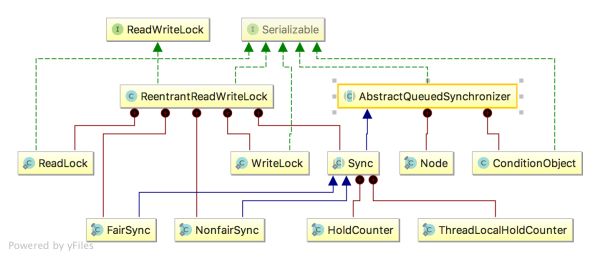
- ReentrantReadWriteLock实现了接口ReadWriteLock,同时ReentrantReadWriteLock也是基于 AbstractQueuedSynchronizer 实现的。
一. 介绍:
1. 获取顺序:
此类不会将读取者优先或写入者优先强加给锁访问的排序。但支持可选的公平模式。
1)非公平模式(默认):
当使用一个非公平模式时,读和写的锁的获得顺序不是特定的,取决于重入的约束。连续竞争的非公平锁可能无限期地推迟一个或多个reader或writer线程,但吞吐量通常要高于公平锁。
2) 公平模式:
线程利用一个近似到达顺序的策略来争夺进入。当释放当前保持的锁时,以下情况二选一:
1.可以为等待时间最长的单个writer线程分配写入锁。
2.如果有一组等待时间大于所有正在等待的writer线程的reader,将为该组分配读者锁。
对于一个试图获取公平读锁的线程:如果写锁没被释放,或有一个等待的读线程,这时这个试图获取公平读锁的线程将会被阻塞。这个线程(试图获得读锁的线程)只有在最老的等待的写线程获得并释放写锁,才能获得读锁。当然,如果一个等待的写线程放弃了它的等待,随着写锁的释放,一个或更多的读线程将会获取读锁。
对于一个试图获取公平写锁的线程: 除非读锁和写锁都是空闲的(暗示没有等待线程),不然这个线程会被阻塞。 (注意非阻塞的ReadLock的tryLock()方法和WriteLock的tryLock()方法不会遵从公平锁的设置,并且将会立即尝试获取锁,如何能获得锁,无论有没有其他等待线程都会获得锁。)
2. 重入:
此锁允许reader和writer按照 ReentrantLock 的样式重新获取读取锁或写入锁。在写入线程保持的所有写入锁都已经释放后,才允许重入reader使用读取锁。writer可以获取读取锁,但reader不能获取写入锁。
3.锁降级:
重入还允许从写入锁降级为读取锁,实现方式是:先获取写入锁,然后获取读取锁,最后释放写入锁。但是,从读取锁升级到写入锁是不可能的。
锁降级的例子:
class CachedData {
Object data;
volatile boolean cacheValid;
final ReentrantReadWriteLock rwl = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
void processCachedData() {
rwl.readLock().lock();
if (!cacheValid) {
// Must release read lock before acquiring write lock
rwl.readLock().unlock();
rwl.writeLock().lock();
try {
// Recheck state because another thread might have
// acquired write lock and changed state before we did.
if (!cacheValid) {
data = ...
cacheValid = true;
}
// Downgrade by acquiring read lock before releasing write lock
rwl.readLock().lock();
} finally {
rwl.writeLock().unlock(); // Unlock write, still hold read
}
}
try {
use(data);
} finally {
rwl.readLock().unlock();
}
}
}
}
4.锁获取的中断:
读取锁和写入锁都支持锁获取期间的中断。
5.Condition 支持:
写入锁提供了一个 Condition 实现,对于写入锁来说,该实现的行为与ReentrantLock.newCondition() 提供的 Condition 实现对 ReentrantLock 所做的行为相同。当然,此 Condition 只能用于写入锁。读取锁不支持 Condition,readLock().newCondition() 会抛出 UnsupportedOperationException。
ReentrantReadWriteLocks能被用于提升某些集合的某些操作的并发性。特别是当集合预计会变大而且读线程比写线程多,并且操作的开销大于同步的开销,这样会体现ReentrantReadWriteLocks的价值。如下面TreeMap预计会变大而且会有大量的并发访问:
class RWDictionary {
private final Map m = new TreeMap();
private final ReentrantReadWriteLock rwl = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
private final Lock r = rwl.readLock();
private final Lock w = rwl.writeLock();
public Data get(String key) {
r.lock();
try { return m.get(key); }
finally { r.unlock(); }
}
public String[] allKeys() {
r.lock();
try { return m.keySet().toArray(); }
finally { r.unlock(); }
}
public Data put(String key, Data value) {
w.lock();
try { return m.put(key, value); }
finally { w.unlock(); }
}
public void clear() {
w.lock();
try { m.clear(); }
finally { w.unlock(); }
}
}
}
6.监测:
此类支持一些确定是读取锁还是写入锁的方法。这些方法设计用于监视系统状态,而不是同步控制。
从类的层次关系看,ReentrantReadWriteLock与ReentrantLock没有一点关系。
ReentrantReadWriteLock实现了接口ReadWriteLock。
ReentrantReadWriteLock通过一系列内部类和工具类AbstractQueuedSynchronizer实现读锁,写锁,以及线程的同步。
ReentrantReadWriteLock有5个内部类分别是,ReadLock, WriteLock, Sync,FairSync,
NofairSync。其中FairSync和NofairSync是Sync的子类。Sync有两个内部类分别是HoldCounter和ThreadLocalHoldCounter。
二.状态保存:
1. 保存获得读锁的线程数和写锁重入的状态
ReentrantLock用一个int变量c保存重入的次数,ReentrantReadWriteLock也有一个c变量,但是要保存获得读锁的线程数和写锁重入状态。解决方案,掰成两半:
AQS 的状态是32位(int 类型)的,辦成两份,读锁用高16位,表示持有读锁的线程数(sharedCount),写锁低16位,表示写锁的重入次数 (exclusiveCount)。状态值为 0 表示锁空闲,sharedCount不为 0 表示分配了读锁,exclusiveCount 不为 0 表示分配了写锁,sharedCount和exclusiveCount 肯定不会同时不为 0。
abstract static class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer {
//
//
static final int SHARED_SHIFT = 16;
// 由于读锁用高位部分,所以读锁个数加1,其实是状态值加 2^16
static final int SHARED_UNIT = (1 << SHARED_SHIFT);
// 写锁的可重入的最大次数、读锁允许的最大数量
static final int MAX_COUNT = (1 << SHARED_SHIFT) - 1;
// 写锁的掩码,用于状态的低16位有效值
static final int EXCLUSIVE_MASK = (1 << SHARED_SHIFT) - 1;
// 读锁计数,当前持有读锁的线程数
static int sharedCount(int c) { return c >>> SHARED_SHIFT; }
// 写锁的计数,也就是它的重入次数
static int exclusiveCount(int c) { return c & EXCLUSIVE_MASK; }
}
2.读锁重入计数:
abstract static class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer {
/**
* 每个线程特定的 read 持有计数。存放在ThreadLocal,不需要是线程安全的。
*/
static final class HoldCounter {
int count = 0;
// 使用id而不是引用是为了避免保留垃圾。注意这是个常量。
final long tid = Thread.currentThread().getId();
}
/**
* 采用继承是为了重写 initialValue 方法,这样就不用进行这样的处理:
* 如果ThreadLocal没有当前线程的计数,则new一个,再放进ThreadLocal里。
* 可以直接调用 get。
* */
static final class ThreadLocalHoldCounter
extends ThreadLocal {
public HoldCounter initialValue() {
return new HoldCounter();
}
}
/**
* 保存当前线程重入读锁的次数的容器。在读锁重入次数为 0 时移除。
*/
private transient ThreadLocalHoldCounter readHolds;
/**
* 最近一个成功获取读锁的线程的计数。这省却了ThreadLocal查找,
* 通常情况下,下一个释放线程是最后一个获取线程。这不是 volatile 的,
* 因为它仅用于试探的,线程进行缓存也是可以的
* (因为判断是否是当前线程是通过线程id来比较的)。
*/
private transient HoldCounter cachedHoldCounter;
/**
* firstReader是这样一个特殊线程:它是最后一个把 共享计数 从 0 改为 1 的
* (在锁空闲的时候),而且从那之后还没有释放读锁的。如果不存在则为null。
* firstReaderHoldCount 是 firstReader 的重入计数。
*
* firstReader 不能导致保留垃圾,因此在 tryReleaseShared 里设置为null,
* 除非线程异常终止,没有释放读锁。
*
* 作用是在跟踪无竞争的读锁计数时非常便宜。
*
* firstReader及其计数firstReaderHoldCount是不会放入 readHolds 的。
*/
private transient Thread firstReader = null;
private transient int firstReaderHoldCount;
Sync() {
readHolds = new ThreadLocalHoldCounter();
setState(getState()); // 确保 readHolds 的内存可见性,利用 volatile 写的内存语义。
}
}
三.读锁lock方法操作流程和调用分析:
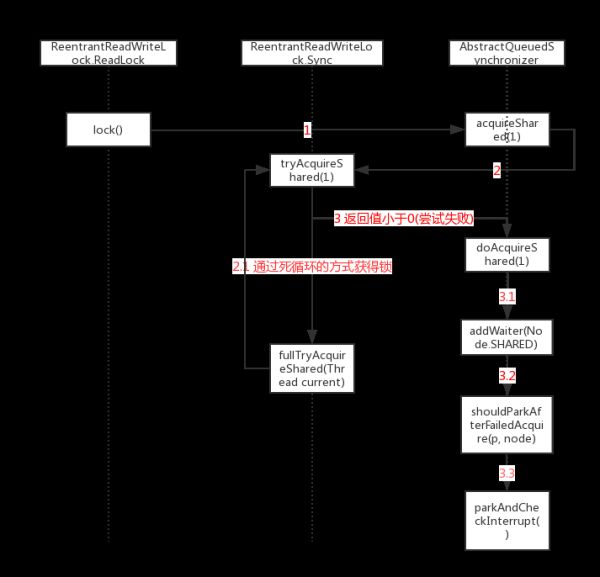
1.ReadLock的lock()方法的类关系图:
1) lock():
读锁发起锁资源请求
/**
* Acquires the read lock.
*
* Acquires the read lock if the write lock is not held by
* another thread and returns immediately.
*
*
If the write lock is held by another thread then
* the current thread becomes disabled for thread scheduling
* purposes and lies dormant until the read lock has been acquired.
*/
public void lock() {
sync.acquireShared(1);
}
2. acquireShared(1):获取共享锁,方法tryAcquireShared()尝试获取锁资源,如果没有获得再通过doAcquireShared()不断尝试,直到获得锁资源。
/*
* Acquires in shared mode, ignoring interrupts. Implemented by
* first invoking at least once {@link #tryAcquireShared},
* returning on success. Otherwise the thread is queued, possibly
* repeatedly blocking and unblocking, invoking {@link
* #tryAcquireShared} until success.
*
* @param arg the acquire argument. This value is conveyed to
* {@link #tryAcquireShared} but is otherwise uninterpreted
* and can represent anything you like.
*/
public final void acquireShared(int arg) {
if (tryAcquireShared(arg) < 0)
doAcquireShared(arg);
}
3. tryAcquireShared():尝试获得共享锁。
1) 如果有另一个线程获得了写锁还没释放,则获取失败。
2) 如果没有写锁被持有,这个线程请求是否被队列策略阻塞。如果没有被策略阻塞,尝试通过cas和更新数量去获得锁资源。主要这个方法只能处理线程第一次获得读锁资源的情况,不能处理重入的情况。重入的情况的处理延迟到完整版的获取读锁资源方法处理(fullTryAcquireShared(current))。
3) 如果第二步中,获取读锁被队列策略阻塞或CAS尝试失败,或读锁数量饱和,会进入方法fullTryAcquireShared():
// 参数变为 unused 是因为读锁的重入计数是内部维护的。
protected final int tryAcquireShared(int unused) {
/*
* Walkthrough:
* 1. If write lock held by another thread, fail.
* 2. Otherwise, this thread is eligible for
* lock wrt state, so ask if it should block
* because of queue policy. If not, try
* to grant by CASing state and updating count.
* Note that step does not check for reentrant
* acquires, which is postponed to full version
* to avoid having to check hold count in
* the more typical non-reentrant case.
* 3. If step 2 fails either because thread
* apparently not eligible or CAS fails or count
* saturated, chain to version with full retry loop.
*/
Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
// 这个if语句是说:持有写锁的线程可以获取读锁。
if (exclusiveCount(c) != 0 && // 已分配了写锁
getExclusiveOwnerThread() != current) // 且当前线程不是持有写锁的线程
return -1;
int r = sharedCount(c); // 取读锁计数
if (!readerShouldBlock() && // 由子类根据其公平策略决定是否允许获取读锁
r < MAX_COUNT && // 读锁数量还没达到最大值
// 尝试获取读锁。注意读线程计数的单位是 2^16
compareAndSetState(c, c + SHARED_UNIT)) {
// 成功获取读锁
// 注意下面对firstReader的处理:firstReader是不会放到readHolds里的
// 这样,在读锁只有一个的情况下,就避免了查找readHolds。
if (r == 0) { // 是 firstReader,计数不会放入 readHolds。
firstReader = current;
firstReaderHoldCount = 1;
} else if (firstReader == current) { // firstReader 重入
firstReaderHoldCount++;
} else {
// 非 firstReader 读锁重入计数更新
HoldCounter rh = cachedHoldCounter; // 首先访问缓存
if (rh == null || rh.tid != current.getId())
cachedHoldCounter = rh = readHolds.get();
else if (rh.count == 0)
readHolds.set(rh);
rh.count++;
}
return 1;
}
// 获取读锁失败,放到循环里重试。
return fullTryAcquireShared(current);
}
4) fullTryAcquireShared(current):
这个方法是会不断重试让当前线程获得读锁资源。处理了tryAcquireShared方法没有处理的cas赋值失败和重入读锁的情况。
/**
* Full version of acquire for reads, that handles CAS misses
* and reentrant reads not dealt with in tryAcquireShared.
*/
final int fullTryAcquireShared(Thread current) {
/*
* This code is in part redundant with that in
* tryAcquireShared but is simpler overall by not
* complicating tryAcquireShared with interactions between
* retries and lazily reading hold counts.
*/
HoldCounter rh = null;
for (;;) {
int c = getState();
if (exclusiveCount(c) != 0) {
if (getExclusiveOwnerThread() != current)
return -1;
// else we hold the exclusive lock; blocking here
// would cause deadlock.
} else if (readerShouldBlock()) {
// Make sure we're not acquiring read lock reentrantly
if (firstReader == current) {
// assert firstReaderHoldCount > 0;
} else {
if (rh == null) {
rh = cachedHoldCounter;
if (rh == null || rh.tid != getThreadId(current)) {
rh = readHolds.get();
if (rh.count == 0)
readHolds.remove();
}
}
if (rh.count == 0)
return -1;
}
}
if (sharedCount(c) == MAX_COUNT)
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
if (compareAndSetState(c, c + SHARED_UNIT)) {
if (sharedCount(c) == 0) {
firstReader = current;
firstReaderHoldCount = 1;
} else if (firstReader == current) {
firstReaderHoldCount++;
} else {
if (rh == null)
rh = cachedHoldCounter;
if (rh == null || rh.tid != getThreadId(current))
rh = readHolds.get();
else if (rh.count == 0)
readHolds.set(rh);
rh.count++;
cachedHoldCounter = rh; // cache for release
}
return 1;
}
}
}
5) doAcquireShared():
step 1:addWaiter(Node.SHARED)。当 tryAcquireShared()尝试获得共享锁失败返回负数时,线程进入等待读锁的队列。
step 2:node.predecessor()。判断当前线程节点的前驱节点是否是头节点,是头结点就调用tryAcquireShared(arg)再尝试获得一次锁资源。
/**
* Acquires in shared uninterruptible mode.
* @param arg the acquire argument
*/
private void doAcquireShared(int arg) {
final Node node = addWaiter(Node.SHARED);
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head) {
int r = tryAcquireShared(arg);
if (r >= 0) {
setHeadAndPropagate(node, r);
p.next = null; // help GC
if (interrupted)
selfInterrupt();
failed = false;
return;
}
}
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
6) addWaiter(Node mode):把当前线程包装成Node,放入队列。
/**
* Creates and enqueues node for current thread and given mode.
*
* @param mode Node.EXCLUSIVE for exclusive, Node.SHARED for shared
* @return the new node
*/
private Node addWaiter(Node mode) {
Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode);
// Try the fast path of enq; backup to full enq on failure
Node pred = tail;
if (pred != null) {
node.prev = pred;
if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) {
pred.next = node;
return node;
}
}
enq(node);
return node;
}
7) parkAndCheckInterrupt():对于暂时不能获取读锁资源的线程进行阻塞。
/**
* Convenience method to park and then check if interrupted
*
* @return {@code true} if interrupted
*/
private final boolean parkAndCheckInterrupt() {
LockSupport.park(this);
return Thread.interrupted();
}
四.读锁unlock方法操作流程和调用分析:
0)unlock():
/**
* Attempts to release this lock.
*
* If the number of readers is now zero then the lock
* is made available for write lock attempts.
*/
public void unlock() {
sync.releaseShared(1);
}
1) releaseShared(int arg)
/**
* Releases in shared mode. Implemented by unblocking one or more
* threads if {@link #tryReleaseShared} returns true.
*
* @param arg the release argument. This value is conveyed to
* {@link #tryReleaseShared} but is otherwise uninterpreted
* and can represent anything you like.
* @return the value returned from {@link #tryReleaseShared}
*/
public final boolean releaseShared(int arg) {
if (tryReleaseShared(arg)) {
doReleaseShared();
return true;
}
return false;
}
2) tryReleaseShared(int unused)
protected final boolean tryReleaseShared(int unused) {
Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
// 清理firstReader缓存 或 readHolds里的重入计数
if (firstReader == current) {
// assert firstReaderHoldCount > 0;
if (firstReaderHoldCount == 1)
firstReader = null;
else
firstReaderHoldCount--;
} else {
HoldCounter rh = cachedHoldCounter;
if (rh == null || rh.tid != getThreadId(current))
rh = readHolds.get();
int count = rh.count;
if (count <= 1) {
// 没释放前重入是1,就完全释放读锁
readHolds.remove();
if (count <= 0)
throw unmatchedUnlockException();
}
--rh.count;// 主要用于重入退出
}
// 循环在CAS更新状态值,主要是把读锁数量减 1
for (;;) {
int c = getState();
//
int nextc = c - SHARED_UNIT;//SHARED_UNIT表示高位的1
if (compareAndSetState(c, nextc))
// Releasing the read lock has no effect on readers,
// but it may allow waiting writers to proceed if
// both read and write locks are now free.
return nextc == 0;
}
}
3)doReleaseShared():
* Release action for shared mode -- signals successor and ensures
* propagation. (Note: For exclusive mode, release just amounts
* to calling unparkSuccessor of head if it needs signal.)
*/
private void doReleaseShared() {
/*
* Ensure that a release propagates, even if there are other
* in-progress acquires/releases. This proceeds in the usual
* way of trying to unparkSuccessor of head if it needs
* signal. But if it does not, status is set to PROPAGATE to
* ensure that upon release, propagation continues.
* Additionally, we must loop in case a new node is added
* while we are doing this. Also, unlike other uses of
* unparkSuccessor, we need to know if CAS to reset status
* fails, if so rechecking.
*/
for (;;) {
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h != tail) {
int ws = h.waitStatus;
if (ws == Node.SIGNAL) {
if (!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, Node.SIGNAL, 0))
continue; // loop to recheck cases
unparkSuccessor(h);
}
else if (ws == 0 &&
!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, 0, Node.PROPAGATE))
continue; // loop on failed CAS
}
if (h == head) // loop if head changed
break;
}
}
4) unparkSuccessor(h):
/**
* Wakes up node's successor, if one exists.
*
* @param node the node
*/
private void unparkSuccessor(Node node) {
/*
* If status is negative (i.e., possibly needing signal) try
* to clear in anticipation of signalling. It is OK if this
* fails or if status is changed by waiting thread.
*/
int ws = node.waitStatus;
if (ws < 0)
compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, ws, 0);
/*
* Thread to unpark is held in successor, which is normally
* just the next node. But if cancelled or apparently null,
* traverse backwards from tail to find the actual
* non-cancelled successor.
*/
Node s = node.next;
if (s == null || s.waitStatus > 0) {
s = null;
for (Node t = tail; t != null && t != node; t = t.prev)
if (t.waitStatus <= 0)
s = t;
}
if (s != null)
LockSupport.unpark(s.thread);
}