前言
下面是我对realm研究的第一篇文章的传送门:YYWebImage工作原理介绍-----下载单张图片。接下来我会介绍YYWebImage的另一大功能------gif动态图播放。
如何使用
YYImage加载gif使用的是YYAnimatedImageView类。我们首先要新建一个YYAnimatedImageView对象:
YYAnimatedImageView *imageView=[YYAnimatedImageView new];
然后后两种加载UIimage的方式:
- 直接通过url加载:
NSURL *path = [[NSBundle mainBundle]URLForResource:@"guidegif" withExtension:@"gif"];
imageView.yy_imageURL = path;
- 通过YYImage加载:
NSURL *path = [[NSBundle mainBundle]URLForResource:@"guidegif_loop" withExtension:@"gif"];
YYImage * image = [YYImage imageWithContentsOfFile:path.path];
imageView.image = image;
YYAnimatedImageView类
他是YYImage加载gif的专供类。他继承于UIImageView,提供了位数不多的几个接口:
@property (nonatomic) BOOL autoPlayAnimatedImage;
@property (nonatomic) NSUInteger currentAnimatedImageIndex;
@property (nonatomic, readonly) BOOL currentIsPlayingAnimation;
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *runloopMode;
@property (nonatomic) NSUInteger maxBufferSize;
其中一个还是只读的,并不能设置。这里很不人性化,因为连最起码的loop数量都不开放出来,都写在了.m里面。
我们进入YYAnimatedImageView.m后会发现其实YYAnimatedImageView作为子类重写了很多父类的方法,所以很多设置方法我们要点入进去才能看到。我们顺着运行顺序看下去,首先是对image属性的赋值,这里面最核心的方法是:
- (void)setImage:(id)image withType:(YYAnimatedImageType)type {
[self stopAnimating];
if (_link) [self resetAnimated];
_curFrame = nil;
switch (type) {
case YYAnimatedImageTypeNone: break;
case YYAnimatedImageTypeImage: super.image = image; break;
case YYAnimatedImageTypeHighlightedImage: super.highlightedImage = image; break;
case YYAnimatedImageTypeImages: super.animationImages = image; break;
case YYAnimatedImageTypeHighlightedImages: super.highlightedAnimationImages = image; break;
}
[self imageChanged];
}
所有的对image的设置都会走到这里。主要是暂停动画,然后对image的一个设置,同时进入imageChanged。imageChanged里面主要是一些逻辑处理没什么说的,里面最关键的一句就是:
[self resetAnimated];
resetAnimated是整个实现gif动画的核心,想要高效的展现gif动画就必须重写系统的动画。那这里YYImage的实现方式和FLImage是一样,通过CADisplayLink定时器去绘制gif动画。这样就会使得内存大大的减少,但是CPU的占用会比较大,是以时间换空间的做法:
- (void)resetAnimated {
dispatch_once(&_onceToken, ^{
_lock = dispatch_semaphore_create(1);
_buffer = [NSMutableDictionary new];
_requestQueue = [[NSOperationQueue alloc] init];
_requestQueue.maxConcurrentOperationCount = 1;
_link = [CADisplayLink displayLinkWithTarget:[_YYImageWeakProxy proxyWithTarget:self] selector:@selector(step:)];
if (_runloopMode) {
[_link addToRunLoop:[NSRunLoop mainRunLoop] forMode:_runloopMode];
}
_link.paused = YES;
[[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter] addObserver:self selector:@selector(didReceiveMemoryWarning:) name:UIApplicationDidReceiveMemoryWarningNotification object:nil];
[[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter] addObserver:self selector:@selector(didEnterBackground:) name:UIApplicationDidEnterBackgroundNotification object:nil];
});
[_requestQueue cancelAllOperations];
LOCK(
if (_buffer.count) {
NSMutableDictionary *holder = _buffer;
_buffer = [NSMutableDictionary new];
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_global_queue(DISPATCH_QUEUE_PRIORITY_LOW, 0), ^{
// Capture the dictionary to global queue,
// release these images in background to avoid blocking UI thread.
[holder class];
});
}
);
_link.paused = YES;
_time = 0;
if (_curIndex != 0) {
[self willChangeValueForKey:@"currentAnimatedImageIndex"];
_curIndex = 0;
[self didChangeValueForKey:@"currentAnimatedImageIndex"];
}
_curAnimatedImage = nil;
_curFrame = nil;
_curLoop = 0;
_totalLoop = 0;
_totalFrameCount = 1;
_loopEnd = NO;
_bufferMiss = NO;
_incrBufferCount = 0;
}
这里要注意的是,yyimage对播放做了优化,他在显示了一张图片后,立马缓存好下一张为接下来的播放做准备,这就是他比FL更流程的关键,这句代码在他的:
- (void)step:(CADisplayLink *)link
方法中,这个方法是被CADisplayLink绑定了的。
优化的代码:
if (!bufferIsFull && _requestQueue.operationCount == 0) { // if some work not finished, wait for next opportunity
_YYAnimatedImageViewFetchOperation *operation = [_YYAnimatedImageViewFetchOperation new];
operation.view = self;
operation.nextIndex = nextIndex;
operation.curImage = image;
[_requestQueue addOperation:operation];
}
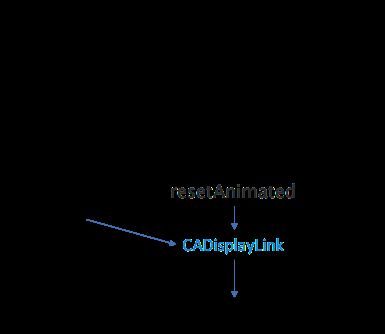
整个流程大致如下:
总结
YYImage播放gif的能力,是我见过的图片库中最强的。他的流畅和易用值得我们把FL替换掉。美中不足的是他给我们提供的借口太少,我们能完成的功能也就是不停的播放gif。虽然YYImage还提供了一个YYSpriteSheetImage,但是配置比较复杂,而且不能加载gif,只能是图片数组。加载UIImage的时候,推荐用第二种方法--先变成YYImag,因为直接用url可能一开始会找不到图片,造成屏幕闪烁的情况。