launchctl 是一个统一的服务管理框架,可以启动、停止和管理进程、应用程序、脚本等。
launchctl 可以通过 plist 文件来指定执行周期性任务。
查看已存在的任务
- ~/Library/LaunchAgents :由用户自己定义的任务项
- /Library/LaunchAgents :由管理员为用户定义的任务项
- /Library/LaunchDaemons :由管理员定义的守护进程任务项
- /System/Library/LaunchAgents :由Mac OS X为用户定义的任务项
- /System/Library/LaunchDaemons :由Mac OS X定义的守护进程任务项
看下电脑中一些应用任务:
上面这些就是目前系统中,一些程序的服务。
我们随便点看查看一些其中的任务配置:
Label
org.getlantern
ProgramArguments
/Applications/Lantern.app/Contents/MacOS/lantern
-startup
RunAtLoad
解读:
Label 对应的 org.getlantern 表示任务名称,必须唯一。
ProgramArguments 表示程序参数,数组的形式,第一个为 需要执行的程序或者脚本等,这里的 /Applications/Lantern.app/Contents/MacOS/lantern 和 -startup 意味着打开程序 lantern 。
RunAtLoad 是个布尔值,表示开启自启项。
因此,该任务配置表示:设置 lantern 应用为开机自起项。
实例
下面我们举个简单的例子演示一下,这里执行一份 python 脚本,保存当前执行的时间。
首先我们需要准备需要执行的脚本任务。
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import datetime
def add(path, content):
with open(path,'a') as f:
f.write(content + '\n')
path = '/Users/luoliang/Documents/项目/PythonProject/Test/content.txt'
now_time = "{}".format(datetime.datetime.now())
add(path, now_time)
然后我们编写 任务配置 plist 文件。
Label
com.test.task
Program
/Users/luoliang/Documents/项目/PythonProject/Test/task.py
StartInterval
30
StandardErrorPath
/Users/luoliang/Desktop/errorlog
最后,我们需要将任务配置放到任务目录中,(这里建议在:~/Library/LaunchAgents )然后启动任务。
开启终端,进入到对应任务配置目录:
// 加载任务
$ launchctl load com.test.task.plist // 进入该目录后执行
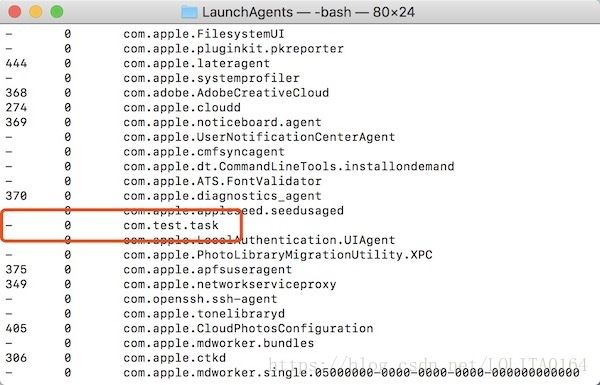
查看任务是否添加:
// 查看任务列表
$ launchctl list
这样,我们的脚本就可以按照指定时刻被系统执行了。
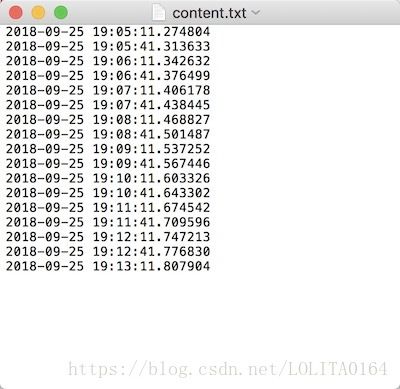
我们检查一下脚本输出目录文件:
上图可以看出,脚本正在以每30秒的间隔不断的被执行。两次执行的时间在1秒内。
launchctl 的一些命令:
// 加载任务
$ launchctl load com.test.task.plist
// 删除任务
$ launchctl unload com.test.task.plist
// 查看任务列表, 使用 grep '任务部分名字' 过滤
$ launchctl list | grep 'com.test.task.plist'
// 开始
$ launchctl start com.test.task.plist
// 停止
$ launchctl stop com.test.task.plist
plist 文件的字段说明
Label
com.uniflor.notifier
Program
/Users/uniflor/script.sh
ProgramArguments
/Users/uniflor/script.sh
StartCalendarInterval
Minute
30
Hour
9
Day
1
Month
5
Weekday
0
StartInterval
30
StandardInPath
/Users/uniflor/run-in.log
StandardOutPath
/Users/uniflor/Bin/run-out.log
StandardErrorPath
/Users/uniflor/Bin/run-err.log
1、Label:对应的需要保证全局唯一性;
2、Program:要运行的程序;
3、ProgramArguments:命令语句
4、StartCalendarInterval:运行的时间,单个时间点使用dict,多个时间点使用 array
5、StartInterval:时间间隔,与StartCalendarInterval使用其一,单位为秒
6、StandardInPath、StandardOutPath、StandardErrorPath:标准的输入输出错误文件,这里建议不要使用 .log 作为后缀,会打不开里面的信息。
补充说明
1、权限问题。
有时候,脚本需要改成可执行的权限,例如:
$ chmod 777 task.py
2、脚本需正常编译
在上述的例子中,python脚本文件最开始的部分有两行说明:
#!/usr/bin/env python // 声明编译环境,即指定编译器
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- // 编码问题
如果你的脚本本身就无法编译通过,更不要说系统去执行了。
如果你的也是python脚本,并且脚本文件本身在项目中,有时候爆出找不到自身目录的错误,那么请保证上面的声明之后,将你的目录移至到 site-packages 中去。
另外,如果你的电脑中存在多个版本的编译器,请将 #!/usr/bin/env python 替换为脚本对应的编译器的绝对路径,否则会出现因编译器版本产生的语法错误。
3、验证脚本的正确性
你可以将执行时间设置为较近的时间,也可以使用下面语句直接执行一次脚本:
// 开始
$ launchctl start com.test.task.plist
参考
1、Mac中的定时任务利器:launchctl
2、Mac使用Launchd命令行lauchctl操作服务的简单用法
3、mac使用launchctl定时运行程序