1. RPC
这个框架需要的知识点:socket、zookeeper、动态代理、反射、spring
这个框架的socketServer部分,之前学习的demo程序只是一个基础,这里需要更高级的netty nio
2. NIO-New IO
2.1. 定义
nio是New IO的简称,从jdk1.4开始提供的新的api包。特性:为所有的原始类型提供buffer缓存支持,字符集编码解码解决方案。
channel:一个新的原始I/O抽象。
支持锁和内存映射文件的文件访问接口。提供多路non-blocking非阻塞式的高伸缩性网络IO。
2.2. socket nio原理
2.2.1. 传统的I/O
传统I/O程序读取文件内容,写到另一个文件或socket:
File.read(fileDesc, buf, len);
Socket.send(socket, buf, len);
以上是传统IO做法,会有较大性能开销,主要表现在两个方面:
1. 上下文切换(context switch), 此处有4次用户态和内核态的切换
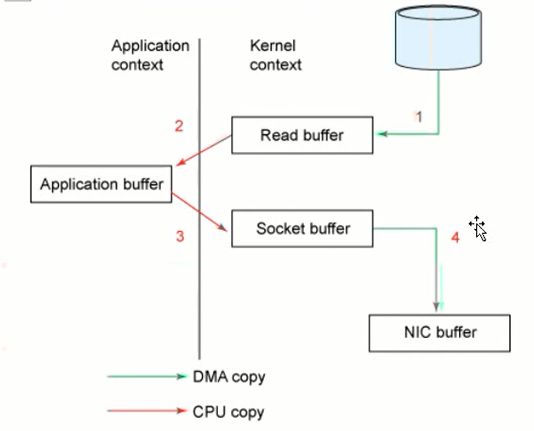
2. Buffer内存开销,一个是应用程序buffer,另一个是系统读取buffer以及socket buffer其运行示意图如下
1)先将文件内容从磁盘中拷贝到操作系统buffer
2)再从OS buffer拷贝到程序应用buffer
3)从程序buffer拷贝到socket buffer
4)从socket buffer拷贝到协议引擎
2.2.2. NIO
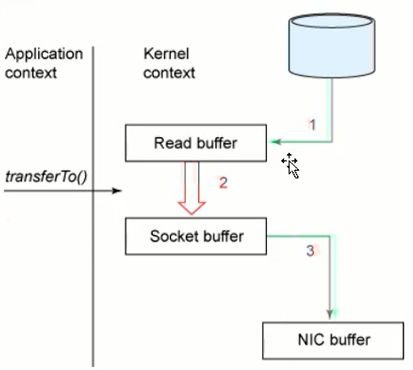
NIO技术相比传统IO技术,省去了上面步骤2)、3),直接将read buffer拷贝到socket buffer。FileChannel.transferTo() 方法就是这样的实现,这个实现是依赖于OS底层的sendFile()实现的。
如下图:
2.2.3. 传统IO和NIO服务器端对比
传统IO服务器端如果有多个客户端连接,服务器每accept一个客户端,都会创建一个Thread去跟客户端通信。这样看起来服务器端是没有阻塞的,实际上服务器端是阻塞的,是一个伪异步方式的IO,阻塞在accept。如下图:
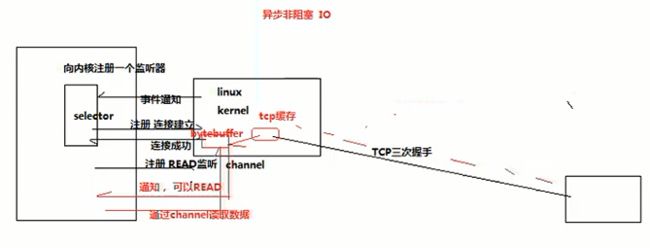
NIO是使用select方式,接收linux kernel的消息通知模式来处理多客户端的连接和消息收发。如下图:
原始NIO demo代码结构如下:
服务器端:
public class MultiplexerTimeServer implements Runnable{
private Selector selector;
private ServerSocketChannel servChannel;
private volatile boolean stop;
public MultiplexerTimeServer(int port){
try {
selector = Selector.open();
servChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
servChannel.configureBlocking(false);
servChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(port), 1024);
servChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
out.println("The time server is start in port : " + port);
}
public void stop(){
this.stop = true;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while(!stop){
try {
selector.select(1000);
Set
selectedKeys = selector.selectedKeys(); Iterator
it = selectedKeys.iterator(); SelectionKey key = null;
while(it.hasNext()){
key = it.next();
it.remove();
handleInput(key);
if(key != null){
key.cancel();
if (key.channel() != null){
key.channel().close();
}
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(selector != null){
try {
selector.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
private void handleInput(SelectionKey key) throws IOException{
if(key.isValid()){
//process the new connection
if(key.isAcceptable()){
//accept the new connection
ServerSocketChannel ssc = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
SocketChannel sc = ssc.accept();
sc.configureBlocking(false);
//add the new connection to the selector
sc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}
if(key.isReadable()){
//read the data
SocketChannel sc = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
ByteBuffer readBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int readBytes = sc.read(readBuffer);
if (readBytes > 0){
readBuffer.flip();
byte[] bytes = new byte[readBuffer.remaining()];
readBuffer.get(bytes);
String body = new String(bytes, "UTF-8");
out.println("The time server receive order : " + body);
String currentTime = "QUERY TIME ORDER".equalsIgnoreCase(body) ? new java.util.Date(System.currentTimeMillis()).toString() : "BAD ORDER";
doWrite(sc, currentTime);
}else if(readBytes < 0){
//client is disconnect
key.cancel();
sc.close();
}else{
//read 0 byte do nothing
;
}
}
}
}
private void doWrite(SocketChannel channel, String response) throws IOException{
if(response != null && response.trim().length() > 0){
byte[] bytes = response.getBytes();
ByteBuffer writeBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(bytes.length);
writeBuffer.put(bytes);
writeBuffer.flip();
channel.write(writeBuffer);
}
}
}
客户端:
public class TimeClientHandle implements Runnable{
private String host;
private int port;
private Selector selector;
private SocketChannel socketChannel;
private volatile boolean stop;
public TimeClientHandle(String host, int port) {
this.host = host == null ? "127.0.0.1" : host;
this.port = port;
try {
selector = Selector.open();
socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.exit(1);
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
doConnect();
} catch (IOException e2) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e2.printStackTrace();
}
while(!stop){
try {
selector.select(1000);
Set
selectedKeys = selector.selectedKeys(); Iterator
it = selectedKeys.iterator(); SelectionKey key = null;
while(it.hasNext()){
key = it.next();
it.remove();
try{
handleInput(key);
}catch(Exception e){
if(key != null){
key.cancel();
if(key.channel() != null){
key.channel().close();
}
}
}
}
} catch (IOException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
System.exit(1);
}
}
if(selector != null){
try {
selector.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
private void doConnect() throws IOException{
if(socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress(host, port))){
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
doWrite(socketChannel);
}else{
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT);
}
}
private void doWrite(SocketChannel sc) throws IOException{
byte[] req = "Query Time Order".getBytes();
ByteBuffer writeBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(req.length);
writeBuffer.put(req);
writeBuffer.flip();
sc.write(writeBuffer);
if(!writeBuffer.hasRemaining()){
out.println("Send order 2 server succeed.");
}
}
private void handleInput(SelectionKey key) throws IOException{
if (key.isValid()){
//check if connet succ
SocketChannel sc = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
if(key.isConnectable()){
if(sc.finishConnect()){
sc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
doWrite(sc);
}else{
System.exit(1); //connect error
}
}
if(key.isReadable()){
ByteBuffer readBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int readBytes = sc.read(readBuffer);
if (readBytes > 0){
readBuffer.flip();
byte[] bytes = new byte[readBuffer.remaining()];
readBuffer.get(bytes);
String body = new String(bytes, "UTF-8");
out.println("Now is : " + body);
this.stop = true;
}else if(readBytes < 0){
key.cancel();
sc.close();
}else{
;
}
}
}
}
}