Overview of the Types of Hadoop-based application:
Databases/Stores
Avro: It lets us use date structures within context of Hadoop MapReduce jobs, so process data very efficiently.
HBase: distributed non-relational database
Cassandra: distributed data management system
Querying
Pig: analyzing large data sets in HDFS, it has its own high-level language (Pig Latin) for you.
Hive: Query and manage large datasets in HDFS or in HBase, with a SQL-like interface.
Impala: High-performance and low-tatency query with SQL-like interface, providing from Cloudera VM (Hue).
Spark: General processing engine for streaming, SQL, machine learning and graph processing
Machine Learning/Graph Processing
Giraph: Iterative graph processing using Hadoop framework
Mahout: Framework for machine learning applications using Hadoop, Spark.
Spark: General processing engine for streaming, SQL, machine learning and graph processing
Apache Pig
Two componets:
Own script language - PigLatin. PigLatin can be embedded in host language like Java
Infrastructure Layer - it takes what we wrote in PigLatin, and transforms into back-end jobs of Tez or MapReduce, etc.
Usage:
extract / transform / load / handling "raw" data. more
Extendibility:
It has built-in operators and functions, as well as supporting us to write constant functions if we have complex processing to do.
Use cases:
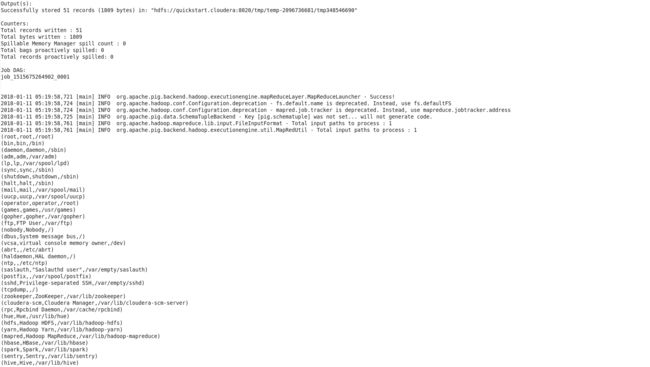
Step1 . Put a passwd into HDFS
[cloudera@quickstart ~]$ hadoop fs -put /etc/passwd /user/cloudera/
* Command "hadoop fs ..." == "hdfs dfs ..."
Step 2. With MapReduce as execution type and launch Pig inteactive shell "grunt"
[cloudera@quickstart ~]$ pig -x mapreduce --> it use MapReduce to track data and print it out.
grunt>
Step 3. wrote PigLatin - PigLatin need ';' to end one command. Like below:
grunt> A = load '/user/cloudera/passwd' using PigStorage(':'); --> telling the deparator is colon
grunt> B = foreach A generate $0, $4, $5 ; --> doing the sub-setting part
grunt> dump B;
Step 4. Store B output into HDFS
grunt> store B into 'userinfo.out';
grunt> quit;
Step 5. Check the result
[cloudera@quickstart ~]$ hdfs dfs -ls /user/cloudera/
Apache Hive
Two componets:
SQL Language - HiveQL.
Interactive Client - beeline / Hive own CLI / Hcatalog / WebHcat. It takes what we wrote in HiveQL, and transforms into back-end jobs of Tez or Spark, MapReduce, Yarn, etc.
Usage:
As Data warehouse software, handling data in HDFS, HBase. It can do:
Date mining, analytics
Machine Learning
Ad hoc analysis
Extendibility:
It has built-in operators and functions.
Use cases:
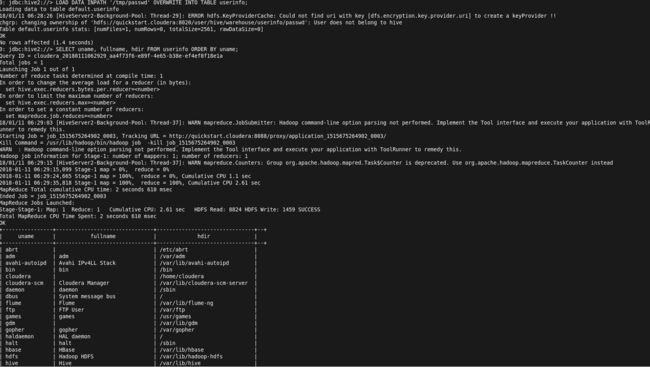
Step 1. Put a passwd into HDFS
[cloudera@quickstart ~]$ hadoop fs -put /etc/passwd /tmp/
Step 2. lauch beeline with DB URL
[cloudera@quickstart ~]$ beeline -u jdbc:hive2://
step 3. Create table 'userinfo'
Step 4. Overwrite table with the data from HDFS /tmp/passwd and then do querying
Apache HBase
Two componets:
SQL Language - like Hive, Spart, Impala.
Interactive Shell - hbase shell (Other options: HBase MapReduce / HBase API/ HBase External API). It takes what we wrote, and runs it on top of HDFS.
Usage:
Scalable data store as Non-relational distributed database
Feature:
Compression - lower the network traffic and the size of data on the disk
In-memory operations - MemStore, BlockCache
Consistency - data transation between ?? without intermediate changes
High Availability - spreads out "keys" across nodes/various regions, and it has its owne replication as well as HDFS replication mechanism.
Automatic Shareing - table is distributed in regions that could benifit performance
Security - authorization process for both client side and server side
Use cases:
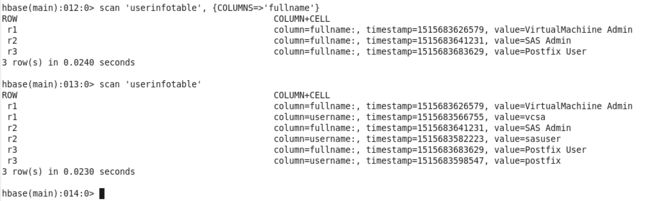
Step 1. Launch hbase shell
[cloudera@quickstart ~]$ hbase shell
hbase(main):001:0>
Step 2. Create table 'userinfotable'
Step 3. Fill data for the table and scan data
Lesson 5 Slides
Other applications/Services start/check , for zookeeper, Hive-metastore, hadoop-httpfs
Following are references for some of the material covered:
Pig Documentation:
http://pig.apache.org/docs/r0.15.0/start.html
Pig Latin basics:
http://pig.apache.org/docs/r0.15.0/basic.html
HIVE Language Manual:
https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/Hive/LanguageManual
HBase Reference Guide:
http://hbase.apache.org/book.html#arch.overview