Course Digest
正则表达式30min教程
- 格式化字符串??
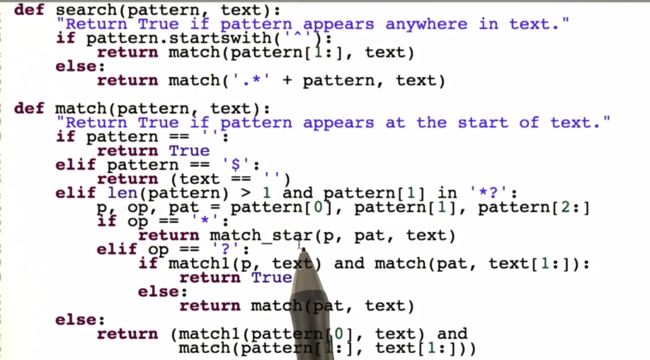
def matchset(pattern, text):
"Match pattern at start of text; return a set of remainders of text."
op, x, y = components(pattern)
if 'lit' == op:
return set([text[len(x):]]) if text.startswith(x) else null
elif 'seq' == op:
return set(t2 for t1 in matchset(x, text) for t2 in matchset(y, t1))
elif 'alt' == op:
return matchset(x, text) | matchset(y, text)
elif 'dot' == op:
return set([text[1:]]) if text else null
elif 'oneof' == op:
# return set([text[1:]]) if text[0] in x else null
return set(text[1:]]) if text.startwith(x)
elif 'eol' == op:
return set(['']) if text == '' else null
elif 'star' == op:
return (set([text]) |
set(t2 for t1 in matchset(x, text)
for t2 in matchset(pattern, t1) if t1 != text))
else:
raise ValueError('unknown pattern: %s' % pattern)
null = frozenset()
def components(pattern):
"Return the op, x, and y arguments; x and y are None if missing."
x = pattern[1] if len(pattern) > 1 else None
y = pattern[2] if len(pattern) > 2 else None
return pattern[0], x, y
def test():
assert matchset(('lit', 'abc'), 'abcdef') == set(['def'])
assert matchset(('seq', ('lit', 'hi '),
('lit', 'there ')),
'hi there nice to meet you') == set(['nice to meet you'])
assert matchset(('alt', ('lit', 'dog'),
('lit', 'cat')), 'dog and cat') == set([' and cat'])
assert matchset(('dot',), 'am i missing something?') == set(['m i missing something?'])
assert matchset(('oneof', 'a'), 'aabc123') == set(['abc123'])
assert matchset(('eol',),'') == set([''])
assert matchset(('eol',),'not end of line') == frozenset([])
assert matchset(('star', ('lit', 'hey')), 'heyhey!') == set(['!', 'heyhey!', 'hey!'])
return 'tests pass'
print test()
- str.startwith(x) 中x可以是一个tuple
字节码参考信息:
官方Doc
博客1
博客2
博客3-推荐Recognizer & Generator
def test(a):
return 1 if a>0 else 0 if a == 0 else -1
- 编译器优化之一:避免重复
- 函数式编程(装饰器用法)
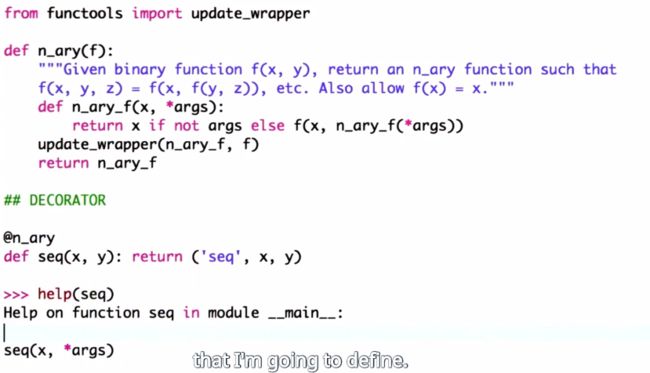
def n_ary(f):
"""Given binary function f(x, y), return an n_ary function such
that f(x, y, z) = f(x, f(y,z)), etc. Also allow f(x) = x."""
def n_ary_f(x, *args):
# return f(x) if len(args)==0 else f(x, args[0]) \
# if len(args)==1 else f(x, n_ary_f(args[0], *args[1:]))
return x if not args else f(x, n_ary_f(*args))
return n_ary_f
@n_ary
def seq(x, y):
return ('seq', x, y)
print(seq(1, 2, 3, 4, 5))
# output: ('seq', 1, ('seq', 2, ('seq', 3, ('seq', 4, 5))))
- @decorator 该函数定义了一些迁移文档的语句块(大概)。这样很是方便。
后面的函数名称会在命名空间中覆写掉之前的定义
def test():
print('test')
def test():
print('Fake test')
test()
# Out: Fake test
- Memoization: look-up, computation, store
- Interesting:老师随意给出一个数字——42。_
- 字典的键值必须immutable.s
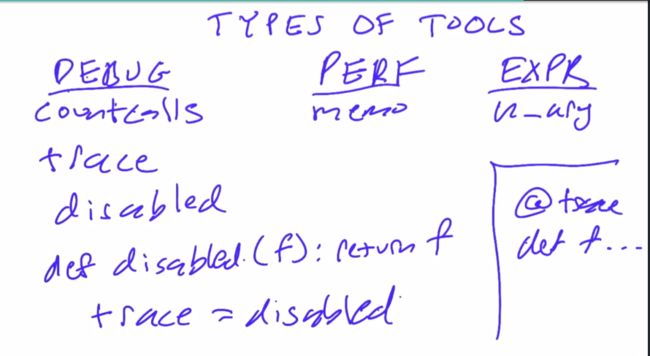
Tools types
debugging tool
performance tool
expressive tool
** Usefule trace decorator**
from functools import update_wrapper
def decorator(d):
"Make function d a decorator: d wraps a function fn."
def _d(fn):
return update_wrapper(d(fn), fn)
update_wrapper(_d, d)
return _d
@decorator
def trace(f):
indent = ' '
def _f(*args):
signature = '%s(%s)' % (f.__name__, ', '.join(map(repr, args)))
print '%s--> %s' % (trace.level*indent, signature)
trace.level += 1
try:
result = f(*args)
print '%s<-- %s == %s' % ((trace.level-1)*indent,
signature, result)
finally:
trace.level -= 1
return result
trace.level = 0
return _f
@trace
def fib(n):
if n == 0 or n == 1:
return 1
else:
return fib(n-1) + fib(n-2)
fib(6)
- ** Context-free languages**
- ** Wishful Thinking**
# ---------------
# User Instructions
#
# Modify the parse function so that it doesn't repeat computations.
# You have learned about a tool in this unit that prevents
# repetitive computations. Try using that!
#
# For this question, the grader will be looking for a specific
# solution. Hint: it should only involve adding one line of code
# (and that line should only contain 5 characters).
from functools import update_wrapper
import re
def parse(start_symbol, text, grammar):
"""Example call: parse('Exp', '3*x + b', G).
Returns a (tree, remainder) pair. If remainder is '', it parsed the whole
string. Failure iff remainder is None. This is a deterministic PEG parser,
so rule order (left-to-right) matters. Do 'E => T op E | T', putting the
longest parse first; don't do 'E => T | T op E'
Also, no left recursion allowed: don't do 'E => E op T'"""
tokenizer = grammar[' '] + '(%s)'
def parse_sequence(sequence, text):
result = []
for atom in sequence:
tree, text = parse_atom(atom, text)
if text is None: return Fail
result.append(tree)
return result, text
@memo # This decorator makes parser work faster.
def parse_atom(atom, text):
if atom in grammar: # Non-Terminal: tuple of alternatives
for alternative in grammar[atom]:
tree, rem = parse_sequence(alternative, text)
if rem is not None: return [atom]+tree, rem
return Fail
else: # Terminal: match characters against start of text
m = re.match(tokenizer % atom, text)
return Fail if (not m) else (m.group(1), text[m.end():])
# Body of parse:
return parse_atom(start_symbol, text)
Fail = (None, None)
# The following decorators may help you solve this question. HINT HINT!
def decorator(d):
"Make function d a decorator: d wraps a function fn."
def _d(fn):
return update_wrapper(d(fn), fn)
update_wrapper(_d, d)
return _d
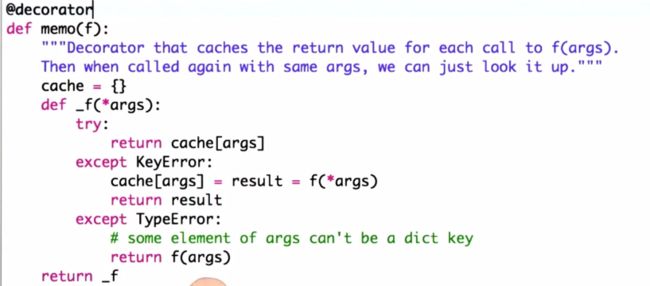
@decorator
def memo(f):
"""Decorator that caches the return value for each call to f(args).
Then when called again with same args, we can just look it up."""
cache = {}
def _f(*args):
try:
return cache[args]
except KeyError:
cache[args] = result = f(*args)
return result
except TypeError:
# some element of args can't be a dict key
return f(args)
return _f