Varnish 是一款高性能且开源的反向代理服务器和 HTTP 加速器,其采用全新的软件体系机构,和现在的硬件体系紧密配合,与传统的 squid 相比,varnish 具有性能更高、速度更快、管理更加方便等诸多优点。
挪威的最大的在线报纸 Verdens Gang(vg.no) 使用 3 台 Varnish 代替了原来的 12 台 Squid,性能比以前更好,这是 Varnish 最成功的应用案例。
代理缓存软件:squid --> varnish
程序的运行具有局部性特征:
时间局部性:一个数据被访问过之后,可能很快会被再次访问到;
空间局部性:一个数据被访问时,其周边的数据也有可能被访问到;
Cache:命中
热区:局部性;
时效性:
缓存空间耗尽:LRU,最近最少使用;
过期:缓存清理
缓存命中率:hit/(hit+miss),hit(命中)、miss(未命中)
(0,1)
页面命中率:基于页面数量进行衡量
字节命中率:基于页面的体积进行衡量
缓存与否:
私有数据:private,private cache;
公共数据:public, public or private cache;
Cache-related Headers Fields
The most important caching header fields are:
Expires:过期时间;
Expires:Thu, 22 Oct 2026 06:34:30 GMT
Cache-Control:max-age=
条件式缓存,HTTP1.1才开始支持;
Etag/If-None-Match:基于校验码(hash,客户端和服务器进行比对;,客户端会发送缓存的标记给缓存服务器进行询问标记是不是不匹配。如果不匹配服务器响应客户端“OK”。
Last-Modified/If-Modified-Since:基于时间戳(客户端获取缓存的时间)比对,客户端会询问服务器时间戳记录的时间之后资源是否改变过。如果没有改变服务器回应客户端304(未改变),如果改变服务器告诉客户端资源已经改变。客户端重新请求。
Vary
Age
缓存有效性判断机制:
过期时间:Expires
HTTP/1.0
Expires:过期
HTTP/1.1
Cache-Control: maxage=
Cache-Control: s-maxage=
条件式请求:
Last-Modified/If-Modified-Since:基于文件的修改时间戳来判别;
Etag/If-None-Match:基于文件的校验码(hash)来判别;
Expires:Thu, 13 Aug 2026 02:05:12 GMT
Cache-Control:max-age=315360000(缓存有效时间)
ETag:"1ec5-502264e2ae4c0"
Last-Modified:Wed, 03 Sep 2014 10:00:27 GMT
Cache-Control的可用值:
public:所有内容都将被缓存(客户端和代理服务器都可缓存)。
private:内容只缓存到私用缓存中(仅客户端可以缓存,代理服务器不可缓存)。
no-cache:必须先与服务器确认返回的响应是否被更改,然后才能使用该缓存。因此,如果存在合适的ETag,no-cache会发起往返通信来验证缓存。
no-store:所有内容都不会被缓存到Internet临时文件中,不允许缓存。
must-revalidation/proxy-revalidaton:如果缓存的内容失效,请求必须发送到服务器已进行重新验证。 max-age=xxx:缓存的内容将在xxx秒后失效,这个选项只在HTTP 1.1可用, 如果和Last-Modified一起使用时, 优先级较高。
s-maxage:类似于max-age,一般用在缓存服务器上(比如CDN),并只对public(公有)缓存有效
缓存层级:
私有缓存:用户代理附带的本地缓存机制;
公共缓存:反向代理服务器的缓存功能;
User-Agent <--> private cache <--> public cache <--> public cache 2 <--> Original Server
请求报文用于通知缓存服务如何使用缓存响应请求:
cache-request-directive =
"no-cache",
| "no-store"
| "max-age" "=" delta-seconds
| "max-stale" [ "=" delta-seconds ]
| "min-fresh" "=" delta-seconds
| "no-transform"
| "only-if-cached"
| cache-extension
服务端响应报文用于通知缓存服务器如何存储上级服务器响应的内容:
cache-response-directive =
"public"
| "private" [ "=" <"> 1#field-name <"> ]
| "no-cache" [ "=" <"> 1#field-name <"> ],可缓存,但响应给客户端之前需要revalidation,即必须发出条件式请求进行缓存有效性验正;
| "no-store" ,不允许存储响应内容于缓存中
| "no-transform"
| "must-revalidate"
| "proxy-revalidate"
| "max-age" "=" delta-seconds
| "s-maxage" "=" delta-seconds
| cache-extension
开源解决方案:
squid:
varnish:
varnish官方站点:http://www.varnish-cache.org/
Community
Enterprise
This is Varnish Cache, a high-performance HTTP accelerator.
程序架构:varnish属于单进程多线程。
Manager进程,管理进程
Cacher进程,包含多种类型的线程:
accept, worker, expiry, ...
shared memory log:
统计数据:计数器;
日志区域:日志记录;
工具:varnishlog, varnishncsa, varnishstat...
配置接口:VCL
Varnish Configuration Language,
vcl complier --> c complier --> shared object
varnish的程序环境:
/etc/varnish/varnish.params:配置varnish服务进程的工作特性,例如监听的地址和端口,缓存机制;
/etc/varnish/default.vcl:配置各Child/Cache线程的缓存策略;
/etc/varnish/secret 密钥文件
主程序:
/usr/sbin/varnishd
CLI interface:
/usr/bin/varnishadm管理
Shared Memory Log交互工具:
/usr/bin/varnishhist
/usr/bin/varnishlog
/usr/bin/varnishncsa
/usr/bin/varnishstat
/usr/bin/varnishtop
测试工具程序:
/usr/bin/varnishtest
VCL配置文件重载程序:
/usr/sbin/varnish_reload_vcl
Systemd Unit File:
/usr/lib/systemd/system/varnish.service
varnish服务
/usr/lib/systemd/system/varnishlog.service
/usr/lib/systemd/system/varnishncsa.service
日志持久的服务;
varnish的缓存存储机制( Storage Types):
-s [name=]type[,options]
malloc[,size],内存存储,[,size]用于定义空间大小;重启后所有缓存项失效;
file[,path[,size[,granularity]]],磁盘文件存储,黑盒;重启后所有缓存项失效;
default:创建一个/tmp/varnish.bin文件,可以自己指定目录和文件以及文件大小。
persistent,path,size,文件存储,黑盒;重启后所有缓存项有效;处于实验阶段;
varnish http服务默认使用6081端口
varnish 管理端口默认监听在127.0.0.1的6082端口
安装varnish时的依赖包jemalloc,进行内存分配和回收的软件,支持并行运行。
varnish程序的选项:
程序选项:/etc/varnish/varnish.params文件
-a address[:port][,address[:port][...],默认为6081端口;
-b 管理服务的端口,默认为6082端口;
-T address[:port],使用telnet管理服务的监听端口,不建议
-C 把脚本转换成C语言格式查看
-s [name=]type[,options],定义缓存存储机制;
-S secret-file 指定密钥文件
-u user 指定运行服务的用户
-g group 组
-f config:VCL配置文件;
-F:运行于前台;
运行时参数:/etc/varnish/varnish.params文件, DEAMON_OPTS DAEMON_OPTS="-p thread_pool_min=5 -p thread_pool_max=500 -p thread_pool_timeout=300"
-p param=value:设定运行参数及其值; 可重复使用多次;
-r param[,param...]: 设定指定的参数为只读状态;
varnish.params文件
RELOAD_VCL=1
将其设置为1以使systemd重新加载尝试切换VCL而不重新启动。
VARNISH_VCL_CONF=/etc/varnish/default.vcl 指定配置文件
VARNISH_LISTEN_ADDRESS=192.168.1.5 varnish服务监听的IP地址,默认为所有地址
VARNISH_LISTEN_PORT=6081 监听的端口默认为6081
VARNISH_ADMIN_LISTEN_ADDRESS=127.0.0.1 接受管理程序监听的IP
VARNISH_ADMIN_LISTEN_PORT=6082 端口
VARNISH_SECRET_FILE=/etc/varnish/secret 密钥文件的路径
VARNISH_STORAGE="malloc,256M" 使用的缓存机制
后端存储规范详情参考man帮助:man 5 varnish
VARNISH_USER=varnish 使用varnish用户运行varnishi服务
VARNISH_GROUP=varnish varnish组
#DAEMON_OPTS="-p thread_pool_min=5 -p thread_pool_max=500 -p thread_pool_timeout=300"
thread_pool_mai=5 指定线程池的最小空闲线程数
thread_pool_max=500
thread_pool_timeout=300
default.vcl 文件
backend default {
.host = "127.0.0.1"; 后端服务器地址
.port = "8080"; 端口
}
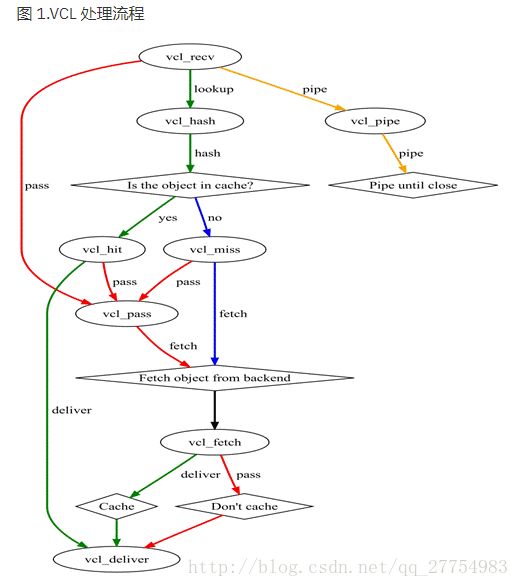
varnish的一些状态引擎
vcl_recv 接受请求,检查请求是否可以缓存。如果不可缓存的服务直接发往后端服务器。
cacheable 收到可以缓存的服务,检查请求是否可以缓存。不可以发往vcl_fetch()引擎。
vcl_hash 对请求进行hash
ln cache 对请求的hash码进行比较,命中发往vcl_hit(),未命中发往vcl_miss()。
vcl_hit 调用资源给客户端,调用的资源发往下一个引擎vcl_deliver()。
vcl_miss 为命中把请求发往vcl_fetch()去取资源,
vcl_fetch 向后端服务器请求资源,把请求到的资源发往vcl_deliver()
vcl_deliver 生成响应报文,发个客户端。
vcl_lookup 将请求交给vcl_lookup函数处理,然后lookup函数经过判断会将请求交给acl_hit or acl_miss函数进行下一步处理
vcl_pass函数 这种模式下,该请求被传递到后端,后端的响应将被传递给客户端,但还没有进入到高速缓存中。
...
重载vcl配置文件:varnish_reload_vcl
varnishadm -S /etc/varnish/secret -T [ADDRESS:]PORT
-n ident 通过这个名字连接varnish
-S file 指定密钥文件
-t 指定超时时间
-T 指定varnish地址和管理端口
内建命令
help [] 帮助
ping []
auth
quit 退出
banner
status varnish服务状态
start 启动工作线程
stop 关闭线程
vcl.load 编译、装载 val脚本
vcl.inline
vcl.use 使用vcl脚本
vcl.discard 删除val脚本
vcl.list 列出所有的val脚本
param.show [-l] [] 查看val脚本的详细信息
param.set 设置运行时参数
panic.show 显示varnish崩溃时的信息
panic.clear
storage.list 列出缓存
vcl.show [-v]
backend.list [] 列出后端服务器列表
backend.set_health 对后端服务器设置
ban [&& ] 设置要清理的缓存项
ban.list 列出后端要清理的缓存项
varnish_reload_vcl 编译vcl脚本并替换之前的
配置文件相关:
vcl.list
vcl.load:装载,加载并编译;
vcl.use:激活;
vcl.discard:删除;
vcl.show [-v] :查看指定的配置文件的详细信息;
运行时参数:
param.show -l:显示列表;
param.show
param.set
缓存存储:storage.list
后端服务器:backend.list
VCL:
”域“专有类型的配置语言;
state engine:状态引擎;
VCL有多个状态引擎,状态之间存在相关性,但状态引擎彼此间互相隔离;每个状态引擎可使用return(x)指明关联至哪个下一级引擎;每个状态引擎对应于vcl文件中的一个配置段,即为subroutine
vcl_hash --> return(hit) --> vcl_hit
vcl_recv的默认配置:
sub vcl_recv {
if (req.method == "PRI") {
/* We do not support SPDY or HTTP/2.0 */
return (synth(405));
}
if (req.method != "GET" &&
req.method != "HEAD" &&
req.method != "PUT" &&
req.method != "POST" &&
req.method != "TRACE" &&
req.method != "OPTIONS" &&
req.method != "DELETE") {
/* Non-RFC2616 or CONNECT which is weird. */
return (pipe);
}
if (req.method != "GET" && req.method != "HEAD") {
/* We only deal with GET and HEAD by default */
return (pass);
}# req.method 请求报文中的方法
if (req.http.Authorization || req.http.Cookie) {
/* Not cacheable by default */
return (pass);
}#req.http 请求报文中的http的指定首部信息
return (hash);
}
}
Client Side:引擎
vcl_recv, vcl_pass, vcl_hit, vcl_miss, vcl_pipe, vcl_purge, vcl_synth,vcl_deliver
vcl_recv:
hash:vcl_hash
pass: vcl_pass
pipe: vcl_pipe
synth: vcl_synth
purge: vcl_hash --> vcl_purge
vcl_hash:
lookup:
hit: vcl_hit
miss: vcl_miss
pass, hit_for_pass: vcl_pass
purge: vcl_purge
Backend Side:
vcl_backend_fetch, vcl_backend_response, vcl_backend_error
两个特殊的引擎:
vcl_init:在处理任何请求之前要执行的vcl代码:主要用于初始化VMODs;
vcl_fini:所有的请求都已经结束,在vcl配置被丢弃时调用;主要用于清理VMODs;
vcl的语法格式:
(1) VCL files start with vcl 4.0; #版本号
(2) //, # and /* foo */ for comments; 注释的格式
(3) Subroutines are declared with the sub keyword; 例如sub vcl_recv { ...};
(4) No loops, state-limited variables(受限于引擎的内建变量); 不支持循环,支持条件判断、支持受限与引擎的内建变量。
(5) Terminating statements with a keyword for next action as argument of the return() function, i.e.: return(action);用于实现状态引擎转换;
(6) Domain-specific;所有的代码都是域专有
The VCL Finite State Machine,VCL有限状态机
(1) Each request is processed separately;每个请求单独处理;
(2) Each request is independent from others at any given time;每个请求在任何给定的时间都是独立的;
(3) States are related, but isolated;
(4) return(action); exits one state and instructs Varnish to proceed to the next state;
(5) Built-in VCL code is always present and appended below your own VCL;Built-in VCL code is always present and appended below your own VCL;
三类主要语法:
sub subroutine {
...
}
if CONDITION {
...
} else {
...
}
return(), hash_data()
VCL Built-in Functions and Keywords
函数:
regsub(str, regex, sub) 正则表达式替换,只替换第一次匹配到的内容
regsuball(str, regex, sub) 替换匹配到的全部内容
ban(boolean expression) 指定正则表达式来删除匹配到的缓存
hash_data(input) 指定哪些内容做key来进行hash计算
synthetic(str)
Keywords:
call subroutine, return(action),new,set,unset
操作符:
==, !=, ~, >, >=, <, <=
逻辑操作符:&&, ||, !
变量赋值:=
举例:obj.hits是内建变量,用于保存某缓存项的从缓存中命中的次数;
if (obj.hits>0) {
set resp.http.X-Cache = "HIT via " + server.ip; +号表示连接
} else {
set resp.http.X-Cache = "MISS from" + server.ip;
}
变量类型:
内建变量:
req.*:request,表示由客户端发来的请求报文相关;
req.http.*
req.http.User-Agent, req.http.Referer, ...
bereq.*: 由varnish发往后端主机的httpd请求相关;
bereq.http.*
beresp.*:由后端主机响应给varnish的响应报文相关;
beresp.http.*
resp.*:由varnish响应给client相关;
obj.* :存储在缓存空间中的缓存对象的属性;只读;
常用变量:
bereq.*, req.*:
bereq.http.HEADERS
bereq.request:请求方法;
bereq.url:请求的url;
bereq.proto:请求的协议版本;
bereq.backend:指明要调用的后端主机;
req.http.Cookie:客户端的请求报文中Cookie首部的值;
req.http.User-Agent ~ "chrome" 获取客户端浏览器类型
beresp.*, resp.*:后端服务器响应给客户端
beresp.http.HEADERS
beresp.status:响应的状态码;
reresp.proto:协议版本;
beresp.backend.name:BE主机的主机名;
beresp.ttl:BE主机响应的内容的余下的可缓存时长;
obj.*
obj.hits:此对象从缓存中命中的次数;
obj.ttl:对象的ttl值,可缓存时长过期后的宽限期
server.*
server.ip varnish服务器IP
server.hostname varnish的主机名
client.*
client.ip 客户端的IP
常用变量的可用位置
recv :req.(R/W)
fetch :req.(R/W)、bereq.(R/W)、beresp.(R/W)
pass :req.(R/W)、bereq.(R/W)
miss :req.(R/W)、bereq.(R/W)
hit :req.(R/W)、obj.hits(R) 、obj.ttl(R/W)、obj.grace(R/W)、obj.(R)
error :req.(R/W)、obj.ttl(R/W)、obj.(R/W) 、resp.(R/W)
deliver :req.(R/W)、obj.hits(R) 、resp.(R/W)
pipe :req.(R/W)、bereq.(R/W)
hash :req.(R/W)
引擎
vcl_recv:
vcl_pipe:和后端服务器建立一个通道把不能理解的内容,直接发给后端服务器
vcl_syntn:合成响应给用户的报文,如果不希望客户端访问服务器可以合成一个响应报文给客户端
vcl_purge:对请求报文进行修剪
vcl_hash:对客户端的请求进行hash计算,
vcl_pass:把请求发给后端服务器
用户自定义:
set
unset
示例1:强制对某类资源的请求不检查缓存:req.url用户请求的路径
vcl_recv {
if (req.url ~ "(?i)^/(login|admin)") {
return(pass);
}
}
示例2:对于特定类型的资源,例如公开的图片等,取消其私有标识,并强行设定其可以由varnish缓存的时长;定义在vcl_backend_response中;
if (beresp.http.cache-control !~ "s-maxage") {
if (bereq.url ~ "(?i)\.(jpg|jpeg|png|gif|css|js)$") {
unset beresp.http.Set-Cookie;
set beresp.ttl = 3600s;
}
}
示例3:定义在vcl_recv中;
if (req.restarts == 0) {
if (req.http.X-Forwarded-For) {
set req.http.X-Forwarded-For = req.http.X-Forwarded-For + "," + client.ip;
} else {
set req.http.X-Forwarded-For = client.ip;
}
}
缓存对象的修剪:purge, ban
(1) 能执行purge操作
sub vcl_purge {
return (synth(200,"Purged"));
}
(2) 何时执行purge操作
sub vcl_recv {
if (req.method == "PURGE") {
return(purge);
}
...
}
添加此类请求的访问控制法则:
acl purgers {
"127.0.0.0"/8;
"10.1.0.0"/16;
}
sub vcl_recv {
if (req.method == "PURGE") {
if (!client.ip ~ purgers) {
return(synth(405,"Purging not allowed for " + client.ip));
}
return(purge);
}
}
Banning:
(1) varnishadm:
格式:ban
示例:ban req.url ~ ^/javascripts
(2) 在配置文件中定义,使用ban()函数;
示例:
if (req.method == "BAN") {
ban("req.http.host == " + req.http.host + " && req.url == " + req.url);
# Throw a synthetic page so the request won't go to the backend.
return(synth(200, "Ban added"));
}
req.http.host 客户端请求的主机地址如:www.baidu.com req.url请求的页面如:/abc.html
如何设定使用多个后端主机:
backend default {
.host = "172.16.100.6";
.port = "80";
}
max_connections 可以设置后端连接的最大并发数目限制。
first_byte_timeout 等待后端返回第一个字节的超时时间。
between_bytes_timeout 接收每一个字节之间的等待时间。
backend appsrv {
.host = "172.16.100.7";
.port = "80";
}
sub vcl_recv {
if (req.url ~ "(?i)\.php$") {
set req.backend_hint = appsrv;
} else {
set req.backend_hint = default;
}
}
Director:调度器
算法
random() 随机抽取后端对象,支持权重
客户端方式 按客户端的session和cookie来分配后端对象
hash 抽取最佳状态的一个后端对象让其出来此次请求的URL
round-robin 轮询,不支持权重
DNS 像dns轮循一样引用一个列表 不支持后端对象的健康测试 开销很大
fallback 类似与故障转移集群 首先将请求交给列表中第一个健康的主机
varnish module;
使用前需要导入:
import directors;
示例:
import directors; # load the directors
backend server1 {
.host =
.port =
}
backend server2 {
.host =
.port =
}
sub vcl_init { 把多个后端服务器定义为一个组
new GROUP_NAME = directors.round_robin();
GROUP_NAME.add_backend(server1);
GROUP_NAME.add_backend(server2);
} directors 表示模块,round_robin()表示rr轮询算法,在主机后面加上权重就是wrr算法。
sub vcl_recv {
# send all traffic to the bar director:
set req.backend_hint = GROUP_NAME.backend();
}
基于cookie的session sticky:
sub vcl_init {
new h = directors.hash();
h.add_backend(one, 1); # backend 'one' with weight '1'
h.add_backend(two, 1); # backend 'two' with weight '1'
}
sub vcl_recv {
// pick a backend based on the cookie header of the client
set req.backend_hint = h.backend(req.http.cookie);
}
对每个后端主机进行健康状态检查
第一种:BE Health Check: 对每个主机进行健康状态检查
backend BE_NAME {
.host =
.port =
.probe = {
.url=
.timeout=
.interval=
.window=
.threshold=
}
}
.probe:定义健康状态检测方法;
.url 检测时要请求的URL,默认为”/";
.request 发出的具体请求;
.request =
"GET /.healthtest.html HTTP/1.1"
"Host: www.magedu.com"
"Connection: close"
.window 基于最近的多少次检查来判断其健康状态;
.threshold 最近.window中定义的这么次检查中至有.threshhold定义的次数是成功的;
.interval 检测频度;
.timeout 超时时长;
.expected_response 期望的响应码,默认为200;
健康状态检测的配置方式:
(1) probe PB_NAME { }
backend NAME = {
.probe = PB_NAME;
...
}
示例:
probe check {
.url = "/.healthcheck.html";
.window = 8;
.threshold = 4;
.interval = 2s;
.timeout = 1s;
}
backend default {
.host = "10.1.0.68";
.port = "80";
.probe = check;
}
backend appsrv {
.host = "10.1.0.69";
.port = "80";
.probe = check;
}
在varnishadm中可以把后端主机手动设置的状态
sick: down
healthy:up
auto: 自动
第二种方法:设置后端的主机属性:
backend BE_NAME {
...
.connect_timeout = 0.5s; 后端服务器的连接超时时间
.first_byte_timeout = 20s; 首字节的响应超时时间
.between_bytes_timeout = 5s; 字节与字节相隔时间的超时时间
.max_connections = 50; 最大并发连接数
}
varnish的运行时参数:
线程模型:
cache-worker
cache-main
ban lurker
acceptor:
epoll/kqueue:
...
线程相关的参数:varnish使用线程池机制管理线程
在线程池内部,其每一个请求由一个线程来处理;其worker线程的最大数决定了varnish的并发响应能力;
thread_pools:Number of worker thread pools.定义线程池的数量,最好小于或等于CPU核心数量;
thread_pool_max:The maximum number of worker threads in each pool. 每线程池的最大线程数;
thread_pool_min:The minimum number of worker threads in each pool. 额外意义为“最大空闲线程数”;
最大并发连接数=thread_pools * thread_pool_max
thread_pool_timeout:Thread idle threshold. Threads in excess of thread_pool_min, which have been idle for at least this long, will be destroyed.
线程空闲时间阈值。 线程超过thread_pool_min设置的时间,将被销毁。
thread_pool_add_delay:Wait at least this long after creating a thread.
创建线程的等待时长,创建线程是需要等待这个时间才可以创建
thread_pool_destroy_delay:Wait this long after destroying a thread.
到达线程空闲时间之后的宽限期时长。
Timer相关的参数:
send_timeout:发送客户端连接超时。 如果响应报文在这么多秒内没有被接收,会话被关闭。
timeout_idle:客户端连接的空闲超时。
timeout_req: 接收客户端请求的超时时长。
cli_timeout:Timeout for the childs replies to CLI requests from the mgt_param. 客户端连接的超时时间
设置方式:
vcl.param
param.set 选项 参数
永久有效的方法:
varnish.params
DEAMON_OPTS="-p PARAM1=VALUE -p PARAM2=VALUE"
添加 -r 选项禁止在服务启动是禁止修改
varnish日志区域:shared memory log,有两种记录信息
1.计数器
2.日志信息
1、varnishstat -Varnish Cache statistics 这个工具可以用来显示计数器
varnishstat 动态显示所有统计数据
-1 显示全部的统计信息
-1 -f FILED_NAME 显示指定引擎的信息,加上^表示排除这个
-l 显示所有字段和字段的意义,可用于-f选项指定的字段名称列表:
-n varnish_name#获取日志的varnishd实例
??? ?-V显示版本号并退出
???? -w delay等待更新之间的延迟秒。 默认值为1秒。可以和-1、-x、-j组合使用
???? -x 将统计信息打印为XML格式。
???? -j 将统计信息打印为JSON格式。
MAIN.cache_hit
MAIN.cache_miss
# varnishstat -1 -f MAIN.cache_hit -f MAIN.cache_miss
# varnishstat -l -f MAIN -f MEMPOOL
2、varnishtop - Varnish log entry ranking 进行排序,不跟参数显示实时统计
-1
-i taglist,可以同时使用多个-i选项,也可以一个选项跟上多个标签;
-I <[taglist:]regex> 和-i相同但是支持正则表达式
-x taglist:排除指定列表
-X <[taglist:]regex>和-x相同但是支持正则表达式
3、varnishlog -显示日志
-a 追加到文件
-b 仅显示后端记录
-B 二进制输出
-c 仅显示客户端记录
-C 无规则的正则表达式
-d 启动时处理旧日志条目
-D 以守护程序方式启动
-g 分组模式(默认值:vxid)
-i taglist 包含标签
-I <[taglist:] regex> 包含正则表达式
-n name varnish实例名称
-N file VSM文件名
-P file PID文件
-q query VSL查询
-r filename 读取二进制文件
-T 事务结束超时
-v 详细记录打印
-w filename 输出文件名
-x taglist 排除标签
-X <[taglist:]regex> 由正则表达式排除
4、varnishncsa 显示日志,显示的格式和varnishlog不同,和http的访问日志格式相似
参数和varnishlog相同
varnishncsa -a -w /var/log/varnish.log -D 把日志记录到文件中,
内建函数:
hash_data():指明哈希计算的数据;减少差异,以提升命中率;
regsub(str,regex,sub):把str中被regex第一次匹配到字符串替换为sub;主要用于URL重写
regsuball(str,regex,sub):把str中被regex每一次匹配到字符串均替换为sub;
return():指定下一个引擎
ban(expression):
ban_url(regex):Bans所有的其URL可以被此处的regex匹配到的缓存对象;
synth(status,"STRING"):purge操作;
总结:
varnish: state engine, vcl
varnish 4.0:
vcl_init
vcl_recv
vcl_hash
vcl_hit
vcl_pass
vcl_miss
vcl_pipe
vcl_waiting
vcl_purge
vcl_deliver
vcl_synth
vcl_fini
vcl_backend_fetch
vcl_backend_response
vcl_backend_error
博客作业:以上所有内容;
实战项目:两个lamp部署wordpress,用Nginx反代,做压测;nginx后部署varnish缓存,调整vcl,多次压测;
课外实践:(1) zabbix监控varnish业务指标;
(2) ansible实现varnish快速部署;
ab, http_load, webbench, seige, jmeter, loadrunner,...
补充资料:varnish book
http://book.varnish-software.com/4.0/
示例:
backend imgsrv1 {
.host = "192.168.10.11";
.port = "80";
}
backend imgsrv2 {
.host = "192.168.10.12";
.port = "80";
}
backend appsrv1 {
.host = "192.168.10.21";
.port = "80";
}
backend appsrv2 {
.host = "192.168.10.22";
.port = "80";
}
sub vcl_init {
new imgsrvs = directors.random();
imgsrvs.add_backend(imgsrv1,10);
imgsrvs.add_backend(imgsrv2,20);
new staticsrvs = directors.round_robin();
appsrvs.add_backend(appsrv1);
appsrvs.add_backend(appsrv2);
new appsrvs = directors.hash();
appsrvs.add_backend(appsrv1,1);
appsrvs.add_backend(appsrv2,1);
}
sub vcl_recv {
if (req.url ~ "(?i)\.(css|js)$" {
set req.backend_hint = staticsrvs.backend();
}
if (req.url ~ "(?i)\.(jpg|jpeg|png|gif)$" {
set req.backend_hint = imgsrvs.backend();
} else {
set req.backend_hint = appsrvs.backend(req.http.cookie);
}
}