科普一下
- 2013年谷歌i/o大会上介绍了两个新的layout: SlidingPaneLayout和DrawerLayout,现在这俩个类被广泛的运用,其实研究他们的源码你会发现这两个类都运用了ViewDragHelper来处理拖动。ViewDragHelper是Framework中不为人知却非常有用的一个工具。ViewDragHelper解决了android中手势处理过于复杂的问题,在DrawerLayout出现之前,侧滑菜单都是由第三方开源代码实现的,其中著名的当属MenuDrawer,MenuDrawer重写onTouchEvent方法来实现侧滑效果,代码量很大,实现逻辑也需要很大的耐心才能看懂。如果每个开发人员都从这么原始的步奏开始做起,那对于安卓生态是相当不利的。所以说ViewDragHelper等的出现反映了安卓开发框架已经开始向成熟的方向迈进。引用了网上的片段,其实说了那么多,ViewDragHelper就如名字说的一样,一个拖拽View的帮助类。只要我们这些普通开发者使用这个类,就可以轻松实现以前写了一大堆代码才实现的效果,代码更简洁,更优雅。
ViewDragHelper基本用法
- 创建ViewDragHelper,建议在ViewGroup内部创建使用,而不是在外面使用。
//第二个参数设置滑动灵敏度
mViewDragHelper = ViewDragHelper.create(this, 1.0f,mCallback);
- 看看mCallback回调接口ViewDragHelper.Callback,到底有什么重要的方法,直接上源码。
public static abstract class Callback {
/**
* 当ViewDragHelper状态发生变化时回调(IDLE,DRAGGING,SETTING[自动滚动时])
* @see #STATE_IDLE
* @see #STATE_DRAGGING
* @see #STATE_SETTLING
*/
public void onViewDragStateChanged(int state) {}
/**
* 当captureView的位置发生改变时回调
* @param changedView View whose position changed
* @param left New X coordinate of the left edge of the view
* @param top New Y coordinate of the top edge of the view
* @param dx Change in X position from the last call
* @param dy Change in Y position from the last call
*/
public void onViewPositionChanged(View changedView, int left, int top, int dx, int dy) {}
/**
*当CaptureView被捕获时回调
* @param capturedChild Child view that was captured
* @param activePointerId Pointer id tracking the child capture
*/
public void onViewCaptured(View capturedChild, int activePointerId) {}
/**
*手指释放的时候回调
*
* @param releasedChild The captured child view now being released
* @param xvel X velocity of the pointer as it left the screen in pixels per second.
* @param yvel Y velocity of the pointer as it left the screen in pixels per second.
*/
public void onViewReleased(View releasedChild, float xvel, float yvel) {}
/**
* 当触摸到边界时回调。
*
* @param edgeFlags A combination of edge flags describing the edge(s) currently touched
* @param pointerId ID of the pointer touching the described edge(s)
* @see #EDGE_LEFT
* @see #EDGE_TOP
* @see #EDGE_RIGHT
* @see #EDGE_BOTTOM
*/
public void onEdgeTouched(int edgeFlags, int pointerId) {}
/**
*true的时候会锁住当前的边界,false则unLock。
*
* @param edgeFlags A combination of edge flags describing the edge(s) locked
* @return true to lock the edge, false to leave it unlocked
*/
public boolean onEdgeLock(int edgeFlags) {
return false;
}
/**
*
*在边界拖动时状态回调
* @param edgeFlags A combination of edge flags describing the edge(s) dragged
* @param pointerId ID of the pointer touching the described edge(s)
* @see #EDGE_LEFT
* @see #EDGE_TOP
* @see #EDGE_RIGHT
* @see #EDGE_BOTTOM
*/
public void onEdgeDragStarted(int edgeFlags, int pointerId) {}
/**
* 改变同一个坐标(x,y)去寻找captureView位置的方法
*
* @param index the ordered position to query for
* @return index of the view that should be ordered at position index
*/
public int getOrderedChildIndex(int index) {
return index;
}
/**
*
*水平方向,子View要是消耗事件,就要重写此方法返回大于1的数。
* @param child Child view to check
* @return range of horizontal motion in pixels
*/
public int getViewHorizontalDragRange(View child) {
return 0;
}
/**
*垂直方向,子View要是消耗事件,就要重写此方法返回大于1的数。
*
* @param child Child view to check
* @return range of vertical motion in pixels
*/
public int getViewVerticalDragRange(View child) {
return 0;
}
/**
*tryCaptureView如何返回ture则表示可以捕获该view即是哪个View可以滑动,哪个不可以滑动,在这个方
*法里面控制
* @param child Child the user is attempting to capture
* @param pointerId ID of the pointer attempting the capture
* @return true if capture should be allowed, false otherwise
*/
public abstract boolean tryCaptureView(View child, int pointerId);
/**
* 水平滑动的边界处理
*
*
* @param child Child view being dragged
* @param left Attempted motion along the X axis
* @param dx Proposed change in position for left
* @return The new clamped position for left
*/
public int clampViewPositionHorizontal(View child, int left, int dx) {
return 0;
}
/**
* 垂直滑动的边界处理
*
*
* @param child Child view being dragged
* @param top Attempted motion along the Y axis
* @param dy Proposed change in position for top
* @return The new clamped position for top
*/
public int clampViewPositionVertical(View child, int top, int dy) {
return 0;
}
}
大概了解所有的回调方法后,回归主题。
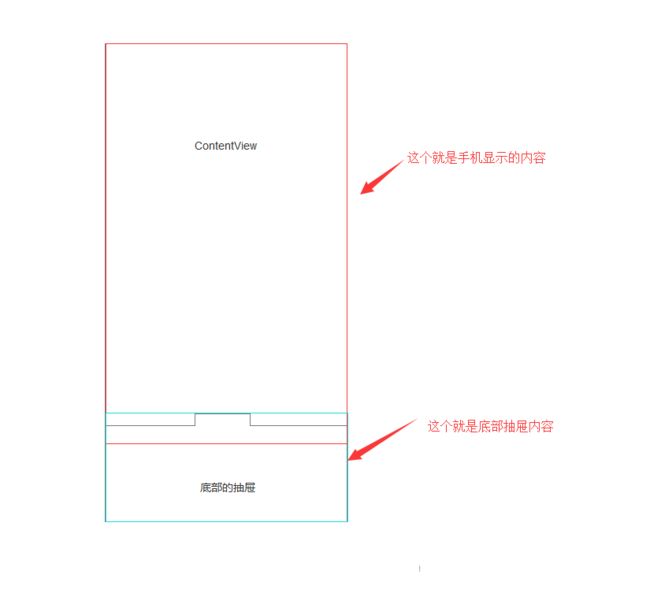
一个上拉抽屉布局,我脑子里首先想到的就是这样一个东东,图1。
既然是这样,新建一个PullUpDragLayout直接继承ViewGroup,代码如下:
/**
* @作 用:上拉的抽屉布局
* @创 建 人: linguoding 邮箱:[email protected]
* @日 期: 2016年11月16日 10:32
*/
public class PullUpDragLayout extends ViewGroup {
private ViewDragHelper mViewDragHelper;//拖拽帮助类
private View mBottomView;//底部内容View
private View mContentView;//内容View
private int mBottomBorderHeigth = 20;//底部边界凸出的高度
public PullUpDragLayout(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public PullUpDragLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
public PullUpDragLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean b, int i, int i1, int i2, int i3) {
}
}
PullUpDragLayout 有两个子View,这两个子View怎么创建?可以java代码new,可以在xml布局里面写,也可以自定义属性,引用属性得到。new 的话就pass掉,这里直接使用后面两种方式。
有了属性,接下来就可以实例化mBottomView , mContentView ,还有得到边界高度 mBottomBorderHeigth的值。代码如下:
/**
* @作 用:上拉的抽屉布局
* @创 建 人: linguoding 邮箱:[email protected]
* @日 期: 2016年11月16日 10:32
*/
public class PullUpDragLayout extends ViewGroup {
private ViewDragHelper mViewDragHelper;//拖拽帮助类
private View mBottomView;//底部内容View
private View mContentView;//内容View
private LayoutInflater mLayoutInflater;
private int mBottomBorderHeigth = 20;//底部边界凸出的高度
public PullUpDragLayout(Context context) {
this(context, null, 0);
}
public PullUpDragLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public PullUpDragLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
init(context);
initCustomAttrs(context, attrs);
}
private void init(Context context) {
mLayoutInflater = LayoutInflater.from(context);
}
/**
* 初始化自定义属性,并实例化子View
* @param context
* @param attrs
*/
private void initCustomAttrs(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
TypedArray typedArray = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.PullUpDragLayout);
if (typedArray != null) {
if (typedArray.hasValue(R.styleable.PullUpDragLayout_PullUpDrag_ContentView)) {
inflateContentView(typedArray.getResourceId(R.styleable.PullUpDragLayout_PullUpDrag_ContentView, 0));
}
if (typedArray.hasValue(R.styleable.PullUpDragLayout_PullUpDrag_BottomView)) {
inflateBottomView(typedArray.getResourceId(R.styleable.PullUpDragLayout_PullUpDrag_BottomView, 0));
}
if (typedArray.hasValue(R.styleable.PullUpDragLayout_PullUpDrag_BottomBorderHeigth)) {
mBottomBorderHeigth = (int) typedArray.getDimension(R.styleable.PullUpDragLayout_PullUpDrag_BottomBorderHeigth, 20);
}
typedArray.recycle();
}
}
private void inflateContentView(int resourceId) {
mContentView = mLayoutInflater.inflate(resourceId, this, true);
}
private void inflateBottomView(int resourceId) {
mBottomView = mLayoutInflater.inflate(resourceId, this, true);
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean b, int i, int i1, int i2, int i3) {
}
}
实例化了子View后,PullUpDragLayout 既然是直接继承ViewGroup,那肯定要计算子View,还有子View在PullUpDragLayout怎么布局。那就要重写onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec),还有onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int top, int right, int bottom)方法。
- onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec)方法计算子View的大小
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
mContentView = getChildAt(0);
mBottomView = getChildAt(1);
measureChild(mBottomView, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
int bottomViewHeight = mBottomView.getMeasuredHeight();
measureChild(mContentView, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
int contentHeight = mContentView.getMeasuredHeight();
setMeasuredDimension(MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec), bottomViewHeight +contentHeight + getPaddingBottom() + getPaddingTop());
}
- onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int top, int right, int bottom)方法排列子View的位置
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
mContentView = getChildAt(0);
mBottomView = getChildAt(1);
mContentView.layout(getPaddingLeft(), getPaddingTop(), getWidth() - getPaddingRight(), mContentView.getMeasuredHeight());
mBottomView.layout(getPaddingLeft(), mContentView.getHeight() - mBottomBorderHeigth, getWidth() - getPaddingRight(), getMeasuredHeight() - mBottomBorderHeigth);
}
应用ViewDragHelper实现上拉效果
到此,就实现上面图1的静态效果啦。想要底部可以上拉,或者点击上拉到指定位置。那就要用到ViewDragHelper。在init()方法中创建ViewDragHelper.create(this, 1.0f,mCallback)。重写onInterceptTouchEvent()、onTouchEvent,将event事件交给ViewDragHelper拦截及处理,代码如下:
private void init(Context context) {
mLayoutInflater = LayoutInflater.from(context);
mViewDragHelper = ViewDragHelper.create(this, 1.0f, mCallback);
}
ViewDragHelper.Callback mCallback = new ViewDragHelper.Callback() {
@Override
public boolean tryCaptureView(View child, int pointerId) {
return mBottomView == child;
}
};
@Override
public boolean onInterceptTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
return mViewDragHelper.shouldInterceptTouchEvent(ev);
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
mViewDragHelper.processTouchEvent(event);
return true;
}
这样底部抽屉就可以随意滑动啦,但是这样还远远没有达到我要的效果。我们要实现以下效果
- 指定方向滑动
- 边界检测、加速度检测
- 手指抬起,自动展开/收缩
- 点击Button,展开/关闭
- 监听展开/关闭,上拉过程发生改变时回调
慢慢来,下面一个一个地去实现。
- 指定方向滑动
控制水平方向不滑动,上下滑动。重写ViewDragHelper.Callback中的clampViewPositionHorizontal()方法,还有这个clampViewPositionVertical()。代码如下:
@Override
public int clampViewPositionHorizontal(View child, int left, int dx) {
final int leftBound = getPaddingLeft();
final int rightBound = getWidth() - mBottomView.getWidth() - leftBound;
final int newLeft = Math.min(Math.max(left, leftBound), rightBound);
return newLeft;
}
@Override
public int clampViewPositionVertical(View child, int top, int dy) {
int topBound = mContentView.getHeight() - mBottomView.getHeight();
int bottomBound = mContentView.getHeight() - mBottomBorderHeigth;
return Math.min(bottomBound, Math.max(top, topBound));
}
- 手指抬起,自动展开/收缩
重写onViewReleased()方法:代码如下:
//手指释放的时候回调
@Override
public void onViewReleased(View releasedChild, float xvel, float yvel) {
if (releasedChild == mBottomView) {
if (releasedChild.getY() < mBoundTopY || yvel <= -1000) {
mViewDragHelper.settleCapturedViewAt(mAutoBackTopPos.x, mAutoBackTopPos.y);
isOpen = true;
if (mOnStateListener != null) mOnStateListener.open();
} else if (releasedChild.getY() >= mBoundTopY || yvel >= 1000) {
mViewDragHelper.settleCapturedViewAt(mAutoBackBottomPos.x, mAutoBackBottomPos.y);
isOpen = false;
if (mOnStateListener != null) mOnStateListener.close();
}
invalidate();
}
}
};
@Override
public void computeScroll() {
if (mViewDragHelper.continueSettling(true)) { invalidate();
}
}
- 点击Button,展开/关闭
/**
* 切换底部View
*/
public void toggleBottomView() {
if (isOpen) {
mViewDragHelper.smoothSlideViewTo(mBottomView, mAutoBackBottomPos.x, mAutoBackBottomPos.y);
if (mOnStateListener != null) mOnStateListener.close();
} else {
mViewDragHelper.smoothSlideViewTo(mBottomView, mAutoBackTopPos.x, mAutoBackTopPos.y);
if (mOnStateListener != null) mOnStateListener.open();
}
invalidate();
isOpen = !isOpen;
}
- 监听展开/关闭,上拉过程发生改变时回调
定义两个接口
public void setOnStateListener(OnStateListener onStateListener) {
mOnStateListener = onStateListener;
}
public void setScrollChageListener(OnScrollChageListener scrollChageListener) {
mScrollChageListener = scrollChageListener;
}
public interface OnStateListener {
void open();
void close();
}
public interface OnScrollChageListener {
void onScrollChange(float rate);
}
重写onViewPositionChanged 监听位置的改变,计算上拉过程的比率值0-1。代码如下:
@Override
public void onViewPositionChanged(View changedView, int left, int top, int dx, int dy) {
if (changedView == mBottomView) {
float startPosition = mContentView.getHeight() - mBottomView.getHeight();
float endPosition = mContentView.getHeight() - mBottomBorderHeigth;
float totalLength = endPosition - startPosition;
float rate = 1 - ((top - startPosition) / totalLength);
if (mScrollChageListener != null) {
mScrollChageListener.onScrollChange(rate);
}
}
}
到此,整个过程就走一遍了。下面放上完整代码:
/**
* @作 用:上拉的抽屉布局
* @创 建 人: linguoding 邮箱:[email protected]
* @日 期: 2016年10月28日 14:13
*/
public class PullUpDragLayout extends ViewGroup {
private ViewDragHelper mViewDragHelper;//拖拽帮助类
private View mBottomView;//底部内容View
private View mContentView;//内容View
LayoutInflater mLayoutInflater;
private int mBottomBorderHeigth = 20;//底部边界凸出的高度
private Point mAutoBackBottomPos = new Point();
private Point mAutoBackTopPos = new Point();
private int mBoundTopY;
private boolean isOpen;
private OnStateListener mOnStateListener;
private OnScrollChageListener mScrollChageListener;
public void setOnStateListener(OnStateListener onStateListener) {
mOnStateListener = onStateListener;
}
public void setScrollChageListener(OnScrollChageListener scrollChageListener) {
mScrollChageListener = scrollChageListener;
}
public interface OnStateListener {
void open();
void close();
}
public interface OnScrollChageListener {
void onScrollChange(float rate);
}
public PullUpDragLayout(Context context) {
this(context, null, 0);
}
public PullUpDragLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public PullUpDragLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
init(context);
initCustomAttrs(context, attrs);
}
private void init(Context context) {
mLayoutInflater = LayoutInflater.from(context);
mViewDragHelper = ViewDragHelper.create(this, 1.0f,mCallback);
}
ViewDragHelper.Callback mCallback = new ViewDragHelper.Callback() {
@Override
public boolean tryCaptureView(View child, int pointerId) {
return mBottomView == child;
}
@Override
public int getViewHorizontalDragRange(View child) {
return getMeasuredWidth() - child.getMeasuredWidth();
}
@Override
public int getViewVerticalDragRange(View child) {
return getMeasuredHeight() - child.getMeasuredHeight();
}
@Override
public int clampViewPositionHorizontal(View child, int left, int dx) {
final int leftBound = getPaddingLeft();
final int rightBound = getWidth() - mBottomView.getWidth() - leftBound;
final int newLeft = Math.min(Math.max(left, leftBound), rightBound);
return newLeft;
}
@Override
public int clampViewPositionVertical(View child, int top, int dy) {
int topBound = mContentView.getHeight() - mBottomView.getHeight();
int bottomBound = mContentView.getHeight() - mBottomBorderHeigth;
return Math.min(bottomBound, Math.max(top, topBound));
}
@Override
public void onViewPositionChanged(View changedView, int left, int top, int dx, int dy) {
if (changedView == mBottomView) {
float startPosition = mContentView.getHeight() - mBottomView.getHeight();
float endPosition = mContentView.getHeight() - mBottomBorderHeigth;
float totalLength = endPosition - startPosition;
float rate = 1 - ((top - startPosition) / totalLength);
if (mScrollChageListener != null) {
mScrollChageListener.onScrollChange(rate);
}
}
}
//手指释放的时候回调
@Override
public void onViewReleased(View releasedChild, float xvel, float yvel) {
if (releasedChild == mBottomView) {
if (releasedChild.getY() < mBoundTopY || yvel <= -1000) {
mViewDragHelper.settleCapturedViewAt(mAutoBackTopPos.x, mAutoBackTopPos.y);
isOpen = true;
if (mOnStateListener != null) mOnStateListener.open();
} else if (releasedChild.getY() >= mBoundTopY || yvel >= 1000) {
mViewDragHelper.settleCapturedViewAt(mAutoBackBottomPos.x, mAutoBackBottomPos.y);
isOpen = false;
if (mOnStateListener != null) mOnStateListener.close();
}
invalidate();
}
}
};
public boolean isOpen() {
return isOpen;
}
/**
* 切换底部View
*/
public void toggleBottomView() {
if (isOpen) {
mViewDragHelper.smoothSlideViewTo(mBottomView, mAutoBackBottomPos.x, mAutoBackBottomPos.y);
if (mOnStateListener != null) mOnStateListener.close();
} else {
mViewDragHelper.smoothSlideViewTo(mBottomView, mAutoBackTopPos.x, mAutoBackTopPos.y);
if (mOnStateListener != null) mOnStateListener.open();
}
invalidate();
isOpen = !isOpen;
}
private void initCustomAttrs(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
TypedArray typedArray = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.PullUpDragLayout);
if (typedArray != null) {
if (typedArray.hasValue(R.styleable.PullUpDragLayout_PullUpDrag_ContentView)) {
inflateContentView(typedArray.getResourceId(R.styleable.PullUpDragLayout_PullUpDrag_ContentView, 0));
}
if (typedArray.hasValue(R.styleable.PullUpDragLayout_PullUpDrag_BottomView)) {
inflateBottomView(typedArray.getResourceId(R.styleable.PullUpDragLayout_PullUpDrag_BottomView, 0));
}
if (typedArray.hasValue(R.styleable.PullUpDragLayout_PullUpDrag_BottomBorderHeigth)) {
mBottomBorderHeigth = (int) typedArray.getDimension(R.styleable.PullUpDragLayout_PullUpDrag_BottomBorderHeigth, 20);
}
typedArray.recycle();
}
}
private void inflateContentView(int resourceId) {
mContentView = mLayoutInflater.inflate(resourceId, this, true);
}
private void inflateBottomView(int resourceId) {
mBottomView = mLayoutInflater.inflate(resourceId, this, true);
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
mContentView = getChildAt(0);
mBottomView = getChildAt(1);
measureChild(mBottomView, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
int bottomViewHeight = mBottomView.getMeasuredHeight();
measureChild(mContentView, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
int contentHeight = mContentView.getMeasuredHeight();
setMeasuredDimension(MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec), bottomViewHeight + contentHeight + getPaddingBottom() + getPaddingTop());
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
mContentView = getChildAt(0);
mBottomView = getChildAt(1);
mContentView.layout(getPaddingLeft(), getPaddingTop(), getWidth() - getPaddingRight(), mContentView.getMeasuredHeight());
mBottomView.layout(getPaddingLeft(), mContentView.getHeight() - mBottomBorderHeigth, getWidth() - getPaddingRight(), getMeasuredHeight() - mBottomBorderHeigth);
mAutoBackBottomPos.x = mBottomView.getLeft();
mAutoBackBottomPos.y = mBottomView.getTop();
mAutoBackTopPos.x = mBottomView.getLeft();
mAutoBackTopPos.y = mContentView.getHeight() - mBottomView.getHeight();
mBoundTopY = mContentView.getHeight() - mBottomView.getHeight() / 2;
}
@Override
public boolean onInterceptTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
return mViewDragHelper.shouldInterceptTouchEvent(ev);
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
mViewDragHelper.processTouchEvent(event);
return true;
}
@Override
public void computeScroll() {
if (mViewDragHelper.continueSettling(true)) {
invalidate();
}
}
}
XML中使用:
效果大概可以是这样的:
展开时:
大概就是这样的...............................