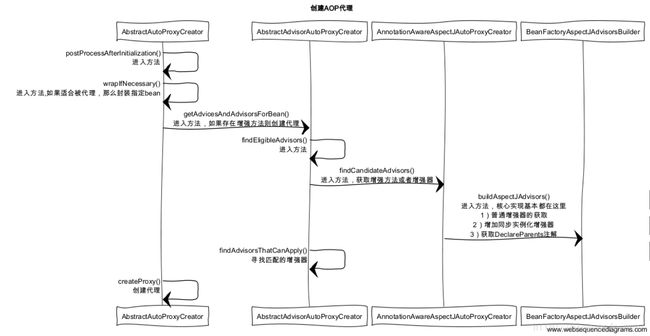
1、时序图
2、源码分析
(1)、AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator实现了BeanPostProcessor接口,而实现Bean-PostProcessor后,当Spring加载这个Bean时会在实例化前调用其postProcessAfterInitialization方法
//AbstractAutoProxyCreator
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (bean != null) {
// 根据给定的bean 的class 和name 构建出个key ,格式:beanClassName_beanName
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName);
if (!this.earlyProxyReferences.containsKey(cacheKey)) {
// 如果它适合被代理,则需要封装指定bean。
return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);
}
}
return bean;
}
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) {
// 如果已经 处理过
if (beanName != null && this.targetSourcedBeans.containsKey(beanName)) {
return bean;
}
//无需增强
if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(this.advisedBeans.get(cacheKey))) {
return bean;
}
// 给定的bean 类是否代表一个基础设施类,基础设施类不应代理,或者配置了指定bean 不需要自动代理
if (isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) || shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName)) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
// Create proxy if we have advice.
Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null);
// 如果获取到了增强则需要针对增强创建代理
if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE);
//创建代理
Object proxy = createProxy(bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean));
this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());
return proxy;
}
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
创建代理
(1)获取当前类中的属性。
(2)添加代理接口。
(3)封装Advisor并加入到ProxyFactory中。
(4)设置要代理的类。
(5)当然在Spring中还为子类提供了定制的函数customizeProxyFactory,子类可以在此函数中进行对ProxyFactory的进一步封装。
(6)进行获取代理操作。
其中,封装Advisor并加入到ProxyFactory中以及创建代理是两个相对繁琐的过程,可以通过ProxyFactory提供的addAdvisor方法直接将增强器置入代理创建工厂中,但是将拦截器封装为增强器还是需要一定的逻辑的。
//AbstractAutoProxyCreator
protected Object createProxy(
Class beanClass, String beanName, Object[] specificInterceptors, TargetSource targetSource) {
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory();
// Copy our properties (proxyTargetClass etc) inherited from ProxyConfig.
//获取当前类中的属性
proxyFactory.copyFrom(this);
//决定对于给定的bean 是否应该使用targetClass 而不是他的接口代理,
//检查proxyTargeClass 设置以及preserveTargetClass 属性
if (!shouldProxyTargetClass(beanClass, beanName)) {
// Must allow for introductions; can't just set interfaces to
// the target's interfaces only.
Class[] targetInterfaces = ClassUtils.getAllInterfacesForClass(beanClass, this.proxyClassLoader);
for (Class targetInterface : targetInterfaces) {
proxyFactory.addInterface(targetInterface);
}
}
Advisor[] advisors = buildAdvisors(beanName, specificInterceptors);
for (Advisor advisor : advisors) {
proxyFactory.addAdvisor(advisor);
}
proxyFactory.setTargetSource(targetSource);
customizeProxyFactory(proxyFactory);
proxyFactory.setFrozen(this.freezeProxy);
if (advisorsPreFiltered()) {
proxyFactory.setPreFiltered(true);
}
//ProxyFactory的getProxy方法,默认也是由DefaultAopProxyFactory的createAopProxy方法实现,同ProxyFactoryBean中
return proxyFactory.getProxy(this.proxyClassLoader);
}
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
DefaultAopProxyFactory中createAopProxy方法,调用JdkDynamicAopProxy或者ObjenesisCglibAopProxy
@Override
public AopProxy createAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException {
if (config.isOptimize() || config.isProxyTargetClass() || hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(config)) {
Class targetClass = config.getTargetClass();
if (targetClass == null) {
throw new AopConfigException("TargetSource cannot determine target class: " +
"Either an interface or a target is required for proxy creation.");
}
if (targetClass.isInterface() || Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass)) {
return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);
}
return new ObjenesisCglibAopProxy(config);
}
else {
return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);
}
}
AbstractAutoProxyCreator 封装Advisor并加入到ProxyFactory中
protected Advisor[] buildAdvisors(String beanName, Object[] specificInterceptors) {
// Handle prototypes correctly...
Advisor[] commonInterceptors = resolveInterceptorNames();
List(2)、获取增强
getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean开始的
(1)获取增强方法或者增强器;
(2)根据获取的增强进行代理。
获取所有的增强以及寻找所有增强中适用于bean的增强并应用,那么findCandidateAdvisors与findAdvisorsThatCanAp-ply便是做了这两件事情。当然,如果无法找到对应的增强器便返回DO_NOT_PROXY,其中DO_NOT_PROXY=null。
//AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator
@Override
protected Object[] getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(Class beanClass, String beanName, TargetSource targetSource) {
List advisors = findEligibleAdvisors(beanClass, beanName);
if (advisors.isEmpty()) {
return DO_NOT_PROXY;
}
return advisors.toArray();
}
protected List findEligibleAdvisors(Class beanClass, String beanName) {
List candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors();
List eligibleAdvisors = findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass, beanName);
extendAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);
if (!eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty()) {
eligibleAdvisors = sortAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);
}
return eligibleAdvisors;
}
由于我们分析的是使用注解进行的AOP,所以对于findCandidateAdvisors的实现其实是由AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator类完成的
//AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator
protected List findCandidateAdvisors() {
// Add all the Spring advisors found according to superclass rules.
List advisors = super.findCandidateAdvisors();
// Build Advisors for all AspectJ aspects in the bean factory.
advisors.addAll(this.aspectJAdvisorsBuilder.buildAspectJAdvisors());
return advisors;
}
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator间接继承了AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator,在实现获取增强的方法中除了保留父类的获取配置文件中定义的增强外,同时添加了获取Bean的注解增强的功能,那么其实现正是由this.aspectJAdvisorsBuilder.buildAspectJAdvisors()来实现的。
最终通过ReflectiveAspectJAdvisorFactory.getAdvice方法获取增强,可以看不这里有不同类型的增强。最终,在jdk或者cglib代理方法中,调用不同的invoke方法
public Advice getAdvice(Method candidateAdviceMethod, AspectJExpressionPointcut expressionPointcut,
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory, int declarationOrder, String aspectName) {
Class candidateAspectClass = aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass();
validate(candidateAspectClass);
AspectJAnnotation aspectJAnnotation =
AbstractAspectJAdvisorFactory.findAspectJAnnotationOnMethod(candidateAdviceMethod);
if (aspectJAnnotation == null) {
return null;
}
// If we get here, we know we have an AspectJ method.
// Check that it's an AspectJ-annotated class
if (!isAspect(candidateAspectClass)) {
throw new AopConfigException("Advice must be declared inside an aspect type: " +
"Offending method '" + candidateAdviceMethod + "' in class [" +
candidateAspectClass.getName() + "]");
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Found AspectJ method: " + candidateAdviceMethod);
}
AbstractAspectJAdvice springAdvice;
switch (aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotationType()) {
case AtBefore:
springAdvice = new AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
break;
case AtAfter:
springAdvice = new AspectJAfterAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
break;
case AtAfterReturning:
springAdvice = new AspectJAfterReturningAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
AfterReturning afterReturningAnnotation = (AfterReturning) aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotation();
if (StringUtils.hasText(afterReturningAnnotation.returning())) {
springAdvice.setReturningName(afterReturningAnnotation.returning());
}
break;
case AtAfterThrowing:
springAdvice = new AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
AfterThrowing afterThrowingAnnotation = (AfterThrowing) aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotation();
if (StringUtils.hasText(afterThrowingAnnotation.throwing())) {
springAdvice.setThrowingName(afterThrowingAnnotation.throwing());
}
break;
case AtAround:
springAdvice = new AspectJAroundAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
break;
case AtPointcut:
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Processing pointcut '" + candidateAdviceMethod.getName() + "'");
}
return null;
default:
throw new UnsupportedOperationException(
"Unsupported advice type on method: " + candidateAdviceMethod);
}
// Now to configure the advice...
springAdvice.setAspectName(aspectName);
springAdvice.setDeclarationOrder(declarationOrder);
String[] argNames = this.parameterNameDiscoverer.getParameterNames(candidateAdviceMethod);
if (argNames != null) {
springAdvice.setArgumentNamesFromStringArray(argNames);
}
springAdvice.calculateArgumentBindings();
return springAdvice;
}
public class AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor, AfterAdvice, Serializable {
private final AfterReturningAdvice advice;
/**
* Create a new AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor for the given advice.
* @param advice the AfterReturningAdvice to wrap
*/
public AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor(AfterReturningAdvice advice) {
Assert.notNull(advice, "Advice must not be null");
this.advice = advice;
}
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
Object retVal = mi.proceed();
this.advice.afterReturning(retVal, mi.getMethod(), mi.getArguments(), mi.getThis());
return retVal;
}
}
refer
http://blog.csdn.net/fighterandknight/article/details/51209822
http://blog.csdn.net/followmyinclinations/article/details/52210186