OCUnit(即用XCTest进行测试
)苹果自带的测试框架,GHUnit是一个可视化的测试框架。(有了它,你可以点击APP来决定测试哪个方法,并且可以点击查看测试结果等。)OCMock就是模拟某个方法或者属性的返回值,你可能会疑惑为什么要这样做?使用用模型生成的模型对象,再传进去不就可以了?答案是可以的,但是有特殊的情况。比如你测试的是方法A,方法A里面调用到了方法B,而且方法B是有参数传入,但又不是方法A所提供。这时候,你可以使用OCMock来模拟方法B返回的值。(在不影响测试的情况下,就可以这样去模拟。)除了这些,在没有网络的情况下,也可以通过OCMock模拟返回的数据。UITests就是通过代码化来实现自动点击界面,输入文字等功能。靠人工操作的方式来覆盖所有测试用例是非常困难的,尤其是加入新功能以后,旧的功能也要重新测试一遍,这导致了测试需要花非常多的时间来进行回归测试,这里产生了大量重复的工作,而这些重复的工作有些是可以自动完成的,这时候UITests就可以帮助解决这个问题。
先来简单的了解一下单元测试
使用快捷键Command+U,这个快捷键是全部测试。
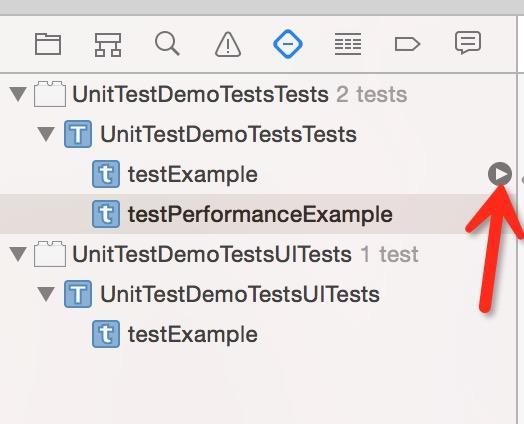
也可以单个方法的测试:
表示测试通过就会出现绿色的菱形
熟悉单元测试类
UnitTestsDemoTests类是继承与 XCTestCase的
- (void)setUp {
[super setUp];
// Put setup code here. This method is called before the invocation of each test method in the class.
//每个test方法执行之前调用
}
- (void)tearDown {
// Put teardown code here. This method is called after the invocation of each test method in the class.
[super tearDown];
// 每个test方法执行之后调用
}
- (void)testExample {
// This is an example of a functional test case.
// Use XCTAssert and related functions to verify your tests produce the correct results.
// 命名为Example的测试方法
}
//性能测试
- (void)testPerformanceExample {
// This is an example of a performance test case.
//主要检测代码的执行性能
[self measureBlock:^{
// Put the code you want to measure the time of here.
}];
}
Xcode7默认带了测试性能的方法- (void)testPerformanceExample
- (void)testPerformanceExample {
// This is an example of a performance test case.
[self measureBlock:^{
// Put the code you want to measure the time of here.
for(int i=0;i<1000;i++) {
NSLog(@"%d",i);
}
}];
}
重复执行上面的代码,会收集每次执行的时间,并计算出平均值,每次执行后会跟平均值进行比较,给你参考性的提示。
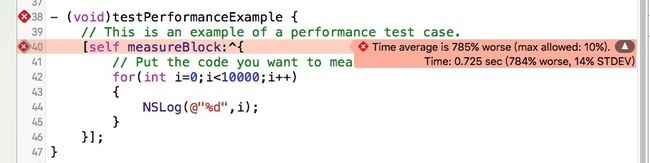
当我们把i的值后面增添一个0后:
XCode检测到这一次运行,远超过了平均值,给出了红色的警告
自定义测试方法
- 自定义测试方法必须以test方法名开头(testXXX),例如testExample
- 自定义方法必须为void返回类型
断言
大部分的测试方法使用断言决定的测试结果。所有断言都有一个类似的形式:比较,表达式为真假,强行失败等。
//通用断言
XCTAssert(expression, format...)
//常用断言:
XCTAssertTrue(expression, format...)
XCTAssertFalse(expression, format...)
XCTAssertEqual(expression1, expression2, format...)
XCTAssertNotEqual(expression1, expression2, format...)
XCTAssertEqualWithAccuracy(expression1, expression2, accuracy, format...)
XCTAssertNotEqualWithAccuracy(expression1, expression2, accuracy, format...)
XCTAssertNil(expression, format...)
XCTAssertNotNil(expression, format...)
XCTFail(format...) //直接Fail的断言
举个栗子
- (void)testExample {
//设置变量和设置预期值
NSUInteger a = 10;
NSUInteger b = 15;
NSUInteger expected = 24;
//执行方法得到实际值
NSUInteger actual = [self add:a b:b];
//断言判定实际值和预期是否符合
XCTAssertEqual(expected, actual,@"add方法错误!");
}
-(NSUInteger)add:(NSUInteger)a b:(NSUInteger)b{
return a+b;
}
从这也能看出一个测试用例比较规范的写法,1:定义变量和预期,2:执行方法得到实际值,3:断言
性能测试
性能测试主要使用measureBlock
方法 ,用于测试一组方法的执行时间,通过设置baseline(基准)和stddev(标准偏差)来判断方法是否能通过性能测试。
举个栗子:
- (void)testPerformanceExample {
// This is an example of a performance test case.
[self measureBlock:^{
//Put the code you want to measure the time of here.
//你的性能测试的代码放在这里
}];
}
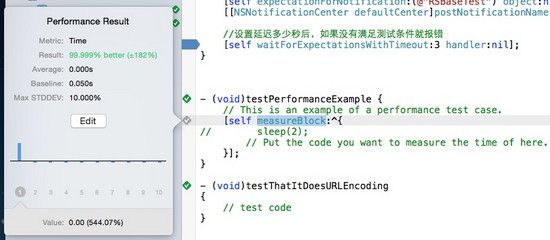
直接执行方法,因为block中没有内容,所以方法的执行时间为0.0s,如果我们把baseline设成0.05,偏差10%,是可以通过的测试的。但是如果设置如果我们把baseline为1,偏差10%,那测试会失败,因为不满足条件。
异步测试
测试异步方法时,因为结果并不是立刻获得,所以在异步方法测试有一些特殊的方法和技巧。
举个栗子:
- (void)testAsynExample {
XCTestExpectation *exp = [self expectationWithDescription:@"这里可以是操作出错的原因描述。。。"];
NSOperationQueue *queue = [[NSOperationQueue alloc]init];
[queue addOperationWithBlock:^{
//模拟这个异步操作需要2秒后才能获取结果,比如一个异步网络请求
sleep(2);
//模拟获取的异步操作后,获取结果,判断异步方法的结果是否正确
XCTAssertEqual(@"a", @"a");
//如果断言没问题,就调用fulfill宣布测试满足
[exp fulfill];
}]; //设置延迟多少秒后,如果没有满足测试条件就报错
[self waitForExpectationsWithTimeout:3 handler:^(NSError * _Nullable error) {
if (error) {
NSLog(@"Timeout Error: %@", error); }
}];
}
这个测试肯定是通过的,因为设置延迟为3秒,而异步操作2秒就除了一个正确的结果,并宣布了条件满足[exp fulfill]
,但是当我们把延迟改成1秒,这个测试用例就不会成功,错误原因是expectationWithDescription:@"这里可以是操作出错的原因描述。。。
异步测试除了使用expectationWithDescription
以外,还可以使用expectationForPredicate和expectationForNotification
下面这个例子使用expectationForPredicate
测试方法,代码来自于AFNetworking,用于测试backgroundImageForState
方法
- (void)testThatBackgroundImageChanges {
XCTAssertNil([self.button backgroundImageForState:UIControlStateNormal]);
NSPredicate *predicate = [NSPredicate predicateWithBlock:^BOOL(UIButton * _Nonnull button, NSDictionary * _Nullable bindings) {
return [button backgroundImageForState:UIControlStateNormal] != nil;
}];
[self expectationForPredicate:predicate evaluatedWithObject:self.button handler:nil];
[self waitForExpectationsWithTimeout:20 handler:nil];
}
利用谓词计算,button是否正确的获得了backgroundImage,如果正确20秒内正确获得则通过测试,否则失败。
expectationForNotification
方法 ,该方法监听一个通知,如果在规定时间内正确收到通知则测试通过。
-(void)testAsynExample1 {
[self expectationForNotification:(@"监听通知的名称xxx") object:nil handler:nil];
[[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter]postNotificationName:@"监听通知的名称xxx" object:nil];
//设置延迟多少秒后,如果没有满足测试条件就报错
[self waitForExpectationsWithTimeout:3 handler:nil];
}
命令行测试
测试不仅可以在xcode中执行,也可以在命令行中执行,这个便于代码持续集成和构建,在git提交中也编译检查代码
如果你有development-enabled设备插入,你可以按照名称或 id 调用他们。例如,如果你有一个名为”Development iPod touch”的 iPod 设备连接了测试的代码,可以使用下面的命令来测试代码> xcodebuild test -project MyAppProject.xcodeproj -scheme MyApp -destination 'platform=iOS,name=Development iPod touch
测试也可以在 iOS模拟器上运行。使用模拟器可以应对不同的外形因素和操作系统版本。例如> xcodebuild test -project MyAppProject.xcodeproj -scheme MyApp -destination 'platform=iOS Simulator,name=iPhone,0S=7.0'
-destination 参数可以被连接在一起,这样你只需使用一个命令,就可以跨目标进行指定集成共享方案。例如,下面的命令把之前的三个例子合并到一个命令中
> xcodebuild test -project MyAppProject.xcodeproj -scheme MyApp
-destination 'platform=OS X,arch=x86_64'
-destination 'platform=iOS,name=Development iPod touch'
-destination 'platform=iOS Simulator,name=iPhone,0S=7.0'
关于更多xcodebuild的使用可以查看man手册> man xcodebuild
执行测试快捷键
cmd + 5 切换到测试选项卡后会看到很多小箭头,点击可以单独或整体测试
cmd + U 运行整个单元测试
注意点
使用pod的项目中,在XC测试框架中测试内容包括第三方包时,需要手动去设置Header Search Paths才能找到头文件 ,还需要设置test target的PODS_ROOT。
参考阅读
http://www.tuicool.com/articles/jUrqiqR