简介
我们做app经常会接触到service这个组件,书上也经常说,我们应该把一些耗时的操作放到service中,那么问题来了,为什么我们要把耗时的操作放到service中,service有什么特殊的意义?放到service中就安然无恙了吗?我们带着这些问题,来看看我们今天的主角service,故事就这样展开了。
扫个盲
- AMP:ActivityManagerProxy
- AMN:ActivityManagerNative
- AMS:ActivityManagerService
- AT:ApplicationThread
- ATP:ApplicationThreadProxy
- ATN:ApplicationThreadNative
我们看看这些宝贝类或者接口的关系图:
使用
在代码中:
..............
Intent serviceIntent = new Intent(mContext, TestService.class);
serviceIntent.putExtra("Args", mArgs);
mContext.startService(serviceIntent);
..............
public class TestService extends Service {
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return null;
}
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
...........
}
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId);
..............
return START_STICKY;
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
..........
}
}
使用结果说明:
- onBind() :bind service的时候使用
- onCreate()
- onStartCommand()
- START_STICKY
当Service因为内存不足而被系统kill后,在接下来的某个时间内,当系统内存足够可用的情况下,系统将会尝试重新创建此Service; 一旦创建成功后,将回调onStartCommand方法,但一般情况下,参数中的Intent将是null。 - START_NOT_STICKY
当Service因为内存不足而被系统kill后,在接下来的某个时间内,即使系统内存足够可用,系统也不会尝试重新创建此Service。 - START_REDELIVER_INTENT
与START_STICKY相同,当Service因为内存不足而被系统kill后,在接下来的某个时间内,当系统内存足够可用的情况下,系统将会尝试重新创建此Service; 唯一不同的是,Service创建成功后,回调onStartCommand方法时,传入的参数将是最后一次调用startService时使用的intent。
- START_STICKY
需要注意的是,只有系统kill掉Service时上述返回值才有意义,如果是人为地kill掉Service进程,系统不会按照onStartCommand的返回值重启Service。
最后,客户端无论调用多少次startService,只需要一次stopService即可将此Service终止(毕竟onCreate函数也之调用过一次),此时AMS将回调Service的onDestroy函数。
service启动的两种方式
-
显示启动
........... Intent startIntent = new Intent(); ComponentName componentName = new ComponentName("service的packagename", "service的classname"); startIntent.setComponent(componentName); mContext.startService(startIntent); ....................... Intent startIntent = new Intent(mContext, TestService.class); mContext.startService(startIntent); ............ -
隐式启动
............ Intent startIntent = new Intent(); startIntent.setAction("com.android.server.TestService.TestAction"); mContext.startService(startIntent); ............
隐式启动在5.0以后废弃
分析
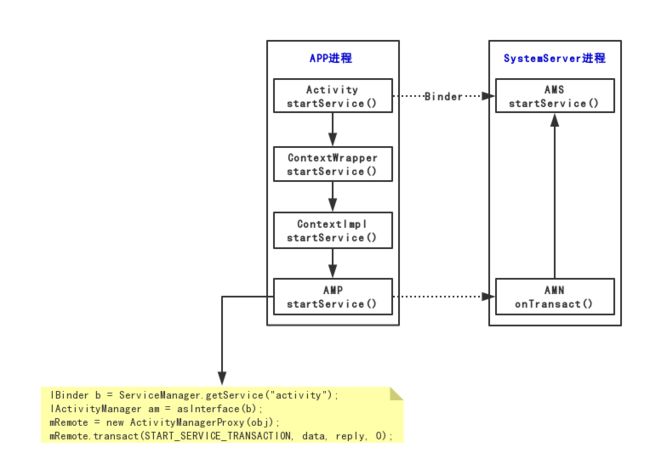
先从Acvitiy说起,比如我们现在最常见的就是从Activity进行startService(),我们先看一下继承关系
Context
ContextWrapper
ContextThemeWrapper
Activity
当我们调用startService的时候,其实是调用了ContextWrapper中的方法。当我们分析Activity如何创建的时候我们在来说ContextWrapper是在那里创建的。
- 黄色表示当前要启动service的进程
- 绿色表示systemserver进程
- service所在进程(有可能在同一个进程,也有可能不再同一个进程)
核心方法
AS.startServiceLocked()
part1
ComponentName startServiceLocked(IApplicationThread caller, Intent service, String resolvedType,
int callingPid, int callingUid, String callingPackage, final int userId)
throws TransactionTooLargeException {
................
final boolean callerFg;
if (caller != null) {
//通过AMS得到调用方的进程信息
final ProcessRecord callerApp = mAm.getRecordForAppLocked(caller);
................
//判断调用方是否属于前台进程
callerFg = callerApp.setSchedGroup != ProcessList.SCHED_GROUP_BACKGROUND;
} else {
callerFg = true;
}
//检索待启动的Service
ServiceLookupResult res =
retrieveServiceLocked(service, resolvedType, callingPackage,
callingPid, callingUid, userId, true, callerFg, false);//[part1-1]
..................
//从ServiceLookupResult中取出ServiceRecord
ServiceRecord r = res.record;
.................
如果调用者为null,则callerFg = true,否则callerFg = callerApp.setSchedGroup != ProcessList.SCHED_GROUP_BACKGROUND;通过这个来判断是不是处于后台
补充知识:
- 内核负责了进程的CPU调度,所有运行中的进程并非能平等的能获取相等的时间片。在ProcessRecord中,通过Schedule Group来记录进程的调度组:
- 它们可能的取值定义在ProcessList.java中:
// Activity manager's version of Process.THREAD_GROUP_BG_NONINTERACTIVE
static final int SCHED_GROUP_BACKGROUND = 0;
// Activity manager's version of Process.THREAD_GROUP_DEFAULT
static final int SCHED_GROUP_DEFAULT = 1;
// Activity manager's version of Process.THREAD_GROUP_TOP_APP
static final int SCHED_GROUP_TOP_APP = 2;
// Activity manager's version of Process.THREAD_GROUP_TOP_APP
// Disambiguate between actual top app and processes bound to the top app
static final int SCHED_GROUP_TOP_APP_BOUND = 3;
其中获取CPU资源的能力来看,
SCHED_GROUP_TOP_APP_BOUND最高,其次SCHED_GROUP_TOP_APP应该强于SCHED_GROUP_DEFAULT, 最后才轮到SCHED_GROUP_BACKGROUND
part1-1 retrieveServiceLocked()
private ServiceLookupResult retrieveServiceLocked(.......) {
ServiceRecord r = null;
..........
//得到当前用户的UserId
userId = mAm.mUserController.handleIncomingUser(callingPid, callingUid, userId, false,
ActivityManagerService.ALLOW_NON_FULL_IN_PROFILE, "service", null);
//每个UserId有对应的ServiceMap,统一保存在ActiveServices中
ServiceMap smap = getServiceMap(userId);
//对于显示启动
final ComponentName comp = service.getComponent();
if (comp != null) {
//根据ComponentName从ServiceMap中取出对应的ServiceRecord
r = smap.mServicesByName.get(comp);
}
//对于隐式启动
if (r == null && !isBindExternal) {
Intent.FilterComparison filter = new Intent.FilterComparison(service);
//根据Intent对应的Filter,从ServiceMap中取出匹配的ServiceRecord
r = smap.mServicesByIntent.get(filter);
}
//特殊情况的处理
//对于包含FLAG_EXTERNAL_SERVICE的service,将运行于调用方进程中
//对于这种特殊服务,
//如果根据Component或Filter找到了一个正在运行的Service,但其运行进程与当前调用进程不一致
//那么必须重新在调用进程中创建该ServiceRecord,于是将r置为null
if (r != null && (r.serviceInfo.flags & ServiceInfo.FLAG_EXTERNAL_SERVICE) != 0
&& !callingPackage.equals(r.packageName)) {
// If an external service is running within its own package, other packages
// should not bind to that instance.
r = null;
}
//以上均是在缓存信息中,查找ServiceRecord
//如果查询不到,则必须通过PKMS进行查找
if (r == null) {
try {
//PKMS根据参数得到对应Pkg中Serivce的ResolveInfo
ResolveInfo rInfo = AppGlobals.getPackageManager().resolveService(service,
resolvedType, ActivityManagerService.STOCK_PM_FLAGS
| PackageManager.MATCH_DEBUG_TRIAGED_MISSING,
userId);
//从ResolveInfo中取出ServiceInfo
ServiceInfo sInfo =
rInfo != null ? rInfo.serviceInfo : null;
//构造出Service对应的ComponentName
ComponentName name = new ComponentName(
sInfo.applicationInfo.packageName, sInfo.name);
//特殊情况处理
if ((sInfo.flags & ServiceInfo.FLAG_EXTERNAL_SERVICE) != 0) {
if (isBindExternal) {
..............
// Run the service under the calling package's application.
//FLAG_EXTERNAL_SERVICE将运行在调用方进程中,此处就是修改PKMS检索出的ServiceInfo
//先得到调用方的应用信息
ApplicationInfo aInfo = AppGlobals.getPackageManager().getApplicationInfo(
callingPackage, ActivityManagerService.STOCK_PM_FLAGS, userId);
............
//将ServiceInfo中的信息,改为调用方应用的信息
sInfo = new ServiceInfo(sInfo);
sInfo.applicationInfo = new ApplicationInfo(sInfo.applicationInfo);
sInfo.applicationInfo.packageName = aInfo.packageName;
sInfo.applicationInfo.uid = aInfo.uid;
name = new ComponentName(aInfo.packageName, name.getClassName());
service.setComponent(name);
} else {
//抛出异常
.....
}
} else if(isBindExternal) {
//抛出异常
............
}
//多用户的处理
if (userId > 0) {
//检查服务是否为单例且可被调用的
if (mAm.isSingleton(sInfo.processName, sInfo.applicationInfo,
sInfo.name, sInfo.flags)
&& mAm.isValidSingletonCall(callingUid, sInfo.applicationInfo.uid)) {
//对于多用户而言,每个用户启动的服务,运行于对应用户所在进程组中
//但如果待启动服务为单例的,那么该服务还是得运行在系统用户的进程组中
//于是此次将userId置为0
userId = 0;
//ServiceMap都被调整为系统用户对应的
smap = getServiceMap(0);
}
sInfo = new ServiceInfo(sInfo);
//此处使用了userId
sInfo.applicationInfo = mAm.getAppInfoForUser(sInfo.applicationInfo, userId);
}
r = smap.mServicesByName.get(name);
if (r == null && createIfNeeded) {
..............
//创建出对应的ServiceRecord
r = new ServiceRecord(mAm, ss, name, filter, sInfo, callingFromFg, res);
..............
//保存到ServiceMap中
smap.mServicesByName.put(name, r);
smap.mServicesByIntent.put(filter, r);
}
} catch(RemoteException ex) {
...........
}
}
if (r != null) {
//进行一些权限检查和有效性检查
.................
//没有问题时,返回正常结果
return new ServiceLookupResult(r, null);
}
return null;
}
- 得到当前用户的userId
- 根据userId得到ServiceMap,这个ServiceMap保存在ActiveServices中
- 根据显示启动和隐式启动从ServiceMap中拿出来ServiceRecord
- 上面信息都是从当前ActiveServices中的ServiceMap(缓存)中查找,如果没有找到则通过PKMS进行查找
- 最后确保没有问题返回一个包装ServiceRecord对象的ServiceLookupResult对象
part2
//进行一些检查工作
.............
if (res.record == null) {
return new ComponentName("!", res.permission != null
? res.permission : "private to package");
}
ServiceRecord r = res.record;
if (!mAm.getUserManagerLocked().exists(r.userId)) { //检查是否存在启动服务的user
return null;
}
//如果这个服务在重启列表中,清空对应的信息
if (unscheduleServiceRestartLocked(r, callingUid, false)) {
.................
}
r.lastActivity = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
r.startRequested = true;
r.delayedStop = false;
//startService可以多次向Service传递信息,每次的信息都是一个StartItem,对应着一个StartId
r.pendingStarts.add(new ServiceRecord.StartItem(r, false, r.makeNextStartId(),
service, neededGrants));
............
//addToStarting决定是否将待启动的Service
//加入到ActiveServices维护的mStartingBackground队列
boolean addToStarting = false;
//如果启动服务的不是前台进程
//同时服务对应的ServiceRecord中没有记录对应进程的信息(即初次使用)
if (!callerFg && r.app == null
//并且user已经启动过其它进程
&& mAm.mUserController.hasStartedUserState(r.userId)) {
//通过AMS查询Service对应的进程信息
ProcessRecord proc = mAm.getProcessRecordLocked(r.processName, r.appInfo.uid, false);
//若Service对应的进程未启动,或优先级过低,则有可能需要延迟启动服务
if (proc == null || proc.curProcState > ActivityManager.PROCESS_STATE_RECEIVER) {
.....................
if (r.delayed) {
// This service is already scheduled for a delayed start; just leave
// it still waiting.
return r.name;
}
//若当前用户启动的后台服务数量过多,则延迟启动服务
if (smap.mStartingBackground.size() >= mMaxStartingBackground) {
................
smap.mDelayedStartList.add(r);
r.delayed = true;
return r.name;
}
..............
addToStarting = true;
} else if (proc.curProcState >= ActivityManager.PROCESS_STATE_SERVICE) {
addToStarting = true;
................
} ..........
............
} ............
...............
return startServiceInnerLocked(smap, service, r, callerFg, addToStarting);
}
- 做一些检查工作
- 如果这个服务在重启列表中将晴空对应信息
- startService可以多次向Service传递信息,每次的信息都是一个StartItem,对应着一个StartId
- boolean addToStarting决定是否将待启动的Service加入到ActiveServices维护的mStartingBackground队列
- 如果启动服务的不是前台进程,同时服务对应的ServiceRecord中没有记录对应进程的信息(即初次使用)并且user已经启动过其它进程则
- 通过AMS查询Service对应的进程信息
- 如果Service对应进程没有启动,或者优先级低,则有可能需要延迟启动服务
- 如果当前用户启动的后台服务数量大于后台启动最大服务数量,则延迟启动
//若当前用户启动的后台服务数量过多,则延迟启动服务 if (smap.mStartingBackground.size() >= mMaxStartingBackground) { ................ smap.mDelayedStartList.add(r); r.delayed = true; return r.name; } - addToStarting = true;(当服务对应的ServiceRecord没有记录对应的进程信息,如果不是延迟启动)||(包含service的进程已经存在并且proc.curProcState >= ActivityManager.PROCESS_STATE_SERVICE//
Process is in the background running a service.)
概述:
判断当前Service是否需要延迟启动。
若需要延迟启动,则将ServiceRecord保存到smap中的mDelayedStartList中,并结束本启动流程;
否则,调用startServiceInnerLocked函数,进入启动Service的下一个阶段。
AS.startServiceInnerLocked()
ComponentName startServiceInnerLocked(ServiceMap smap, Intent service, ServiceRecord r,
boolean callerFg, boolean addToStarting) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
ProcessStats.ServiceState stracker = r.getTracker();
if (stracker != null) {
//更新ServiceRecord的ServiceState
stracker.setStarted(true, mAm.mProcessStats.getMemFactorLocked(), r.lastActivity);
}
r.callStart = false;
synchronized (r.stats.getBatteryStats()) {
r.stats.startRunningLocked(); //用于耗电统计,开启运行的状态
}
//核心启动service的方法
String error = bringUpServiceLocked(r, service.getFlags(), callerFg, false);
if (error != null) {
return new ComponentName("!!", error);
}
//
if (r.startRequested && addToStarting) {
boolean first = smap.mStartingBackground.size() == 0;
smap.mStartingBackground.add(r);
r.startingBgTimeout = SystemClock.uptimeMillis() + BG_START_TIMEOUT;
if (first) {
smap.rescheduleDelayedStarts();
}
} else if (callerFg) {
smap.ensureNotStartingBackground(r);
}
return r.name;
}
- 通过
bringUpServiceLocked真正启动service - 当启动完成的时候设置启动超时时间
- 启动成功之后将ServiceRecord加入到smap中的mStartingBackground中
- 如果是第一次启动则需要从smap.rescheduleDelayedStarts();中移除MSG_BG_START_TIMEOUT(service未启动ANR)并且从mStartingBackground(后台启动service列表中)移除,仔细研究见下文
AS.rescheduleDelayedStarts()
void rescheduleDelayedStarts() {
//前面的注释已经提到过,后台进程启动Service超时会发送MSG_BG_START_TIMEOUT消息
//该消息被处理时,也会调用rescheduleDelayedStarts函数
//因此,进入该函数时,先移除掉该信息
removeMessages(MSG_BG_START_TIMEOUT);
final long now = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
for (int i=0, N=mStartingBackground.size(); i 0
&& mStartingBackground.size() < mMaxStartingBackground) {
ServiceRecord r = mDelayedStartList.remove(0);
.................
r.delayed = false;
try {
//启动延迟Service,启动后会修改mStartingBackground.size
startServiceInnerLocked(this, r.pendingStarts.get(0).intent, r, false, true);
} catch (TransactionTooLargeException e) {
..........
}
if (mStartingBackground.size() > 0) {
ServiceRecord next = mStartingBackground.get(0);
//决定延迟发送消息的时间
long when = next.startingBgTimeout > now ? next.startingBgTimeout : now;
................
Message msg = obtainMessage(MSG_BG_START_TIMEOUT);
//一旦超时,就会发送MSG_BG_START_TIMEOUT
sendMessageAtTime(msg, when);
}
.....................
}
}
- 移除MSG_BG_START_TIMEOUT消息
- 将超时的Service从mStartingBackground中移除
- 存在延时service并且没有达到后台启动service最大数量的时候启动延时的service
- 在mStartingBackground.size()>0后,发送延时启动消息一旦时间到达或者时间时间超出,则发送信号重新调用rescheduleDelayedStarts()
概述:
- 判断mStartingBackground中启动的Service是否超时
- 判断能否启动mDelayedStartList中,被延迟启动的服务。
AS.bringUpServiceLocked()
private final String bringUpServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r, int intentFlags, boolean execInFg,
boolean whileRestarting) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
//处理Service已经启动的情况,此时只是发送新的StartItem
if (r.app != null && r.app.thread != null) {
//调用service.onStartCommand()过程
sendServiceArgsLocked(r, execInFg, false);
return null;
}
if (!whileRestarting && r.restartDelay > 0) {
return null; //等待延迟重启的过程,则直接返回
}
// 启动service前,把service从重启服务队列中移除
if (mRestartingServices.remove(r)) {
r.resetRestartCounter();
clearRestartingIfNeededLocked(r);
}
//service正在启动,将delayed设置为false
if (r.delayed) {
getServiceMap(r.userId).mDelayedStartList.remove(r);
r.delayed = false;
}
//确保拥有该服务的user已经启动,否则停止;
if (mAm.mStartedUsers.get(r.userId) == null) {
String msg = "";
bringDownServiceLocked(r);
return msg;
}
//服务正在启动,设置package停止状态为false
AppGlobals.getPackageManager().setPackageStoppedState(
r.packageName, false, r.userId);
final boolean isolated = (r.serviceInfo.flags&ServiceInfo.FLAG_ISOLATED_PROCESS) != 0;
final String procName = r.processName;
ProcessRecord app;
if (!isolated) {
//根据进程名和uid,查询ProcessRecord
app = mAm.getProcessRecordLocked(procName, r.appInfo.uid, false);
//能进入此循环说明对应进程已经启动
if (app != null && app.thread != null) {
try {
app.addPackage(r.appInfo.packageName, r.appInfo.versionCode, mAm.mProcessStats);
// 启动服务
realStartServiceLocked(r, app, execInFg);
return null;
} catch (TransactionTooLargeException e) {
throw e;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Exception when starting service " + r.shortName, e);
}
}
} else {
app = r.isolatedProc;
}
//对于进程没有启动的情况
if (app == null) {
//启动service所要运行的进程
if ((app=mAm.startProcessLocked(procName, r.appInfo, true, intentFlags,
"service", r.name, false, isolated, false)) == null) {
String msg = ""
bringDownServiceLocked(r); // 进程启动失败
return msg;
}
if (isolated) {
r.isolatedProc = app;
}
}
//mPendingServices保存待启动服务,当进程启动后,会重新启动该服务
if (!mPendingServices.contains(r)) {
mPendingServices.add(r);
}
//服务还未完成启动,就收到结束请求时,会直接停止该服务
if (r.delayedStop) {
r.delayedStop = false;
if (r.startRequested) {
stopServiceLocked(r); //停止服务
}
}
return null;
}
- service已经启动过了,则调用sendServiceArgsLocked函数,将新的待处理信息发送给Service
- service未启动过,但对应的进程已启动,那么调用realStartServiceLocked函数,启动服务即可;
- service对应的进程并没有启动,那么先启动进程。在启动进程过程中会调用realStartServiceLocked启动service
所以这里,如果service启动过了,现在重新调用启动函数的话,则只是将intent的信息发送给service进行处理,如果service没有启动但是进程启动了,那么就会启动service,如果连进程都没有启动则会启动进程,然后在启动进程的过程中会启动service
AS.realStartServiceLocked()
private final void realStartServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r,
ProcessRecord app, boolean execInFg) throws RemoteException {
...
r.app = app;
r.restartTime = r.lastActivity = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
final boolean newService = app.services.add(r);
//发送delay消息
bumpServiceExecutingLocked(r, execInFg, "create");
//更新进程对应的优先级信息
mAm.updateLruProcessLocked(app, false, null);
mAm.updateOomAdjLocked();
boolean created = false;
try {
synchronized (r.stats.getBatteryStats()) {
r.stats.startLaunchedLocked();
}
mAm.ensurePackageDexOpt(r.serviceInfo.packageName);
//更改进程状态为PROCESS_STATE_SERVICE
app.forceProcessStateUpTo(ActivityManager.PROCESS_STATE_SERVICE);
//服务进入 onCreate()
//此时又是Binder通信,发送消息给目标进程的ApplicationThread,通知去创建服务
app.thread.scheduleCreateService(r, r.serviceInfo,
mAm.compatibilityInfoForPackageLocked(r.serviceInfo.applicationInfo),
app.repProcState);
r.postNotification();
created = true;
} catch (DeadObjectException e) {
mAm.appDiedLocked(app); //当是被时候会让这个进程也挂掉
throw e;
} finally {
if (!created) {
//如果服务创建失败,则看是不是mDestroyingServices列表中有记录,如果有则执行一些销毁动作
final boolean inDestroying = mDestroyingServices.contains(r);
serviceDoneExecutingLocked(r, inDestroying, inDestroying);
if (newService) {
app.services.remove(r);
r.app = null;
}
//尝试重新启动服务
if (!inDestroying) {
scheduleServiceRestartLocked(r, false);
}
}
}
//Service被绑定过,才会调用onBind函数
requestServiceBindingsLocked(r, execInFg);
//如果客户端Bind Service成功,按需更新服务端进程优先级
updateServiceClientActivitiesLocked(app, null, true);
if (r.startRequested && r.callStart && r.pendingStarts.size() == 0) {
r.pendingStarts.add(new ServiceRecord.StartItem(r, false, r.makeNextStartId(),
null, null));
}
//会调用sendServiceArgsLocked()方法发送参数
sendServiceArgsLocked(r, execInFg, true);
//如果Service是延迟启动的,那么此时可以将其从mDelayedStartList移除
if (r.delayed) {
getServiceMap(r.userId).mDelayedStartList.remove(r);
r.delayed = false;
}
//若Service被要求停止,那么结束服务
if (r.delayedStop) {
r.delayedStop = false;
if (r.startRequested) {
stopServiceLocked(r); //停止服务
}
}
}
- 对service的状态进行记录(bumpServiceExecutingLocked)
- 更新进程对应的优先级信息(mAm.updateOomAdjLocked();)
- 强制更改进程的状态(为PROCESS_STATE_SERVICE)
- 通过Binder通信发送消息给进程的ApplicationThread,创建服务(app.thread.scheduleCreateService())
- 如果创建失败则会kill进程
- 如果符合重启条件则会重启service
- 如果调用过Bind service,则会调用(requestServiceBindingsLocked()---> OnBind函数)
- 如果Bind成功则会按照需求更新service进程的优先级
- 构造一个StartItem然后通过sendServiceArgsLocked发送参数(sendServiceArgsLocked())
- 如果service是延时启动的则将其从mDelayedStartList中移除(getServiceMap(r.userId).mDelayedStartList.remove(r);)
- 如果service被主动要求停止那么调用(stopServiceLocked(r))
小节重点:
- 对service的状态进行记录(bumpServiceExecutingLocked)
- 通过Binder通信发送消息给进程的ApplicationThread,创建服务(app.thread.scheduleCreateService())
- 构造一个StartItem然后通过sendServiceArgsLocked发送参数(sendServiceArgsLocked())
AS.bumpServiceExecutingLocked()
private final void bumpServiceExecutingLocked(ServiceRecord r, boolean fg, String why) {
..............
long now = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
//executeNesting用于记录Service待处理的请求数量
if (r.executeNesting == 0) {
//处理第一个命令时,即初次启动Service时
r.executeFg = fg;
ServiceState stracker = r.getTracker();
if (stracker != null) {
//记录时间
stracker.setExecuting(true, mAm.mProcessStats.getMemFactorLocked(), now);
}
if (r.app != null) {
//更新进程ProcessRecord中关于Service的记录
r.app.executingServices.add(r);
r.app.execServicesFg |= fg;
if (r.app.executingServices.size() == 1) {
//设置启动Service超时的时间
//即Service初次启动时,如果进程中只有这一个Service
//那么一旦启动超时,将触发AMS发送ANR
scheduleServiceTimeoutLocked(r.app);
}
}
} else if (r.app != null && fg && !r.app.execServicesFg) {
//前台进程向后台服务发送命令时,也会设置超时时间,一旦超时,也会ANR
//发送一次后,该值变为true,相当与变成前台服务了
r.app.execServicesFg = true;
scheduleServiceTimeoutLocked(r.app);
}
r.executeFg |= fg;
//每处理一个命令,executeNesting均会+1
r.executeNesting++;
r.executingStart = now;
}
这个方法主要将service和进程关联起来(更新ServiceRecord中的信息),并且如果进程中只有一个service那么一旦超时就会给AMS发送ANR信息
void scheduleServiceTimeoutLocked(ProcessRecord proc) {
//进程中需要执行service和当前进程都得存活
if (proc.executingServices.size() == 0 || proc.thread == null) {
return;
}
long now = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
Message msg = mAm.mHandler.obtainMessage(
ActivityManagerService.SERVICE_TIMEOUT_MSG);
msg.obj = proc;
mAm.mHandler.sendMessageAtTime(msg,
//前台超时的时间为20s,后台为200s
proc.execServicesFg ? (now+SERVICE_TIMEOUT) : (now+ SERVICE_BACKGROUND_TIMEOUT));
}
这里看到没,是通过proc.execServicesFg判断service是否在前后台
AS.scheduleCreateService()
AS.scheduleCreateService()-->ActivityThread发送H.CREATE_SERVICE-->ActivityThread.handleCreateService()
private void handleCreateService(CreateServiceData data) {
....................
//得到这个进程对应的LoadedApk
LoadedApk packageInfo = getPackageInfoNoCheck(
data.info.applicationInfo, data.compatInfo);
Service service = null;
try {
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = packageInfo.getClassLoader();
//通过反射创建出实例
service = (Service) cl.loadClass(data.info.name).newInstance();
} catch (Exception e) {
..................
}
try {
............
//创建service的ContextImpl对象
ContextImpl context = ContextImpl.createAppContext(this, packageInfo);
//实际工作类为ContextImpl,其代理设置为service
context.setOuterContext(service);
//得到app的Application对象
Application app = packageInfo.makeApplication(false, mInstrumentation);
//将一些重要的信息和对象绑定到service中
//此处传递的this是ActivityThread,这就是大家常说的:service也是运行在主线程中的原因
service.attach(context, this, data.info.name, data.token, app,
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault());
//调用Service的onCreate函数
service.onCreate();
//mServices中存储了ActivityThread中运行的服务
//key值为Service对应的IBinder,是从Service对应的ServiceRecord中取出的
mServices.put(data.token, service);
try {
//通知AMS service启动成功,进行取消超时消息等操作
//后文再分析该函数
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().serviceDoneExecuting(
data.token, SERVICE_DONE_EXECUTING_ANON, 0, 0);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
.............
}
}
- 得到Service对应的LoadedApk信息
- 通过反射创建出service实例
- 创建service的ContextImpl
- 将service类设置成代理,实际工作的是ContextImpl
- 将service绑定一些常用的对象(service.attach(context, this, data.info.name, data.token, app, ActivityManagerNative.getDefault());)其中this是当前进程的ActiveThread对象
- 调用service.onCreate()方法
- 将当前service添加到ActivityThread的mServices中利用键值对方式(mServices.put(data.token, service);)
- 通知AMS service启动成功,进行取消ANR那个消息(ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().serviceDoneExecuting(data.token, SERVICE_DONE_EXECUTING_ANON, 0, 0);)
小节:
- 得到LoadedApk反射得到service
- 让service持有当前进程的核心对象(service.attach(context, this, data.info.name, data.token, app, ActivityManagerNative.getDefault());)其中this是当前进程的ActiveThread对象
- 调用service.onCreate()方法
- 移除启动爆发那个ANR消息
AS.sendServiceArgsLocked()
private final void sendServiceArgsLocked(ServiceRecord r, boolean execInFg,
boolean oomAdjusted) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
...............
//本次需发送的信息,在调用sendServiceArgsLocked前,已经加入到了pendingStarts中
//通过循环,将pending的信息发送完
while (r.pendingStarts.size() > 0) {
...........
try {
//依次取出
si = r.pendingStarts.remove(0);
............
si.deliveredTime = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
//记录发送时间和发送次数
r.deliveredStarts.add(si);
si.deliveryCount++;
...........
int flags = 0;
//发送次数大于1,添加对应flag
if (si.deliveryCount > 1) {
flags |= Service.START_FLAG_RETRY;
}
//这个应该是service被kill掉后,系统重启服务发送的Intent,于是添加对应的flag
if (si.doneExecutingCount > 0) {
flags |= Service.START_FLAG_REDELIVERY;
}
//Binder通信给ApplicationThread
r.app.thread.scheduleServiceArgs(r, si.taskRemoved, si.id, flags, si.intent);
} ..........
...........
}
}
r.pendingStarts.add(new ServiceRecord.StartItem(r, false, r.makeNextStartId(),service, neededGrants));这个方法我们在许多地方调用比如在startServiceLocked()中,我们是将需要给service传递的信息封装成一个startItem,在这个方法中我们将其发送给setvice,下面我们就看发送流程
- 取出StartItem消息
- 记录发送时间和次数
- 当发送次数大于1,则添加对应的flag
- 通过binder方式给ApplicationThread发送这个startItem
r.app.thread.scheduleServiceArgs()-->H.SERVICE_ARGS-->ActivityThread.handleServiceArgs()
ActivityThread.handleServiceArgs()
private void handleServiceArgs(ServiceArgsData data) {
//取出IBinder对应的Service
Service s = mServices.get(data.token);
if (s != null) {
try {
.........
int res;
//通常情况,taskRemoved为false
if (!data.taskRemoved) {
//调用Service的onStartCommand函数,处理Intent携带的内容
res = s.onStartCommand(data.args, data.flags, data.startId);
} else {
s.onTaskRemoved(data.args);
res = Service.START_TASK_REMOVED_COMPLETE;
}
//在通知AMS消息处理完成前,现完成本地等待处理的任务
//这里与启动BroadcastReceiver对应进程的情况相似
//进程可能是由于创建Service才被启动的,Service处理完毕后,AMS可能进行进程管理
//杀死Service对应进程,因此先确保工作做完
QueuedWork.waitToFinish();
try {
//再次调用AMS的serviceDoneExecuting函数,通知AMS消息处理完毕
//本次的flag为SERVICE_DONE_EXECUTING_START
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().serviceDoneExecuting(
data.token, SERVICE_DONE_EXECUTING_START, data.startId, res);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
ensureJitEnabled();
} catch(Exception e) {
........
}
}
}
很明确这里是会调用Service.onConmmand函数,处理Intent携带的内容
所以我们可以知道,Service.onConmmand函数可以调用多次,但是Service.onCreate()方法只能调用一次
然后再次调用AMS的serviceDoneExecuting函数通知执行结果。
不过这里需要注意的是当前调用onStartCommand之后会有一个结果返回,要根据这个结果AMS要做一些处理。我们先补充一点使用onStartCommand的知识。
(1):onstart()方法和onStartCommand()方法的区别:
onstart()方法是在android2.0一下的版本中使用。而在android2.0以上则使用onstartCommand()方法。它们两个方法放在一起使用时,不会产生冲突。
(2):onStartComand使用时,返回的是一个(int)整形。
这个整形可以有四个返回值:start_sticky、start_no_sticky、START_REDELIVER_INTENT、START_STICKY_COMPATIBILITY。
它们的含义分别是:
1):START_STICKY:如果service进程被kill掉,保留service的状态为开始状态,但不保留递送的intent对象。随后系统会尝试重新创建service,由于服务状态为开始状态,所以创建服务后一定会调用onStartCommand(Intent,int,int)方法。如果在此期间没有任何启动命令被传递到service,那么参数Intent将为null。
2):START_NOT_STICKY:“非粘性的”。使用这个返回值时,如果在执行完onStartCommand后,服务被异常kill掉,系统不会自动重启该服务
3):START_REDELIVER_INTENT:重传Intent。使用这个返回值时,如果在执行完onStartCommand后,服务被异常kill掉,系统会自动重启该服务,并将Intent的值传入。
4):START_STICKY_COMPATIBILITY:START_STICKY的兼容版本,但不保证服务被kill后一定能重启。
然后我们看看通过 ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().serviceDoneExecuting(data.token, SERVICE_DONE_EXECUTING_START, data.startId, res);调用之后的结果
public void serviceDoneExecuting(IBinder token, int type, int startId, int res) {
synchronized(this) {
............
mServices.serviceDoneExecutingLocked((ServiceRecord)token, type, startId, res);
}
}
void serviceDoneExecutingLocked(ServiceRecord r, int type, int startId, int res) {
//Service每执行完一次命令都会通知AMS,serviceDoneExecutingLocked将被多次调用
//因此,该函数中需要处理的场景比较多
//先判断该Service是否destroy
boolean inDestroying = mDestroyingServices.contains(r);
if (r != null) {
//Service的onStartCommand函数被调用后,通知AMS的type为SERVICE_DONE_EXECUTING_START
if (type == ActivityThread.SERVICE_DONE_EXECUTING_START) {
r.callStart = true;
//处理onStartCommand的返回值
switch (res) {
case Service.START_STICKY_COMPATIBILITY:
case Service.START_STICKY: {
//找到startId对应的StartItem,并移除(true)
r.findDeliveredStart(startId, true);
//这个值置为false后,Service被杀掉还有机会重启
r.stopIfKilled = false;
break;
}
case Service.START_NOT_STICKY: {
//找到startId对应的StartItem,并移除(true)
r.findDeliveredStart(startId, true);
if (r.getLastStartId() == startId) {
//服务kill掉,不再重启
r.stopIfKilled = true;
}
break;
}
case Service.START_REDELIVER_INTENT: {
//找到startId对应的StartItem,不移除(false)
ServiceRecord.StartItem si = r.findDeliveredStart(startId, false);
if (si != null) {
si.deliveryCount = 0;
si.doneExecutingCount++;
r.stopIfKilled = true;
}
break;
}
.............
}
} else if (type == ActivityThread.SERVICE_DONE_EXECUTING_STOP) {
//Service的onStop函数被调用时,通知AMS的type为SERVICE_DONE_EXECUTING_STOP
//打一些log而已,无实际操作
..................
}
..........
serviceDoneExecutingLocked(r, inDestroying, inDestroying);
..........
} else {
........
}
}
主要针对处理onStartCommand的返回值
- Service.START_STICKY_COMPATIBILITY+Service.START_STICKY
1.找到startId对应的StartItem,并移除(true) 2.这个值置为false后,Service被杀掉还有机会重启 - Service.START_NOT_STICKY
1.找到startId对应的StartItem,并移除(true) 2.服务kill掉,不再重启 - Service.START_REDELIVER_INTENT
1.找到startId对应的StartItem,不移除(false) 2.重传Intent。使用这个返回值时,如果在执行完onStartCommand后,服务被异常kill掉,系统会自动重启该服务,并将Intent的值传入。
随后调用serviceDoneExecutingLocked()方法
private void serviceDoneExecutingLocked(ServiceRecord r, boolean inDestroying,
boolean finishing) {
...............
//ServiceRecord的一个命令执行完毕,executeNesting -1
//这些操作与前面提过的bumpServiceExecutingLocked函数,一一对应
r.executeNesting--;
//所有命令执行完毕
if (r.executeNesting <= 0) {
if (r.app != null) {
..............
r.app.execServicesFg = false;
//ServiceRecord被从executingServices移除,处理超时消息时,不会处理该Service
r.app.executingServices.remove(r);
//整个进程所有的Service命令均处理完毕
if (r.app.executingServices.size() == 0) {
............
//移除time out消息
mAm.mHandler.removeMessages(ActivityManagerService.SERVICE_TIMEOUT_MSG, r.app);
} else if (r.executeFg) {
// Need to re-evaluate whether the app still needs to be in the foreground.
for (int i=r.app.executingServices.size()-1; i>=0; i--) {
if (r.app.executingServices.valueAt(i).executeFg) {
//有一个Service是前台服务,则app仍是前台的
r.app.execServicesFg = true;
break;
}
}
}
if (inDestroying) {
.......
mDestroyingServices.remove(r);
r.bindings.clear();
}
mAm.updateOomAdjLocked(r.app);
}
r.executeFg = false;
if (r.tracker != null) {
//更新ServiceRecord的ServiceState
r.tracker.setExecuting(false, mAm.mProcessStats.getMemFactorLocked(),
SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
if (finishing) {
r.tracker.clearCurrentOwner(r, false);
r.tracker = null;
}
}
if (finishing) {
//若Service结束,将其从进程对应的记录信息中移除
if (r.app != null && !r.app.persistent) {
r.app.services.remove(r);
.............
}
r.app = null;
}
}
}
主要进行对ServiceRecord的收尾工作