MD,视觉语言,它所设计的世界,来源于真实的物理现实(降低用户的学习成本,使其快速上手),但又高于现实(大胆而理想,让用户沉浸其中体验)。
我一直觉得,不懂UI设计的AndroidRD不是好程序员。
所以就有了这篇blog。
也许你不能改变,但是你需要具备辨别能力,知道什么是好的、符合MD规范的UI设计/交互,什么是不好的。
本文对https://material.io/guidelines/material-design/introduction.html中的内容做一个简单的整理。
算是一篇读书笔记。
引入
先祭出官方Introduction中的一段原文:
We challenged ourselves to create a visual language for our users that synthesizes the classic principles of good design with the innovation and possibility of technology and science. This is material design. This spec is a living document that will be updated as we continue to develop the tenets and specifics of material design.
以上文字的重点有三:
- MD是一种可视化的语言。
- MD创新性地继承了优秀设计规范中的经典设计原则,并且融入了科技的力量。
- MD规范会持续更新,不断完善。
1.制定MD规范的目的是什么
- Create a visual language that synthesizes classic principles of good design with the innovation and possibility of technology and science.
可视化的语言,创新性地继承了优秀设计规范中的经典设计原则,且融入了科技的力量。 - Develop a single underlying system that allows for a unified experience across platforms and device sizes. Mobile precepts are fundamental, but touch, voice, mouse, and keyboard are all first-class input methods.
在不同设备上的体验一致。
2.MD的原则/规范是什么
- Material是一种比喻 Material is the metaphor
A material metaphor is the unifying theory of a rationalized space and a system of motion. The material is grounded in tactile reality, inspired by the study of paper and ink, yet technologically advanced and open to imagination and magic.
MD来源于现实(tactile reality, paper and ink)而高于现实(technologically advanced and open to imagination and magic)。
Surfaces and edges of the material provide visual cues that are grounded in reality. The use of familiar tactile attributes helps users quickly understand affordances. Yet the flexibility of the material creates new affordances that supercede those in the physical world, without breaking the rules of physics.
来源于现实,可使用户能快速上手使用,减少用户的学习成本。
affordances这个单词的意思是:功能可见性。也就是看着它就知道该怎么用它。
The fundamentals of light, surface, and movement are key to conveying how objects move, interact, and exist in space and in relation to each other. Realistic lighting shows seams, divides space, and indicates moving parts.
MD的基础:光影、平面、移动。
- 大胆/超现实,图形,意图 Bold, graphic, intentional
The foundational elements of print-based design – typography, grids, space, scale, color, and use of imagery – guide visual treatments. These elements do far more than please the eye. They create hierarchy, meaning, and focus. Deliberate color choices, edge-to-edge imagery, large-scale typography, and intentional white space create a bold and graphic interface that immerse the user in the experience.
An emphasis on user actions makes core functionality immediately apparent and provides waypoints for the user.
Print-based Design的基础元素( 排版,网格,空间,尺度,颜色,以及意象的使用)指导着MD的视觉处理。这些元素创造着设计的层次,意义和聚焦点。 有意图的颜色选择(我个人确实很喜欢MD的色彩与搭配),边到边的意象,大规模排版和有意的空白空间,创建一个大胆的图形界面,让用户沉浸在体验中。
- 动作要体现一定的意义 Motion provides meaning
Motion respects and reinforces the user as the prime mover. Primary user actions are inflection points that initiate motion, transforming the whole design.
All action takes place in a single environment. Objects are presented to the user without breaking the continuity of experience even as they transform and reorganize.
Motion is meaningful and appropriate, serving to focus attention and maintain continuity. Feedback is subtle yet clear. Transitions are efficient yet coherent.
移动/运动的意义是什么:为了引起注意起而起强调的作用,保持变换的连贯性,交互反馈。
环境 Environment
MD设计所构造的世界是一个三维空间(X轴,Y轴和Z轴),且包括了光,material和投射的阴影。
其中,关于shadows包括了:directional shadows 和 soft shadows
Within the material environment, virtual lights illuminate the scene.** Key lights **create directional shadows, while ambient light creates soft shadows from all angles.
Shadows in the material environment are cast by these two light sources. In Android development, shadows occur when light sources are blocked by sheets of material at various positions along the z-axis. On the web, shadows are depicted by manipulating the y-axis only. The following example shows the card with a height of 6dp.
关于Material的若干条属性与规范(DO & DO NOT)
以下基本每一条在官方文档中都配有视频来进行形象地说明。
1.物理属性 Physical properties
- Material has varying x & y dimensions (measured in dp) and a uniform thickness (1dp).
厚度只能是1dp。 - Material casts shadows. Shadows result naturally from the relative elevation (z-position) between material elements.
阴影体现了不同material元素之间的相对高度差。 - Content is displayed on material, in any shape and color. Content does not add thickness to material.
- Content can behave independently of the material, but is limited within the bounds of the material.
- Material is solid.Input events cannot pass through material.
输入事件不能穿透material。 - Multiple material elements cannot occupy the same point in space simultaneously.
所以当两个material重叠时,要通过z轴来体现高度差。 - Material cannot pass through other material.For example, one sheet of material cannot pass through another sheet of material when changing elevation.
material不能被穿透。
2.material变换 Transforming material
- Material can change shape.
- Material grows and shrinks only along its plane.
- Material never bends or folds.
不能被弯曲或折叠。 - Sheets of material can join together to become a single sheet of material.
多个material可以合并成为一个material。 - When split, material can heal. For example, if you remove a portion of material from a sheet of material, the sheet of material will become a whole sheet again.
That is, material can split and become whole again.
3.material运动 Movement of material
- Material can be spontaneously generated or destroyed anywhere in the environment.
自主产生/销毁。 - Material can move along any axis.
可沿任何轴运动。 - Z-axis motion is typically a result of user interaction with material.
在Z轴上的运动通常用来代表交互。
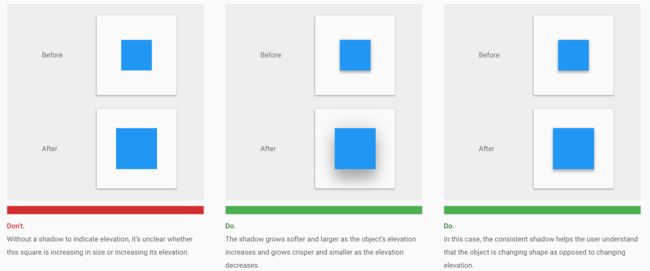
高度与阴影 Elevation & shadows
关于这部分,官网在讲解时给了足够多的图像和视频示例,帮助理解。
1.高度
Objects in material design possess similar qualities to objects in the physical world.
- Elevation
Measured from the front of one surface to the front of another, an element’s elevation indicates the distance between surfaces and the depth of its shadow. - Resting elevation/Default elevation
这个在MD里是有规范的哟,哪些控件的默认高度是多高都是有规定的。比如,Dialog的默认高度是24dp。
All material objects, regardless of size, have a resting elevation, or default elevation that does not change. If an object changes elevation, it should return to its resting elevation as soon as possible.
- Dynamic elevation offsets
Dynamic elevation offsets are the goal elevation that a component moves towards, relative to its resting state.
2.阴影
Shadows provide important visual cues about objects’ depth and directional movement. They are the only visual cue indicating the amount of separation between surfaces. An object’s elevation determines the appearance of its shadow.
In motion, shadows provide useful cues about an object’s direction of movement and whether the distance between surfaces is increasing or decreasing.
阴影的变化能表现出交互反馈的效果
What's new
MD一直在进步,持续在发展,不断在完善
去看看吧https://material.io/guidelines/material-design/whats-new.html#