W7L5
1.你认为电商运营的成本包括哪些?在电子商务实际运营中发现有哪些利用价格去吸引消费者的方法?
电商运营成本包括:平台固定成本、运营成本、货品成本和人员成本。
方法:淘宝购物满多少可领取优惠券;双十一降价活动;过季服装打折活动。
2.隐藏题(上课时发布)
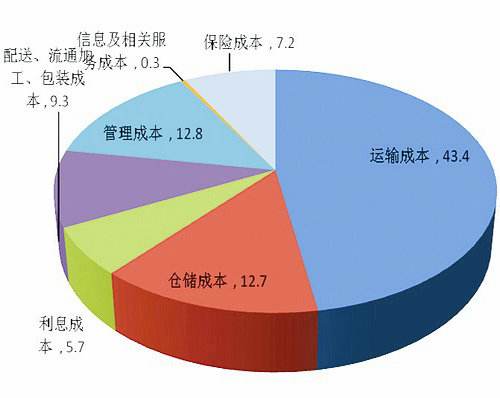
物流运输成本分析
3.阅读一篇以上price(价格)相关英文文章,按最新要求列出相关内容
链接:https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Price
In ordinary usage, price is the quantity of payment or compensation given by one party to another in return for goods or services.[1]
In modern economies, prices are generally expressed in units of some form of currency. (For commodities, they are expressed as currency per unit weight of the commodity, e.g. euros per kilogram.) Although prices could be quoted as quantities of other goods or services this sort of barter exchange is rarely seen. Prices are sometimes quoted in terms of vouchers such as trading stamps and air miles. In some circumstances, cigarettes have been used as currency, for example in prisons, in times of hyperinflation, and in some places during World War 2. In a black market economy, barter is also relatively common.
In many financial transactions, it is customary to quote prices in other ways. The most obvious example is in pricing a loan, when the cost will be expressed as the percentage rate of interest. The total amount of interest payable depends upon credit risk, the loan amount and the period of the loan. Other examples can be found in pricing financial derivatives and other financial assets. For instance the price of inflation-linked government securities in several countries is quoted as the actual price divided by a factor representing inflation since the security was issued.
Price sometimes refers to the quantity of payment requested by a seller of goods or services, rather than the eventual payment amount. This requested amount is often called the asking price or selling price, while the actual payment may be called the transaction price or traded price. Likewise, the bid price or buying price is the quantity of payment offered by a buyer of goods or services, although this meaning is more common in asset or financial markets than in consumer markets.
Economists sometimes define price more generally as the ratio of the quantities of goods that are exchanged for each other.
Economic price theory asserts that in a free market economy the market price reflects interaction between supply and demand: the price is set so as to equate the quantity being supplied and that being demanded. In turn these quantities are determined by the marginal utility of the asset to different buyers and to different sellers. In reality, the price may be distorted by other factors, such as tax and other government regulations.
When a commodity is for sale at multiple locations, the law of one price is generally believed to hold. This essentially states that the cost difference between the locations cannot be greater than that representing shipping, taxes, other distribution costs and more. In the case of the majority of consumer goods and services, distribution costs are quite a high proportion of the overall price, so the law may not be very useful.
关键单词 price价格
W7L6
1.选择一个你相对了解/感兴趣的商业APP,使用商业模式画布9个模块对其进行分析。
2.阅读一篇以上 business model 相关英文文章,按最新要求列出相关内容
链接:https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Business_model
A business model describes the rationale of how an organization creates, delivers, and captures value,[1] in economic, social, cultural or other contexts. The process of business model construction is part of business strategy.
In theory and practice, the term business model is used for a broad range of informal and formal descriptions to represent core aspects of a business, including purpose, business process, target customers, offerings, strategies, infrastructure, organizational structures, sourcing, trading practices, and operational processes and policies including culture.
关键单词business model 商业模式