spring容器的启动过程是什么?
spring在web容器中,启动过程是Servlet 容器对spring环境的构造,初始化,装配的过程。
spring的启动过程
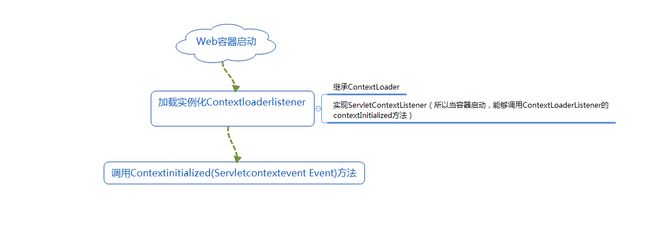
1.通过ContextLoaderListener监听作为启动spring的入口
启动必要条件:在web.xml中配置
ContextLoaderListener(spring中的类)继承ContextLoader(spring中的类),并实现ServletContextListener(servlet中的接口),ServletContextListener监听ServletContext,当容器启动时,会触发ServletContextEvent事件,该事件由ServletContextListener来处理,启动初始化ServletContext时,调用contextInitialized方法。而ContextLoaderListener实现了ServletContextListener,所以,当容器启动时,触发ServletContextEvent事件,让ContextLoaderListener执行实现方法contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce);
这部分源码为:
public class ContextLoaderListener extends ContextLoader implements ServletContextListener {
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
this.contextLoader = createContextLoader();
if (this.contextLoader == null) {
this.contextLoader = this;
}
this.contextLoader.initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
}
}
2.通过initWebApplicationContext方法来初始化WebApplicationContext
WebApplicationContext是spring中的上下文。它的作用等同于Servlet中的ServletContext。
(部分注释源码被我删掉)
public WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
if (servletContext.getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE) != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot initialize context because there is already a root application context present - " +
"check whether you have multiple ContextLoader* definitions in your web.xml!");
}
try {
if (this.context == null) {
this.context = createWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
}
if (this.context instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) this.context;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
ApplicationContext parent = loadParentContext(servletContext);
cwac.setParent(parent);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext);
}
}
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context);
ClassLoader ccl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
if (ccl == ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader()) {
currentContext = this.context;
}
else if (ccl != null) {
currentContextPerThread.put(ccl, this.context);
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Published root WebApplicationContext as ServletContext attribute with name [" +
WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE + "]");
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization completed in " + elapsedTime + " ms");
}
return this.context;
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, ex);
throw ex;
}
catch (Error err) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", err);
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, err);
throw err;
}
}
initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext)方法是ContextLoader中的方法。它的作用是制作一个WebApplicationContext上下文,并将这个上下文保存在servletContext中,并保存在当前ContextLoader实例中。
3.如何初始化WebApplicationContext
上面源码中的
this.context = createWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
用来制造一个WebApplicationContext,制造的过程,依赖ServletContext。
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(ServletContext sc) {
Class contextClass = determineContextClass(sc);
if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Custom context class [" + contextClass.getName() +
"] is not of type [" + ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.getName() + "]");
}
return (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
}
通过determineContextClass(ServletContext servletContext)方法获取需要实例化的context类的class,通过BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass)将这个class用反射的手段实例化WebApplicationContext 。
那么determineContextClass怎样来确定实例化那个context类那?(spring有很多的context类实现了WebApplicationContext ,当然这个context类也可以是我们自己写的,具体实例化那个类,在web.xml中配置)
protected Class determineContextClass(ServletContext servletContext) {
String contextClassName = servletContext.getInitParameter(CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM);
if (contextClassName != null) {
try {
return ClassUtils.forName(contextClassName, ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader());
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Failed to load custom context class [" + contextClassName + "]", ex);
}
}
else {
contextClassName = defaultStrategies.getProperty(WebApplicationContext.class.getName());
try {
return ClassUtils.forName(contextClassName, ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader());
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Failed to load default context class [" + contextClassName + "]", ex);
}
}
}
从上面的代码可以看出,先从servletContext中找我们在web.xml中有没有配置要实例化那个上下文context,如果配置了
contextClass
rg.springframework.web.context.support.StaticWebApplicationContext
那么将实例化StaticWebApplicationContext这个上下文。注意:这个地方的param-name必须是contextClass(约定成俗的,其实就是是程序写死的)。如果没有这个配置,那么程序将找到一个叫ContextLoader.properties的配置文件,这个配置文件注明了一个默认的上下文:XmlWebApplicationContext。这个XmlWebApplicationContext实例化的过程是制造一个ResourcePatternResolver的实例,这个实例将会在后面的spring启动过程中起到关键作用。
最后流程图: