Java默认的序列化机制效率很低、序列化后的码流也较大,所以涌现出了非常多的优秀的Java序列化框架,例如:hessian、protobuf、thrift、protostuff、kryo、msgpack、avro、fst 等等。
本文主要介绍hessian、kryo、protostuff的使用,其它的可以去查看官方documentation。
使用
hessian
maven依赖:
com.caucho
hessian
4.0.38
序列化,代码如下:
public void serialize(){
Car car = new Car();
car.setName("X5");
car.setBrand("BMW");
car.setPrice(64.5);
car.setSpeed(200);
System.out.println("序列化:"+car);
//Serialization
Hessian2Output out = null;
try {
File objectFile = new File("car.bin");
out = new Hessian2Output(new FileOutputStream(objectFile));
out.startMessage();
out.writeObject(car);
out.completeMessage();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
try {
out.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
反序列化
public void deserialize(){
InputStream bin = null;
Hessian2Input in = null;
try {
File objectFile = new File("car.bin");
bin = new FileInputStream(objectFile);
in = new Hessian2Input(bin);
in.startMessage();
Car car = (Car) in.readObject();
in.completeMessage();
System.out.println("反序列化:"+car);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
try {
in.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
bin.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
kryo
maven依赖:
com.esotericsoftware
kryo
4.0.0
kryo 序列化如下:
Author author = new Author("Ricky", 28);
System.out.println(author);
Kryo kryo = new Kryo();
// Write Obj to File
Output output = null;
try {
File file = new File("author.bin");
output = new Output(new FileOutputStream(file));
kryo.writeObject(output, author);
output.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (KryoException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
IoUtils.closeQuietly(output);
}
反序列化如下:
// Read Obj from File
Input input = null;
try {
File file = new File("author.bin");
input = new Input(new FileInputStream(file));
Author newAuthor = kryo.readObject(input, Author.class);
System.out.println(newAuthor);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (KryoException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
IoUtils.closeQuietly(input);
}
protostuff
maven依赖:
io.protostuff
protostuff-core
1.5.3
io.protostuff
protostuff-runtime
1.5.3
protostuff 序列化如下:
Person person = new Person("ricky", "feng", "[email protected]");
person.setFriends(Arrays.asList("Paul", "Kobe", "James"));
person.setAddress(new Address("湖北省", "武汉市", "武昌区", "珞喻路"));
Map tag = new HashMap<>();
tag.put("aa", "abc");
person.setTag(tag);
Schema schema = RuntimeSchema.getSchema(Person.class);
LinkedBuffer buffer = LinkedBuffer.allocate();
byte[] protostuff = null;
// 序列化
try {
protostuff = ProtostuffIOUtil.toByteArray(person, schema, buffer);
System.out.println("bytes len:"+protostuff.length);
} finally {
buffer.clear();
}
反序列化如下:
byte[] protostuff = ...;
Schema schema = RuntimeSchema.getSchema(Person.class);
// 反序列化
Person p = schema.newMessage();
ProtostuffIOUtil.mergeFrom(protostuff, p, schema);
System.out.println(p);
完整示例源码下载:https://github.com/TiFG/daily-codelab/tree/master/serialization-sample
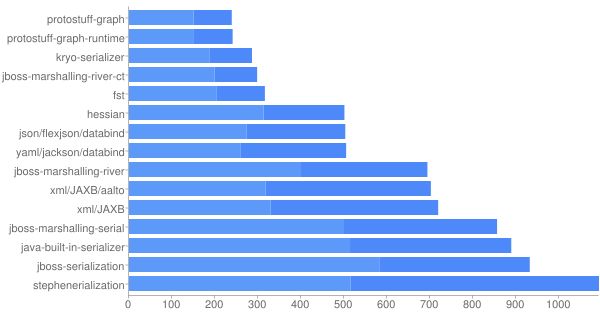
Java序列化框架性能比较
序列化框架Serializers(无共享引用)
- 无循环引用。 一个对象如果被引用两次则会序列化两次
- 没有手工优化
- schema预先已知
Ser Time+Deser Time (ns)
Size, Compressed size in bytes
全对象图序列化(Full Object Graph Serializers)
- 支持全部的object graph读写. Object graph可能包含循环引用.
- 无预先处理, 没有预先的类生成,注册. 所有都运行时产生, 比如使用反射.
- 注意通常不会跨编程语言。 然而JSON/XML格式由于其特殊性可以跨语言.
Ser Time+Deser Time (ns)
Size, Compressed size in bytes
参考
jvm-serializers:https://github.com/eishay/jvm-serializers
jvm-serializers bench-mark:https://github.com/eishay/jvm-serializers/wiki