使用构造方法
var p1 = Point(2, 2);
var p2 = Point.fromJson({'x': 1, 'y': 2});
var p1 = new Point(2, 2);
var p2 = new Point.fromJson({'x': 1, 'y': 2});
上面这两种写法都是可以的,Dart2中new关键字已经成为一个可选项
常量构造方法
有些类提供常量构造函数。要使用常量构造函数创建编译时常量,请将const关键字放在构造函数名称之前
var p = const ImmutablePoint(2, 2);
构造两个相同的编译时常量会产生一个规范的实例:
var a = const ImmutablePoint(1, 1);
var b = const ImmutablePoint(1, 1);
assert(identical(a, b)); // They are the same instance!
如果将const关键字前置的话,后面的const是可以省略的,比如
// Lots of const keywords here.
const pointAndLine = const {
'point': const [const ImmutablePoint(0, 0)],
'line': const [const ImmutablePoint(1, 10), const ImmutablePoint(-2, 11)],
};
上面的代码可以写成
// Only one const, which establishes the constant context.
const pointAndLine = {
'point': [ImmutablePoint(0, 0)],
'line': [ImmutablePoint(1, 10), ImmutablePoint(-2, 11)],
};
获取运行时类型
要在运行时获取对象的类型,可以使用Object的runtimeType属性,该属性返回Type对象。
print('The type of a is ${a.runtimeType}');
声明构造函数
class Point {
num x, y;
// Syntactic sugar for setting x and y
// before the constructor body runs.
Point(this.x, this.y);
}
上面是一种简化版的构造函数,只是为了赋值,所以省略了方法体
如果您未声明构造函数,则会为您提供默认构造函数。
默认构造函数没有参数,并在超类中调用无参数构造函数。
命名构造函数
使用命名构造函数为类实现多个构造函数或提供额外的清晰度:
class Point {
num x, y;
Point(this.x, this.y);
// Named constructor
Point.origin() {
x = 0;
y = 0;
}
}
跟Java等语言不同,Dart的多重构造方法是一种类名.自定义方法名来实现的,如果你按照传统的方法来写的话,例如这样:
class Grammar2 {
var x, y, z;
Grammar2(this.x,this.y); //错误
Grammar2(this.x); //不能同时拥有两个这样的构造函数
}
正确的写法
class Grammar2 {
var x, y, z;
Grammar2.translate(this.x, this.y); //TODO 构造方法的重载
Grammar2(this.x,this.y);
printRealVar() {
print('x=' + x.toString() + "y=" + y.toString());
return 2;
}
@override
String toString() {
// TODO: implement toString
return "this is Grammar2";
}
}
调用非默认的超类构造函数
默认情况下,子类中的构造函数调用超类的未命名的无参数构造函数。
超类的构造函数在构造函数体的开头被调用。
如果还使用初始化列表,则在调用超类之前执行。
总之,执行顺序如下:
class Person {
String firstName;
Person.fromJson(Map data) {
print('in Person');
}
}
class Employee extends Person {
// Person does not have a default constructor;
// you must call super.fromJson(data).
Employee.fromJson(Map data) : super.fromJson(data) {
print('in Employee');
}
}
main() {
var emp = new Employee.fromJson({});
// Prints:
// in Person
// in Employee
if (emp is Person) {
// Type check
emp.firstName = 'Bob';
}
(emp as Person).firstName = 'Bob';
}
这段代码的执行结果就是:
in Person
in Employee
除了调用超类构造函数之外,还可以在构造函数体运行之前初始化实例变量。
用冒号分隔初始化程序。
// Initializer list sets instance variables before
// the constructor body runs.
Point.fromJson(Map json)
: x = json['x'],
y = json['y'] {
print('In Point.fromJson(): ($x, $y)');
}
这个示例中,我们在调用fromjson这个构造方法之前我们抢先初始化了x和y的值,中间用冒号隔开
你也可以在调用初始化方法之前进行一些参数的验证,比如:
Point.withAssert(this.x, this.y) : assert(x >= 0) {
print('In Point.withAssert(): ($x, $y)');
}
这个示例中,构造方法调用之前,我们验证了x必须为正数
构造函数的重定向
我们在开发中经常会有这样的情景,我们构造了好几个构造方法,但是这些构造方法本身并不执行任何操作,只是为了调用其他构造 方法,在Dart中,我们称之为构造方法的重定向(这个语法在前面示例中出现过)
class Point {
num x, y;
// The main constructor for this class.
Point(this.x, this.y);
// Delegates to the main constructor.
Point.alongXAxis(num x) : this(x, 0);
}
常量构造方法
假如你的示例在整个程序从始至终都不会变更实例,这个时候你可以考虑一下使用常量构造方法,在构造方法前面加上const关键字(是不是很像单例模式?)
class ImmutablePoint {
static final ImmutablePoint origin =
const ImmutablePoint(0, 0);
final num x, y;
const ImmutablePoint(this.x, this.y);
}
工厂构造方法
跟工厂设计模式类似,需要什么给你什么,根据一个特定的标识产生不同的实例,在Dart中,通过传入一个特定的标识符,来查看我的静态缓存里面有没有这个缓存,如果有,直接返回,如果没有,我便new 一个对象存入缓存再返回
class Logger {
final String name;
bool mute = false;
// _cache is library-private, thanks to
// the _ in front of its name.
static final Map _cache =
{};
factory Logger(String name) {
if (_cache.containsKey(name)) {
return _cache[name];
} else {
final logger = Logger._internal(name);
_cache[name] = logger;
return logger;
}
}
Logger._internal(this.name);
void log(String msg) {
if (!mute) print(msg);
}
}
工厂构造函数无权访问 this
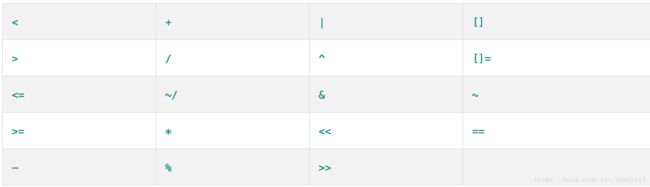
对象之间的操作符运算
您可以覆盖下表中显示的运算符。
例如,如果定义Vector类,则可以定义一个+方法来添加两个向量。(翻译自官网)
来个示例,自己体会
class Vector {
final int x, y;
Vector(this.x, this.y);
Vector operator +(Vector v) => Vector(x + v.x, y + v.y);
Vector operator -(Vector v) => Vector(x - v.x, y - v.y);
// Operator == and hashCode not shown. For details, see note below.
// ···
}
void main() {
final v = Vector(2, 3);
final w = Vector(2, 2);
assert(v + w == Vector(4, 5));
assert(v - w == Vector(0, 1));
}
要在代码尝试使用不存在的方法或实例变量时检测或做出反应,您可以覆盖noSuchMethod():
class A {
// Unless you override noSuchMethod, using a
// non-existent member results in a NoSuchMethodError.
@override
void noSuchMethod(Invocation invocation) {
print('You tried to use a non-existent member: ' +
'${invocation.memberName}');
}
}
枚举类
enum Color { red, green, blue }
枚举中的每个值都有一个索引getter,它返回枚举声明中值的从零开始的位置。
例如,第一个值具有索引0,第二个值具有索引1。
assert(Color.red.index == 0);
assert(Color.green.index == 1);
assert(Color.blue.index == 2);
要获取枚举中所有值的列表,请使用枚举值常量。
List
assert(colors[2] == Color.blue);
switch case中使用枚举
var aColor = Color.blue;
switch (aColor) {
case Color.red:
print('Red as roses!');
break;
case Color.green:
print('Green as grass!');
break;
default: // Without this, you see a WARNING.
print(aColor); // 'Color.blue'
}
Mixin
Mixins是一种在多个类层次结构中重用类代码的方法,B继承于A,但是B也要用到C的一些特性,多继承在很多语言中是行不通的,Dart中的Mixin就是为了解决这种问题出现的
要使用mixin,请使用with关键字,后跟一个或多个mixin名称。
以下示例显示了两个使用mixins的类:
class Musician extends Performer with Musical {
// ···
}
class Maestro extends Person
with Musical, Aggressive, Demented {
Maestro(String maestroName) {
name = maestroName;
canConduct = true;
}
}
注意:要实现一个mixin,创建一个扩展Object的类,声明没有构造函数,并且没有调用super。
例如:
abstract class Musical {
bool canPlayPiano = false;
bool canCompose = false;
bool canConduct = false;
void entertainMe() {
if (canPlayPiano) {
print('Playing piano');
} else if (canConduct) {
print('Waving hands');
} else {
print('Humming to self');
}
}
}
泛型方法(只看代码不解释,跟java几乎一样)
T first(List ts) {
// Do some initial work or error checking, then...
T tmp = ts[0];
// Do some additional checking or processing...
return tmp;
}
导入
Dart目前都要手动导入包,Dart内置的library可以直接用import 'Interface.dart';方法导入,自定义的包可以在前面加入一个package关键字导入
import 'package:flutter_app/Grammar2.dart';
import 'SuperGrammar.dart';
import 'Interface.dart';
import 'FactoryClass.dart';
import 'package:meta/meta.dart';
import 'ConstantClass.dart';
有一种情况例外,加入导入的两个包里面有同名的类,这个时候如何区分,java 是用全路径来标识,Dart里面可以给这个包里面所有的类设置一个别名
import 'package:lib1/lib1.dart';
import 'package:lib2/lib2.dart' as lib2; //这里利用as来设置 别名
// Uses Element from lib1.
Element element1 = Element();
// Uses Element from lib2.
lib2.Element element2 = lib2.Element();
如果你想导入的是一个包中的部分类
// Import only foo.
import 'package:lib1/lib1.dart' show foo;
// Import all names EXCEPT foo.
import 'package:lib2/lib2.dart' hide foo;
设置这个功能的出发点是可以降低包体积么??? 不得而知
improt 懒加载
这个是为了在使用导入的类的时候才会去载入这个包,主要是为了提升启动效率
如果需要使用懒加载的功能,请使用deferred as 关键字
import 'package:greetings/hello.dart' deferred as hello;
//需要的时候调用别名.loadLibiary方法
Future greet() async {
await hello.loadLibrary();
hello.printGreeting();
}
在前面的这段代码中 await 关键字的作用是暂停程序的运行直到包导入完成
延迟库的常量不是导入文件中的常量。
请记住,在加载延迟库之前,这些常量不存在。您不能在导入文件中使用延迟库中的类型。
相反,请考虑将接口类型移动到由延迟库和导入文件导入的库。Dart隐式地将loadLibrary()插入到使用deferred as namespace定义的命名空间中。loadLibrary()函数返回Future。