概述
微服务所使用的协议自然要根据服务的特点和类型来选择
| 微服务类型 | 推荐协议 | 推荐理由 |
|---|---|---|
| Web Service | Restful via HTTP | 简单实用, 应用广泛 |
| VoIP 及 Telephony Service | 信令用SIP, 媒体用RTP | 支持的终端和媒体网关众多 |
| 多媒体流服务 Multimedia Stream Service | RTP/SRTP/RTSP | 基于传输延迟考虑 |
| 实时消息服务 Realtime Message Service | XMPP, PDU via TCP | XMPP 是开源的标准协议, 效率不高,手机应用不推荐 |
| 异步消息服务 Async Message Service | JMS/AMQP | ActiveMQ 用 JMS, RabbitMQ 用后者 |
这里说的协议主要是指应用层协议, 传输层协议一般都是TCP, 除非是媒体传输考虑用低延迟的 UDP
简单来说, 一般的信令控制协议用基于 HTTP 的 REST 协议就够了, 或者是基于 TCP /WebSocket 的用 Protobuf 来封装应用层消息体也不错.
SIP/SDP/MGCP 在电话及语音服务领域应用较广
媒体传输一般用 RTP 及 SRTP 或 RTSP 来承载音频或视频, 在多方会议共享及远程控制应用中也常用如下协议
- BFCP -- Binary Floor Control Protocol 二进制层控制协议, 用来管理共享的资源
- RDP -- Remote Desktop Protocol, 远程桌面协议, 微软提出并使用在它的远程桌面中
- RFB -- Remote Frame Buffer, 远程帧缓冲协议, VNC(Virtual Network Computing )中使用的
REST
先从应用最广的 REST 说起, REST (Representational State Transfer) 可表现的状态迁移, 是2000年由 Roy Fielding 在他的关于REST的博士论文中提出的.
REST准确来说不算是一种协议, 而是一种设计分布式系统的架构风格, 它是指资源在网络中以某种表现形式进行状态转移.
也就是说它是面向资源的, 每种资源都有相对应的URI, 每个URI 都指向一个资源, 而资源是可展现的(Representational ) 和有状态的(state), 而HTTP 请求则是无状态的, 即它不需要依赖其它的请求, 每个请求都是相对独立的, 超媒体 Hypermedia 可以通过 链接Link 和 URI 把资源连接起来, Web成功的秘诀也就是用链接把世界连接起来.
这里主要指用 HTTP 和 Json 承载的面向资源的 Restful 风格的协议.
由于HTTP协议比较简单, 系统对外的接口被分为多个资源 API, 都可以独立地进行测试, 并且符合无状态通信的原则, 天然具有比较好的松耦合性和可伸缩性.
在介绍完它的特性之后, 我们就会明白它为什么会在分布式系统中大受欢迎
REST 的特点
- REpresentational State Transfer 可表现的状态迁移
- Nouns, not verbs, in endpoints 在各端点中资源是名词而非动词
- All state the client needs is queryable 客户端所需的所有状态是可查询到的
- Server has a complete picture of system state 服务端具有完整的系统状态
- Particularly useful for intermittently-connected clients 对间断性连接的客户端特别有用
REST 的好处
简单
HTTP + Json 地球人都知道,HTTP method 表示对于资源的 CRUD 简单明了可伸缩
短连接,无状态,易于横向扩展松耦合
基于 URL 和 API 的协作,保持接口简单,一致和稳定,避免产生复杂的网状结构和闭环,耦合自然没那么紧
REST 的风格
客户-服务器(Client-Server)
通信只能由客户端单方面发起,表现为请求-响应的形式。无状态(Stateless)
通信的会话状态(Session State)应该全部由客户端负责维护。缓存(Cache)
响应内容可以在通信链的某处被缓存,以改善网络效率。统一接口(Uniform Interface)
通信链的组件之间通过统一的接口相互通信,以提高交互的可见性。分层系统(Layered System)
通过限制组件的行为(即,每个组件只能“看到”与其交互的紧邻层),将架构分解为若干等级的层。按需代码(Code-On-Demand,可选)
支持通过下载并执行一些代码(例如Java Applet、Flash或JavaScript),对客户端的功能进行扩展。
REST 的特性
- 面向资源 Resource Oriented
要考虑合适的粒度, 可缓存性, 修改频率和可变性 - 可寻址 Addressability
- 连通性 Connectedness
- 无状态 Statelessness
- 统一接口 Uniform Interface
POST, GET, PUT, DELETE , PATCH, HEAD, OPTIONS, TRACE, Connect - 超文本驱动 Hypertext Driven
REST 的原则
- 它基于无状态, 客户端-服务器, 可缓存的通讯协议
- 资源以易于理解的目录结构的URI 来公布
- 以JSON或XML形式传输来表示数据对象和属性。
- 消息明确地使用了 HTTP 方法(例如,GET,POST,PUT和DELETE)。
- 在HTTP请求与请求之间的无状态交互不在服务器上存储客户端上下文。
状态依赖性限制了可扩展性, 所以在客户端存储会话状态使得横向扩展更加容易
用 HTTP 方法来表示 CRUD
格式为 [HTTP Method] https://host/{service}/{apiclass}/v{version}
| HTTP 方法 | 含义 | 幂等吗? |
|---|---|---|
| POST | 创建资源 Create | N |
| GET | 获取或查询资源 Retrieve | Y |
| PUT | 全部替换资源 Update | Y |
| DELETE | 删除资源 Delete | Y |
| PATCH | 部分修改资源 | N |
| HEAD | 类似于 GET, 但是只传输状态行和 HTTP 头 | Y |
| OPTIONS | 描述目标资源的通信选项 | Y |
| TRACE | 执行沿目标资源路径的消息环回测试。 | Y |
| CONNECT | 建立到由给定URI标识的服务器的隧道 | Y |
所谓幂等性 Idempotence, 它的意思是你调用一次和调用多次的效果是一样的
简单列举一下一些在 REST 中常用的 Http header
常见的 Http 头域
| Header name | Header value example | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| Accept | application/json | Respond 406 not acceptable if not support the format |
| Content-Type | application/json | 媒体内容类型, |
| If-Modified-Since | Respond 304 not modified if the data is not changed | |
| If-None-Match | Respond 304 not modified if the data is not changed | |
| If-Match | 412 precondition failed if the ETag is not matched | |
| ETag | The version of the resource for integrity | |
| Location | 201 response contains it contains the URI of the new created resource |
还有一些扩展头:
X-Forwarded-For
HTTP 请求到达 HTTP Server 的时候往往已经过了反向代理服务器,所以这时候看到的 TCP 源地址已经不是真正的客户端应用的地址了,这个扩展头就是代理服务器所添加的真正的 source IP 地址, 它由 https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7239 定义
比如在 Citrix 的负载均衡器 netscaler 可以这样配置, 参见insert client ip to http header
set service Service-HTTP-1 -CIP enabled X-Forwarded-For
Origin 和 Access-Control-Allow-Origin
现代浏览器允许突破同源策略(Same Origin Policy), 使用称为跨域资源共享 CORS(Cross-Origin Resource Sharing), 微软的 IE8/9 并不支持,需要用 XDomainRequest 替换 XHTTPRequest
例如请求头如下,表示请求源自哪里:
Origin: https://www.example.com
响应头有
Access-Control-Allow-Headers: AppId, MetricsTicket, ConfID, SiteID, TimeStamp, APPName, Ver
Access-Control-Allow-Methods: OPTIONS, POST, PUT
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: https://www.example.com
这样一来, XHTTPRequest 对 www.example.com 的访问就是合法的。
X-RateLimit-Limit
现在许多 public API 都限定了客户端的请求频率, 比如 twitter, github 等,在响应头中有如下扩展头:
- X-RateLimit-Limit: 单位时间的访问上限
- X-RateLimit-Remaining: 剩余的访问次数
- X-RateLimit-Reset 访问次数重置的时间
常见的 Http 状态码
2xx
- 200 OK with Etag head
- 201 Created with Location head
- 204 No content
- 206 Partial content
3xx
- 301 Move Permanently
- 302 Found
- 304 Not Modified
4xx
- 401 Unauthorized with WWW-Authorizate head
- 403 Forbidden
- 404 Not Found
- 405 Not Allowed with Allow head
- 406 Not Acceptable
- 409 Conflict
- 410 Gone
- 412 Precondition Failed
- 413 Request Entity Too Large
- 415 Unsupported Media Type
- 451 Unavailable For Legal Reasons
5xx
- 500 Internal Server Error
- 501 Not Implemented
- 502 Bad Gateway
- 503 Service Unavailable with Retry-After head
- 504 Gateway Timeout
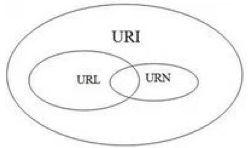
URI 设计
REST 是面向资源的, 如何定位和寻找资源呢, 就象找人一样, 资源也需要象人那样的身份证号码 URI
- URI - Uniform Resource Identifier 是指统一资源标识符, 包括 URL 和 URN
- URL - Uniform Resource Locator 是指统一资源定位符, 常见如下的web url , ftp url 等等
- http://www.sina.com.cn
- ftp://ftp.linux.org.uk/pub/linux/Networking/netkit
- URN - A Uniform Resource Name 是指统一资源名称, 例如
- tel:+1-816-555-1212
在设计资源URI 的时候,
- 一是要注意它们是名词,
- 二是要注意区分单复数
- 三是要注意 URI 有长度限制, 建议小于1k
- 四是要注意在 URI 中不要放未经加密的敏感信息, 即使使用TLS/HTTPS
我们可以用
/ 来表示层次关系, 例如
[http://api.t.sina.com.cn/groups/groupId/users/$userId-
;, 来表示并列关系, 例如
- https://www.citys.com/axis;x=0,y=9
- sip:[email protected];foo=bar;x=y
-
用 - 来提高可读性, 最好全用小写, 例如
- https://www.apple-fan.com/
-
用参数或者HTTP Range Header 来限定范围, 例如
- https://www.citys.com/sortbyAsc=name&fileds=email,title&limit=10&start=20
常用方法
缓存控制
我们可以利用一些 HTTP Header 来控制资源的缓存以及防止并发问题
- ETag 实体标签: 一般为资源实体的哈希值
- Expires 过期的时间:
Expires: Thu, 01 Feb 2015 17:00:00 GMT - Cache-Control 可以有如下属性
- public 公有缓存
- private 私有缓存
- no-cache 不可缓存
- max-age 缓存的最大时间, 单位为秒, 一般来说 max-age是相对时间, 比 Expires 的绝对时间要好, 不会有客户端和服务器时间误差的问题, 优先使用它
- Age 缓存了多少秒
- Last-Modified 资源的最后修改时间
- If-None-Match 如果不匹配的话
- If-Modified-Since 从何时起资源有更新
- If-Match 如果匹配的话
- if-Unmodified-Since 从何时起资源无更新
当服务器发现Http请求的 Header 中有 If-None-Match, 就取出它的值, 与缓存中的资源的Etag 比较, 如果一致的话, 返回 304 Not Modified, 节省从数据库查询和网络传输成本
当服务器发现Http请求的 Header 中 If-Modified-Since, 就取出它的值, 与缓存中的资源的Last-Modified 比较, 如果 If-Modified-Since中指示的最后修改时间大于或等于资源的Last-Modified时间的话, 也返回 304 Not Modified, 即它是从资源最后一次修改之后获取的, 最近无更改, 无需重新查询
当然, 如果不一致的话, 则得重新查询数据库并刷新缓存, 返回最新的资源信息, 状态为 200 OK
并发控制
如果多个请求对资源进行修改, 会出现丢失修改或者无效删除的情况
试想, 张三和李四都是公司的会计, 张三管考勤, 发现王二上个月迟到了三次, 要扣王二三百元钱, 李四管绩效, 要给王二增加一千元奖金, 假设王二工资为八千元.
张三修改王二工资为 8000 - 300 = 7700
update payroll set salary=7700 where username="wang2" and salary=8000
李四修改王二工资为 8000 + 1000 = 9000
update payroll set salary=9000 where username="wang2" and salary=8000
强一致性的关系数据库使用行级锁, 张三和李四只有一个会成功, 另一个会修改失败, 返回给其中一个用户412错误, 让用户重新修改. 从而使王二的最终薪水为8000-300+1000=8700
一些不支持强事务的NOSQL存储, 特别是一些KV系统只能根据key - username来修改数据, 就极有可能出现张三和李四都返回成功, 王二工资变成了7700或9000, 而不是正确的8700, 这时候我们就可以用下面的方法来减少这种情况的发生.
- 更新数据
当服务器发现Http Header 中有 If-Match, 就取出它的值, 与当前资源的Etag 比较, 如果一致的话, 修改数据返回200 OK, 否则返回 412 Precondition Failed
当服务器发现Http Header 中有if-Unmodified-Since, 就取出它的值, 与当前资源的 Last-Modified 进行比较, 如果发现if-Unmodified-Since值大于或等于Last-Modified资源的的话, 修改数据返回200 OK, 否则返回 412 Precondition Failed
- 删除数据
当服务器发现Http Header 中有 if-Match, 就取出它的值, 与当前资源的Etag 比较, 如果一致的话,删除数据返回 204 No Content, 否则返回 412 Precondition Failed
当服务器发现Http Header 中有 if-Unmodified-Since, 就取出它的值, 与当前资源的 Last-Modified 进行比较, 如果发现if-Unmodified-Since值大于或等于Last-Modified资源的的话, 修改数据返回 204 No Content, 否则返回 412 Precondition Failed
批量处理
例如我们想一次提交多个请求, 可以用这种方法
Request
POST /api/v1/batch
{
"requests": [
{
"method": "POST",
"path": "/phonenumbers",
“headers”: [ {“Content-Type”: “application/json”}]
"body": {
"number": "86-01012345678",
"type": "mobile"
}
},
{
"method": "POST",
"path": "/telephonydomains/$telephonyDomainID/dialnumbers",
"body": {
"number": "86-01022345678",
"type": "office"
}
}
]
}
Response
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
{
“response” [
{
“status”: 200,
“message”: “OK”
“headers”: [ {“Content-Type”: “application/json”}]
“body”: {}
},
{
“status”: 412,
“message”: “Preconditionl Failed”
“body”: {}
}
]
}
查询条件超长或者查询参数有敏感信息
用 POST 来代替 GET , 意谓创建一个查询
Request:
POST /accounts/queries
{
“userIds”: [111, 222, 333]
}
Response:
HTTP/1.1200 OK
[
…accounts …
]
异步请求
与同步请求不同的是, 不是立即返回结果, 而是先给一个 taskId, 可供稍后查询结果, 或者在请求时给一个回调URL, 稍后把结果通知回去
Request
POST https://abc.cde.com/api/v1.0/migrations HTTP 1.1
{
pool: "china",
notifyUri: 'https://abc.cde.com/api/v1/migrations/123'
}
Response
{
"status": 'pending',
"taskID": 'f47ac10b-58cc-4372-a567-0e02b2c3d479'
}
实例: 帐号管理的微服务
光说不练假把式, 先拿python 来写一个微服务原型, 我们平常会使用诸多网站, 帐号密码经常忘记, 所以让我们花一点时间写一个帐号管理的微服务, 基本功能是记录我们常用的帐号和密码, 以免遗忘, 一切从简, 不用id, 而是用sitename 作为主键
| method | description |
|---|---|
| GET /accounts | 帐户列表 |
| GET /accounts/ |
帐户获取 |
| POST /accounts | 帐户创建 |
| PUT /accounts/ |
帐户修改 |
| DELETE /accounts/ |
帐户删除 |
- 客户端用 httpie 来作测试
- 服务器端用 python flask 框架来实现
- 页面的UI 暂且省略
先安装python 和 virtualenv
brew install python
brew install pyenv-virtualenv
or
sudo pip install virtualenv
再运行 virtual env
virtualenv venv
source venv/bin/activate
再安装所需的类库
pip install flask
pip install flask-httpauth
pip install requests
pip install httpie
为简单起见, 用 json 文件代替数据库: account.json
{
"jianshu":{
"userName": "walterfan",
"password": "password",
"siteName": "jianshu",
"siteUrl": "http://www.jianshu.com/users/e0b365801f48"
},
"weibo":{
"userName": "fanyamin",
"password": "password",
"siteName": "weibo",
"siteUrl": "http://weibo.com/fanyamin"
}
}
源码如下, 不算空行, 100行之内搞定: account.py, 可读写json file, 并对其中的记录进行增删改查, 暂不考虑性能和其他异常及并发处理, 差强人意, 仅供演示, 个人日常使用也行
import os
import json
import requests
from flask_httpauth import HTTPBasicAuth
from flask import make_response
from flask import Flask
from flask import request
from werkzeug.exceptions import NotFound, ServiceUnavailable
app = Flask(__name__)
current_path = os.path.dirname(os.path.realpath(__file__))
auth = HTTPBasicAuth()
users = {
"walter": "pass1"
}
json_file = "{}/account.json".format(current_path)
def read_data():
json_fp = open(json_file, "r")
return json.load(json_fp)
def save_data(accounts):
json_fp = open(json_file, "w")
json.dump(accounts, json_fp, sort_keys = True, indent = 4)
@auth.get_password
def get_pw(username):
if username in users:
return users.get(username)
return None
def generate_response(arg, response_code=200):
response = make_response(json.dumps(arg, sort_keys = True, indent=4))
response.headers['Content-type'] = "application/json"
response.status_code = response_code
return response
@app.route("/", methods=['GET'])
@auth.login_required
def index():
return generate_response({
"username": auth.username(),
"description": "account micro service /accounts"
})
@auth.login_required
@app.route("/accounts", methods=['GET'])
def list_account():
accounts = read_data()
return generate_response(accounts)
#Create account
@auth.login_required
@app.route('/accounts', methods=['POST'])
def create_account():
account = request.json
sitename = account["siteName"]
accounts = read_data()
if sitename in accounts:
return generate_response({"error": "conflict"}, 409)
accounts[sitename] = account
save_data(accounts)
return generate_response(account)
#Retrieve account
@auth.login_required
@app.route('/accounts/', methods=['GET'])
def retrieve_account(sitename):
accounts = read_data()
if sitename not in accounts:
return generate_response({"error": "not found"}, 404)
return generate_response(accounts[sitename])
#Update account
@auth.login_required
@app.route('/accounts/', methods=['PUT'])
def update_account(sitename):
accounts = read_data()
if sitename not in accounts:
return generate_response({"error": "not found"}, 404)
account = request.json
print(account)
accounts[sitename] = account
save_data(accounts)
return generate_response(account)
#Delete account
@auth.login_required
@app.route('/accounts/', methods=['DELETE'])
def delete_account(sitename):
accounts = read_data()
if sitename not in accounts:
return generate_response({"error": "not found"}, 404)
del(accounts[sitename])
save_data(accounts)
return generate_response("", 204)
if __name__ == "__main__":
app.run(port=5000, debug=True)
直接运行 python account.py 这个帐户管理的RESTful 微服务就启动了, 用 httpie 测试一下
- list accounts
(venv) $ http --json --auth walter:pass GET http://localhost:5000/accounts
HTTP/1.0 200 OK
Content-Length: 347
Content-type: application/json
Date: Sat, 10 Dec 2016 15:43:53 GMT
Server: Werkzeug/0.11.11 Python/3.5.1
{
"jianshu": {
"password": "password",
"siteName": "jianshu",
"siteUrl": "http://www.jianshu.com/users/e0b365801f48",
"userName": "walterfan"
},
"weibo": {
"password": "password",
"siteName": "weibo",
"siteUrl": "http://weibo.com/fanyamin",
"userName": "fanyamin"
}
}
- create account
http --auth walter:pass --json POST http://localhost:5000/accounts userName=walter password=pass siteName=163 siteUrl=http://163.com
HTTP/1.0 200 OK
Content-Length: 108
Content-type: application/json
Date: Sat, 10 Dec 2016 15:48:59 GMT
Server: Werkzeug/0.11.11 Python/3.5.1
{
"password": "pass",
"siteName": "163",
"siteUrl": "http://163.com",
"userName": "walter"
}
- retrieve account
http --auth walter:pass --json GET http://localhost:5000/accounts/163
HTTP/1.0 200 OK
Content-Length: 108
Content-type: application/json
Date: Sat, 10 Dec 2016 15:49:21 GMT
Server: Werkzeug/0.11.11 Python/3.5.1
{
"password": "pass",
"siteName": "163",
"siteUrl": "http://163.com",
"userName": "walter"
}
- update account
http --auth walter:pass --json PUT http://localhost:5000/accounts/163 userName=walter password=pass123 siteName=163 siteUrl=http://163.com
HTTP/1.0 200 OK
Content-Length: 111
Content-type: application/json
Date: Sat, 10 Dec 2016 15:49:47 GMT
Server: Werkzeug/0.11.11 Python/3.5.1
{
"password": "pass123",
"siteName": "163",
"siteUrl": "http://163.com",
"userName": "walter"
}
- delete account
http --auth walter:pass --json DELETE http://localhost:5000/accounts/163
HTTP/1.0 204 NO CONTENT
Content-Length: 0
Content-type: application/json
Date: Sat, 10 Dec 2016 15:50:18 GMT
Server: Werkzeug/0.11.11 Python/3.5.
参考文档与链接
- Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP/1.1): Semantics and Content
- https://www.tutorialspoint.com/http/http_methods.htm
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Representational_state_transfer