#多项式回归
import numpyas np
import tensorflowas tf
import matplotlib.pyplotas plt
plt.rcParams["figure.figsize"] = (14,8)
#准备好数据
n_observations =100
xs = np.linspace(-3,3,n_observations)
ys = np.sin(xs)+np.random.uniform(-0.5,0.5,n_observations)
plt.scatter(xs,ys)
plt.show()
#准备好placeholder
X = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,name='X')
Y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,name='Y')
#初始化权重和偏置
W = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1]),name='Weight')#权重一
W_2 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1]),name='Weight_2')#权重二
W_3 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1]),name='Weight_3')#权重三
b = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1]),name='bias')
#计算预测结果
Y_pred = tf.add(tf.multiply(X,W),b)#y1 = X*W+b
Y_pred = tf.add(tf.multiply(tf.pow(X,2),W_2),Y_pred)# y2 =X*X*W_2+y1
Y_pred = tf.add(tf.multiply(tf.pow(X,3),W_3),Y_pred)#y3 = X*X*X*W_3+y2
#y = X*X*X*W_3+X*X*W_2+X*W+b
#计算损失函数值
sample_num = xs.shape[0]
loss = tf.reduce_sum(tf.pow(Y_pred-Y,2))/sample_num#均方误差
#初始化optimizer
learning_rate =0.01
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(loss)
#制定迭代次数,并在session中执行graph
n_samples = xs.shape[0]
with tf.Session()as sess:
#初始化说有变量
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
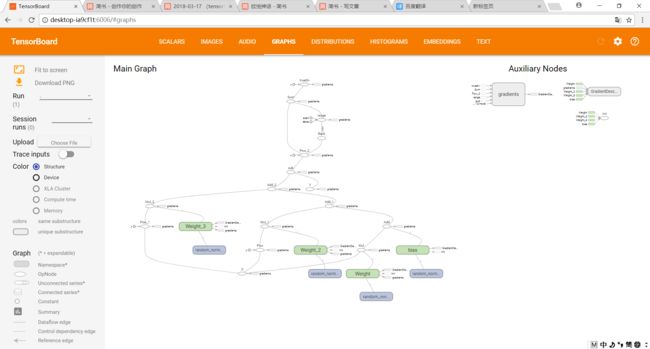
writer = tf.summary.FileWriter('./graphs/poplynomial_reg_2',sess.graph)
#训练模型
for iin range(1000):
total_loss =0
for x,yin zip(xs,ys):
#通过feed_dict将参数传入
_,l = sess.run([optimizer,loss],feed_dict={X:x,Y:y})
total_loss += l
if i%20==0:
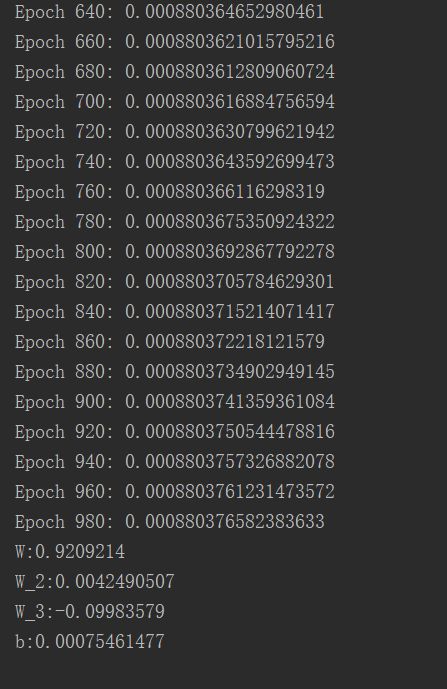
print('Epoch {0}: {1}'.format(i,total_loss/n_samples))
writer.close()
W,W_2,W_3,b = sess.run([W,W_2,W_3,b])
print("W:"+str(W[0]))
print("W_2:"+str(W_2[0]))
print("W_3:"+str(W_3[0]))
print("b:"+str(b[0]))
plt.plot(xs, ys, 'bo', label='Real data')
plt.plot(xs, xs*W + np.power(xs,2)*W_2 + np.power(xs,3)*W_3 + b, 'r', label='Predicted data')
plt.legend()
plt.show()