欢迎关注公众号:【爱编码】
如果有需要后台回复2019赠送1T的学习资料哦!!
简介
Netty框架的主要线程就是I/O线程,线程模型的设计决定了系统的吞吐量、并发性和安全性等架构质量属性。所以了解一下NioEventLoop。
Reactor线程模型
基本上所有的网络处理程序都有以下基本的处理过程:
Read request
Decode request
Process service
Encode reply
Send reply
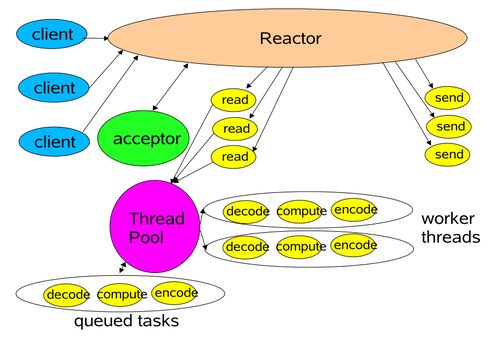
Reactor单线程模型
这是最简单的单Reactor线程模型,它负责多路分离套接字,Accept新连接,并分派请求到处理器链中。该模型适用于处理器链中业务处理组件能快速完成的场景。但这种模型并不能充分利用多核资源,实际使用少。
Reactor多线程模型
相比上一种模型,该模型在处理器链部分采用了多线程(线程池),也就是后端程序常见的模型。但Reactor仍为单个线程。
Reactor主从模型
主从Reactor多线程:多个acceptor的NIO线程池用于接受客户端的连接。将Reactor分成两部分,mainReactor负责监听Server socket,accpet新连接,并将简历的socket分派给subReactor。subReactor负责多路分离已连接的socket,读写网络数据,将业务处理功能扔给worker线程池完成。通常subReactor个数上与CPU个数等同。
以上就是对Reactor线程模型的学习。更加详细可以参考Doug Lea大神的PPT
http://gee.cs.oswego.edu/dl/cpjslides/nio.pdf
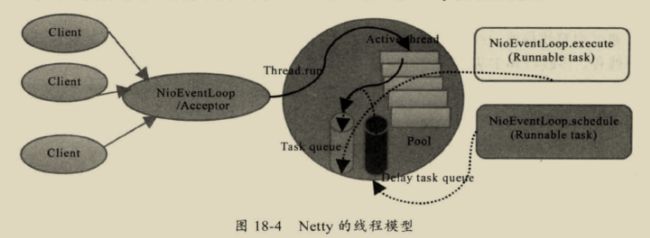
Netty的线程模型
netty的线程模型是可以通过设置启动类的参数来配置的,设置不同的启动参数,netty支持Reactor单线程模型、多线程模型和主从Reactor多线程模型。
Boss线程池职责如下:
(1)接收客户端的连接,初始化Channel参数
(2)将链路状态变更时间通知给ChannelPipeline
worker线程池作用是:
(1)异步读取通信对端的数据报,发送读事件到ChannelPipeline
(2)异步发送消息到通信对端,调用ChannelPipeline的消息发送接口
(3)执行系统调用Task;
(4)执行定时任务Task;
通过配置boss和worker线程池的线程个数以及是否共享线程池等方式,netty的线程模型可以在单线程、多线程、主从线程之间切换。
为了提升性能,netty在很多地方都进行了无锁设计。比如在IO线程内部进行串行操作,避免多线程竞争造成的性能问题。表面上似乎串行化设计似乎CPU利用率不高,但是通过调整NIO线程池的线程参数,可以同时启动多个串行化的线程并行运行,这种局部无锁串行线程设计性能更优。
NioEventLoop源码分析
基于Netty4.1.36
问题:
1.默认情况下,netty服务端起多少线程?何时启动?
2.Netty是如何解决jdk空轮询bug的?
3.Netty如何保证异步串行无锁化?
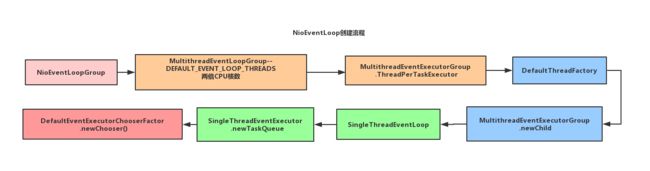
NioEventLoop创建流程
大致来说,从new NioEventLoopGroup()入手,然后到MultithreadEventLoopGroup的构造中明确的写明了默认为CPU的2倍的线程,接着new ThreadPerTaskExecutor()[线程创建器],然后就是一个死循环newChild()构造NioEventLoop,最后就是newChooser()[线程选择器]为后面的启动和执行做准备。
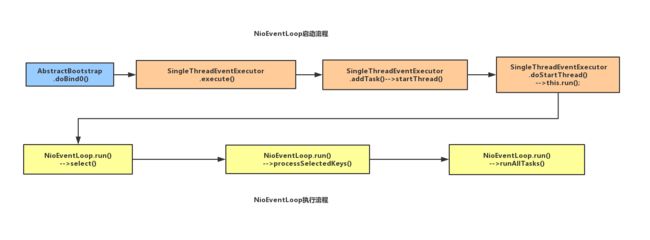
NioEventLoop启动流程和执行逻辑
NioEventLoop启动从客户端bind()入手,然后跟踪到doBind0(),接着到SingleThreadEventExecutor中execute(),该方法主要是添加任务addTask(task)和运行线程startThread(),然后在startThread()-->doStartThread()-->SingleThreadEventExecutor.this.run();开始执行NioEventLoop运行逻辑。
NioEventLoop启动后主要的工作
1.select() -- 检测IO事件,轮询注册到selector上面的io事件
2.processSelectedKeys() -- 处理io事件
3.runAllTasks() -- 处理外部线程扔到TaskQueue里面的任务
1.select() -- 检测IO事件
检测IO事件主要有三个部分:
deadline以及任务穿插逻辑处理:
计算本次执行select截止时间(根据NioEventLoop当时是否有定时任务处理)以及判断在select的时候是否有任务要处理。
阻塞式select:
未到截止时间或者任务队列为空进行一次阻塞式select操作
避免JDK空轮询的Bug:
判断这次select操作是否阻塞timeoutMillis时间,未阻塞timeoutMillis时间表示触发JDK空轮询;判断触发JDK空轮询的次数是否超过阈值,达到阈值调用rebuildSelector()方法替换原来的selector操作方式避免下次JDK空轮询继续发生
private void select(boolean oldWakenUp) throws IOException {
Selector selector = this.selector;
try {
int selectCnt = 0;
long currentTimeNanos = System.nanoTime();
long selectDeadLineNanos = currentTimeNanos + delayNanos(currentTimeNanos);
for (;;) {
/** 1.deadline以及任务穿插逻辑处理-- 开始**/
long timeoutMillis = (selectDeadLineNanos - currentTimeNanos + 500000L) / 1000000L;
if (timeoutMillis <= 0) {
if (selectCnt == 0) {
selector.selectNow();
selectCnt = 1;
}
break;
}
// If a task was submitted when wakenUp value was true, the task didn't get a chance to call
// Selector#wakeup. So we need to check task queue again before executing select operation.
// If we don't, the task might be pended until select operation was timed out.
// It might be pended until idle timeout if IdleStateHandler existed in pipeline.
if (hasTasks() && wakenUp.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
selector.selectNow();
selectCnt = 1;
break;
}
/** 1.deadline以及任务穿插逻辑处理-- 结束**/
/**2.阻塞select--开始**/
int selectedKeys = selector.select(timeoutMillis);
selectCnt ++;
/**2.阻塞select--结束**/
if (selectedKeys != 0 || oldWakenUp || wakenUp.get() || hasTasks() || hasScheduledTasks()) {
// - Selected something,
// - waken up by user, or
// - the task queue has a pending task.
// - a scheduled task is ready for processing
break;
}
if (Thread.interrupted()) {
// Thread was interrupted so reset selected keys and break so we not run into a busy loop.
// As this is most likely a bug in the handler of the user or it's client library we will
// also log it.
//
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2426
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Selector.select() returned prematurely because " +
"Thread.currentThread().interrupt() was called. Use " +
"NioEventLoop.shutdownGracefully() to shutdown the NioEventLoop.");
}
selectCnt = 1;
break;
}
/**3.避免jdk空轮询的bug -- 开始 **/
long time = System.nanoTime();
if (time - TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.toNanos(timeoutMillis) >= currentTimeNanos) {
// timeoutMillis elapsed without anything selected.
selectCnt = 1;
} else if (SELECTOR_AUTO_REBUILD_THRESHOLD > 0 &&
selectCnt >= SELECTOR_AUTO_REBUILD_THRESHOLD) {
// The code exists in an extra method to ensure the method is not too big to inline as this
// branch is not very likely to get hit very frequently.
selector = selectRebuildSelector(selectCnt);
selectCnt = 1;
break;
}
currentTimeNanos = time;
}
/**3.避免jdk空轮询的bug -- 结束**/
if (selectCnt > MIN_PREMATURE_SELECTOR_RETURNS) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Selector.select() returned prematurely {} times in a row for Selector {}.",
selectCnt - 1, selector);
}
}
} catch (CancelledKeyException e) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug(CancelledKeyException.class.getSimpleName() + " raised by a Selector {} - JDK bug?",
selector, e);
}
// Harmless exception - log anyway
}
}
2. processSelectedKeys()-- 处理IO事件
selected keySet优化
select操作每次把已就绪状态的io事件添加到底层HashSet(时间复杂度为O(n))数据结构,通过反射方式将HashSet替换成数组的实现.
NioEventLoop.openSelector()
private SelectorTuple openSelector() {
final Selector unwrappedSelector;
try {
unwrappedSelector = provider.openSelector();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new ChannelException("failed to open a new selector", e);
}
if (DISABLE_KEY_SET_OPTIMIZATION) {
return new SelectorTuple(unwrappedSelector);
}
Object maybeSelectorImplClass = AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedActionprocessSelectedKeysOptimized()
遍历SelectionKey数组获取SelectionKey的attachment即NioChannel;
SelectionKey合法获取SelectionKey的io事件进行事件处理
NioEventLoop.processSelectedKeysOptimized()
private void processSelectedKeysOptimized() {
for (int i = 0; i < selectedKeys.size; ++i) {
final SelectionKey k = selectedKeys.keys[i];
// null out entry in the array to allow to have it GC'ed once the Channel close
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2363
selectedKeys.keys[i] = null;
final Object a = k.attachment();
if (a instanceof AbstractNioChannel) {
processSelectedKey(k, (AbstractNioChannel) a);
} else {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
NioTask task = (NioTask) a;
processSelectedKey(k, task);
}
if (needsToSelectAgain) {
// null out entries in the array to allow to have it GC'ed once the Channel close
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2363
selectedKeys.reset(i + 1);
selectAgain();
i = -1;
}
}
}
3. runAllTasks()
Task的分类和添加
MpscQueue创建NioEventLoop构造,外部线程使用addTask()方法添加task;
ScheduledTaskQueue调用schedule()封装ScheduledFutureTask添加到普通任务队列
普通任务Task
SingleThreadEventExecutor.execute()-->addTask()
protected void addTask(Runnable task) {
if (task == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("task");
}
if (!offerTask(task)) {
reject(task);
}
}
定时任务Task
将线程外的任务是通过加入队列实现,从而保证了线程安全。
AbstractScheduledEventExecutor.schedule() -->ScheduledFuture
ScheduledFuture schedule(final ScheduledFutureTask task) {
if (inEventLoop()) {
scheduledTaskQueue().add(task);
} else {
execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
scheduledTaskQueue().add(task);
}
});
}
return task;
}
任务的聚合
将定时任务队列任务聚合到普通任务队列
SingleThreadEventExecutor.fetchFromScheduledTaskQueue()
private boolean fetchFromScheduledTaskQueue() {
long nanoTime = AbstractScheduledEventExecutor.nanoTime();
Runnable scheduledTask = pollScheduledTask(nanoTime);
while (scheduledTask != null) {
if (!taskQueue.offer(scheduledTask)) {
// No space left in the task queue add it back to the scheduledTaskQueue so we pick it up again.
scheduledTaskQueue().add((ScheduledFutureTask) scheduledTask);
return false;
}
scheduledTask = pollScheduledTask(nanoTime);
}
return true;
}
ScheduledFutureTask中可以看到任务Task是先按照截止时间排序,然后按照id进行排序的。
public int compareTo(Delayed o) {
if (this == o) {
return 0;
}
ScheduledFutureTask that = (ScheduledFutureTask) o;
long d = deadlineNanos() - that.deadlineNanos();
if (d < 0) {
return -1;
} else if (d > 0) {
return 1;
} else if (id < that.id) {
return -1;
} else if (id == that.id) {
throw new Error();
} else {
return 1;
}
}
任务的执行
获取普通任务队列待执行任务,使用safeExecute()方法执行任务,每次当累计任务数量达到64判断当前时间是否超过截止时间中断执行后续任务
NioEventLoop.runAllTasks()
protected boolean runAllTasks(long timeoutNanos) {
fetchFromScheduledTaskQueue();
Runnable task = pollTask();
if (task == null) {
afterRunningAllTasks();
return false;
}
final long deadline = ScheduledFutureTask.nanoTime() + timeoutNanos;
long runTasks = 0;
long lastExecutionTime;
for (;;) {
safeExecute(task);
runTasks ++;
// Check timeout every 64 tasks because nanoTime() is relatively expensive.
// XXX: Hard-coded value - will make it configurable if it is really a problem.
if ((runTasks & 0x3F) == 0) {
lastExecutionTime = ScheduledFutureTask.nanoTime();
if (lastExecutionTime >= deadline) {
break;
}
}
task = pollTask();
if (task == null) {
lastExecutionTime = ScheduledFutureTask.nanoTime();
break;
}
}
afterRunningAllTasks();
this.lastExecutionTime = lastExecutionTime;
return true;
}
总结
主要学习了NioEventLoop的基本知识,如果有更多知识欢迎各位分享,我还是个小菜鸟。
最后
如果对 Java、大数据感兴趣请长按二维码关注一波,我会努力带给你们价值。觉得对你哪怕有一丁点帮助的请帮忙点个赞或者转发哦。
关注公众号【爱编码】,回复2019有相关资料哦。