之前一篇文章分析了Android Activity启动过程源码 这里单独拿出来一篇文章分析Activity 启动模式的源码
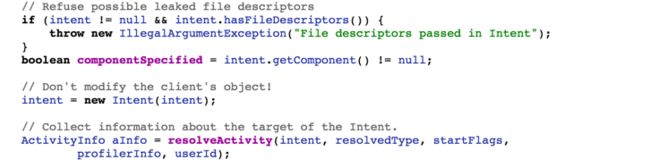
我们知道Activity的start是走到Instrumentation的execStartActivity方法中,而这里是调用了ActivityManagerNative的getDefault方法 来获得一个ActivityManagerService(以下简称AMS)的远程代理对象,要走到AMS的startActivity方法。
int result = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault()
.startActivity(whoThread, who.getBasePackageName(), intent,
intent.resolveTypeIfNeeded(who.getContentResolver()),
token, target != null ? target.mEmbeddedID : null,
requestCode, 0, null, null, options);
checkStartActivityResult(result, intent);
这里先解释一下startActivity方法里的一些参数
| 参数 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| whoThread | IApplicationThread的binder对象 用于AMS进行进程间通信 |
| who | 上下文对象 其实就是Activity |
| intent | 目标intent |
| intent.resolveTypeIfneed | 若没有在Manifest文件里面注明Activity的mime类型,返回null |
| token | Binder对象 通过它可以获得Activity的相关信息 后边会保存到sourceRecord这个对象里面 |
| target | 我们调用的Activity |
| requestCode | 若没有设置结果就是小于0 |
| 0 | flags |
| ProfilerInfo | null |
| options | 是一个bunder对象,记录用intent传递的信息 |
这里对应着AMS 中startactivity的参数
@Override
public final int startActivity(IApplicationThread caller, String callingPackage,
Intent intent, String resolvedType, IBinder resultTo, String resultWho, int requestCode,
int startFlags, ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, Bundle options) {
return startActivityAsUser(caller, callingPackage, intent, resolvedType, resultTo,
resultWho, requestCode, startFlags, profilerInfo, options,
UserHandle.getCallingUserId());
}
@Override
public final int startActivityAsUser(IApplicationThread caller, String callingPackage,
Intent intent, String resolvedType, IBinder resultTo, String resultWho, int requestCode,
int startFlags, ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, Bundle options, int userId) {
enforceNotIsolatedCaller("startActivity");
userId = handleIncomingUser(Binder.getCallingPid(), Binder.getCallingUid(), userId,
false, ALLOW_FULL_ONLY, "startActivity", null);
// TODO: Switch to user app stacks here.
return mStackSupervisor.startActivityMayWait(caller, -1, callingPackage, intent,
resolvedType, null, null, resultTo, resultWho, requestCode, startFlags,
profilerInfo, null, null, options, userId, null, null);
}
然后会调用ActivityStackSupervisor的startActivityMayWait方法
而ActivityStackSupervisor 就是专门管理activity的堆栈的类
这里会先解析我们的intent来获取信息,通过调用函数resoleActivity方法获取ActivityInfo,这里主要是activity在AndroidManifest.xml里的信息
再往下看,进入到startActivityLocked 方法中
另提一下activity 在 AMS 中的形式是 ActivityRecord,task 在 AMS 中的形式为TaskRecord,进程在 AMS 中的管理形式为 ProcessRecord
我们发现这里有两个ActivityRecord对象 有sourceRecord 和resultRecord
sourceRecord 代表的是最开始的activity
这就是通过resultTo这个binder对象获得Mainactivity的相关信息然后保存到这个对象中
resultRecord 代表的是接受启动结果的Activity
因为requestcode==-1 所以这里resultRecord==null
final int launchFlags = intent.getFlags();
这里获取Intent的启动Flag 就是我们在Intent.setFlag里面设置的标志
这个函数的主要作用就是处理sourceRecord和resultRecord两个对象
在这里sourceRecord和resultRecord指向的应该是同一个activity
然后调用startActivityUncheckedLocked来处理本次的启动Activity的请求
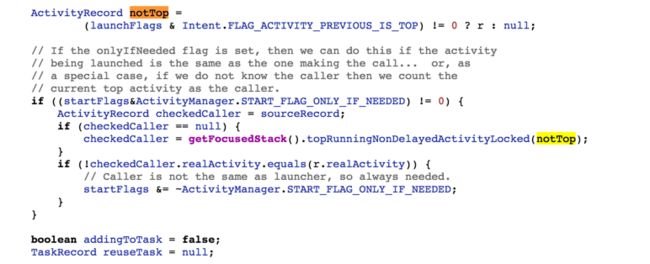
从这里我们可以看到 获取了activity的launchModel ,也就是对launchModel的判断处理应该是在这里
这里先判断是否FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_DOCUMENT,这个平时用的比较少,在android5.0上主要是决定你的task和activity是如何展现在overview screen 中的,详细请看 Android 5.0 Overview Screen--总览画面
再往下看
startFlags == 0 所以此时不会进入这个判断,没有设置这个FLAG_ACTIVITY_PREVIOUS_IS_TOP,所以我们的notTop==null
接着 系统默认addingToTask= false 默认是开启新的Task,从后面的判断也可以看出来
之前说过 sourceRecord就是最开始的activity 所以它不会为null,这样就到了else 中 inTask = null;
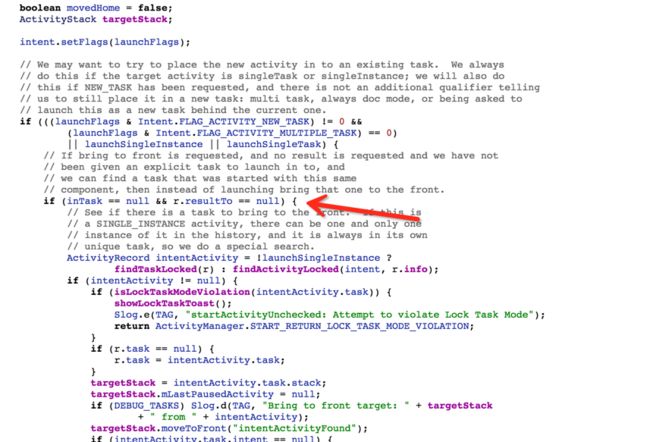
在这里判断了启动模式,判断当前activity的启动模式和要启动的activity的启动模式,根据相应的启动模式设置launchFlags
这里目的是判断启动的activity是否在堆栈里存在,如果存在就直接在进行相应的操作
在文章开头 resultRecord 默认为null而且requestCode假如没有设置的话,requestCode小于0,所以resultRecord没有被赋值,所以我们构造ActivityRecord 时传入的是null,也就是可以进入这个if判断里
再往里看
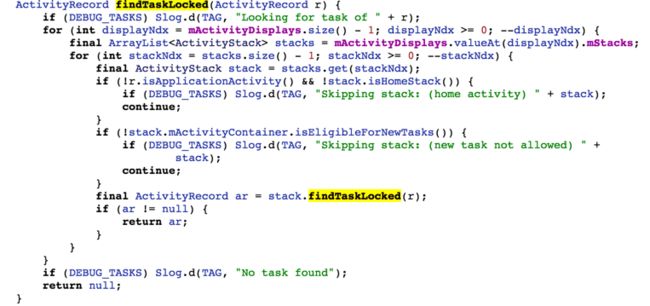
这里会判断启动的activity是否是SingleInstance,根据此进入不同的方法,目的是找到activity,如果有就返回,如果没有就返回null,先来看 findTaskLocked方法
stack里的findTaskLocked方法比较长,顶部activity,如果没有就返回null,从注释上来看就是返回堆栈里的activity,简单说一下就是返回发起请求的activity,也是这个函数返回的activity
/**
* Returns the top activity in any existing task matching the given
* Intent. Returns null if no such task is found.
*/
ActivityRecord findTaskLocked(ActivityRecord target) {
Intent intent = target.intent;
ActivityInfo info = target.info;
ComponentName cls = intent.getComponent();
if (info.targetActivity != null) {
cls = new ComponentName(info.packageName, info.targetActivity);
}
final int userId = UserHandle.getUserId(info.applicationInfo.uid);
boolean isDocument = intent != null & intent.isDocument();
// If documentData is non-null then it must match the existing task data.
Uri documentData = isDocument ? intent.getData() : null;
if (DEBUG_TASKS) Slog.d(TAG, "Looking for task of " + target + " in " + this);
for (int taskNdx = mTaskHistory.size() - 1; taskNdx >= 0; --taskNdx) {
final TaskRecord task = mTaskHistory.get(taskNdx);
if (task.voiceSession != null) {
// We never match voice sessions; those always run independently.
if (DEBUG_TASKS) Slog.d(TAG, "Skipping " + task + ": voice session");
continue;
}
if (task.userId != userId) {
// Looking for a different task.
if (DEBUG_TASKS) Slog.d(TAG, "Skipping " + task + ": different user");
continue;
}
final ActivityRecord r = task.getTopActivity();
if (r == null || r.finishing || r.userId != userId ||
r.launchMode == ActivityInfo.LAUNCH_SINGLE_INSTANCE) {
if (DEBUG_TASKS) Slog.d(TAG, "Skipping " + task + ": mismatch root " + r);
continue;
}
final Intent taskIntent = task.intent;
final Intent affinityIntent = task.affinityIntent;
final boolean taskIsDocument;
final Uri taskDocumentData;
if (taskIntent != null && taskIntent.isDocument()) {
taskIsDocument = true;
taskDocumentData = taskIntent.getData();
} else if (affinityIntent != null && affinityIntent.isDocument()) {
taskIsDocument = true;
taskDocumentData = affinityIntent.getData();
} else {
taskIsDocument = false;
taskDocumentData = null;
}
if (DEBUG_TASKS) Slog.d(TAG, "Comparing existing cls="
+ taskIntent.getComponent().flattenToShortString()
+ "/aff=" + r.task.rootAffinity + " to new cls="
+ intent.getComponent().flattenToShortString() + "/aff=" + info.taskAffinity);
if (!isDocument && !taskIsDocument && task.rootAffinity != null) {
if (task.rootAffinity.equals(target.taskAffinity)) {
if (DEBUG_TASKS) Slog.d(TAG, "Found matching affinity!");
return r;
}
} else if (taskIntent != null && taskIntent.getComponent() != null &&
taskIntent.getComponent().compareTo(cls) == 0 &&
Objects.equals(documentData, taskDocumentData)) {
if (DEBUG_TASKS) Slog.d(TAG, "Found matching class!");
//dump();
if (DEBUG_TASKS) Slog.d(TAG, "For Intent " + intent + " bringing to top: "
+ r.intent);
return r;
} else if (affinityIntent != null && affinityIntent.getComponent() != null &&
affinityIntent.getComponent().compareTo(cls) == 0 &&
Objects.equals(documentData, taskDocumentData)) {
if (DEBUG_TASKS) Slog.d(TAG, "Found matching class!");
//dump();
if (DEBUG_TASKS) Slog.d(TAG, "For Intent " + intent + " bringing to top: "
+ r.intent);
return r;
} else if (DEBUG_TASKS) {
Slog.d(TAG, "Not a match: " + task);
}
}
return null;
}
这里简单说一下,先是从mTaskHistory中遍历得到一个任务Task,并根据userid找到当前的task ,找到这个任务的顶部activity,并且保证它启动模式不是singleInstance,都满足了返回以下条件的activity
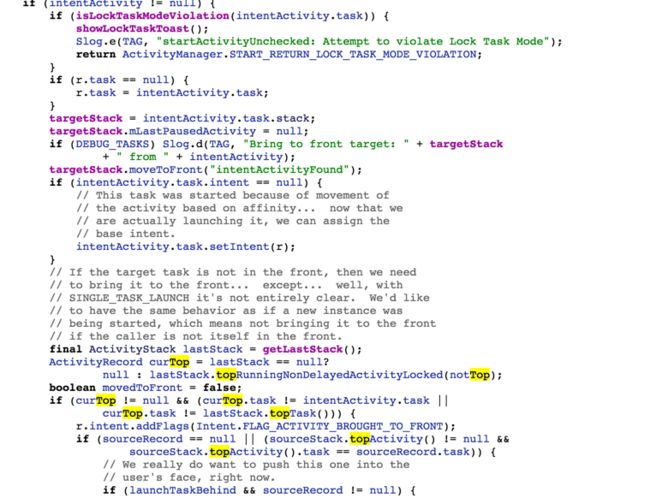
再回到刚才的方法往下看
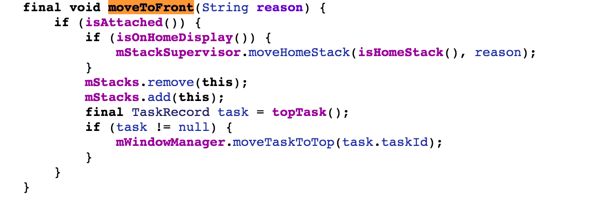
这里先去activitystack里的moveToFront()方法
// If the caller has requested that the target task be
// reset, then do so.
if ((launchFlags&Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_RESET_TASK_IF_NEEDED) != 0) {
intentActivity = targetStack.resetTaskIfNeededLocked(intentActivity, r);
}
if ((startFlags&ActivityManager.START_FLAG_ONLY_IF_NEEDED) != 0) {
// We don't need to start a new activity, and
// the client said not to do anything if that
// is the case, so this is it! And for paranoia, make
// sure we have correctly resumed the top activity.
if (doResume) {
resumeTopActivitiesLocked(targetStack, null, options);
} else {
ActivityOptions.abort(options);
}
return ActivityManager.START_RETURN_INTENT_TO_CALLER;
}
if ((launchFlags &
(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK|Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_TASK))
== (Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK|Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_TASK)) {
// The caller has requested to completely replace any
// existing task with its new activity. Well that should
// not be too hard...
reuseTask = intentActivity.task;
reuseTask.performClearTaskLocked();
reuseTask.setIntent(r);
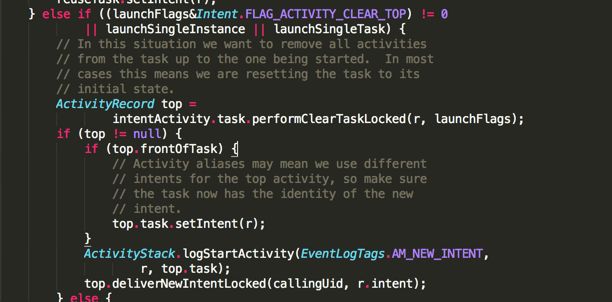
} else if ((launchFlags&Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_TOP) != 0
|| launchSingleInstance || launchSingleTask) {
// In this situation we want to remove all activities
// from the task up to the one being started. In most
// cases this means we are resetting the task to its
// initial state.
ActivityRecord top =
intentActivity.task.performClearTaskLocked(r, launchFlags);
if (top != null) {
if (top.frontOfTask) {
// Activity aliases may mean we use different
// intents for the top activity, so make sure
// the task now has the identity of the new
// intent.
top.task.setIntent(r);
}
ActivityStack.logStartActivity(EventLogTags.AM_NEW_INTENT,
r, top.task);
top.deliverNewIntentLocked(callingUid, r.intent);
} else {
// A special case: we need to
// start the activity because it is not currently
// running, and the caller has asked to clear the
// current task to have this activity at the top.
addingToTask = true;
// Now pretend like this activity is being started
// by the top of its task, so it is put in the
// right place.
sourceRecord = intentActivity;
}
} else if (r.realActivity.equals(intentActivity.task.realActivity)) {
// In this case the top activity on the task is the
// same as the one being launched, so we take that
// as a request to bring the task to the foreground.
// If the top activity in the task is the root
// activity, deliver this new intent to it if it
// desires.
if (((launchFlags&Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_SINGLE_TOP) != 0 || launchSingleTop)
&& intentActivity.realActivity.equals(r.realActivity)) {
ActivityStack.logStartActivity(EventLogTags.AM_NEW_INTENT, r,
intentActivity.task);
if (intentActivity.frontOfTask) {
intentActivity.task.setIntent(r);
}
intentActivity.deliverNewIntentLocked(callingUid, r.intent);
} else if (!r.intent.filterEquals(intentActivity.task.intent)) {
// In this case we are launching the root activity
// of the task, but with a different intent. We
// should start a new instance on top.
addingToTask = true;
sourceRecord = intentActivity;
}
} else if ((launchFlags&Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_RESET_TASK_IF_NEEDED) == 0) {
// In this case an activity is being launched in to an
// existing task, without resetting that task. This
// is typically the situation of launching an activity
// from a notification or shortcut. We want to place
// the new activity on top of the current task.
addingToTask = true;
sourceRecord = intentActivity;
} else if (!intentActivity.task.rootWasReset) {
// In this case we are launching in to an existing task
// that has not yet been started from its front door.
// The current task has been brought to the front.
// Ideally, we'd probably like to place this new task
// at the bottom of its stack, but that's a little hard
// to do with the current organization of the code so
// for now we'll just drop it.
intentActivity.task.setIntent(r);
}
if (!addingToTask && reuseTask == null) {
// We didn't do anything... but it was needed (a.k.a., client
// don't use that intent!) And for paranoia, make
// sure we have correctly resumed the top activity.
if (doResume) {
targetStack.resumeTopActivityLocked(null, options);
} else {
ActivityOptions.abort(options);
}
return ActivityManager.START_TASK_TO_FRONT;
}
这里主要看
这里走到了ActivityStack的performClearTaskLocked方法里
/**
* Perform clear operation as requested by
* {@link Intent#FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_TOP}: search from the top of the
* stack to the given task, then look for
* an instance of that activity in the stack and, if found, finish all
* activities on top of it and return the instance.
*
* @param newR Description of the new activity being started.
* @return Returns the old activity that should be continued to be used,
* or null if none was found.
*/
final ActivityRecord performClearTaskLocked(ActivityRecord newR, int launchFlags) {
int numActivities = mActivities.size();
for (int activityNdx = numActivities - 1; activityNdx >= 0; --activityNdx) {
ActivityRecord r = mActivities.get(activityNdx);
if (r.finishing) {
continue;
}
if (r.realActivity.equals(newR.realActivity)) {
// Here it is! Now finish everything in front...
final ActivityRecord ret = r;
for (++activityNdx; activityNdx < numActivities; ++activityNdx) {
r = mActivities.get(activityNdx);
if (r.finishing) {
continue;
}
ActivityOptions opts = r.takeOptionsLocked();
if (opts != null) {
ret.updateOptionsLocked(opts);
}
if (stack.finishActivityLocked(r, Activity.RESULT_CANCELED, null, "clear",
false)) {
--activityNdx;
--numActivities;
}
}
// Finally, if this is a normal launch mode (that is, not
// expecting onNewIntent()), then we will finish the current
// instance of the activity so a new fresh one can be started.
if (ret.launchMode == ActivityInfo.LAUNCH_MULTIPLE
&& (launchFlags & Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_SINGLE_TOP) == 0) {
if (!ret.finishing) {
stack.finishActivityLocked(ret, Activity.RESULT_CANCELED, null,
"clear", false);
return null;
}
}
return ret;
}
}
return null;
}
这里就是根据ID找到等于参数taskId的任务,然后在这个任务中查找是否已经存在即将要启动的Activity的实例,如果存在,就会把这个Actvity实例上面直到任务堆栈顶端的Activity通过调用finishActivityLocked函数将它们结束掉。
在这里便引出了manifest文件中
的一个重要属性,taskAffinity。在官方文档中可以得到关于taskAffinity的以下信息
- taskAffinity表示当前activity具有亲和力的一个任务(原句为The task that the activity has an affinity for.),大致可以这样理解,这个 taskAffinity表示一个任务,这个任务就是当前activity所在的任务。
在概念上,具有相同的affinity的activity(即设置了相同taskAffinity属性的activity)属于同一个任务。 - 一个任务的affinity决定于这个任务的根activity(root activity)的taskAffinity。
- 这个属性决定两件事:当activity被re-parent时,它可以被re-paren哪个任务中;当activity以FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK标志启动时,它会被启动到哪个任务中。(这个比较 难以理解,请结合
中的属性allowTaskReparenting和Intent中的标志 FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK加以理解) - 默认情况下,一个应用中的所有activity具有相同的taskAffinity,即应用程序的包名。我们可以通过设置不同的taskAffinity属性给应用中的activity分组,也可以把不同的 应用中的activity的taskAffinity设置成相同的值。
为一个activity的taskAffinity设置一个空字符串,表明这个activity不属于任何task。
回到前面的startActivityUncheckedLocked函数中,这里的变量top就为null了,于是执行下面的else语句
所以 此时将addintToTask=true 并且sourceRecord = 我们的activity,再往下看
if (r.packageName != null) {
// If the activity being launched is the same as the one currently
// at the top, then we need to check if it should only be launched
// once.
ActivityStack topStack = getFocusedStack();
ActivityRecord top = topStack.topRunningNonDelayedActivityLocked(notTop);
if (top != null && r.resultTo == null) {
if (top.realActivity.equals(r.realActivity) && top.userId == r.userId) {
if (top.app != null && top.app.thread != null) {
if ((launchFlags & Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_SINGLE_TOP) != 0
|| launchSingleTop || launchSingleTask) {
ActivityStack.logStartActivity(EventLogTags.AM_NEW_INTENT, top,
top.task);
// For paranoia, make sure we have correctly
// resumed the top activity.
topStack.mLastPausedActivity = null;
if (doResume) {
resumeTopActivitiesLocked();
}
ActivityOptions.abort(options);
if ((startFlags&ActivityManager.START_FLAG_ONLY_IF_NEEDED) != 0) {
// We don't need to start a new activity, and
// the client said not to do anything if that
// is the case, so this is it!
return ActivityManager.START_RETURN_INTENT_TO_CALLER;
}
top.deliverNewIntentLocked(callingUid, r.intent);
return ActivityManager.START_DELIVERED_TO_TOP;
}
}
}
}
} else {
if (r.resultTo != null) {
r.resultTo.task.stack.sendActivityResultLocked(-1, r.resultTo, r.resultWho,
r.requestCode, Activity.RESULT_CANCELED, null);
}
ActivityOptions.abort(options);
return ActivityManager.START_CLASS_NOT_FOUND;
}
根据注释我们能看出这个方法是检查当前任务的顶端是否是我们要启动的activity,接着往下看,便是启动activity
boolean newTask = false;
boolean keepCurTransition = false;
TaskRecord taskToAffiliate = launchTaskBehind && sourceRecord != null ?
sourceRecord.task : null;
// Should this be considered a new task?
if (r.resultTo == null && inTask == null && !addingToTask
&& (launchFlags & Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK) != 0) {
if (isLockTaskModeViolation(reuseTask)) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Attempted Lock Task Mode violation r=" + r);
return ActivityManager.START_RETURN_LOCK_TASK_MODE_VIOLATION;
}
newTask = true;
targetStack = adjustStackFocus(r, newTask);
if (!launchTaskBehind) {
targetStack.moveToFront();
}
if (reuseTask == null) {
r.setTask(targetStack.createTaskRecord(getNextTaskId(),
newTaskInfo != null ? newTaskInfo : r.info,
newTaskIntent != null ? newTaskIntent : intent,
voiceSession, voiceInteractor, !launchTaskBehind /* toTop */),
taskToAffiliate);
if (DEBUG_TASKS) Slog.v(TAG, "Starting new activity " + r + " in new task " +
r.task);
} else {
r.setTask(reuseTask, taskToAffiliate);
}
if (!movedHome) {
if ((launchFlags &
(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK|Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_TASK_ON_HOME))
== (Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK|Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_TASK_ON_HOME)) {
// Caller wants to appear on home activity, so before starting
// their own activity we will bring home to the front.
r.task.setTaskToReturnTo(HOME_ACTIVITY_TYPE);
}
}
} else if (sourceRecord != null) {
final TaskRecord sourceTask = sourceRecord.task;
if (isLockTaskModeViolation(sourceTask)) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Attempted Lock Task Mode violation r=" + r);
return ActivityManager.START_RETURN_LOCK_TASK_MODE_VIOLATION;
}
targetStack = sourceTask.stack;
targetStack.moveToFront();
final TaskRecord topTask = targetStack.topTask();
if (topTask != sourceTask) {
targetStack.moveTaskToFrontLocked(sourceTask, r, options);
} else {
mWindowManager.moveTaskToTop(topTask.taskId);
}
if (!addingToTask && (launchFlags&Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_TOP) != 0) {
// In this case, we are adding the activity to an existing
// task, but the caller has asked to clear that task if the
// activity is already running.
ActivityRecord top = sourceTask.performClearTaskLocked(r, launchFlags);
keepCurTransition = true;
if (top != null) {
ActivityStack.logStartActivity(EventLogTags.AM_NEW_INTENT, r, top.task);
top.deliverNewIntentLocked(callingUid, r.intent);
// For paranoia, make sure we have correctly
// resumed the top activity.
targetStack.mLastPausedActivity = null;
if (doResume) {
targetStack.resumeTopActivityLocked(null);
}
ActivityOptions.abort(options);
return ActivityManager.START_DELIVERED_TO_TOP;
}
} else if (!addingToTask &&
(launchFlags&Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_REORDER_TO_FRONT) != 0) {
// In this case, we are launching an activity in our own task
// that may already be running somewhere in the history, and
// we want to shuffle it to the front of the stack if so.
final ActivityRecord top = sourceTask.findActivityInHistoryLocked(r);
if (top != null) {
final TaskRecord task = top.task;
task.moveActivityToFrontLocked(top);
ActivityStack.logStartActivity(EventLogTags.AM_NEW_INTENT, r, task);
top.updateOptionsLocked(options);
top.deliverNewIntentLocked(callingUid, r.intent);
targetStack.mLastPausedActivity = null;
if (doResume) {
targetStack.resumeTopActivityLocked(null);
}
return ActivityManager.START_DELIVERED_TO_TOP;
}
}
// An existing activity is starting this new activity, so we want
// to keep the new one in the same task as the one that is starting
// it.
r.setTask(sourceTask, null);
if (DEBUG_TASKS) Slog.v(TAG, "Starting new activity " + r
+ " in existing task " + r.task + " from source " + sourceRecord);
} else if (inTask != null) {
// The calling is asking that the new activity be started in an explicit
// task it has provided to us.
if (isLockTaskModeViolation(inTask)) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Attempted Lock Task Mode violation r=" + r);
return ActivityManager.START_RETURN_LOCK_TASK_MODE_VIOLATION;
}
targetStack = inTask.stack;
targetStack.moveTaskToFrontLocked(inTask, r, options);
targetStack.moveToFront();
mWindowManager.moveTaskToTop(inTask.taskId);
// Check whether we should actually launch the new activity in to the task,
// or just reuse the current activity on top.
ActivityRecord top = inTask.getTopActivity();
if (top != null && top.realActivity.equals(r.realActivity) && top.userId == r.userId) {
if ((launchFlags & Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_SINGLE_TOP) != 0
|| launchSingleTop || launchSingleTask) {
ActivityStack.logStartActivity(EventLogTags.AM_NEW_INTENT, top, top.task);
if ((startFlags&ActivityManager.START_FLAG_ONLY_IF_NEEDED) != 0) {
// We don't need to start a new activity, and
// the client said not to do anything if that
// is the case, so this is it!
return ActivityManager.START_RETURN_INTENT_TO_CALLER;
}
top.deliverNewIntentLocked(callingUid, r.intent);
return ActivityManager.START_DELIVERED_TO_TOP;
}
}
if (!addingToTask) {
// We don't actually want to have this activity added to the task, so just
// stop here but still tell the caller that we consumed the intent.
ActivityOptions.abort(options);
return ActivityManager.START_TASK_TO_FRONT;
}
r.setTask(inTask, null);
if (DEBUG_TASKS) Slog.v(TAG, "Starting new activity " + r
+ " in explicit task " + r.task);
} else {
// This not being started from an existing activity, and not part
// of a new task... just put it in the top task, though these days
// this case should never happen.
targetStack = adjustStackFocus(r, newTask);
targetStack.moveToFront();
ActivityRecord prev = targetStack.topActivity();
r.setTask(prev != null ? prev.task : targetStack.createTaskRecord(getNextTaskId(),
r.info, intent, null, null, true), null);
mWindowManager.moveTaskToTop(r.task.taskId);
if (DEBUG_TASKS) Slog.v(TAG, "Starting new activity " + r
+ " in new guessed " + r.task);
}
mService.grantUriPermissionFromIntentLocked(callingUid, r.packageName,
intent, r.getUriPermissionsLocked(), r.userId);
if (sourceRecord != null && sourceRecord.isRecentsActivity()) {
r.task.setTaskToReturnTo(RECENTS_ACTIVITY_TYPE);
}
if (newTask) {
EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.AM_CREATE_TASK, r.userId, r.task.taskId);
}
ActivityStack.logStartActivity(EventLogTags.AM_CREATE_ACTIVITY, r, r.task);
targetStack.mLastPausedActivity = null;
targetStack.startActivityLocked(r, newTask, doResume, keepCurTransition, options);
if (!launchTaskBehind) {
// Don't set focus on an activity that's going to the back.
mService.setFocusedActivityLocked(r);
}
return ActivityManager.START_SUCCESS;
}
首先将newTask变量初始化为false,表示不要在新的任务中启动Activity。由于前面的已经把addingToTask设置为true,因此,这里会执行中间的else if语句,即这里会把r.task设置为sourceRecord.task,即把即将启动的Activity放在原Activity所在的任务中启动。最后,就是调用startActivityLocked函数继续进行启动Activity的操作了