本豺狼最近忙于新需求开发, 荒于研究, 心中倍感焦虑, 不过恰好项目中进行了一些新的尝试, 自觉收获颇丰, 赶紧着与诸位分享!
大体说下情况吧, 豺狼这期的需求中有一块是修改详情页的模块顺序及UI, 由于这个详情页是很老的代码了, 十多个模块并且基于UITableView开发的, 加之迭代中不断新增删除模块, 可想而知UITableView代理方法多么的混乱和不堪入目, 逻辑死板, 牵一发动全身, 总之非常糟糕. 正好借着这期需求, 豺狼将整个详情页的业务逻辑梳理并重构! 好吧, 我们进入正题:
重构思路是什么
重构首先一点就是要有一个整体的思路, 对于详情页而言, 由于不同模块之间差异性大, 模块种类多, 顺序及数量改动多的特点, 网络上部分人选择了UIScrollView作为底层View来开发, 这就涉及到了模块之间高度的计算, 由于豺狼没有亲身实践, 不敢断言合理与否, 但自觉相对麻烦, 灵活性也差一些, 自然维护起来多少会出现问题, 所以豺狼还是继承原有逻辑, 在UITableView上进行模块的添加, 当然如果偏颇之处, 请诸位指点一二, 就不要问我为什么不用H5展示了
底层View确定后就是具体的代码结构逻辑了, 既然详情页有诸多特点, 那么我们如何考虑结构呢? 我的思路是使用一个SectionTypeArray来进行具体模块的管理, 建立一个枚举来体现出所有模块的种类, 这样每次需求变更时, 只要修改相应的SectionTypeArray就可以优雅地管理不同模块.
typedef NS_ENUM(NSUInteger, ViewControllerSectionType) {
ViewControllerSectionTypeUser,
ViewControllerSectionTypeSport,
ViewControllerSectionTypeFavortiteFood,
};
- (NSArray *)sectionTypeArray {
if (_sectionTypeArray == nil) {
_sectionTypeArray = @[@(ViewControllerSectionTypeUser),
@(ViewControllerSectionTypeSport),
@(ViewControllerSectionTypeFavortiteFood)];
}
return _sectionTypeArray;
}
如何管理UITableView的数据
既然我们确定了模块管理策略, 那就要在这个策略基础上构造代码, 首先就是UITableView需要根据这个模块管理策略来灵活变动, 这样的话我们代理方法中就不能把逻辑写死, 给我启发的是早前看过的一个Demo--SigmaTableViewModel.
我们只需要把UITableView的所有数据都用一个模型保存了起来, 具体调用的时候根据NSIndexPath从数组中取出来不就好了? return Array[IndexPath.row]多么优雅的写法! 于是乎问题迎刃而解.
不过我认为这个Demo中封装的过于死板, 所以自己单独封装了一个简易版的.
@interface HRTableViewCellModel : NSObject
@property (nonatomic, assign) CGFloat cellHeight;
@property (nonatomic, copy) UITableViewCell *(^configCellBlock)(NSIndexPath *indexPath, UITableView *tableView);
@property (nonatomic, copy) void (^selectCellBlock)(NSIndexPath *indexPath, UITableView *tableView);
/*
其他属性按需求添加
*/
@end
@interface HRTableViewModel : NSObject
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSMutableArray *cellModelArray;
@property (nonatomic, assign) CGFloat headerHeight;
@property (nonatomic, assign) CGFloat footerHeight;
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSString *headerTitle;
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSString *footerTitle;
@property (nonatomic, strong) UIView *headerView;
@property (nonatomic, strong) UIView *footerView;
@property (nonatomic, copy) UIView * (^headerViewBlock)(NSInteger section, UITableView *tableView);
@property (nonatomic, copy) UIView * (^footerViewBlock)(NSInteger section, UITableView *tableView);
@end
所有的数据都用这个模型保存起来, 用的时候直接读取模型即可, 任你是顺着排列倒着排列还是跳着排列随便你, 想想就激动~
这个模型是用block来传递具体的业务逻辑代码块, 因为是简易版有些功能可以自己拓展, 需要提到的一点就是对于使用block造成的循环引用一定要注意!
灵活的详情页
先来展示下详情页有多么灵活
- (NSInteger)numberOfSectionsInTableView:(UITableView *)tableView {
return self.sectionModelArray.count;
}
- (NSInteger)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView numberOfRowsInSection:(NSInteger)section {
HRTableViewModel *model = self.sectionModelArray[section];
return model.cellModelArray.count;
}
- (CGFloat)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView heightForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath {
HRTableViewModel *model = self.sectionModelArray[indexPath.section];
HRTableViewCellModel *cellModel = model.cellModelArray[indexPath.row];
return cellModel.cellHeight;
}
- (CGFloat)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView estimatedHeightForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath {
return 40;
}
- (UITableViewCell *)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView cellForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath {
HRTableViewModel *model = self.sectionModelArray[indexPath.section];
HRTableViewCellModel *cellModel = model.cellModelArray[indexPath.row];
return cellModel.configCellBlock(indexPath, tableView);
}
- (void)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView didSelectRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath {
HRTableViewModel *model = self.sectionModelArray[indexPath.section];
HRTableViewCellModel *cellModel = model.cellModelArray[indexPath.row];
cellModel.selectCellBlock(indexPath, tableView);
}
就是这样, 没有一行具体的业务逻辑在这里, 所有的相关业务都在外面实现好, 代理方法直接调用即可.
这里是Demo
简单说明一下
首先我们需要一个SectionModelArray来保存UITableView的数据, 然后我们根据SectionTypeArray中的模块类型, 用switch来塞入数据.
+ (NSArray *)reformDataToSectionModelArray:(id)data delegate:(id)delegate {
ViewControllerDataSource *dataSource = [[ViewControllerDataSource alloc] init];
dataSource.delegate = delegate;
[dataSource.sectionModelArray removeAllObjects];
dataSource.dataDic = (NSDictionary *)data;
for (NSNumber *type in dataSource.sectionTypeArray) {
switch (type.integerValue) {
case ViewControllerSectionTypeUser: {
[dataSource configUserCellModel];
}
break;
case ViewControllerSectionTypeSport: {
[dataSource configSportCellModel];
}
break;
case ViewControllerSectionTypeFavortiteFood: {
[dataSource configFavoriteFoodCellModel];
}
break;
default:
break;
}
}
return [dataSource.sectionModelArray copy];
}
// 举例: 塞入UserCell的数据
- (void)configUserCellModel {
// section的数据
HRTableViewModel *sectionModel = [[HRTableViewModel alloc] init];
[sectionModel setHeaderTitle:@"用户信息"];
// 塞入SectionModelArray
[self.sectionModelArray addObject:sectionModel];
// 具体cell的数据
HRTableViewCellModel *cellModel = [[HRTableViewCellModel alloc] init];
[cellModel setConfigCellBlock:^UITableViewCell *(NSIndexPath *indexPath, UITableView *tableView) {
__weak typeof(&*self) weakSelf = self;
UserCell *cell = (UserCell *)[weakSelf configUserCell:tableView indexPath:indexPath];
return cell;
}];
[cellModel setSelectCellBlock:^(NSIndexPath *indexPath, UITableView *tableView) {
__weak typeof(&*self) weakSelf = self;
ViewController *vc = [[ViewController alloc] init];
[((ViewController *)weakSelf.delegate).navigationController pushViewController:vc animated:YES];
}];
// 塞入section的cellModelArray中
[sectionModel.cellModelArray addObject:cellModel];
}
至此一个模块的逻辑就添加好了, 其他模块类似的逻辑一个个添加进去.
另外对于cell的动态高度, 如果是model中计算高度, 直接写就可以, 如果是cell中利用控件计算高度, 就要在configCell方法中重新从数组中取出对应CellModel传入, 并且实现- (CGFloat)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView estimatedHeightForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath方法. 再次强调切忌循环引用!
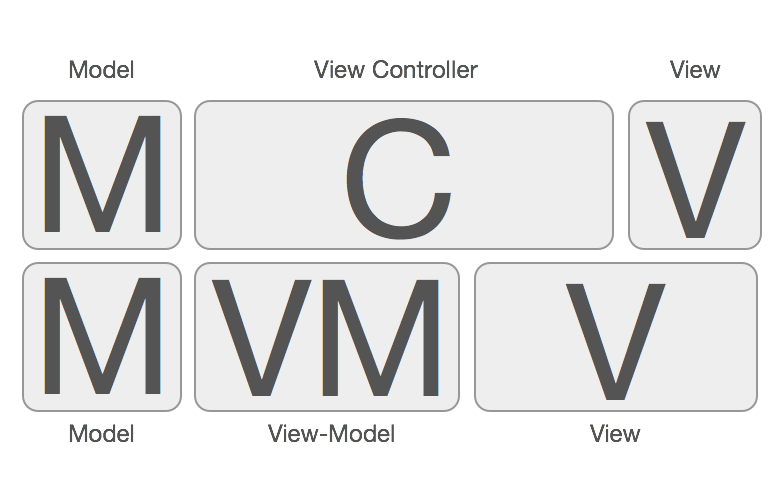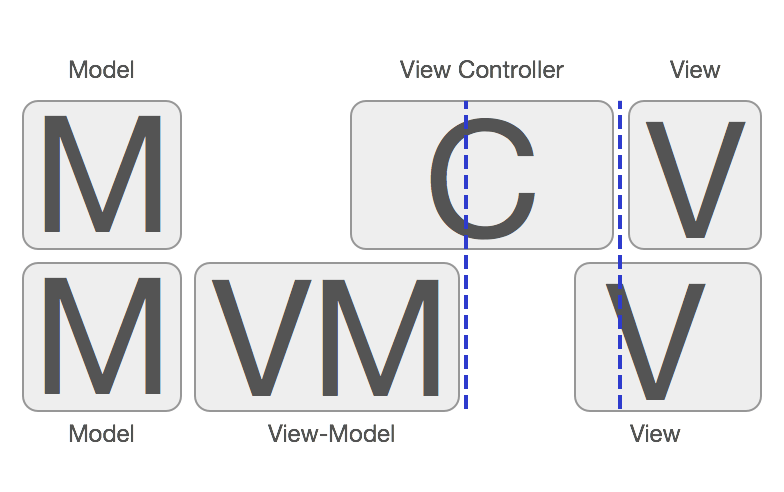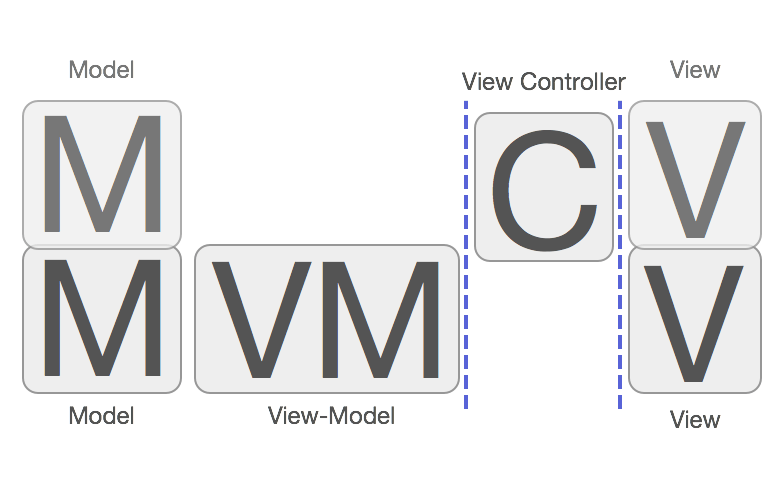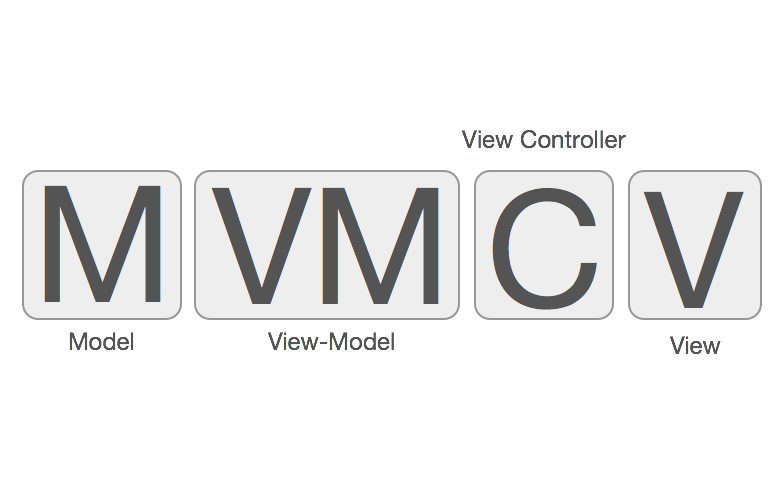
关于MVVM的设计模式感想
对于看着逼格很高的MVVM, 豺狼其实了解的并不多, 但是借用田神Cosa Yaloyum博客中的一张图可以更好地说明, 博客在此, 干货很多.
豺狼对此理解是所谓MVVM模式就是在MVC下不断对其
Controller瘦身而形成具体的处理弱业务的
ViewModel, 我觉得更应该叫做"M-VM-C-V".
随着项目不断迭代更新,
Controller中承载了很多不能在
View和
Model中写的弱业务代码, 造成其体积越来越大, 维护越发困难, 其中就包括
UITableView的
datasource和
delegate的代理用到的逻辑, 所以豺狼尝试着在这个Demo的基础上分离这些弱业务逻辑, 对
Controller进行瘦身!
于是豺狼专门分离出一个用来管理UITableView数据的类ViewControllerDataSource, 按照我的理解, 这里的ViewControllerDataSource就是MVVM中的ViewModel, 负责处理UITableView中涉及到的弱业务(所谓弱业务与强业务也是从田神那偷来的概念~).
// ViewControllerDataSource.h
@interface ViewControllerDataSource : NSObject
+ (NSArray *)reformDataToSectionModelArray:(id)data delegate:(id)delegate;
@end
传入数据->加工成能用的数据模型->具体展示, Controller在里面只起到了逻辑分发转接的作用, 代码量大大减少, 这样就可以集中处理强业务逻辑, 也许这个Demo中看的并不明显, 但豺狼在项目中实践下来, 节省了2000行代码....而且整体逻辑更加清晰, 各司其职.ViewControllerDataSource作为一个Manager就是处理UITableView相关.
豺狼认为以后的Controller可以用这种思路进一步拆分细化, 比如网络请求逻辑可以单独建一个Manager管理, 唐巧的YTKNetwork就是这么做的, 这样一定程度上也可以起到解耦的作用.
最后
重剑无锋,大巧不工。 ---- 《神雕侠侣》
以这句话作为结束语, MVVM作为新的设计模式并不是死板固定的, 更多的还是根据需求进行使用, 简单的页面MVC, 复杂的页面进行拆分, 不拘泥于MVVM的格式, 才是最正确的用法.
最后再次强调田神的高质量博客, 关于架构的部分每一篇都能读一天~
如果诸位能看到这里,希望可以给豺狼点个赞鼓励一下!