概述
Thrift是Facebook实现的一种高效的、支持多种编程语言的远程服务调用的框架
Thrift 服务器包含用于绑定协议和传输层的基础架构,它提供阻塞、非阻塞、单线程和多线程的模式运行在服务器上,可以配合服务器 / 容器一起运行,可以和现有的 J2EE 服务器 /Web 容器无缝的结合
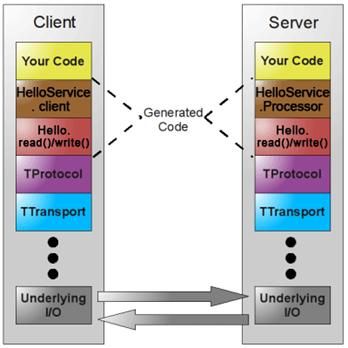
黄色部分是用户实现的业务逻辑
褐色部分是根据 Thrift 定义的服务接口描述文件生成的客户端和服务器端代码框架
红色部分是根据 Thrift 文件生成代码实现数据的读写操作
红色部分以下是 Thrift 的传输体系、协议以及底层 I/O 通信,使用 Thrift 可以很方便的定义一个服务并且选择不同的传输协议和传输层而不用重新生成代码
数据类型
Thrift脚本支持的数据类型
| 类型 | 说明 | java中对应类型 |
|---|---|---|
| bool | 布尔值,bool or false | boolean |
| byte | 8位有符号整数 | byte |
| i16 | 16位有符号整数 | short |
| i32 | 32位有符号整数 | int |
| i64 | 64位有符号整数 | long |
| double | 64位浮点数 | double |
| string | 未知编码文本或二进制字符串 | String |
| struct | 结构体类型 | JavaBean |
| list | 容器类型,数组 | ArrayList |
| set | 容器类型,集合 | HashSet |
| map | 容器类型,映射 | HashMap |
| exception | 异常类型 | Exception |
| service | 服务类型,对应服务的类 | 无 |
协议
大致分为文本和二进制传输协议,一般使用二进制类型协议,以节约带宽,提高传输效率,常用的有
- TBinaryProtocol
二进制编码格式进行数据传输 - TCompactProtocol
高效率的、密集的二进制编码格式进行数据传输
服务器端使用方式
TCompactProtocol.Factory factory = new TCompactProtocol.Factory();
客户端使用方式
TCompactProtocol protocol = new TCompactProtocol( transport ); - TDenseProtocol
类似于TCompactProtocol,但去除了发送端的数据元信息,将其增加在接收方尾部,实验性质的协议 - TJSONProtocol
使用JSON的数据编码协议进行数据传输
服务器端使用方式
TJSONProtocol.Factory factory = new TJSONProtocol.Factory();
客户端使用方式
TJSONProtocol protocol = new TJSONProtocol( transport ) - TSimpleJSONProtocol
JSON只写的协议,使用与脚本语言解析 - TDebugProtocol
使用自然语言文本格式来帮助调试
传输层
常用的传输层有
- TSocket
使用阻塞式I/O进行传输
服务端使用方式:
TServerSocket serverTransport = new TServerSocket( port );
客户端使用方式:
TTransport transport = new TSocket( name, port ) - TFramedTransport
使用非阻塞方式,按块的大小进行传输
服务端使用方式:
TNonblockingServerTransport serverTransport = new TNonblockingServerSocket( port );
Hello.Processor processor = new Hello.Processor( new HelloServiceImpl() );
TServer server = new TNonblockingServer( proessor, serverTransport );
server.serve();
客户端使用方式:
TTransport transport = new TFramedTransport( new TSocket( name, port ) )
使用TFramedTransport,服务端必须修改为非阻塞的服务类型
- TFileTransport
用于写文件,不过这种方式没有进行java实现 - TMemoryTransport
用内存进行I/O,java实现内部使用的简单的ByteArrayOutputStream - TZlibTransport
使用zlib进行数据压缩,没有进行java实现 - TNonblockingTransport
使用非阻塞方式,构建异步客户端
服务端类型
常见的服务端类型有
- TSimpleServer
单线程服务器端使用标准的阻塞式I/O
服务端使用方式
TServerSocker serverTransport = new TServerSocket( port );
TProcessor processor = new Hello.Processor( new XXImpl() );
TServer server = new TSimpleServer( processor, serverTransport );
server.serve();
客户端无影响
- TThreadPoolServer
多线程服务器端使用标准的阻塞式I/O - TNonblockingServer
多线程服务器端使用非阻塞式I/O
Thrift对于一个server仅允许提供一个service,可以通过定义工作组来扩展其他的service,这样模拟多个server的情形
Thrift异步客户端构建
Thrift提供了TAsyncClientManager管理客户端请求,在一个线程上追赃请求和响应,同时,通过接口AsyncClient传递标准的参数和callback对象,服务调用完成后,callback提供处理调用结果和异常的方法
-
HelloServiceAsyncServer.java
创建非阻塞服务端实现代码
package service.server;
import org.apache.thrift.server.TNonblockingServer;
import org.apache.thrift.server.TServer;
import org.apache.thrift.transport.TNonblockingServerSocket;
import org.apache.thrift.transport.TNonblockingServerTransport;
import org.apache.thrift.transport.TTransportException;
import service.demo.Hello;
import service.demo.HelloServiceImpl;
public class HelloServiceAsyncServer {
public static void main( String[] args ) {
TNonblockingServerTransport serverTransport;
try {
serverTransport = new TNonblockingServerSocket( 10005 );
Hello.Processor processor = new HelloProcessor( new HelloServiceImpl() );
TServer server = new TNonblockingServer( processor, serverTransport );
server.serve();
} catch ( TTransportException e ) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
HelloServiceAsyncServer 通过 java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel 创建非阻塞的服务器端等待客户端的连接
MethodCallback.java
package service.callback;
import org.apache.thrift.async.AsyncMethodCallback;
public class MethodCallback implements AsyncMethodCallback {
Object response = null;
public Object getResult() {
return this.response;
}
@Override
public void OnComplete( Object response ) {
this.response = response;
}
@Override
public void onError( Throwable throwable ) {
}
}
onComplete方法接收服务处理后的结果
-
HelloServiceAsyncClient.java
创建异步客户端实现代码,调用 Hello.AsyncClient 访问服务端的逻辑实现,将 MethodCallback 对象作为参数传入调用方法中
package service.client;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.thrift.async.AsyncMethodCallback;
import org.apache.thtift.async.TAsyncClientManeger;
import org.apache.thrift.protocol.TBinaryProtocol;
import org.apache.thrift.protocol.TProtocolFactory;
import org.apache.thrift.transport.TNonblockingSocket;
import org.apache.thrift.transport.TNonblockingTransport;
import service.callback.MethodCallback;
import service.demo.Hello;
public class HelloServiceAsyncClient {
public static void main( String[] args ) throws Exception {
try {
TAsyncClientManager clientManeger = new TAsyncClientManager();
TNonblockingTransport transport = new TNonblockingSocket( "localhost", 10005 );
TProtocolFactory factory = new TBinaryProtocol.Factory();
Hello.AsyncClient asyncClient = new Hello.AsyncClient( factory, clientManager, transport );
MethodCallback callBack = new MethodCallback();
asyncClient.helloString( "HelloWord", callBack );
Object res = callBack.getResult();
while ( res == null )
{
res = callBack.getResult();
}
}
}
}
HelloServiceAsyncClient 通过 java.nio.channels.Socketchannel 创建异步客户端与服务器建立连接
示例
Hello源代码
Hello.thrift
namespace java service.demo
service Hello {
string helloString( 1:string para )
i32 helloInt( 1:i32 para )
bool helloBoolean( 1:bool para )
void helloVoid()
string helloNull()
}
HelloServiceImpl.java
package service.demo;
import org.apache.thrift.TException;
public class HelloServiceImpl implements Hello.Iface {
@Override
public String helloString( String para ) throws TException {
return para;
}
@Override
public int helloInt( int para ) throws TException {
try {
Thread.sleep( 20000 );
} catch ( InterruptedException e ) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return para;
}
@Override
public boolean helloBoolean( boolean para ) throws TException {
return para;
}
@Override
public void helloVoid() throws TException {
System.out.println( "Hello World" );
}
@Override
public String helloNull() throws TException {
return null;
}
}
HelloServiceServer.java
package service.server;
import org.apache.thrift.TProcessor;
import org.apache.thrift.protocol.TBinaryProtocol;
import org.apache.thrift.protocol.TBinaryPortocol.Factory;
import org.apache.thrift.server.TServer;
import org.apache.thrift.server.TThreadPoolServer;
import org.apache.thrift.transport.TServerSocket;
import org.apache.thrift.transport.TTransportException;
import service.demo.Hello;
import service.demo.HelloServiceImpl;
public class HelloServiceServer {
public static void main( String[] args ) {
try {
TServerSocket serverTransport = new TServerSocket( 7911 );
Factory factory = new TBinaryProtocol.Factory();
TProcessor processor = new Hello.Processor( new HelloServiceImpl() );
TServer server = new TThreadPoolServer( processor, serverTransport, factory );
server.serve();
} catch ( TTransportException e ) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
HelloServiceClient.java
package service.client;
import org.apache.thrift.TException;
import org.apache.thrift.protocol.TBinaryProtocol;
import org.apache.thrift.protocol.TProtocol;
import org.apache.thrift.transport.TTransport;
import org.apache.thrift.transport.TSocket;
import org.apache.thrift.transport.TTransportException;
import service.demo.Hello;
public class HelloServiceClient {
public static void main( String[] args ) {
try {
TTransport transport = new TSocket( "localhost", 7911 );
transport.open();
TProtocol protocol = new TBinaryProtocol( transport );
Hello.Client client = new Hello.Client( protocol );
client.helloVoid();
transport.close();
} catch ( TTransportException e ) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch ( TException e ) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Hello服务端和客户端调用流程
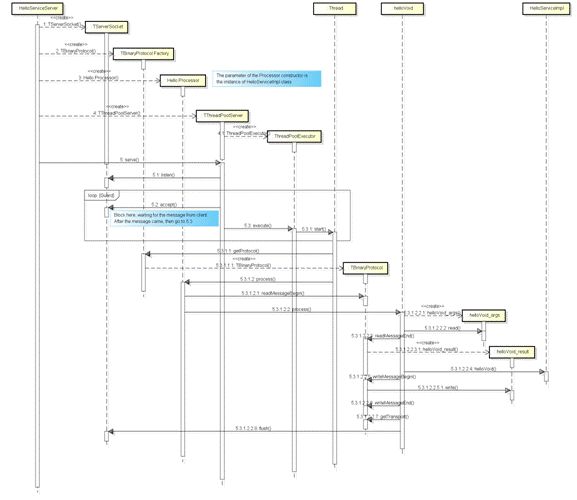
服务端时序
程序调用了 TThreadPoolServer 的 serve 方法后,server 进入阻塞监听状态,其阻塞在 TServerSocket 的 accept 方法上。当接收到来自客户端的消息后,服务器发起一个新线程处理这个消息请求,原线程再次进入阻塞状态。在新线程中,服务器通过 TBinaryProtocol 协议读取消息内容,调用 HelloServiceImpl 的 helloVoid 方法,并将结果写入 helloVoid_result 中传回客户端
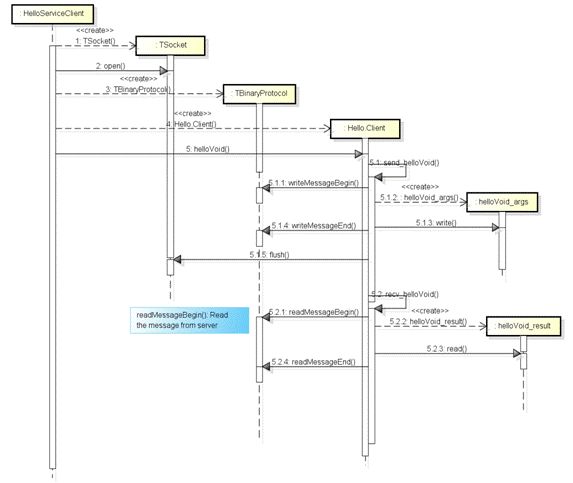
客户端时序
程序调用了 Hello.Client 的 helloVoid 方法,在 helloVoid 方法中,通过 send_helloVoid 方法发送对服务的调用请求,通过 recv_helloVoid 方法接收服务处理请求后返回的结果
NULL问题
在 Thrift 中,直接调用一个返回 null 值的方法会抛出 TApplicationException 异常(异常种类为 MISSING_RESULT)
为了处理返回 null 值情况,我们要捕获该异常,并进行相应的处理
参考链接:
- Apache Thrift - 可伸缩的跨语言服务开发框架
- Apache Thrift - SETT