软件包存储在服务器上,可以利用本地Linux系统上的PMS(package management system,包管理系统)工具通过互联网访问。这些服务器称为仓库(repository,类似于苹果应用商店,或者maven的jar仓库概念)。
Linux中广泛使用的两种主要的PMS基础工具是dpkg和rpm。
基于Red Hat的系统
- yum:
- urpm:
- zypper:
列出已安装包
[root@localhost ~]# yum list installed
输出的信息可能会在屏幕上一闪而过,所以最好是将已安装包的列表重定向到一个文件中。然后用more或less命令查看。
[root@localhost ~]# yum list installed > installed_software
yum擅长找出某个特定软件包的详细信息。
[root@localhost ~]# yum list xterm
Loaded plugins: fastestmirror, refresh-packagekit, security
Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile
* base: mirrors.aliyun.com
* extras: mirrors.aliyun.com
* updates: mirrors.aliyun.com
Available Packages
xterm.x86_64 253-1.el6 base
[root@localhost ~]# yum list installed xterm
Loaded plugins: fastestmirror, refresh-packagekit, security
Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile
* base: mirrors.aliyun.com
* extras: mirrors.aliyun.com
* updates: mirrors.aliyun.com
Error: No matching Packages to list
以上第一个命令是列出远程仓库有没有xterm这个包(Available Packages)。
第二个命令是列出本地是否安装了xterm这个包(Error: No matching Packages to list)。
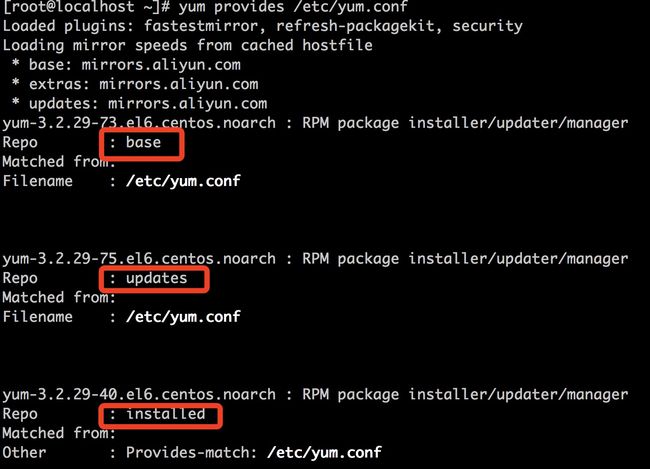
如果需要找出系统上的某个特定文件属于哪个软件包:
[root@localhost ~]# yum provides file_name
yum会分别查找三个仓库:base、updates和installed。
用yum安装软件
命令:
[root@localhost ~]# yum install package_name
也可以手动下载rpm安装文件并用yum安装,这叫作本地安装。
[root@localhost ~]# yum localinstall package_name.rpm
用yum更新软件
列出所有已安装包的可用更新。
[root@localhost ~]# yum list updates
如果这个命令没有输出,就说明没有需要更新的。如果发现某个特定的软件包需要更新,输入如下命令:
[root@localhost ~]# yum update package_name
如果想对更新列表中的所有包进行更新,只需输入如下命令:
[root@localhost ~]# yum update
用yum卸载软件
只删除软件包而保留配置文件和数据文件,用如下命令:
[root@localhost ~]# yum remove package_name
要删除软件和它所有的文件,用如下命令:
[root@localhost ~]# yum erase package_name
处理损坏的包依赖关系
损坏的包依赖关系(broken dependency),如果系统出现了这个问题,先试试下面这个命令:
[root@localhost ~]# yum clean all
然后试着用yum命令的update选项。有时,只要清理了放错位置的文件就可以了。
如果这还解决不了问题,试试下面的命令:
[root@localhost ~]# yum deplist package_name
这个命令显示了所有包的库依赖关系以及什么软件可以提供这些库依赖关系。一旦知道某个包需要的库,就可以安装它们了。
如果这样仍未解决问题,还有最后一招:
[root@localhost ~]# yum update --skip-broken
忽略依赖关系损坏的那个包,继续更新其他软件包。这可能救不了损坏的包,但至少可以更新系统上的其他包。
yum软件仓库
查看本机配置的仓库地址:
[root@localhost ~]# yum repolist
如果仓库中没有需要的软件,可以编辑配置文件。yum的仓库定义文件位于/etc/yum.repos.d。添加正确的URL,并获得必要的加密密钥。
从源码安装
- 将安装包下载到Linux系统上,例如提供了各种系统监测工具的sysstat(sysstat-11.5.5.tar.gz)。然后解压。
- 用cd命令进入解压后的新目录中。仔细阅读README.md或AAAREADME文件,这个文件中包含了软件安装所需要的操作。
- 为系统配置sysstat。它会检查当前Linux系统,确保它拥有合适的编译器能够编译源代码,另外还要具备正确的依赖关系。
[root@localhost sysstat-11.5.5]# ./configure
[......]
config.status: creating man/iostat.1
config.status: creating man/cifsiostat.1
config.status: creating Makefile
Sysstat version: 11.5.5
Installation prefix: /usr/local
rc directory: /etc/rc.d
Init directory: /etc/rc.d/init.d
Systemd unit dir:
Configuration directory: /etc/sysconfig
Man pages directory: ${datarootdir}/man
Compiler: gcc
Compiler flags: -g -O2
[root@localhost sysstat-11.5.5]#
如果哪里有错了,这个步骤会显示一条错误消息说明缺少了什么东西。
- 下一步就是用
make命令来构建各种二进制文件。make命令会编译源码,然后链接器会为这个包创建最终的可执行文件。
[root@localhost sysstat-11.5.5]# make
- make命令结束后,可执行的sysstat软件程序就会出现在目录下。但是从那个目录下运行程序有些不便。你会想将它安装到Linux系统中常用的位置上。就必须以root用户身份登录,然后用
make命令的install选项。
[root@localhost sysstat-11.5.5]# make install