Redux是受Facebook的Flux启发,用来管理React应用的状态的框架。这种管理应用状态的思想也可以用到Android app的UI状态管理中。
Redux的特点:
reducer为纯函数
reduce(state, action) -> state(相同的state和action产生相同的state)state immutable
state 和 view的渲染一一对应。(有了state,就能确定view的显示)
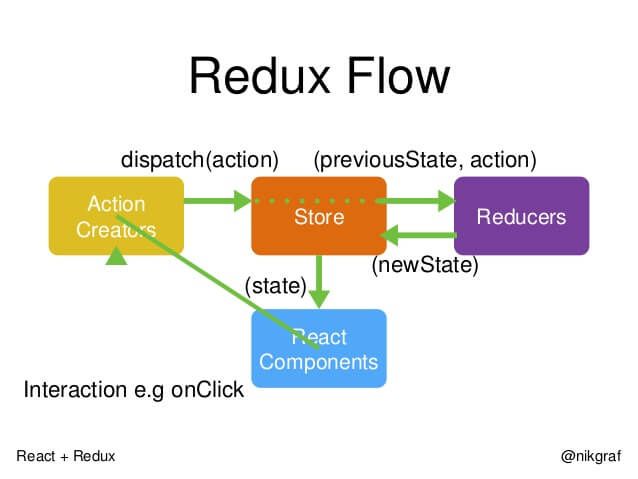
数据单向流动 action -> store -> state -> UI
Redux由三部分组成:
Action Creators: 发起action的组件,可以UI,也可以是网络请求等异步请求
Store:接收action和存储当前状态的组件,通过调用reducer的reduce方法产生新的state。
View:监听Store的state变化,根据state渲染view
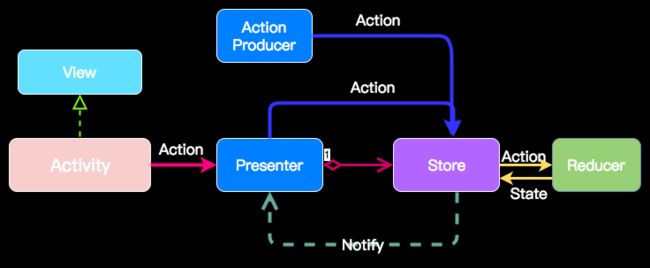
为了在android中使用这套框架,我写了一套开源框架Rodux,借鉴了以下两个库的思想:grox和KUnidirectional
如何使用这套框架
一个Activity对应一个Store,每个Activity定义对应的Action和State。
比如:
Action:
public interface ColorAction {
class ChangeColorAction implements ColorAction {
}
class ColorSuccessAction implements ColorAction {
int color;
public ColorSuccessAction(int color) {
this.color = color;
}
}
class ColorFailAction implements ColorAction {
String errorMessage;
public ColorFailAction(String errorMessage) {
this.errorMessage = errorMessage;
}
}
}
State:
public class ColorState {
public static final int INVALID_COLOR = -1;
public final int color;
public final String error;
public final boolean isRefreshing;
public ColorState(int color, String error, boolean isRefreshing) {
this.color = color;
this.error = error;
this.isRefreshing = isRefreshing;
}
}
定义自己的Reducer
public class ColorReducer implements Reducer {
@Override
public ColorState reduce(ColorAction action, ColorState currentState) {
if (action instanceof ColorAction.ChangeColorAction) {
return ColorState.refreshing();
} else if (action instanceof ColorAction.ColorSuccessAction) {
return ColorState.success(((ColorAction.ColorSuccessAction) action).color);
} else if (action instanceof ColorAction.ColorFailAction) {
return ColorState.error(((ColorAction.ColorFailAction) action).errorMessage);
}
return currentState;
}
}
首先Demo里使用了MVP结构,Activity创建并持有Presenter,同时创建Store,设置初始状态
public class ColorActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements ColorContract.View {
private ColorPresenter mPresenter;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
.....
Store store = new Store<>(Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1),
ColorState.empty(), new ColorReducer(), Arrays.asList(logMiddleware, colorMiddleware));
mPresenter = new ColorPresenter(store, this, new MainThreadExecutor());
}
Activity将用户的操作通知Presenter
findViewById(R.id.button).setOnClickListener(v -> mPresenter.changeColor());
Presenter产生一个Action并通知到Store
public class ColorPresenter extends BasePresenter implements ColorContract.Presenter {
@Override
public void changeColor() {
mStore.dispatch(new ColorAction.ChangeColorAction());
}
}
Store调用Reducer的reduce方法,产生新的State
mReducer.reduce(action, currentState);
最后通知state change事件,一般是由Presenter接收
private void dispatchState(S state) {
for (StateHandler stateHandler: mStateHanlders) {
stateHandler.onNext(state);
}
}
然后通知View对新的state进行render
public void handleState(ColorState next) {
mView.render(next);
}
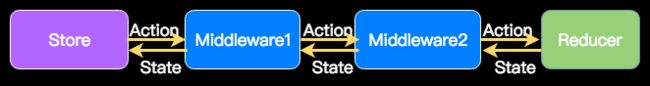
Async Action
如果要由Action触发一些异步请求,比如用户点击button,请求服务器的数据,可以定义自己的middleware,在action传递到reducer之前,发出请求。
比如:
public class ColorMiddleware implements Middleware {
public static final int MAX_COLOR = 256;
private Random mRandom = new Random();
private Executor mExecutor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1);
public ColorMiddleware() {
}
@Override
public void intercept(Chain chain) {
if (chain.getAction() instanceof ColorAction.ChangeColorAction) {
Runnable runnable = () -> {
//simulate network request
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
int rand = mRandom.nextInt(2);
if (rand == 0) {
final int rgb =
Color.rgb(mRandom.nextInt(MAX_COLOR), mRandom.nextInt(MAX_COLOR), mRandom.nextInt(MAX_COLOR));
chain.getStore().dispatch(new ColorAction.ColorSuccessAction(rgb));
} else if (rand == 1) {
chain.getStore().dispatch(new ColorAction.ColorFailAction("Network Error"));
}
};
mExecutor.execute(runnable);
}
chain.proceed(chain.getAction());
}
}
在构建Store的时候,通过构造函数将自定义middlewares设置到store中
具体的使用方法可以参考Demo
好处
这套框架的特别就是数据单向流动,UI state的更新都是串行的,简化了UI的逻辑。
而且在日志中可以将Action和State都打印出来,一旦发现问题,可以很方便复现问题,比如将presenter的initial state设置为发生问题前的state,然后出发最后一个action,就可以复现了。
11-18 12:20:58.816 D/LoggerImpl: action: ChangeColorAction{}
11-18 12:20:58.841 D/LoggerImpl: state: ColorState{color=-1, error='null', isRefreshing=true}
11-18 12:21:00.844 D/LoggerImpl: action: ColorSuccessAction{color=-686133}
11-18 12:21:00.844 D/LoggerImpl: state: ColorState{color=-686133, error='null', isRefreshing=false}
11-18 12:21:03.824 D/LoggerImpl: action: ChangeColorAction{}
11-18 12:21:03.824 D/LoggerImpl: state: ColorState{color=-1, error='null', isRefreshing=true}
11-18 12:21:05.826 D/LoggerImpl: action: ColorSuccessAction{color=-11877933}
11-18 12:21:05.826 D/LoggerImpl: state: ColorState{color=-11877933, error='null', isRefreshing=false}