0.PTA得分截图
![]()
1.本周学习总结
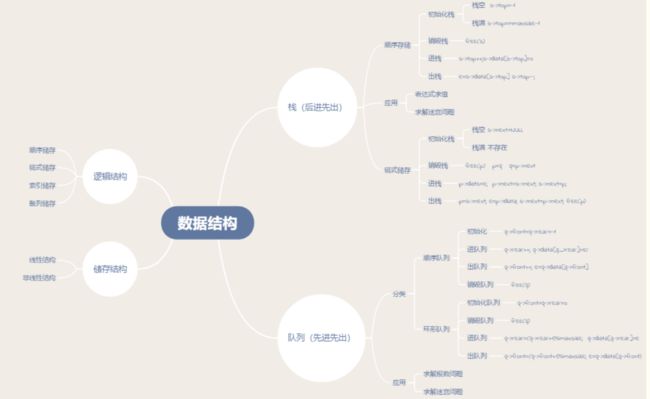
1.1 总结栈和队列内容
思维导图
- ·栈的存储结构及操作
栈:一种运算受限的线性表。其限制是仅允许在表的一端进行插入和删除运算,对于栈的操作有进栈,出栈,销毁栈,初始化栈与取栈顶元素。栈最需要注意的是栈是后进先出表。
顺序栈
typedef struct
{
ElemType str[MaxSize];
int top;
}SqStack;
void InitStack(SqStack*& st) //初始换栈
{
st = new SqStack;
st->top = -1;
}
bool Push(SqStack*& st, ElemType string) //入栈
{
int i;
if (st->top == MaxSize - 1)
{
return false;
}
else
{
st->top++;
st->str[st->top] = string;
return true;
}
}
bool Pop(SqStack*& st, ElemType& e) //出栈
{
if (st->top == -1)
{
return false;
}
else
{
e = st->str[st->top];
st->top--;
return true;
}
}
链栈
typedef struct SNode {
int data;
SNode *next;
}SNode;
typedef struct
{
SNode *top;
}LStack;
void initLStack(LStack &S) //初始化链栈
{
S.top = new SNode;
S.top->data = NULL;
S.top->next = NULL;
return;
}
bool Empty(LStack S) //判断栈是否为空
{
if (S.top->next)
return false;
else
return true;
}
void push(LStack &S,int e) //入栈
{
SNode* newNode = new SNode;
newNode->data = e;
newNode->next = S.top->next;
S.top->next = newNode;
S.top->data++;
return;
}
bool popLStack(LStack &S) //出栈
{
int e;
if (isEmptyLStack(S))
{
return false;
}
SNode* delNode = S.top->next;
S.top->next = delNode->next;
e = delNode->data;
delete delNode;
S.top->data--;
return true;
}
- ·栈的应用
检测括号是否匹配
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
#define Max 80
typedef int ElementType;
bool judge(string str);
int main()
{
string str;
cin >> str;
if (judge(str))
cout << "yes";
else
cout << "no";
return 0;
}
bool judge(string str)
{
char e;
stackst;
int flag = 1, i = 0;
while (str[i])
{
if (str[i] == '(' || str[i] == '[' || str[i] == '{')
st.push(str[i]);
else if (str[i] == ')' || str[i] == ']' || str[i] == '}')
{
if (st.empty())
return false;//如果栈已空,没有俞左括号配对,则错误
e = st.top();//取栈顶
st.pop();//去栈顶
switch (str[i])
{
case')':if (e != '(')flag = 0; break;
case']':if (e != '[')flag = 0; break;
case'}':if (e != '{')flag = 0; break;
}
}
i++;
}
if (st.empty() && flag == 1)
return true;//如果栈已经空了那就是对的
else
{
e = st.top();
cout << e << endl;
return false;
}
}
递归
int fun(int n)//计算斐波那契数列第n项的值
{
if(n==1||n==2)
{
return 1;
}
else
{
return fun(n-1)+fun(n-2);
}
}
int fun(int n)//n的阶乘
{
if(n==1)
{
return 1;
}
else
{
return fun(n-1)*n;
}
}
进制转换
bool Conversion(stack& s,int data,int N)
{
if(N<=0)
{
return false;
}
while (data)
{
push(s,data%N);
data = data/N;
}
while (s)
{
pop(s);
}
return true;
}
- ·队列的存储结构及操作
顺序队
#define MaxSize 10 //队列的最大容量
typedef int DataType; //队列中元素类型
typedef struct Queue
{
DataType Queue[MaxSize];
int fornt; //队头指针
int rear; //队尾指针
}SeqQueue;
void InitQueue(SeqQueue *SQ) //队列初始化,将队列初始化为空队列
{
SQ->fornt = SQ->rear = 0; //把对头和队尾指针同时置0
}
int IsEmpty(SeqQueue* SQ) //判断队列为空
{
if (SQ->fornt == SQ->rear)
{
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
int IsFull(SeqQueue* SQ) //判断队列是否为满
{
if (SQ->rear == MaxSize)
{
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
void EnterQueue(SeqQueue* SQ,DataType data) //入队,将元素data插入到队列SQ中
{
if (IsFull(SQ))
{
printf("队列已满\n");
return 0;
}
SQ->Queue[SQ->rear] = data; //在队尾插入元素data
SQ->rear = SQ->rear + 1; //队尾指针后移一位
}
int DeleteQueue(SeqQueue* SQ,DataType* data) //出队,将队列中队头的元素data出队,出队后队头指针front后移一位
{
if (IsEmpty(SQ))
{
printf("队列为空!\n");
return 0;
}
*data = SQ->Queue[SQ->fornt]; //出队元素值
SQ->fornt = (SQ->fornt)+1; //队尾指针后移一位
return 1;
}
int GetHead(SeqQueue* SQ,DataType* data) //获取队首元素
{
if (IsEmpty(SQ))
{
printf("队列为空!\n");
}
return *data = SQ->Queue[SQ->fornt];
}
void DestoryQueue(SeqQueue* SQ) //销毁链表
{
SQ->fornt = SQ->rear = 0;
}
void PrintQueue(SeqQueue* SQ) //打印队列中的与元素
{
assert(SQ);
int i = SQ->fornt;
while(irear)
{
printf("%-3d", SQ->Queue[i]);
i++;
}
printf("\n");
}
链队
typedef struct QueueNode
{
int e;//数据域
struct QueueNode* next;//指针域
}QueueNode,*LinkQueuePoi;
typedef struct LinkQueue
{
LinkQueuePoi front;//指向头结点
LinkQueuePoi rear;//指向队尾
}LinkQueue;
Status InitLinkQueue(LinkQueue* queue) //初始化链队列.链队列为空时,链队列队头指针队尾指针均指向头结点
{
//空指针
if (!queue)
{
return false;
}
QueueNode* node = (QueueNode*)malloc(sizeof(QueueNode));//头结点
node->next = NULL;
queue->front = queue->rear = node;
return true;
}
Status CleaerLinkQueue(LinkQueue* queue)
{
//空指针
if (!queue)
{
return false;
}
//空链队列
if (queue->front == queue->rear)
{
return false;
}
QueueNode* node = queue->front->next;//队头元素
while (node)
{
queue->front->next = node->next;//指向新的队头结点
if (queue->rear == node)//当删除的是队尾元素时,将队尾指针指向头结点
{
queue->rear = queue->front;
}
free(node);//释放旧的队头结点
node = queue->front->next;
}
return true;
}
Status EmptyLinkQueue(LinkQueue* queue) //判断链队列是否为空队列
{
//空指针
if (!queue)
{
return ERROR;
}
//空链队列
if (queue->front == queue->rear)
{
return ;
}
return false;
}
/*
获取链队列长度
*/
int LengthLinkQueue(LinkQueue* queue)
{
//空指针
if (!queue)
{
return false;
}
//空链队列
if (queue->front == queue->rear)
{
return 0;
}
QueueNode* node = queue->front->next;
int num = 0;
while (node)
{
node = node->next;
num++;
}
return num;
}
bool AddQueue(LinkQueue* queue,EleType e) //在链队列队尾添加元素,先将新元素添加到链表尾部,然后将队列尾指针指向这个新元素
{
//空指针
if (!queue)
{
return flase;
}
QueueNode* node = (QueueNode*)malloc(sizeof(QueueNode));
if (!node)
{
return false;
}
node->next = NULL;
node->e = e;
queue->rear->next = node;//将新结点添加到链表表中
queue->rear = node;//队尾指针指向新的队尾结点
return true;
}
Status DelQueue(LinkQueue* queue, EleType *e) //从链队列中删除队头元素,先将头结结点指向新的队头结点,然后释放原来的队头结点
{
//空指针
if (!queue)
{
return false;
}
//注意queue->front是头结点,头结点指向的结点才是队头结点
QueueNode* node = queue->front->next;//旧队头结点
*e = node->e;
queue->front->next = node->next;//队头指针指向新的队头结点
//当删除的是队尾元素时,将队尾指针指向头结点
if (node = queue->rear)
{
queue->rear = queue->front;
}
return true;
}
void PrintfLinkQueue(LinkQueue* queue) //输出链表
{
if (!queue)
{
return;
}
QueueNode* node = queue->front->next;
while (node)
{
printf("%d,", node->e);
node = node->next;
}
printf("\n");
return;
}
- ·队列应用
广度优先搜索解决迷宫问题
#include
#define MAX 1000
using namespace std;
int m, n;
int mg[MAX][MAX];
int xi, yi, xe, ye;
typedef struct
{
int i, j;
int pre;
}BOX;
typedef struct
{
BOX data[MAX];
int front, rear;
}QuType;
void InitQueue(QuType*& qu);
bool QueueEmpty(QuType* qu);
void enQueue(QuType*& qu, BOX& e);
void deQueue(QuType*& qu, BOX& e);
void InitMg(int mg[][MAX]);
void DestroyQueue(QuType*& qu);
void count(QuType* qu, int front);
bool mgpathl(QuType*& qu, int xi, int yi, int xe, int ye);
int main()
{
QuType* qu;
InitQueue(qu);
InitMg(mg);
cin >> xi >> yi;
cin >> xe >> ye;
mgpathl(qu, xi, yi, xe, ye);
return 0;
}
void InitMg(int mg[][MAX])
{
int num;
cin >> m >> n;
for (int i = 0; i <= 1 + m; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j <= 1 + n; j++)
{
if (i == 0 || j == 0 || i == m + 1 || j == 1 + n)
{
mg[i][j] = 1;
}
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
cin >> num;
mg[i][j] = num;
}
}
}
void InitQueue(QuType*& qu)
{
qu = new QuType;
qu->front = -1;
qu->rear = -1;
}
void enQueue(QuType*& qu, BOX& e)
{
qu->rear++;
qu->data[qu->rear] = e;
}
void deQueue(QuType*& qu, BOX& e)
{
qu->front++;
e = qu->data[qu->front];
}
bool QueueEmpty(QuType* qu)
{
if (qu->rear == -1)return true;
else return false;
}
void DestroyQueue(QuType*& qu)
{
free(qu);
}
void count(QuType* qu, int front) //寻找出迷宫最短路径
{
int k = front, j, ns = 0;
do
{
j = k;
k = qu->data[k].pre;
qu->data[j].pre = -1;
} while (k != 0);
k = 0;
while (k < MAX)
{
if (qu->data[k].pre == -1)
{
printf("(%d,%d)->", qu->data[k].i, qu->data[k].j);
ns++;
}
k++;
}
cout << ns;
}
bool mgpathl(QuType*& qu, int xi, int yi, int xe, int ye) //寻找出迷宫路径
{
BOX e;
int il,jl;
int i, j, find = 0, di;
e.i = xi;
e.j = yi;
e.pre = -1;
enQueue(qu, e);
mg[xi][yi] = -1;
while (qu->front != qu->rear && !find)
{
deQueue(qu, e);
i = e.i;
j = e.j;
if (i == xe && j == ye)
{
find = 1;
count(qu, qu->front);
return true;
}
for (di = 0; di < 4; di++)
{
for (di = 0; di < 4; di++)
{
switch (di)
{
case 0:il = i - 1; jl = j; break;
case 1:il = i; jl = j + 1; break;
case 2:il = i + 1; jl = j; break;
case 3:il = i, jl = j - 1; break;
}
if (mg[il][jl] == 0)
{
e.i = il;
e.j = jl;
e.pre = qu->front;
enQueue(qu, e);
mg[il][jl] = -1;
}
}
}
}
return false;
}
1.2.谈谈你对栈和队列的认识及学习体会
栈和队列相较于前一部分学的线性表,学习难度有所增大,可现的功能更多。在使用线性栈和线性队列时,需要考虑栈和队列是否为满。
而使用链栈和链队时,我们则不需要考虑栈或队列满的情况。
循环队列的空满判断条件需要对最大空间进行取余。
2.PTA实验作业
2.1.题目1:7-8 电路布线
2.1.1代码截图(注意,截图,截图,截图。不要粘贴博客上。)
2.1.2本题PTA提交列表说明。
Q1:代码虽然找到了出迷宫路径,但是该路径并非最短路径
A1:发现是在寻找最短路径时,判断出了错误
Q2:复制代码到PTA时少复制了一个头文件
A2:重新复制了一遍
2.2.题目2:银行排队问题之单队列多窗口服务
2.1.1代码截图(注意,截图,截图,截图。不要粘贴博客上。)
2.1.2本题PTA提交列表说明。
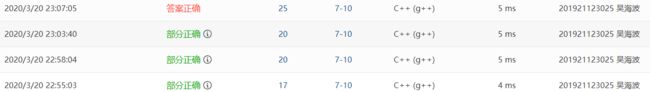
Q1:三次错误原因相同,在统计等待时间时出了问题,在等待时,一开始统计了所有窗口的等待时间
A2:改后,一个人只统计最短窗口的等待时间
3.阅读代码(0--4分)
3.1 列车调度
两端分别是一条入口(Entrance)轨道和一条出口(Exit)轨道,它们之间有N条平行的轨道。每趟列车从入口可以选择任意一条轨道进入,最后从出口离开。在图中有9趟列车,在入口处按照{8,4,2,5,3,9,1,6,7}的顺序排队等待进入。如果要求它们必须按序号递减的顺序从出口离开,则至少需要多少条平行铁轨用于调度?

3.1.1 该题的设计思路
3.1.2 该题的伪代码
定义字符数组str1,str2
输入1,2号铁轨列车顺序
建栈S
定义指针数组way
while(str1[i]!='\0')
如果 str1[i]与str2[j]相等
路径为1->2
如果栈顶与str2[j]相等
路径为3->2,栈顶元素出栈
如果str1[i]与str2[j]不相等
路径为1->3,str[i]入栈
如果S不为空
while栈S不为空
遍历str2余下元素
如果flag==0而且栈顶元素与str2[t]相等
路径为3->2,出栈
否则flag=1,出栈
如果flag为0,输出指针数组way
否则输出Are you kidding me?
3.1.3 运行结果
3.1.4分析该题目解题优势及难点。
加强了对栈空栈满的判断。
3.2 用一个栈实现另一个栈的排序
一个栈中元素的类型为整型,现在想将该栈从顶到底按从大到小的顺序排序,只许申请一个栈。除此之外,可以申请新的变量,但不能申请额外的数据结构。如何完成排序?
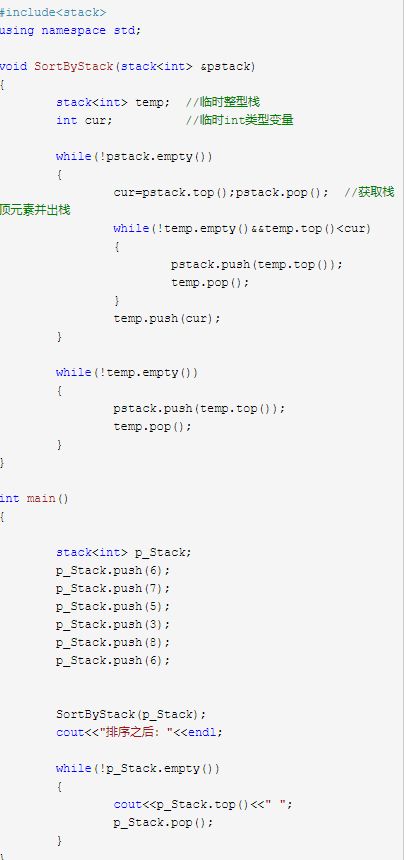
3.2.1 该题的设计思路
题中给出了两个栈,我们可以将要排序的栈记为stack,辅助栈记为help。要实现stack中的元素从顶到底按从大到小排序,则入栈的元素顺序应该为:从小到大。所以,help栈中元素从顶到底要实现由小到大的顺序。那么这就是解题关键了,我们只要实现这个就好。
T=O(n)
S=O(n)
3.2.2 该题的伪代码
在stack上执行pop操作,弹出的元素记为cur。
若cur小于或者等于help的栈顶元素,则将cur直接压入help。
(!!!保持help从栈顶到栈底由小到大的顺序)
2.若cur大于help的栈顶元素(注意:若此时将cur压入help,则会违反help栈
顶到底由小到大的顺序),则将help的元素逐一弹出,逐一压入stack,直到cur小于
或者等于help的栈顶元素,再将cur压入help。
3.重复以上操作,直到stack中的全部元素都压入到help。最后将help中的所有
元素逐一压入stack,即完成排序。
3.2.3 运行结果
3.1.4分析该题目解题优势及难点。
考验做题者对栈的灵活运用