- 【iOS】MVC设计模式
Magnetic_h
iosmvc设计模式objective-c学习ui
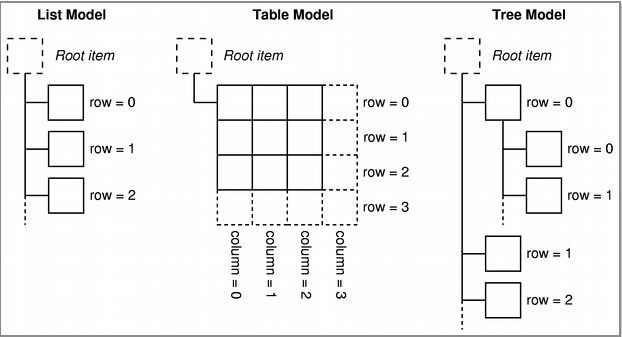
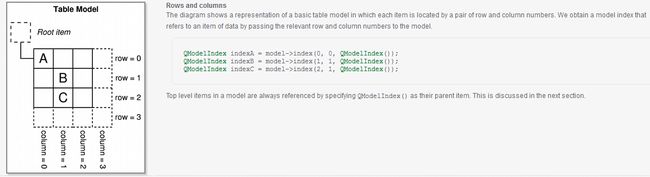
MVC前言如何设计一个程序的结构,这是一门专门的学问,叫做"架构模式"(architecturalpattern),属于编程的方法论。MVC模式就是架构模式的一种。它是Apple官方推荐的App开发架构,也是一般开发者最先遇到、最经典的架构。MVC各层controller层Controller/ViewController/VC(控制器)负责协调Model和View,处理大部分逻辑它将数据从Mod
- Linux下QT开发的动态库界面弹出操作(SDL2)
13jjyao
QT类qt开发语言sdl2linux
需求:操作系统为linux,开发框架为qt,做成需带界面的qt动态库,调用方为java等非qt程序难点:调用方为java等非qt程序,也就是说调用方肯定不带QApplication::exec(),缺少了这个,QTimer等事件和QT创建的窗口将不能弹出(包括opencv也是不能弹出);这与qt调用本身qt库是有本质的区别的思路:1.调用方缺QApplication::exec(),那么我们在接口
- python os.environ_python os.environ 读取和设置环境变量
weixin_39605414
pythonos.environ
>>>importos>>>os.environ.keys()['LC_NUMERIC','GOPATH','GOROOT','GOBIN','LESSOPEN','SSH_CLIENT','LOGNAME','USER','HOME','LC_PAPER','PATH','DISPLAY','LANG','TERM','SHELL','J2REDIR','LC_MONETARY','QT_QPA
- Xinference如何注册自定义模型
玩人工智能的辣条哥
人工智能AI大模型Xinference
环境:Xinference问题描述:Xinference如何注册自定义模型解决方案:1.写个model_config.json,内容如下{"version":1,"context_length":2048,"model_name":"custom-llama-3","model_lang":["en","ch"],"model_ability":["generate","chat"],"model
- K近邻算法_分类鸢尾花数据集
_feivirus_
算法机器学习和数学分类机器学习K近邻
importnumpyasnpimportpandasaspdfromsklearn.datasetsimportload_irisfromsklearn.model_selectionimporttrain_test_splitfromsklearn.metricsimportaccuracy_score1.数据预处理iris=load_iris()df=pd.DataFrame(data=ir
- esp32开发快速入门 8 : MQTT 的快速入门,基于esp32实现MQTT通信
z755924843
ESP32开发快速入门服务器网络运维
MQTT介绍简介MQTT(MessageQueuingTelemetryTransport,消息队列遥测传输协议),是一种基于发布/订阅(publish/subscribe)模式的"轻量级"通讯协议,该协议构建于TCP/IP协议上,由IBM在1999年发布。MQTT最大优点在于,可以以极少的代码和有限的带宽,为连接远程设备提供实时可靠的消息服务。作为一种低开销、低带宽占用的即时通讯协议,使其在物联
- matlab mle 优化,MLE+: Matlab Toolbox for Integrated Modeling, Control and Optimization for Buildings...
Simon Zhong
matlabmle优化
摘要:FollowingunilateralopticnervesectioninadultPVGhoodedrat,theaxonguidancecueephrin-A2isup-regulatedincaudalbutnotrostralsuperiorcolliculus(SC)andtheEphA5receptorisdown-regulatedinaxotomisedretinalgan
- 基于STM32与Qt的自动平衡机器人:从控制到人机交互的的详细设计流程
极客小张
stm32qt机器人物联网人机交互毕业设计c语言
一、项目概述目标和用途本项目旨在开发一款基于STM32控制的自动平衡机器人,结合步进电机和陀螺仪传感器,实现对平衡机器人的精确控制。该机器人可以用于教育、科研、娱乐等多个领域,帮助用户了解自动控制、机器人运动学等相关知识。技术栈关键词STM32单片机步进电机陀螺仪传感器AD采集电路Qt人机界面实时数据监控二、系统架构系统架构设计本项目的系统架构设计包括以下主要组件:控制单元:STM32单片机传感器
- ESP32-C3入门教程 网络篇⑩——基于esp_https_ota和MQTT实现开机主动升级和被动触发升级的OTA功能
小康师兄
ESP32-C3入门教程https服务器esp32OTAMQTT
文章目录一、前言二、软件流程三、部分源码四、运行演示一、前言本文基于VSCodeIDE进行编程、编译、下载、运行等操作基础入门章节请查阅:ESP32-C3入门教程基础篇①——基于VSCode构建HelloWorld教程目录大纲请查阅:ESP32-C3入门教程——导读ESP32-C3入门教程网络篇⑨——基于esp_https_ota实现史上最简单的ESP32OTA远程固件升级功能二、软件流程
- AI大模型的架构演进与最新发展
季风泯灭的季节
AI大模型应用技术二人工智能架构
随着深度学习的发展,AI大模型(LargeLanguageModels,LLMs)在自然语言处理、计算机视觉等领域取得了革命性的进展。本文将详细探讨AI大模型的架构演进,包括从Transformer的提出到GPT、BERT、T5等模型的历史演变,并探讨这些模型的技术细节及其在现代人工智能中的核心作用。一、基础模型介绍:Transformer的核心原理Transformer架构的背景在Transfo
- 使用由 Python 编写的 lxml 实现高性能 XML 解析
hunyxv
python笔记pythonxml
转载自:文章lxml简介Python从来不出现XML库短缺的情况。从2.0版本开始,它就附带了xml.dom.minidom和相关的pulldom以及SimpleAPIforXML(SAX)模块。从2.4开始,它附带了流行的ElementTreeAPI。此外,很多第三方库可以提供更高级别的或更具有python风格的接口。尽管任何XML库都足够处理简单的DocumentObjectModel(DOM
- 漫谈QWidget及其派生类(二)
Caiaolun
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/dbzhang800/article/details/6741344上一部分漫谈QWidget及其派生类(一)介绍了QWidget及其派生类,分:窗口、普通控件两种类型(其实有个Qt::SubWindow没有提,不过本系列中也没有介绍它的打算,因为我不熟)。本文接下来试图看看QLayout与窗口的几何尺寸控制。注意:本文只是试图解释,QLayo
- 【解决内存泄漏的问题】 Qt 框架中的父子对象关系会自动管理内存,父对象会在其销毁时自动销毁所有子对象。
课堂随想
QTqt
修改前的代码这段代码可能会出现内存泄漏问题,主要原因是构造函数中创建的LoginDialog和RegisterDialog对象未在合适的地方被正确释放。具体分析如下:1.构造函数中的问题_login_dlg=newLoginDialog();setCentralWidget(_login_dlg);_login_dlg->show();connect(_login_dlg,&LoginDialog
- 前端three.js的Sprite模拟下雪动画效果
qq_35430208
three.js前端javascript三维场景中下雪效果threejs实现下雪效果
一、效果如图所示:二、原理同下雨一样三、完整代码:index.jsimport*asTHREEfrom'three';import{OrbitControls}from'three/addons/controls/OrbitControls.js';importmodelfrom'./model.js';//模型对象//场景constscene=newTHREE.Scene();scene.add
- 2018-08-16【Swift 4.1】 关于Swift4.0以后调用MJExtension无法模型转换问题
码农happy
1、本人使用swift4.1,弄了一晚上才弄好,结果还是一个小问题真是尴尬,要在model中每个属性前面加上@objcimportUIKitclassUserModel:NSObject{@objcvardix=String()}letdic=["dix":"ffffff"]asNSDictionaryletmodel=UserModel.mj_object(withKeyValues:dic)!
- MacOS Catalina 从源码构建Qt6.2开发库之01: 编译Qt6.2源代码
捕鲸叉
QTmacosc++QT
安装xcode,cmake,ninjabrewinstallnodemac下安装OpenGL库并使之对各项目可见在macOS上安装OpenGL通常涉及到安装一些依赖库,如MGL、GLUT或者是GLEW等,同时确保LLVM的OpenGL框架和相关工具链的兼容性。以下是一个基本的安装步骤,你可以在终端中执行:安装Homebrew(如果还没有安装的话):/bin/bash-c"$(curl-fsSLht
- ComfyUI中的sam模型国内下载方法
jayli517
ComfyUIpythonstablediffusion
was-node-suite-comfyui这个节点安装的时候,有它内部的config配置文件,里面其实给了一些下载地址,配置文件里是这么写的:"sam_model_vith_url":"https://dl.fbaipublicfiles.com/segment_anything/sam_vit_h_4b8939.pth","sam_model_vitl_url":"https://dl.fba
- java的四个层级结构
活跃家族
JAVA
java的四个层级结构首先,最底层的就是dto层,dto层就是所谓的model,dto中定义的是实体类,也就是.class文件,该文件中包含实体类的属性和对应属性的get、set方法;其次,是dao层(dao层的文件习惯以*Mapper命名),dao层会调用dto层,dao层中会定义实际使用到的方法,比如增删改查。一般在dao层下还会有个叫做sqlmap的包,该包下有xml文件,文件内容正是根据之
- 2.8.5Django --8.2 单表操作
寒暄_HX
Django目录:https://www.jianshu.com/p/dc36f62b3dc5Yuan先生-Django模型层(1)Django与SQLAlchemy的ORM操作本质上是一样的,但是语法略有不同,如果是用Django进行开发最好使用原生的ORM或者直接使用原生SQL。创建表app06创建模型在app06中的models.py文件内,新建一个模板。one_exa.app06.mode
- 昇思MindSpore AI框架MindFormers实践3:ChatGLM3-6B对一段文字进行提取
skywalk8163
人工智能项目实践人工智能mindspore
MindSpore和MindFormers安装参见:昇思AI框架实践1:安装MindSpoe和MindFormers_miniconda安装mindspore-CSDN博客使用了MindSpore2.2和MindFormers1.0支持的模型:KeyError:"modelmustbeinodict_keys(['gpt2','gpt2_lora','gpt2_xl','gpt2_xl_lora'
- ResNet的半监督和半弱监督模型
Valar_Morghulis
Billion-scalesemi-supervisedlearningforimageclassificationhttps://arxiv.org/pdf/1905.00546.pdfhttps://github.com/facebookresearch/semi-supervised-ImageNet1K-models/权重在timm中也有:https://hub.fastgit.org/r
- document获取元素的方法
小成语
js平时js
js学习总结----DOM获取元素的方法(8个)DOM:documentobjectmodel文档对象模型DOM就是描述整个html页面中节点关系的图谱,可以如下图理解在DOM中,提供了很多的获取元素的方法和之间关系的属性以及操作这些元素的方法。1、获取页面中元素的方法1)、document.getElementById('元素的ID')在整个文档中,通过元素的ID获取到这个元素对象(获取的是一个
- Android干净架构MVI模板使用指南
井美婵Toby
Android干净架构MVI模板使用指南android-clean-architecture-mvi-boilerplateAforkofourcleanarchitectureboilerplateusingtheModel-View-Intentpattern项目地址:https://gitcode.com/gh_mirrors/an/android-clean-architecture-mv
- 报错 | pydantic.v1.error_wrappers.ValidationError ... subclass of BaseModel expected
程序猿林仔
报错pythonpythonlangchain
文章目录01问题情景02分析问题03阅读源码04解决方案4.1方案1-指定版本安装4.2(通用)方案2-指定v1版本4.3(推荐)方案3-参考源码01问题情景最近在做Langchain的开发,可能是因为我更新了依赖库的版本,在执行下面这部分代码的时候出现了该异常:#出现该异常的代码(仅保留核心逻辑)fromlangchain.output_parsersimportPydanticOutputPa
- Linux删除监听端口进程,linux只端口监听及杀死进程
探旅
Linux删除监听端口进程
itextpdf生成pdf文件一.简介itextpdf是一个开源的允许你去创建和操作PDF文档的库.它使的开发者可以提高web和其他应用来动态地生成或操作PDF文档.通过iText中的Document和PdfWriter类,...QtSizePolicy属性控件的sizePolicy说明控件在布局管理中的缩放方式.Qt提供的控件都有一个合理的缺省sizePolicy,但是这个缺省值有时不能适合所有
- Pyqt5实现listwidget自定义右键菜单
Saudade957
pyqt5前端前端python编程语言
Pyqt5实现listwidget自定义右键菜单基于网上搜到的各种教程失败以后(ps:可能有的可以成功,但是我都没成功),组合了一下一些代码最终成功实现相关内容。首先在ui文件生成的py文件中添加self.listWidget.setContextMenuPolicy(Qt.CustomContextMenu)self.listWidget.customContextMenuRequested.c
- 【十八】【QT开发应用】标签页QTabWidget的常见用法
妖精七七_
QT开发应用qt开发语言
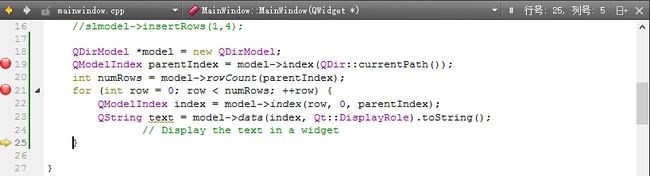
#include"widget.h"//包含自定义的widget头文件#include//包含QHBoxLayout头文件,用于水平布局#include//包含QTabWidget头文件,用于创建标签页控件#include//包含QDebug头文件,用于调试输出widget::widget(QWidget*parent)//widget类的构造函数:QWidget(parent)//调用基类QWi
- 渗透测试的了解
锅盖'awa'
网络安全小白之路安全性测试安全
文章目录概述一、渗透测试分类1.黑盒测试/外部测试2.白盒测试/内部测试3.灰盒测试/组合测试二、渗透测试-目标分类1、主机操作系统渗透2、数据库系统渗透3、应用系统渗透4、网络设备渗透三、渗透测试过程(七个阶段)1.前期交互阶段(Pre-EngagementInteraction)2.情报搜集阶段(InformationGathering)3.威胁建模阶段(ThreatModeling)4.漏洞
- ModuleNotFoundError: No module named ‘timm.layers‘
忽略不计,
BUGpythonYOLO目标检测人工智能深度学习
解决方式:把fromtimm.layersimportDropPath这个修改为fromtimm.models.layersimportDropPath即可。
- 座舱交互的下一个时代
高工智能汽车
交互物联网人工智能
为了满足座舱信息娱乐的更高性能要求,几乎所有的一线品牌都在准备“换芯”。去年开始,不少车型开始推动传统的分布式座舱仪表和中控电子架构进入域控制器时代,高通成为大赢家。今年6月,特斯拉也正式官宣,即将推出的新款ModelS将配备能够运行PS5游戏机性能的AMD芯片,包括专门定制的AMDRyzenCPU和独立的Navi23图形处理器。最新消息,特斯拉将率先在中国市场生产的ModelY高性能版车型换装A
- java封装继承多态等
麦田的设计者
javaeclipsejvmcencapsulatopn
最近一段时间看了很多的视频却忘记总结了,现在只能想到什么写什么了,希望能起到一个回忆巩固的作用。
1、final关键字
译为:最终的
&
- F5与集群的区别
bijian1013
weblogic集群F5
http请求配置不是通过集群,而是F5;集群是weblogic容器的,如果是ejb接口是通过集群。
F5同集群的差别,主要还是会话复制的问题,F5一把是分发http请求用的,因为http都是无状态的服务,无需关注会话问题,类似
- LeetCode[Math] - #7 Reverse Integer
Cwind
java题解MathLeetCodeAlgorithm
原题链接:#7 Reverse Integer
要求:
按位反转输入的数字
例1: 输入 x = 123, 返回 321
例2: 输入 x = -123, 返回 -321
难度:简单
分析:
对于一般情况,首先保存输入数字的符号,然后每次取输入的末位(x%10)作为输出的高位(result = result*10 + x%10)即可。但
- BufferedOutputStream
周凡杨
首先说一下这个大批量,是指有上千万的数据量。
例子:
有一张短信历史表,其数据有上千万条数据,要进行数据备份到文本文件,就是执行如下SQL然后将结果集写入到文件中!
select t.msisd
- linux下模拟按键输入和鼠标
被触发
linux
查看/dev/input/eventX是什么类型的事件, cat /proc/bus/input/devices
设备有着自己特殊的按键键码,我需要将一些标准的按键,比如0-9,X-Z等模拟成标准按键,比如KEY_0,KEY-Z等,所以需要用到按键 模拟,具体方法就是操作/dev/input/event1文件,向它写入个input_event结构体就可以模拟按键的输入了。
linux/in
- ContentProvider初体验
肆无忌惮_
ContentProvider
ContentProvider在安卓开发中非常重要。与Activity,Service,BroadcastReceiver并称安卓组件四大天王。
在android中的作用是用来对外共享数据。因为安卓程序的数据库文件存放在data/data/packagename里面,这里面的文件默认都是私有的,别的程序无法访问。
如果QQ游戏想访问手机QQ的帐号信息一键登录,那么就需要使用内容提供者COnte
- 关于Spring MVC项目(maven)中通过fileupload上传文件
843977358
mybatisspring mvc修改头像上传文件upload
Spring MVC 中通过fileupload上传文件,其中项目使用maven管理。
1.上传文件首先需要的是导入相关支持jar包:commons-fileupload.jar,commons-io.jar
因为我是用的maven管理项目,所以要在pom文件中配置(每个人的jar包位置根据实际情况定)
<!-- 文件上传 start by zhangyd-c --&g
- 使用svnkit api,纯java操作svn,实现svn提交,更新等操作
aigo
svnkit
原文:http://blog.csdn.net/hardwin/article/details/7963318
import java.io.File;
import org.apache.log4j.Logger;
import org.tmatesoft.svn.core.SVNCommitInfo;
import org.tmateso
- 对比浏览器,casperjs,httpclient的Header信息
alleni123
爬虫crawlerheader
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse res) throws ServletException, IOException
{
String type=req.getParameter("type");
Enumeration es=re
- java.io操作 DataInputStream和DataOutputStream基本数据流
百合不是茶
java流
1,java中如果不保存整个对象,只保存类中的属性,那么我们可以使用本篇文章中的方法,如果要保存整个对象 先将类实例化 后面的文章将详细写到
2,DataInputStream 是java.io包中一个数据输入流允许应用程序以与机器无关方式从底层输入流中读取基本 Java 数据类型。应用程序可以使用数据输出流写入稍后由数据输入流读取的数据。
- 车辆保险理赔案例
bijian1013
车险
理赔案例:
一货运车,运输公司为车辆购买了机动车商业险和交强险,也买了安全生产责任险,运输一车烟花爆竹,在行驶途中发生爆炸,出现车毁、货损、司机亡、炸死一路人、炸毁一间民宅等惨剧,针对这几种情况,该如何赔付。
赔付建议和方案:
客户所买交强险在这里不起作用,因为交强险的赔付前提是:“机动车发生道路交通意外事故”;
如果是交通意外事故引发的爆炸,则优先适用交强险条款进行赔付,不足的部分由商业
- 学习Spring必学的Java基础知识(5)—注解
bijian1013
javaspring
文章来源:http://www.iteye.com/topic/1123823,整理在我的博客有两个目的:一个是原文确实很不错,通俗易懂,督促自已将博主的这一系列关于Spring文章都学完;另一个原因是为免原文被博主删除,在此记录,方便以后查找阅读。
有必要对
- 【Struts2一】Struts2 Hello World
bit1129
Hello world
Struts2 Hello World应用的基本步骤
创建Struts2的Hello World应用,包括如下几步:
1.配置web.xml
2.创建Action
3.创建struts.xml,配置Action
4.启动web server,通过浏览器访问
配置web.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="
- 【Avro二】Avro RPC框架
bit1129
rpc
1. Avro RPC简介 1.1. RPC
RPC逻辑上分为二层,一是传输层,负责网络通信;二是协议层,将数据按照一定协议格式打包和解包
从序列化方式来看,Apache Thrift 和Google的Protocol Buffers和Avro应该是属于同一个级别的框架,都能跨语言,性能优秀,数据精简,但是Avro的动态模式(不用生成代码,而且性能很好)这个特点让人非常喜欢,比较适合R
- lua set get cookie
ronin47
lua cookie
lua:
local access_token = ngx.var.cookie_SGAccessToken
if access_token then
ngx.header["Set-Cookie"] = "SGAccessToken="..access_token.."; path=/;Max-Age=3000"
end
- java-打印不大于N的质数
bylijinnan
java
public class PrimeNumber {
/**
* 寻找不大于N的质数
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n=100;
PrimeNumber pn=new PrimeNumber();
pn.printPrimeNumber(n);
System.out.print
- Spring源码学习-PropertyPlaceholderHelper
bylijinnan
javaspring
今天在看Spring 3.0.0.RELEASE的源码,发现PropertyPlaceholderHelper的一个bug
当时觉得奇怪,上网一搜,果然是个bug,不过早就有人发现了,且已经修复:
详见:
http://forum.spring.io/forum/spring-projects/container/88107-propertyplaceholderhelper-bug
- [逻辑与拓扑]布尔逻辑与拓扑结构的结合会产生什么?
comsci
拓扑
如果我们已经在一个工作流的节点中嵌入了可以进行逻辑推理的代码,那么成百上千个这样的节点如果组成一个拓扑网络,而这个网络是可以自动遍历的,非线性的拓扑计算模型和节点内部的布尔逻辑处理的结合,会产生什么样的结果呢?
是否可以形成一种新的模糊语言识别和处理模型呢? 大家有兴趣可以试试,用软件搞这些有个好处,就是花钱比较少,就算不成
- ITEYE 都换百度推广了
cuisuqiang
GoogleAdSense百度推广广告外快
以前ITEYE的广告都是谷歌的Google AdSense,现在都换成百度推广了。
为什么个人博客设置里面还是Google AdSense呢?
都知道Google AdSense不好申请,这在ITEYE上也不是讨论了一两天了,强烈建议ITEYE换掉Google AdSense。至少,用一个好申请的吧。
什么时候能从ITEYE上来点外快,哪怕少点
- 新浪微博技术架构分析
dalan_123
新浪微博架构
新浪微博在短短一年时间内从零发展到五千万用户,我们的基层架构也发展了几个版本。第一版就是是非常快的,我们可以非常快的实现我们的模块。我们看一下技术特点,微博这个产品从架构上来分析,它需要解决的是发表和订阅的问题。我们第一版采用的是推的消息模式,假如说我们一个明星用户他有10万个粉丝,那就是说用户发表一条微博的时候,我们把这个微博消息攒成10万份,这样就是很简单了,第一版的架构实际上就是这两行字。第
- 玩转ARP攻击
dcj3sjt126com
r
我写这片文章只是想让你明白深刻理解某一协议的好处。高手免看。如果有人利用这片文章所做的一切事情,盖不负责。 网上关于ARP的资料已经很多了,就不用我都说了。 用某一位高手的话来说,“我们能做的事情很多,唯一受限制的是我们的创造力和想象力”。 ARP也是如此。 以下讨论的机子有 一个要攻击的机子:10.5.4.178 硬件地址:52:54:4C:98
- PHP编码规范
dcj3sjt126com
编码规范
一、文件格式
1. 对于只含有 php 代码的文件,我们将在文件结尾处忽略掉 "?>" 。这是为了防止多余的空格或者其它字符影响到代码。例如:<?php$foo = 'foo';2. 缩进应该能够反映出代码的逻辑结果,尽量使用四个空格,禁止使用制表符TAB,因为这样能够保证有跨客户端编程器软件的灵活性。例
- linux 脱机管理(nohup)
eksliang
linux nohupnohup
脱机管理 nohup
转载请出自出处:http://eksliang.iteye.com/blog/2166699
nohup可以让你在脱机或者注销系统后,还能够让工作继续进行。他的语法如下
nohup [命令与参数] --在终端机前台工作
nohup [命令与参数] & --在终端机后台工作
但是这个命令需要注意的是,nohup并不支持bash的内置命令,所
- BusinessObjects Enterprise Java SDK
greemranqq
javaBOSAPCrystal Reports
最近项目用到oracle_ADF 从SAP/BO 上调用 水晶报表,资料比较少,我做一个简单的分享,给和我一样的新手 提供更多的便利。
首先,我是尝试用JAVA JSP 去访问的。
官方API:http://devlibrary.businessobjects.com/BusinessObjectsxi/en/en/BOE_SDK/boesdk_ja
- 系统负载剧变下的管控策略
iamzhongyong
高并发
假如目前的系统有100台机器,能够支撑每天1亿的点击量(这个就简单比喻一下),然后系统流量剧变了要,我如何应对,系统有那些策略可以处理,这里总结了一下之前的一些做法。
1、水平扩展
这个最容易理解,加机器,这样的话对于系统刚刚开始的伸缩性设计要求比较高,能够非常灵活的添加机器,来应对流量的变化。
2、系统分组
假如系统服务的业务不同,有优先级高的,有优先级低的,那就让不同的业务调用提前分组
- BitTorrent DHT 协议中文翻译
justjavac
bit
前言
做了一个磁力链接和BT种子的搜索引擎 {Magnet & Torrent},因此把 DHT 协议重新看了一遍。
BEP: 5Title: DHT ProtocolVersion: 3dec52cb3ae103ce22358e3894b31cad47a6f22bLast-Modified: Tue Apr 2 16:51:45 2013 -070
- Ubuntu下Java环境的搭建
macroli
java工作ubuntu
配置命令:
$sudo apt-get install ubuntu-restricted-extras
再运行如下命令:
$sudo apt-get install sun-java6-jdk
待安装完毕后选择默认Java.
$sudo update- alternatives --config java
安装过程提示选择,输入“2”即可,然后按回车键确定。
- js字符串转日期(兼容IE所有版本)
qiaolevip
TODateStringIE
/**
* 字符串转时间(yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss)
* result (分钟)
*/
stringToDate : function(fDate){
var fullDate = fDate.split(" ")[0].split("-");
var fullTime = fDate.split("
- 【数据挖掘学习】关联规则算法Apriori的学习与SQL简单实现购物篮分析
superlxw1234
sql数据挖掘关联规则
关联规则挖掘用于寻找给定数据集中项之间的有趣的关联或相关关系。
关联规则揭示了数据项间的未知的依赖关系,根据所挖掘的关联关系,可以从一个数据对象的信息来推断另一个数据对象的信息。
例如购物篮分析。牛奶 ⇒ 面包 [支持度:3%,置信度:40%] 支持度3%:意味3%顾客同时购买牛奶和面包。 置信度40%:意味购买牛奶的顾客40%也购买面包。 规则的支持度和置信度是两个规则兴
- Spring 5.0 的系统需求,期待你的反馈
wiselyman
spring
Spring 5.0将在2016年发布。Spring5.0将支持JDK 9。
Spring 5.0的特性计划还在工作中,请保持关注,所以作者希望从使用者得到关于Spring 5.0系统需求方面的反馈。