本文通过分析日志输出简单介绍了PG根据查询树生成的执行计划的详细结构。
一、PlannedStmt结构
生成执行计划在函数pg_plan_queries中实现,返回的是链表querytree_list,链表中的元素是PlannedStmt.
回顾PlannedStmt结构:
/* ----------------
* PlannedStmt node
*
* The output of the planner is a Plan tree headed by a PlannedStmt node.
* PlannedStmt holds the "one time" information needed by the executor.
*
* For simplicity in APIs, we also wrap utility statements in PlannedStmt
* nodes; in such cases, commandType == CMD_UTILITY, the statement itself
* is in the utilityStmt field, and the rest of the struct is mostly dummy.
* (We do use canSetTag, stmt_location, stmt_len, and possibly queryId.)
* ----------------
*/
typedef struct PlannedStmt
{
NodeTag type;//这是节点的标识符Tag
//命令类型
CmdType commandType; /* select|insert|update|delete|utility */
//查询ID
uint64 queryId; /* query identifier (copied from Query) */
//是否insert|update|delete命令的RETURNING?(有待进一步研究)
bool hasReturning; /* is it insert|update|delete RETURNING? */
//CTE= Common Table Expressions(With语句)
//WITH语句中是否存在insert|update|delete关键字?
bool hasModifyingCTE; /* has insert|update|delete in WITH? */
//TODO
bool canSetTag; /* do I set the command result tag? */
//TODO
bool transientPlan; /* redo plan when TransactionXmin changes? */
//TODO
bool dependsOnRole; /* is plan specific to current role? */
//并行模式?
bool parallelModeNeeded; /* parallel mode required to execute? */
//使用哪种形式的JIT
int jitFlags; /* which forms of JIT should be performed */
//Plan节点树,这是SQL语句的关键信息
struct Plan *planTree; /* tree of Plan nodes */
//SQL所依赖的RTE(包括子查询等)
List *rtable; /* list of RangeTblEntry nodes */
//INSERT/UPDATE/DELETE命令所影响的关系在rtable中的位置(index)
/* rtable indexes of target relations for INSERT/UPDATE/DELETE */
List *resultRelations; /* integer list of RT indexes, or NIL */
//TODO
/*
* rtable indexes of non-leaf target relations for UPDATE/DELETE on all
* the partitioned tables mentioned in the query.
*/
List *nonleafResultRelations;
//UPDATE/DELETE命令相关
/*
* rtable indexes of root target relations for UPDATE/DELETE; this list
* maintains a subset of the RT indexes in nonleafResultRelations,
* indicating the roots of the respective partition hierarchies.
*/
List *rootResultRelations;
//子查询计划链表
List *subplans; /* Plan trees for SubPlan expressions; note
* that some could be NULL */
//TODO
Bitmapset *rewindPlanIDs; /* indices of subplans that require REWIND */
//TODO
List *rowMarks; /* a list of PlanRowMark's */
//Plan相关的关系OIDs(Relation OIDs),通过pg_class可以查询
List *relationOids; /* OIDs of relations the plan depends on */
//TODO
List *invalItems; /* other dependencies, as PlanInvalItems */
//TODO
List *paramExecTypes; /* type OIDs for PARAM_EXEC Params */
//工具类语句(如CREATE TABLE等)节点
Node *utilityStmt; /* non-null if this is utility stmt */
//SQL语句的起始位置?
/* statement location in source string (copied from Query) */
int stmt_location; /* start location, or -1 if unknown */
//SQL语句的长度
int stmt_len; /* length in bytes; 0 means "rest of string" */
} PlannedStmt;
/* macro for fetching the Plan associated with a SubPlan node */
#define exec_subplan_get_plan(plannedstmt, subplan) \
((Plan *) list_nth((plannedstmt)->subplans, (subplan)->plan_id - 1))
二、日志分析
测试前重置了样例数据库,因此相关信息如数据表Oid与上一节略有不同,敬请注意
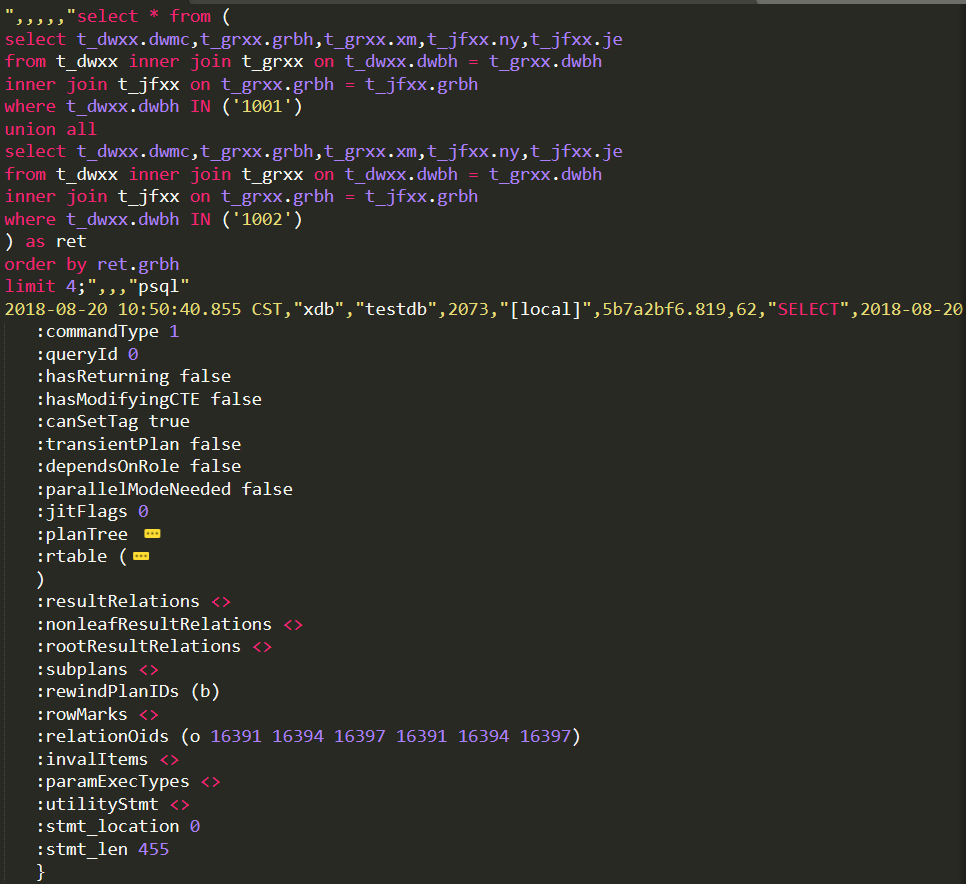
SQL语句:
select t_dwxx.dwmc,t_grxx.grbh,t_grxx.xm,t_jfxx.ny,t_jfxx.je
from t_dwxx,t_grxx,t_jfxx
where t_dwxx.dwbh = t_grxx.dwbh
and t_grxx.grbh = t_jfxx.grbh
and t_dwxx.dwbh IN ('1001','1002')
order by t_grxx.grbh
limit 8;
select * from (
select t_dwxx.dwmc,t_grxx.grbh,t_grxx.xm,t_jfxx.ny,t_jfxx.je
from t_dwxx inner join t_grxx on t_dwxx.dwbh = t_grxx.dwbh
inner join t_jfxx on t_grxx.grbh = t_jfxx.grbh
where t_dwxx.dwbh IN ('1001')
union all
select t_dwxx.dwmc,t_grxx.grbh,t_grxx.xm,t_jfxx.ny,t_jfxx.je
from t_dwxx inner join t_grxx on t_dwxx.dwbh = t_grxx.dwbh
inner join t_jfxx on t_grxx.grbh = t_jfxx.grbh
where t_dwxx.dwbh IN ('1002')
) as ret
order by ret.grbh
limit 4;
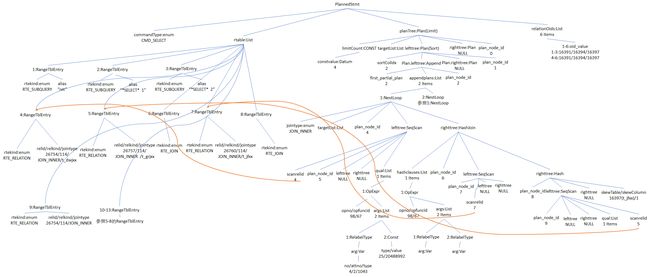
该SQL语句的计划树如下图所示:
查询树中的详细数据结构可以结合相应的日志进行分析:
1.PlannedStmt
如上图所示(planTree、rtable已折叠),commandType值为1,对应的是SELECT,queryID为0,SQL语句长度为455,relationOids的值为(o 16391 16394 16397 16391 16394 16397),分别对应t_dwxx/t_grxx/t_jfxx三张表.
testdb=# select relname from pg_class where oid in (16391,16394,16397);
relname
---------
t_dwxx
t_grxx
t_jfxx
(3 rows)
下面详细看看rtable和planTree中的结构.
2.rtable
rtable链表中的元素为RangeTblEntry,下面先回顾RTE的数据结构:
RangeTblEntry
*/
typedef enum RTEKind
{
RTE_RELATION, /* ordinary relation reference */ //这是常规的Relation,即数据表
RTE_SUBQUERY, /* subquery in FROM */ //出现在From语句中的子查询
RTE_JOIN, /* join */ //连接
RTE_FUNCTION, /* function in FROM */ //FROM中的函数
RTE_TABLEFUNC, /* TableFunc(.., column list) */ //函数
RTE_VALUES, /* VALUES (), (), ... */ //
RTE_CTE, /* common table expr (WITH list element) */ //WITH语句
RTE_NAMEDTUPLESTORE /* tuplestore, e.g. for AFTER triggers */ //
} RTEKind;//RTE类型,本例中涉及三种类型,RTE_RELATION/RTE_SUBQUERY/RTE_JOIN
typedef struct RangeTblEntry
{
//RTEKind=*时使用的结构
NodeTag type;//节点标识
RTEKind rtekind; /* see above */ //RTE类型
/*
* XXX the fields applicable to only some rte kinds should be merged into
* a union. I didn't do this yet because the diffs would impact a lot of
* code that is being actively worked on. FIXME someday.
*/
/*
* Fields valid for a plain relation RTE (else zero):
*
* As a special case, RTE_NAMEDTUPLESTORE can also set relid to indicate
* that the tuple format of the tuplestore is the same as the referenced
* relation. This allows plans referencing AFTER trigger transition
* tables to be invalidated if the underlying table is altered.
*/
Oid relid; /* OID of the relation */ //关系的Oid
char relkind; /* relation kind (see pg_class.relkind) */ //pg_class中的relkind,在这里是'r'
struct TableSampleClause *tablesample; /* sampling info, or NULL */ //采样语句
/*
* Fields valid for a subquery RTE (else NULL):
*/
//RTEKind=RTE_SUBQUERY时使用的结构
Query *subquery; /* the sub-query */ //子查询,如RTEKind=RTE_SUBQUERY时
bool security_barrier; /* is from security_barrier view? */
/*
* Fields valid for a join RTE (else NULL/zero):
*
* joinaliasvars is a list of (usually) Vars corresponding to the columns
* of the join result. An alias Var referencing column K of the join
* result can be replaced by the K'th element of joinaliasvars --- but to
* simplify the task of reverse-listing aliases correctly, we do not do
* that until planning time. In detail: an element of joinaliasvars can
* be a Var of one of the join's input relations, or such a Var with an
* implicit coercion to the join's output column type, or a COALESCE
* expression containing the two input column Vars (possibly coerced).
* Within a Query loaded from a stored rule, it is also possible for
* joinaliasvars items to be null pointers, which are placeholders for
* (necessarily unreferenced) columns dropped since the rule was made.
* Also, once planning begins, joinaliasvars items can be almost anything,
* as a result of subquery-flattening substitutions.
*/
//RTEKind=RTE_JOIN时使用的结构
JoinType jointype; /* type of join */ //连接类型
List *joinaliasvars; /* list of alias-var expansions */ //
/*
* Fields valid for a function RTE (else NIL/zero):
*
* When funcordinality is true, the eref->colnames list includes an alias
* for the ordinality column. The ordinality column is otherwise
* implicit, and must be accounted for "by hand" in places such as
* expandRTE().
*/
//RTEKind=RTE_FUNCTION时使用的结构
List *functions; /* list of RangeTblFunction nodes */
bool funcordinality; /* is this called WITH ORDINALITY? */
//
/*
* Fields valid for a TableFunc RTE (else NULL):
*/
//RTEKind=RTE_TABLEFUNC时使用的结构
TableFunc *tablefunc;
/*
* Fields valid for a values RTE (else NIL):
*/
//RTEKind=RTE_VALUES时使用的结构
List *values_lists; /* list of expression lists */
/*
* Fields valid for a CTE RTE (else NULL/zero):
*/
//RTEKind=RTE_CTE时使用的结构
char *ctename; /* name of the WITH list item */
Index ctelevelsup; /* number of query levels up */
bool self_reference; /* is this a recursive self-reference? */
/*
* Fields valid for table functions, values, CTE and ENR RTEs (else NIL):
*
* We need these for CTE RTEs so that the types of self-referential
* columns are well-defined. For VALUES RTEs, storing these explicitly
* saves having to re-determine the info by scanning the values_lists. For
* ENRs, we store the types explicitly here (we could get the information
* from the catalogs if 'relid' was supplied, but we'd still need these
* for TupleDesc-based ENRs, so we might as well always store the type
* info here).
*
* For ENRs only, we have to consider the possibility of dropped columns.
* A dropped column is included in these lists, but it will have zeroes in
* all three lists (as well as an empty-string entry in eref). Testing
* for zero coltype is the standard way to detect a dropped column.
*/
//RTEKind=RTE_FUNCTION/RTE_VALUES/RTE_CTE时使用的结构
List *coltypes; /* OID list of column type OIDs */
List *coltypmods; /* integer list of column typmods */
List *colcollations; /* OID list of column collation OIDs */
/*
* Fields valid for ENR RTEs (else NULL/zero):
*/
char *enrname; /* name of ephemeral named relation */
double enrtuples; /* estimated or actual from caller */
/*
* Fields valid in all RTEs:
*/
//RTEKind=*时使用的结构
Alias *alias; /* user-written alias clause, if any */
Alias *eref; /* expanded reference names */
bool lateral; /* subquery, function, or values is LATERAL? */
bool inh; /* inheritance requested? */
bool inFromCl; /* present in FROM clause? */
//权限控制
AclMode requiredPerms; /* bitmask of required access permissions */
Oid checkAsUser; /* if valid, check access as this role */
Bitmapset *selectedCols; /* columns needing SELECT permission */
Bitmapset *insertedCols; /* columns needing INSERT permission */
Bitmapset *updatedCols; /* columns needing UPDATE permission */
List *securityQuals; /* security barrier quals to apply, if any */
} RangeTblEntry;
rtable保存的是SQL语句执行时所依赖的RangeTblEntry(简称RTE),就本例而言,有13个RTE.
第1个RTE
:rtable (
{RTE ---------->第1个RTE
:alias
{ALIAS
:aliasname ret //用户自定义的别名:"ret"
:colnames <>
}
:eref
{ALIAS
:aliasname ret //用户自定义的别名:"ret"
:colnames (""dwmc"" ""grbh"" ""xm"" ""ny"" ""je"") //数据列
}
:rtekind 1 //RTE_SUBQUERY,子查询(注意:枚举从0开始)
:subquery <>
:security_barrier false
:lateral false
:inh true
:inFromCl true
:requiredPerms 2
:checkAsUser 0
:selectedCols (b)
:insertedCols (b)
:updatedCols (b)
:securityQuals <>
}
第2个RTE
{RTE ---------->第2个RTE
:alias
{ALIAS
:aliasname *SELECT*\ 1 //第一个子查询
:colnames <>
}
:eref
{ALIAS
:aliasname *SELECT*\ 1
:colnames (""dwmc"" ""grbh"" ""xm"" ""ny"" ""je"")
}
:rtekind 1 //RTE_SUBQUERY
:subquery <>
:security_barrier false
:lateral false
:inh false
:inFromCl false
:requiredPerms 0
:checkAsUser 0
:selectedCols (b)
:insertedCols (b)
:updatedCols (b)
:securityQuals <>
}
集合UNION操作对应的第一个子查询
第3个RTE
类第2个RTE,不同的地方是aliasname为 *SELECT*\ 2
集合UNION操作对应的第二个子查询
第4个RTE
{RTE ---------->第4个RTE
:alias <>
:eref
{ALIAS
:aliasname t_dwxx //单位信息表
:colnames (""dwmc"" ""dwbh"" ""dwdz"") //数据列有dwmc/dwbh/dwdz
}
:rtekind 0 //RTE_RELATION,关系/数据表
:relid 16391 //这是t_dwxx的Oid
:relkind r //pg_class中的relkind
:tablesample <>
:lateral false
:inh false
:inFromCl true
:requiredPerms 2
:checkAsUser 0
:selectedCols (b 9 10) //
:insertedCols (b)
:updatedCols (b)
:securityQuals <>
}
第5个RTE
t_grxx表,参照第4个RTE
第6个RTE
{RTE ---------->第6个RTE
:alias <>
:eref
{ALIAS
:aliasname unnamed_join //未命名的join(连接)
:colnames (""dwmc"" ""dwbh"" ""dwdz"" ""dwbh"" ""grbh"" ""xm"" ""nl"") //单位&个人信息表的数据列
}
:rtekind 2 //RTE_JOIN,连接
:jointype 0 //JOIN_INNER,内连接
:joinaliasvars <>
:lateral false
:inh false
:inFromCl true //是否在From语句中,true=是
:requiredPerms 0
:checkAsUser 0
:selectedCols (b)
:insertedCols (b)
:updatedCols (b)
:securityQuals <>
}
第7个RTE
t_jfxx表,参照第4个RTE
第8个RTE
{RTE ---------->第8个RTE
:alias <>
:eref
{ALIAS
:aliasname unnamed_join //未命名的join
:colnames (""dwmc"" ""dwbh"" ""dwdz"" ""dwbh"" ""grbh"" ""xm"" ""nl"" ""grbh"" ""ny"" ""
je"")//三个表的列
}
:rtekind 2 //RTE_JOIN
:jointype 0 //JOIN_INNER
:joinaliasvars <>
:lateral false
:inh false
:inFromCl true //在From子句中
:requiredPerms 0
:checkAsUser 0
:selectedCols (b)
:insertedCols (b)
:updatedCols (b)
:securityQuals <>
}
第9-13个RTE
与第4-8个RTE一样
3个RTE_RELATION,2个RTE_JOIN
3.planTree
介绍完了RTE,下面要解析的是planTree,指向类型为Plan的指针.
首先回顾Plan结构体:
/* ----------------
* Plan node
*
* All plan nodes "derive" from the Plan structure by having the
* Plan structure as the first field. This ensures that everything works
* when nodes are cast to Plan's. (node pointers are frequently cast to Plan*
* when passed around generically in the executor)
*
* We never actually instantiate any Plan nodes; this is just the common
* abstract superclass for all Plan-type nodes.
* ----------------
*/
typedef struct Plan
{
NodeTag type;//节点标识
/*
* 计划的估算成本,estimated execution costs for plan (see costsize.c for more info)
*/
Cost startup_cost; /* 启动成本,cost expended before fetching any tuples */
Cost total_cost; /*总成本, total cost (assuming all tuples fetched) */
/*
* planner's estimate of result size of this plan step
*/
//plan_rows * plan_width可以大体算出该plan涉及的数据量大小
double plan_rows; /* 该计划涉及的行数,number of rows plan is expected to emit */
int plan_width; /* 该计划涉及的行的平均宽度(大小)average row width in bytes */
/*
* 并行查询所需要的信息,information needed for parallel query
*/
bool parallel_aware; /* engage parallel-aware logic? */
bool parallel_safe; /* OK to use as part of parallel plan? */
/*
* Plan类型的常规信息,Common structural data for all Plan types.
*/
int plan_node_id; /* 计划节点id,unique across entire final plan tree */
List *targetlist; /* 投影列,target list to be computed at this node */
List *qual; /* 条件表达式,implicitly-ANDed qual conditions */
struct Plan *lefttree; /* 作为该计划输入的Plan(执行完某个Plan后才到这个Plan,比如先执行Sort才到Limit),input plan tree(s) */
struct Plan *righttree;//右边树
List *initPlan; /* 用于初始化的Plan,Init Plan nodes (un-correlated expr
* subselects) */
/*
* //参数变化驱动(比如绑定变量?)的再次查询信息,Information for management of parameter-change-driven rescanning
*
* extParam includes the paramIDs of all external PARAM_EXEC params
* affecting this plan node or its children. setParam params from the
* node's initPlans are not included, but their extParams are.
*
* allParam includes all the extParam paramIDs, plus the IDs of local
* params that affect the node (i.e., the setParams of its initplans).
* These are _all_ the PARAM_EXEC params that affect this node.
*/
Bitmapset *extParam;
Bitmapset *allParam;
} Plan;
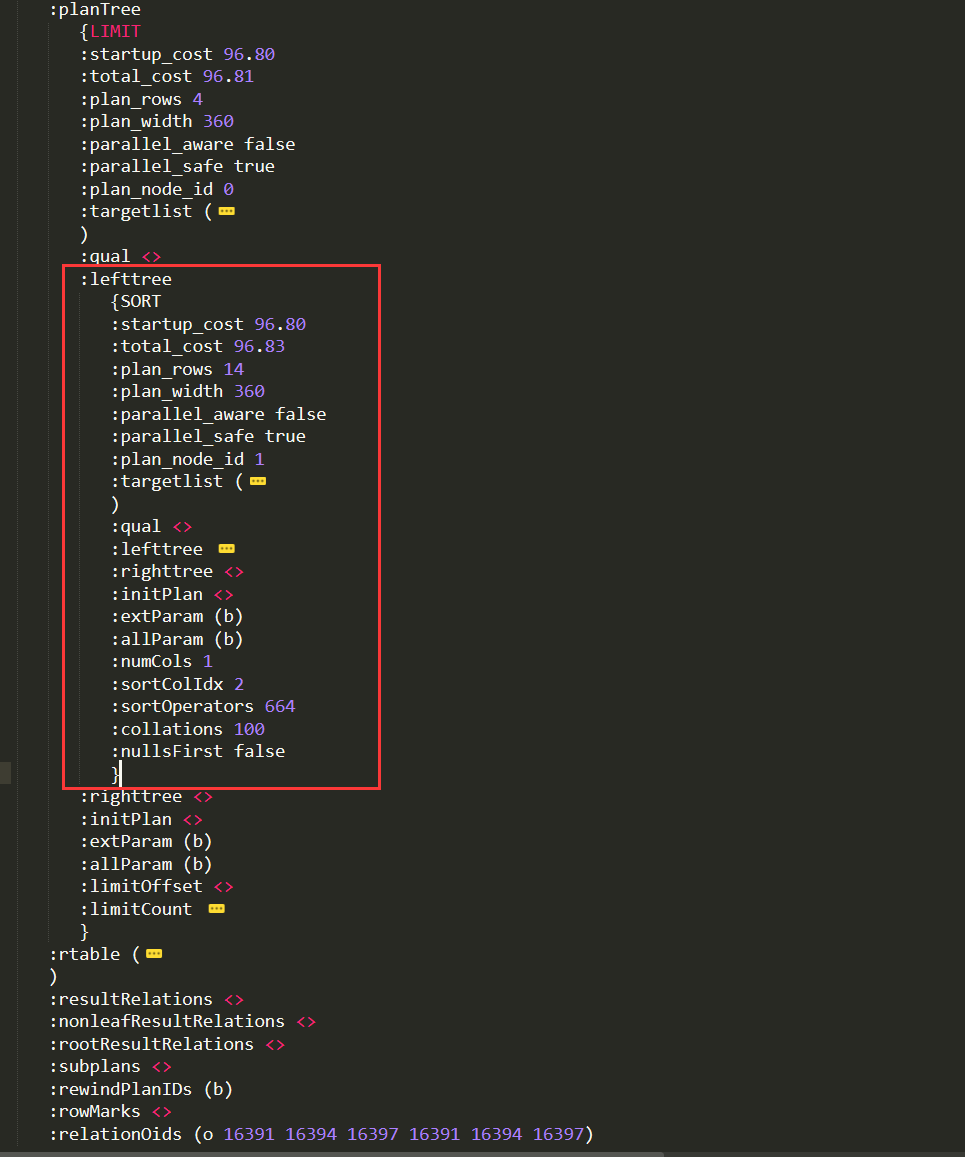
planTree概览
planTree指针指向的Plan是T_LIMIT的Node,其中startup_cost为96.80,total_cost为96.81,该计划涉及的行数为4行(plan_rows),平均行宽度(大小)为360Bytes(plan_width),计划节点id为0(plan_node_id),返回的列有5个(投影列),lefttree不为空,说明进入该Plan前还存在其他的Plan,右树/初始化Plan为空,limitCount为4(对应SQL语句中的limit 4).limitCount的详细解析如下:
//limitCount
:limitCount
{CONST //CONST类型
:consttype 20 //Oid=20,pg_type中oid=20的条目,即typename=int8,即bigint(64Bytes)
:consttypmod -1
:constcollid 0 //pg_collation中Oid=0的条码
:constlen 8 //8Bytes
:constbyval true //是否通过值传递,是,则constvalue即为该Const的值,否则constvalue为指向实际值的指针
:constisnull false //是否为null?
:location -1
:constvalue 8 [ 4 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 ]//常量值为0x4
}
LIMIT->lefttree
刚才提到planTree中的左树不为空,该值同样为指向Plan的指针:
lefttree指向的是类型为T_SORT的Node.与Limit类型,该步骤涉及的行数为14(plan_rows),执行节点id为1,targetlist与Limit类似为投影列,lefttree不为空,说明进入该Plan前还存在其他的Plan,右树/初始化Plan为空.除了Plan常规的列外还有SORT特有的信息,包括排序的列数numCols值为1,排序列在targetlist中的位置值为2,排序的操作类型sortOperators(pg_operator,Oid=664,text_lt),排序依据的collation(pg_collation,Oid=100,默认的规则)
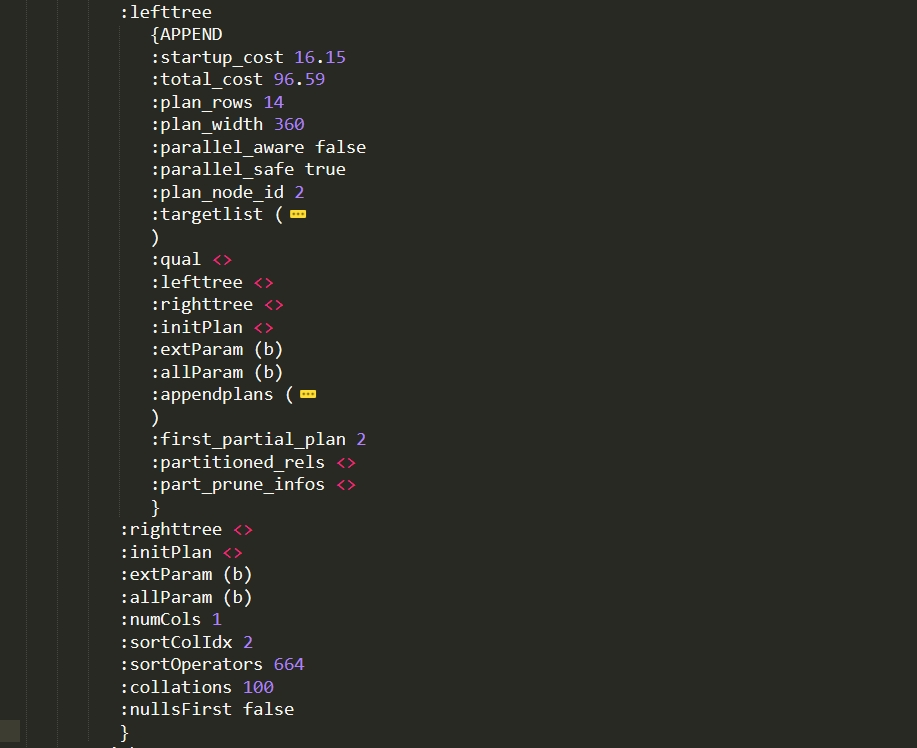
LIMIT->SORT->lefttree
继续进入SORT的左树:
SORT的左树为类型T_APPEND的Node,T_APPEND节点用于UNION等集合操作.该步骤涉及的行数为14(plan_rows),执行节点id为2,targetlist与Limit类似为投影列,lefttree和righttree为空,但appendplans(List类型)不为空,APPEND的结果由子Plan的结果"级联"而成(Generate the concatenation of the results of sub-plans).
LIMIT->SORT->APPEND->appendplans
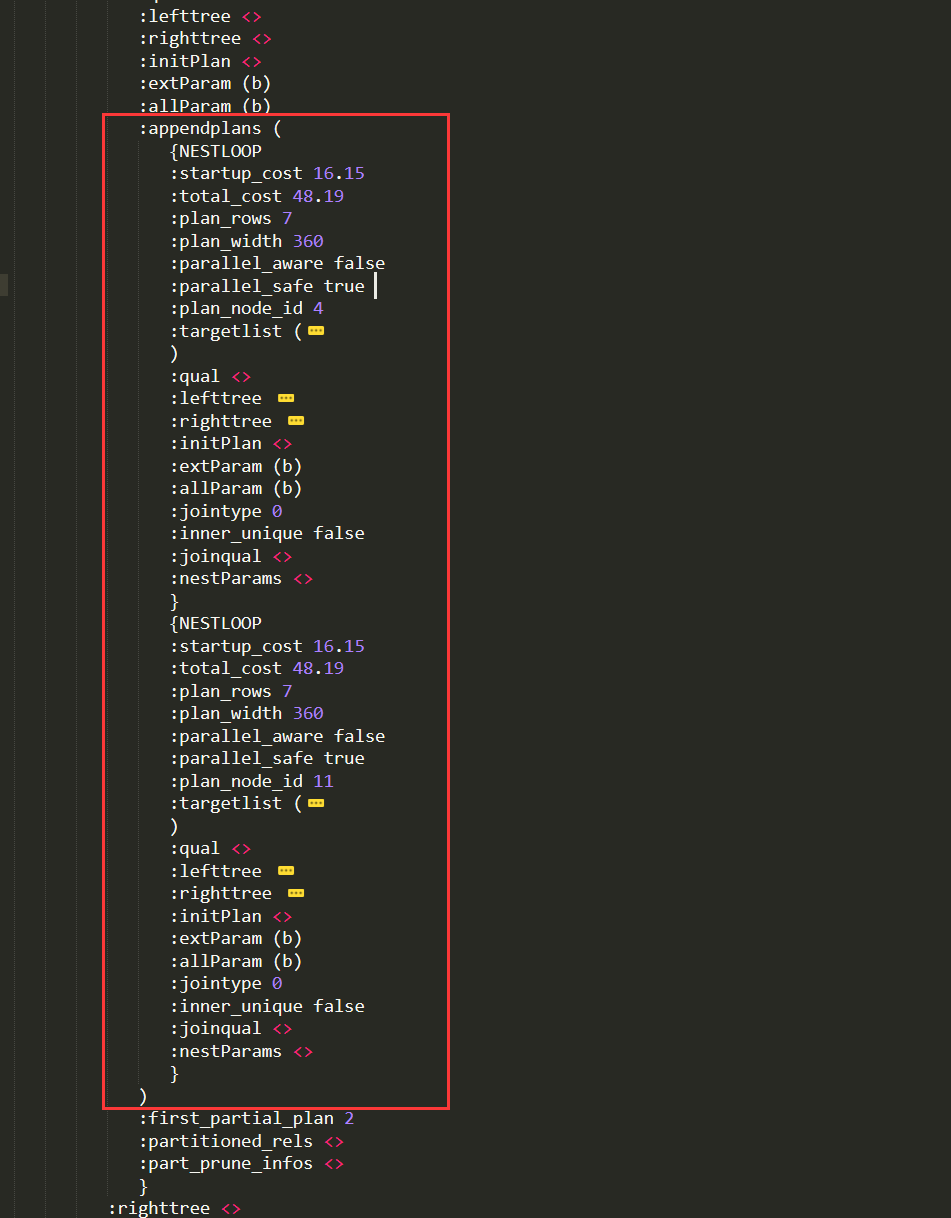
进入APPEND的子计划appendplans:
APPEND->appendplans是链表结构,有2个元素,每个元素的类型为T_NESTLOOP(内嵌循环),通常的信息与其他节点类型类似,重点是lefttree和righttree均不为空,jointype为0表示INNER_JOIN
LIMIT->SORT->APPEND->appendplans->head
lefttree
进入第一个元素的左树
:lefttree
{SEQSCAN /T_SEQSCAN类型的Node,顺序扫描
:startup_cost 0.00
:total_cost 12.00
:plan_rows 1 //涉及的行数
:plan_width 256 //平均行宽
:parallel_aware false
:parallel_safe true
:plan_node_id 5 //Plan id
:targetlist (...) //省略
:qual (
{OPEXPR
:opno 98 //PG_OPERATOR OID of the operator,texteq字符串相等
:opfuncid 67 //PG_PROC OID of underlying function,texteq字符串相等
:opresulttype 16 //PG_TYPE OID of result value,bool值
:opretset false
:opcollid 0 //pg_collation
:inputcollid 100 //输入的collation(default)
:args (//参数,链表类型
{RELABELTYPE //第1个参数为RelabelType类型
:arg //指向Expr的指针,实际类型为VAR
{VAR //第
:varno 4 //在rtable中处于第4个位置的RTE
:varattno 2 //属性编号
:vartype 1043 //类型,pg_type OID,varchar
:vartypmod 14
:varcollid 100
:varlevelsup 0
:varnoold 4 //原始的varno
:varoattno 2 //原始的varattno
:location 110//token位置(在SQL语句中)
}
:resulttype 25
:resulttypmod -1
:resultcollid 100
:relabelformat 2
:location -1
}
{CONST //第2个参数为Const类型
:consttype 25 //pg_type OID
:consttypmod -1 //
:constcollid 100 //
:constlen -1
:constbyval false //传值?如为false,则constvalue中的前4个字节为value的说明,在这个案例中,为32(即2的4次方),从第5个字节开始,长度为4的字符串
:constisnull false
:location 205 //token所在位置
:constvalue 8 [ 32 0 0 0 49 48 48 49 ]//即字符串"1001"
}
)
:location -1
}
)
:lefttree <> //左树为空
:righttree <> //右树为空
:initPlan <> //无初始化Plan
:extParam (b)
:allParam (b)
:scanrelid 4 //扫描第4号RTE
}
rigthtree
进入第一个元素的右树
:righttree
{HASHJOIN //NestLoop右树节点类型是HashJoin(t_grxx join t_jfxx)
:startup_cost 16.15
:total_cost 36.12
:plan_rows 7 //涉及的行数
:plan_width 180 //平均行大小
:parallel_aware false
:parallel_safe true
:plan_node_id 6 //计划节点id
:targetlist (...) //投影列,省略
:qual <> //表达式
:lefttree //左树,暂时折叠
{...}
:righttree //右树,暂时折叠
{...}
:initPlan <> //初始化Plan
:extParam (b)
:allParam (b)
:jointype 0 //INNER_JOIN
:inner_unique false //非唯一inner join
:joinqual <>
:hashclauses (//hash信息,类型为OpExpr
{OPEXPR
:opno 98 //pg_operator Oid,"=",texteq
:opfuncid 67 //pg_proc Oid,texteq
:opresulttype 16
:opretset false
:opcollid 0 //default collation
:inputcollid 100
:args (//参数链表
{RELABELTYPE//第1个元素 RelabelType
:arg
{VAR //VAR类型
:varno 65001 //TODO
:varattno 1 //第1列
:vartype 1043 //字符串,varchar
:vartypmod 14
:varcollid 100
:varlevelsup 0
:varnoold 7 //原varno,7号RTE,即t_jfxx
:varoattno 1 //原属性no
:location 171//SQL语句中的token位置
}
:resulttype 25
:resulttypmod -1
:resultcollid 100
:relabelformat 2
:location -1
}
{RELABELTYPE //第1个元素 RelabelType
:arg
{VAR //VAR类型
:varno 65000
:varattno 1
:vartype 1043
:vartypmod 14
:varcollid 100
:varlevelsup 0
:varnoold 5 //5号RTE,即t_grxx
:varoattno 2 //2号属性
:location 157
}
:resulttype 25
:resulttypmod -1
:resultcollid 100
:relabelformat 2
:location -1
}
)
:location -1
}
)
}
:initPlan <> //无初始化Plan
:extParam (b)
:allParam (b)
:jointype 0 //INNER_JOIN
:inner_unique false
:joinqual <>
:nestParams <>
下面考察HashJoin的左树和右树,首先看左树
...head(Plan)->righttree(HashJoin)->lefttree
:lefttree
{SEQSCAN //顺序扫描
:startup_cost 0.00
:total_cost 17.20
:plan_rows 720
:plan_width 84
:parallel_aware false
:parallel_safe true
:plan_node_id 7 //计划id
:targetlist (...)
:qual <>
:lefttree <>
:righttree <>
:initPlan <>
:extParam (b)
:allParam (b)
:scanrelid 7//编号为7的RTE即t_jfxx
}
再看HashJoin右树
...head(Plan)->righttree(HashJoin)->righttree
:righttree
{HASH //Hash操作(创建Hash表)
:startup_cost 16.12
:total_cost 16.12
:plan_rows 2 //涉及2行
:plan_width 134
:parallel_aware false
:parallel_safe true
:plan_node_id 8
:targetlist (...)
:qual <>
:lefttree //左树也是一个Plan
{SEQSCAN //左树为顺序扫描
:startup_cost 0.00
:total_cost 16.12
:plan_rows 2
:plan_width 134
:parallel_aware false
:parallel_safe true
:plan_node_id 9
:targetlist (...)
:qual (
{OPEXPR //OpExpr类型
:opno 98
:opfuncid 67
:opresulttype 16
:opretset false
:opcollid 0
:inputcollid 100
:args (
{RELABELTYPE
:arg
{VAR
:varno 5 //5号RTE,即t_grxx
:varattno 1 //第1个列,即dwbh
:vartype 1043
:vartypmod 14
:varcollid 100
:varlevelsup 0
:varnoold 5
:varoattno 1
:location 124
}
:resulttype 25
:resulttypmod -1
:resultcollid 100
:relabelformat 2
:location -1
}
{CONST
:consttype 25
:consttypmod -1
:constcollid 100
:constlen -1
:constbyval false //非参数传递
:constisnull false
:location 205
:constvalue 8 [ 32 0 0 0 49 48 48 49 ]//字符串"1001"
}
)
:location -1
}
)
:lefttree <> //子左树的左树为空
:righttree <> //子左树的右树为空
:initPlan <>
:extParam (b)
:allParam (b)
:scanrelid 5//扫描的RTE,5号即t_grxx
}
:righttree <> //右树为空
:initPlan <>
:extParam (b)
:allParam (b)
:skewTable 16397 //HashJoin的表Oid
:skewColumn 1 //列序号
:skewInherit false
:rows_total 0
}
LIMIT->SORT->APPEND->appendplans->head->next
子查询中的第2个NestLoop
参照LIMIT->SORT->APPEND->appendplans->head即可,
条件变为dwbh="1002",其他与链表中的head元素无异,不再累述
三、小结
1、计划树结构:通过日志输出分析计划树结构;
2、重要的数据结构:RTE、Plan等。
四、附录
如何开启跟踪日志?postgresql.conf配置文件设置参数:
log_destination = 'csvlog'
log_directory = 'pg_log' #与postgresql.conf文件在同一级目录
log_filename = 'postgresql-%Y-%m-%d_%H%M%S.log'
log_rotation_age = 2d
log_rotation_size = 100MB
#
debug_print_parse = on #打印parse树
debug_print_rewritten = on #打印parse rewrite树
debug_print_plan = on #打印plan树
debug_pretty_print = on #以pretty方式显示