在学习的过程中,大多时候项目与数据库都在本机上,使用hibernate或者mybatits加上简单的配置就能够打通程序到数据库路径,让程序能够访问到数据库。然而在一些情况下,我们不仅需要访问本机的数据库,还需要访问到另外一个数据库中的资源。本文书写的目的便在于解决访问多资源库的问题,更多的是为了交流与学习。学习,源码是很重要的。文末给出了我的Github中的源码链接,感兴趣的可以下载阅览。
一、项目创建与资源文件配置
建立一个初始的spring项目的方式在我的另一篇文章《springboot整合mybatis注解版与XML配置版》(链接)已经详细介绍了,在这里就不多赘述。当然,网上也有很多详细的教程,你也可以自行搜索阅览。新建好的项目的pom.xml文件中已经集成了必要的依赖包。本文所用到的pom.xml文件如下。
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
mysql
mysql-connector-java
runtime
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
test
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-data-jpa
com.alibaba
fastjson
1.2.40
net.sourceforge.nekohtml
nekohtml
1.9.22
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-devtools
true
org.springframework.data
spring-data-jpa
1.7.0.RELEASE
org.springframework
spring-orm
4.1.1.RELEASE
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-maven-plugin
true
true
当初始化好一个项目后,首先要进行的便是各类资源文件的配置,这时springboot的强大便体现的淋漓尽致,仅需要少量的信息配置就能替代spring大量的xml文件配置。在springboot中甚至都不需要配置web.xml,仅需要在自带的application.properties文件中进行数据库等信息配置。
对于本文的工程Demo资源文件配置,首先,需要数据库吧,还是两个,所以两个数据库源都得配置吧。其次,用到了hibernate,也需要配置一下。至此必要的配置就结束了,就这么简单。
spring.datasource.primary.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test1?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&serverTimezone=UTC&useSSL=true
spring.datasource.primary.username=root
spring.datasource.primary.password=xxxxx
spring.datasource.primary.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.max-active=10
spring.datasource.primary.max-idle=5
spring.datasource.primary.min-idle=0
spring.datasource.secondary.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test2?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&serverTimezone=UTC&useSSL=true
spring.datasource.secondary.username=root
spring.datasource.secondary.password=xxxxx
spring.datasource.secondary.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.secondary.max-active=10
spring.datasource.secondary.max-idle=5
spring.datasource.secondary.min-idle=0
#新设置访问接口,默认为8080
server.port=80
#hibernate配置
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto=update
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect=org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5InnoDBDialect
spring.jpa.show-sql= true
#前端html的配置,解除严格语法检查,前端才用到
spring.thymeleaf.cache=false
spring.thymeleaf.mode=LEGACYHTML5
二、多资源库配置
细心的你或许发现了多资源库时的资源文件配置与单资源库时的配置不一样,默认时的配置为
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test1?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&serverTimezone=UTC&useSSL=true
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=xxxxx
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.max-active=10
spring.datasource.max-idle=5
spring.datasource.min-idle=0
而本文的配置为
spring.datasource.primary.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test1?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&serverTimezone=UTC&useSSL=true
spring.datasource.primary.username=root
spring.datasource.primary.password=xxxxx
spring.datasource.primary.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.max-active=10
spring.datasource.primary.max-idle=5
spring.datasource.primary.min-idle=0
数据库字段做了一些更改,一点变动貌似看起来没啥关系,但是变了之后springboot就不认识这东西,不知道它是数据库的信息配置,因此我们需要重新定义。
首先,定义数据源,并且注明一个主数据源,一个从数据源。直接在java目录下,你所定义的项目文件包(假如为com.springboot.xxx)下,新建一个DataSourceConfig.java文件。
@Configuration
public class DataSourcesConfig {
@Bean(name = "primaryDataSource")
@Qualifier("primaryDataSource")
@Primary
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix="spring.datasource.primary")
public DataSource primaryDataSource() {
System.out.println("primary db built");
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
@Bean(name = "secondaryDataSource")
@Qualifier("secondaryDataSource")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix="spring.datasource.secondary")
public DataSource secondaryDataSource() {
System.out.println("secondary db built");
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
}
这样就相当于告诉程序,程序要用到两个数据库,于是程序就去连接这两个数据库。怎么连接呢,默认的连接已经行不通了,因此,对于每个数据库还需要有一个定义文件告诉程序如何去连接它。
同样,我们在com.springboot.xxx包下新建两个数据库定义文件PrimaryConfig.java与SecondaryConfig.java,分别定义主数据库与从数据库。
PrimaryConfig.java
@Configuration
@EnableTransactionManagement
@EnableJpaRepositories(
entityManagerFactoryRef="entityManagerFactoryPrimary",
transactionManagerRef="transactionManagerPrimary",
basePackages= { "com.springboot.multi_resources.repository.user" }) //设置Repository所在位置
public class PrimaryConfig {
@Autowired @Qualifier("primaryDataSource")
private DataSource primaryDataSource;
@Primary
@Bean(name = "entityManagerPrimary")
public EntityManager entityManager(EntityManagerFactoryBuilder builder) {
return entityManagerFactoryPrimary(builder).getObject().createEntityManager();
}
@Primary
@Bean(name = "entityManagerFactoryPrimary")
public LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean entityManagerFactoryPrimary (EntityManagerFactoryBuilder builder) {
return builder
.dataSource(primaryDataSource)
.properties(getVendorProperties(primaryDataSource))
.packages("com.springboot.multi_resources.entity.user") //设置实体类所在位置
.persistenceUnit("primaryPersistenceUnit")
.build();
}
@Autowired(required=false)
private JpaProperties jpaProperties;
private Map getVendorProperties(DataSource dataSource) {
return jpaProperties.getHibernateProperties(dataSource);
}
@Primary
@Bean(name = "transactionManagerPrimary")
public PlatformTransactionManager transactionManagerPrimary(EntityManagerFactoryBuilder builder) {
return new JpaTransactionManager(entityManagerFactoryPrimary(builder).getObject());
}
}
SecondaryConfig.java
package com.springboot.multi_resources;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.orm.jpa.JpaProperties;
import org.springframework.boot.orm.jpa.EntityManagerFactoryBuilder;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.config.EnableJpaRepositories;
import org.springframework.orm.jpa.JpaTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.orm.jpa.LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean;
import org.springframework.transaction.PlatformTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement;
import javax.persistence.EntityManager;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.util.Map;
@Configuration
@EnableTransactionManagement
@EnableJpaRepositories(
entityManagerFactoryRef="entityManagerFactorySecondary",
transactionManagerRef="transactionManagerSecondary",
basePackages= { "com.springboot.multi_resources.repository.work" }) //设置Repository所在位置
public class SecondaryConfig {
@Autowired
private JpaProperties jpaProperties;
@Autowired @Qualifier("secondaryDataSource")
private DataSource secondaryDataSource;
@Bean(name = "entityManagerSecondary")
public EntityManager entityManager(EntityManagerFactoryBuilder builder) {
return entityManagerFactorySecondary(builder).getObject().createEntityManager();
}
@Bean(name = "entityManagerFactorySecondary")
public LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean entityManagerFactorySecondary (EntityManagerFactoryBuilder builder) {
return builder
.dataSource(secondaryDataSource)
.properties(getVendorProperties(secondaryDataSource))
.packages("com.springboot.multi_resources.entity.work") //设置实体类所在位置
.persistenceUnit("secondaryPersistenceUnit")
.build();
}
private Map getVendorProperties(DataSource dataSource) {
return jpaProperties.getHibernateProperties(dataSource);
}
@Bean(name = "transactionManagerSecondary")
PlatformTransactionManager transactionManagerSecondary(EntityManagerFactoryBuilder builder) {
return new JpaTransactionManager(entityManagerFactorySecondary(builder).getObject());
}
}
3、功能实现
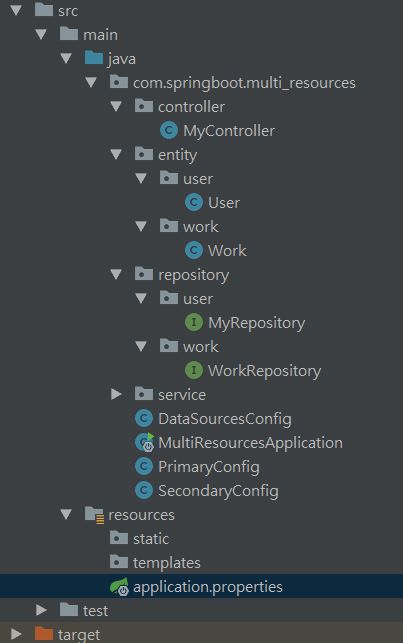
至此,所有的配置类信息就都搞定了,剩下的就是标准化的建四个层,controller层,entity实体层,service层,repository层,先来看下项目结构,两个数据库对应了两个实体,分别为User与Work,对应这来自两个数据库的信息。repository层与service层与单数据源时的配置一样,只是多了一套处理信息。我们来看下较为核心的控制层
@Controller
public class MyController {
@Autowired
MyService myService;
@RequestMapping("/")
public String index()
{
return "index";
}
@RequestMapping("/all")
@ResponseBody
public JSONObject findAll()
{
List userList = myService.findAll();
JSONObject json = new JSONObject();
json.put("data",userList);
return json;
}
@RequestMapping("/add")
@ResponseBody
public JSONObject addOne(User user)
{
myService.addOne(user);
JSONObject json = new JSONObject();
json.put("data",user);
return json;
}
@RequestMapping("/del")
public void delOne(Integer id)
{
myService.delOne(id);
}
@RequestMapping("/find")
@ResponseBody
public JSONObject findOne(Integer id)
{
User user = myService.findOne(id);
JSONObject json = new JSONObject();
json.put("data",user);
return json;
}
@RequestMapping("/modify")
@ResponseBody
public JSONObject modifyOne(User user)
{
User user1 = myService.modifyOne(user);
JSONObject json = new JSONObject();
json.put("data",user1);
return json;
}
@RequestMapping("/workAll")
@ResponseBody
public JSONObject workAll(){
List workList = myService.findWorkAll();
JSONObject json = new JSONObject();
json.put("data",workList);
return json;
}
在服务层中,则是对应了两个注入的数据库访问接口,其实现类如下
@Autowired
MyRepository myRepository;
@Autowired
WorkRepository workRepository;
@Override
public List findAll() {
return myRepository.findAll();
}
@Override
public void addOne(User user) {
myRepository.saveAndFlush(user);
}
@Override
public void delOne(Integer id) {
myRepository.delete(id);
}
@Override
public User findOne(Integer id) {
return myRepository.findOne(id);
}
@Override
public User modifyOne(User user) {
myRepository.modifyOne(user.getUserName(),user.getPassword(),user.getAuthority(),user.getPhone(),user.getId());
return myRepository.findOne(user.getId());
}
@Override
public List findWorkAll() {
return workRepository.findAll();
}
在MyRepository资源层文件中,笔者定义了一个自定义的查询语句,虽然Jpa提供了丰富而便捷的自带方法,但是总会用到自定义查询的。
@Repository
public interface MyRepository extends JpaRepository{
@Modifying
@Transactional
@Query("update User u set u.userName=?1,u.password=?2,u.authority=?3,u.phone=?4 where u.id=?5")
void modifyOne(String userName, String password, String authority, String phone, int id);
}
本片笔者写的比较概括,详细介绍篇幅可能就比较大了,阅读起来就比较困难。一些主要的地方都介绍到了,细节配合源码基本上也能理解。有任何疑问或者建议欢迎留言交流。
源码