q 为不同节点且均存在于给定的二叉树中。
思路
相比起之前的那道题, 这道题去掉了二叉搜索树的条件, 变成了普通的二叉树. 难度也由简单变为中等了
在我看来, 用空间换时间是一个不错的思路, 虽然不是最优解, 但是其他解的思路也是在此之上的一个延伸.
怎么个换法?
为了找到公共祖先, 势必要遍历二叉树找到相应节点, 而找到相应节点的路径我们可以用一个数组保存起来, 再遍历这两个路径数组, 找到第一个不同节点的前一个节点即为公共祖先节点.
于是问题被拆为两部分:
- 遍历寻找节点p, q, 保存路径
- 找到公共祖先节点,
这个思路下用C编写对我这个菜鸡而言难度有点大, 需要去实现类似栈的结构, 感兴趣的同学可以自己试试.(也可以用一个很大的数组去保存路径)
这里只给出 Python 实现
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
def lowestCommonAncestor(self, root, p, q):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:type p: TreeNode
:type q: TreeNode
:rtype: TreeNode
"""
pl = []
ql = []
self.getNodePath(root, p, pl)
self.getNodePath(root, q, ql)
length = min(len(pl), len(ql))
for i in range(length):
if pl[i] != ql[i]:
return pl[i-1]
return pl[length-1]
def getNodePath(self, root, node, path):
if not root:
return False
path.append(root)
found = False
if node == root:
found = True
if not found and root.left:
found = self.getNodePath(root.left, node, path)
if not found and root.right:
found = self.getNodePath(root.right, node, path)
if not found:
path.pop()
return found
更简洁的解法
在这道题的评论中有大佬给出一种思路, 不需要额外构建一个数组保存路径, 而是单纯靠程序栈来找到祖先节点, 本质上是与上面的思路是一样的, 不过理解起来会比较有难度.
Python 实现
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
def lowestCommonAncestor(self, root, p, q):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:type p: TreeNode
:type q: TreeNode
:rtype: TreeNode
"""
if not root:
return root
if root == p or root == q:
return root
left = self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q)
right = self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q)
if(left and right):
return root
if left:
return left
if right:
return right
C实现
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
struct TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(struct TreeNode* root, struct TreeNode* p, struct TreeNode* q) {
if(!root)
return root;
if(root == p || root == q)
return root;
struct TreeNode* left = lowestCommonAncestor(root->left, p, q);
struct TreeNode* right = lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p, q);
if(left && right){
return root;
}
else if(left)
return left;
else if(right)
return right;
return NULL;
}