wchar_t
wchar_t是Unicode字符的数据类型,2个字节。
typedef unsigned short wchar_t;
另外,
typedef char CHAR;
typedef wchar_t WCHAR;
为了让编译器识别Unicode字符串,必须以在前面加一个“L”,例如:
wchar_t *szTest=L"This is a Unicode string."
_UNICODE
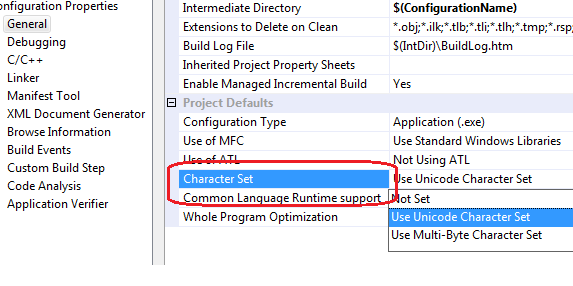
The following project setting in General page describes which Character Set is to be used for compilation: (General -> Character Set)
This way, when your project is being compiled as Unicode, the TCHAR would translate to wchar_t.
If it is being compiled as ANSI/MBCS, it would be translated to char.
You are free to use char and wchar_t, and project settings will not affect any direct use of these keywords.
如果VS中选择Use Unicode Character Set,TCHAR按照wchar_t执行;如果选择是Use Multi-Byte Charactor Set,TCHAR按照char执行。
#ifdef _UNICODE
typedef wchar_t TCHAR;
#else
typedef char TCHAR;
#endif
TCHAR函数
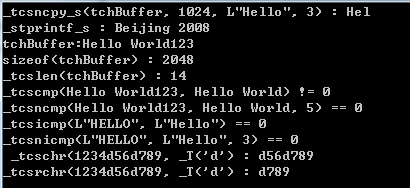
TCHAR tchBuffer[1024] = {0};
_tcsncpy_s(tchBuffer, 1024, L"Hello", 3);
printf("_tcsncpy_s(tchBuffer, 1024, L\"Hello\", 3) : %S\n", tchBuffer);
_stprintf_s(tchBuffer, 1024, L"Beijing %d", 2008);
printf("_stprintf_s : %S\n", tchBuffer);
_tcscpy_s(tchBuffer, 1024, L"Hello");
_tcscat_s(tchBuffer, 1024, L" World");
_tcsncat_s(tchBuffer, 1024, L"1234", 3);
printf("tchBuffer:%S\n", tchBuffer);
printf("sizeof(tchBuffer) : %d\n", sizeof(tchBuffer));
printf("_tcslen(tchBuffer) : %d\n", _tcslen(tchBuffer));
TCHAR tchBuffer2[1024] = L"Hello World";
int nRet = _tcscmp(tchBuffer, tchBuffer2);
if (0 == nRet)
{
printf("_tcscmp(%S, %S) == 0\n", tchBuffer, tchBuffer2);
}
else
{
printf("_tcscmp(%S, %S) != 0\n", tchBuffer, tchBuffer2);
}
nRet = _tcsncmp(tchBuffer, tchBuffer2, 5);
if (0 == nRet)
{
printf("_tcsncmp(%S, %S, 5) == 0\n", tchBuffer, tchBuffer2);
}
else
{
printf("_tcsncmp(%S, %S, 5) != 0\n", tchBuffer, tchBuffer2);
}
nRet = _tcsicmp(L"HELLO", L"Hello");
if (0 == nRet)
{
printf("_tcsicmp(L\"HELLO\", L\"Hello\") == 0\n");
}
else
{
printf("_tcsicmp(L\"HELLO\", L\"Hello\") != 0\n");
}
nRet = _tcsnicmp(L"HELLO", L"Hello", 3);
if (0 == nRet)
{
printf("_tcsnicmp(L\"HELLO\", L\"Hello\", 3) == 0\n");
}
else
{
printf("_tcsnicmp(L\"HELLO\", L\"Hello\", 3) != 0\n");
}
TCHAR str[64] = _T("1234d56d789");
LPTSTR substr = _tcschr(str, _T('d'));
printf(" _tcschr(%S, _T('d') : %S\n", str, substr);
LPTSTR substr2 = _tcsrchr(str, _T('d'));
printf("_tcsrchr(%S, _T('d') : %S\n", str, substr2);
References:
http://blog.csdn.net/wangqifeng10_16/article/details/5784811
http://blog.csdn.net/wskelan/article/details/5017131
https://www.codeproject.com/Articles/76252/What-are-TCHAR-WCHAR-LPSTR-LPWSTR-LPCTSTR-etc